Aortic aneurysm - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of aortic aneurysms is aimed at preventing its rupture. It can be conservative or surgical.
Conservative treatment
The main purpose of conservative therapy is to reduce blood pressure and the force of heart contraction, as well as the correction of concomitant diseases, such as coronary heart disease, diabetes, kidney disease, etc. [1]
Surgery
Modern surgical techniques for treating aortic aneurysms are divided into endovascular and traditional surgical interventions.
The endovascular method is the remote implantation of special tubular prostheses (stent grafts) into the affected area of the aorta from the inside through a catheter installed in the femoral artery. This method of treatment is performed under local or regional anesthesia, it is low-traumatic, low-painful and reduces hospital stay, and also reduces mortality. Increasingly, in the practice of vascular surgery, minimally invasive endovascular technologies are used in the treatment of aneurysms of the thoracic and abdominal aorta, although it is still too early to discount open surgical interventions [4].
Major operations for thoracic aneurysms are among the most difficult in medicine. They are performed in specialized cardiac surgery centers with the heart turned off during artificial circulation. The technology of the operation consists of replacing the dilated section of the aorta with a special tubular prosthesis, which is sewn into place of the aneurysmal sac [5][10]. The surgeon makes an incision to provide access to the aneurysm, excises the affected part and replaces it with a prosthesis. But in some cases, for example after injury, the aorta can be sutured end to end without the use of a prosthesis.
Abdominal aortic aneurysms with a diameter of more than 5.5 cm in men and 5.2 cm in women have a high risk of rupture, and therefore require immediate consultation with a vascular surgeon to determine indications for surgical treatment. It is performed in the vascular departments with access through the anterior abdominal wall (laparotomy) and also aims to replace the affected segment of the aorta with a prosthesis. Some medical centers have mastered laparoscopic treatment of aneurysms, which does not require incisions [4][7].
During surgical treatment of such severe diseases (as with other therapeutic and diagnostic interventions), there is a possibility of complications. It is also worth noting that not all regional, regional and republican medical centers have specialists who work on open heart surgery.
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
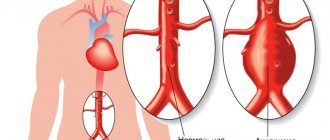
The aorta is the largest blood artery in the human body. It is located near the heart. Any disturbances or pathologies in it can lead to death, as, for example, in the case of a thoracic aortic aneurysm.
Aneurysm classification
An aneurysm of the thoracic aorta is characterized by the expansion of a certain section of the blood vessel due to changes in the structure of its walls. Pathology is classified depending on the location of the lesion:
- sinus;
- ascending/descending aneurysm;
- thoracoabdominal;
- with damage to the arterial arch.
A dissecting aneurysm is isolated separately. This pathology develops quickly, affecting a large area of the aorta.
8
24/7
Causes of the disease
Many diseases can lead to the development of a thoracic aortic aneurysm. Doctors identify congenital and acquired factors that served as the impetus for the development of pathology. Acquired ones are also divided into diseases with inflammatory and non-inflammatory forms.
Among the congenital causes:
- coarctation of the aorta: complete or partial narrowing of the lumen of the vessel; from the first days of life, the child experiences shortness of breath, cold legs, varying degrees of development of the upper and lower halves of the body;
- Marfan syndrome: pathology of connective tissue, affecting the visual organs, bones, heart and blood vessels; patients have disproportionately long fingers, protruding chest, abnormal joint mobility;
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: dysfunction of the production of collagen cells, which is accompanied by fragility of blood vessels;
- Loys-Deets syndrome: the disease affects the heart, blood vessels and bone tissue, accompanied by an aneurysm of the thoracic aorta, bifurcation of the palatal arch and eyes far apart from each other;
- Shershevsky-Turner syndrome: the patient is missing one X chromosome, the pathology often occurs in girls, is characterized by short stature, disproportionate body structure, and problems with the cardiovascular system.
Acquired inflammatory causes include:
- Takayasu syndrome (inflammatory process in the aortic walls with a chronic course);
- Kawasaki syndrome (bacterial or viral damage to the vascular walls);
- Adamantiadis-Behçet syndrome (pathology from the category of systemic inflammation in the aortic walls);
- aortitis (an inflammatory process throughout the entire wall of a vessel or one layer of it, when it is stretched and deformed, causing the occurrence of an aneurysm);
- Gsell-Erdheim syndrome (damage to the elastic layer of the middle aortic membrane).
The cause of thoracic aortic aneurysm among acquired pathologies without an inflammatory process can be:
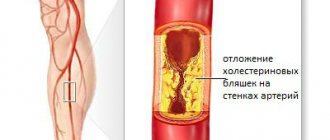
- atherosclerosis - blockage of arteries with cholesterol plaques, narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, as a result of which blood pressure increases and an aneurysm develops;
- arterial hypertension – provokes the appearance of an aneurysm due to the high load on the vascular walls;
- trauma - an accidental blow to the area of the aorta can cause both early and late development of an aneurysm;
- Iatrogenesis is a consequence of incompetent actions of physicians when, after a diagnostic examination or operation, the aortic wall is damaged.
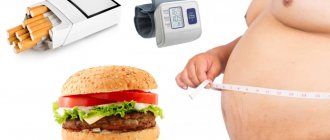
Risk factors
Particular attention to the condition of the aorta should be paid to people at risk:
- with bad heredity;
- male representatives;
- with chronic hypertension;
- overweight;
- persons over 55 years of age;
- diabetics;
- with previous sternum injuries;
- with bad habits.
Even in the absence of a congenital defect, a thoracic aneurysm can develop at any age.
Symptoms
The pathology manifests itself with different symptoms, depending on the location of the aneurysm and the extent of the affected area of the artery. In any case, the disease causes pressure on nearby organs, which is manifested by complaints of:
- chest pain;
- dry cough;
- shortness of breath;
- difficulties with eating (difficulty swallowing when the aneurysm presses on the walls of the esophagus);
- voice changes, often hoarseness;
- constriction of the pupils;
- excessive sweating;
- feeling of pulsation in the chest.
The main danger is that with a thoracic aortic aneurysm, symptoms may be completely absent, which complicates its timely diagnosis. Left untreated, the artery can rupture, which is fatal in most cases.
Diagnostics
Several instrumental methods are used for diagnosis.
- Radiography. The study helps determine the expansion of the shadow of blood vessels and their deformation. X-rays allow you to see organs that are damaged due to pressure from the artery walls.
- IVUS. Ultrasound examination inside the vessels helps to visualize the layer-by-layer structure of the aorta and determine in which part of it the aneurysm arose. The method also allows you to detect cholesterol deposits on the walls of blood vessels, thrombosis, and deformation of the aorta.
- ECHOCG. Using echocardiography, doctors examine the structural structure of the arteries, determine the location of the aneurysm and its size.
- Ultrasound Doppler. Dopplerography shows the severity of the pathology, the degree of stenosis and the quality of blood flow.
- CT. Gives a visual picture of the structural structure of the aorta and allows you to determine any changes in its walls.
- Aortography. The artery is filled with a contrast agent, which makes it possible to determine the width of its lumen on the device’s monitor. Any changes will be recorded by a doctor. Based on the results obtained, a diagnosis is made.
- KTA. Angiography with CT is the most reliable diagnostic method with visualization of changes in the walls of blood vessels. The method also makes it possible to detect aortic dissection.
In case of thoracic aortic aneurysm, it is extremely important to carry out timely diagnosis. Otherwise, the likelihood of death will increase significantly due to lack of treatment.
8
24/7
Drug therapy
The sooner an aneurysm is diagnosed, the more successful and easier the treatment will be. When there are no indications for surgical intervention, drug therapy is prescribed to support the patient’s condition. In this case, the patient must undergo regular examination so that the doctor can promptly detect the progress of the pathology and take appropriate measures.
Drug therapy is aimed at treating the underlying cause of the developing thoracic aortic aneurysm. Its main tasks:
- stabilization of blood pressure (Captopril, Enalapril);
- decreased contractile cardiac function (Atenolol, Propranolol);
- restoration of lipid balance (Simvastatin, Atorvastatin).
The patient must completely abandon bad habits, limit physical activity, and avoid stressful situations.
Indications for surgical treatment
For thoracic aortic aneurysm, surgery is performed only when absolutely necessary. The intervention can be planned or emergency. A planned operation is performed when the pathology increases in size, blood flow dysfunction, or increased symptoms. Emergency intervention is indicated when there is a high risk of aneurysm rupture and the likelihood of patient death.
Direct indications for surgery:
- expansion of the vessel up to 5 cm in diameter or more;
- dissection of the aortic walls;
- rapid development of pathology, when the diameter of the lumen increases by more than 3 mm per year;
- existing cases of aortic rupture in relatives;
- excruciating pain and vivid symptoms of pathology, which significantly depress the patient’s condition.
Contraindications for surgery:
- recent heart attack (no more than 3 months);
- respiratory, renal, liver failure;
- terminal cancer;
- dysfunction of the blood supply to the brain;
- acute course of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
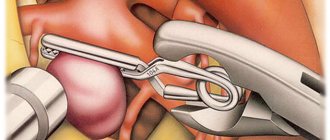
There are 3 types of surgical intervention:
- open – installation of the prosthesis into a blood vessel;
- intravascular - a metal frame is implanted into the patient’s aorta;
- hybrid – using open and endovascular surgery methods.
8
24/7
Before any surgical intervention, a complete diagnosis is carried out, the patient’s condition and the possibility of surgical treatment are determined. If there are contraindications, factors that can cause complications are eliminated (if possible), and only then the operation is performed.
Prevention
People with an aneurysm should definitely adhere to a moderate lifestyle, following their main recommendations:
- moderate activity - do not perform heavy exercises, do not undergo constant physical activity, observe a work-rest regime;
- diet – exclude fatty, sweet and unhealthy foods (fried, smoked, etc.) from the diet;
- giving up harmful addictions - you should overcome addiction to nicotine and alcohol;
- compliance with medical recommendations - undergo timely treatment of emerging diseases, do not skip taking prescribed medications.
Forecast
Depending on the size of the thoracic aortic aneurysm, location and degree of development, a prognosis for its further course is made. If diagnosis and treatment were not carried out on time, then further developments will be unfavorable.
When performing a planned operation, when the patient follows all the doctor’s recommendations, the mortality rate does not exceed 5% of all cases. With aortic rupture, the mortality rate is more than 80%.
Aneurysm rupture occurs in half of patients with this diagnosis. According to statistics, more than 90% of them do not seek timely medical help.
Based on the unfavorable prognosis, we can conclude that with a thoracic aneurysm, the main thing is to start treatment on time. Advanced forms of the disease cannot be treated, and even after a successful operation there remains a high probability of death within the first year.