Atmospheric pressure is the force with which the atmosphere (air) presses on the earth's surface. Despite the fact that we cannot see air and it seems weightless to us, it is not so. Air has weight, which is transmitted in the form of pressure. The atmosphere presses on every square centimeter of the earth's surface with a column that originates from the extreme point of the atmosphere to a point on the earth's surface. The pressure force of such a column per 1 cm square is 1.33 kg. It is easy to calculate that at what pressure each person (statistically calculated that the average area is 1.6 square meters) is pressed by an air mass of approximately 16 tons. It would seem that such pressure should crush people, but this does not happen. This is due to the physiology of the body, which also has its own pressure, which is comparable to what acts on it from the atmosphere.
As normal atmospheric pressure, the pressure that is characteristic of 45 latitude and absolute sea level is used. Under these conditions, normal atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg .
General information
Balloon bursting in the TranslatorsCafe.com office
In physics, pressure is defined as the force acting on a unit surface area. If two equal forces act on one larger and one smaller surface, then the pressure on the smaller surface will be greater. Agree, it is much worse if someone who wears stilettos steps on your foot than someone who wears sneakers. For example, if you press the blade of a sharp knife onto a tomato or carrot, the vegetable will be cut in half. The surface area of the blade in contact with the vegetable is small, so the pressure is high enough to cut that vegetable. If you press with the same force on a tomato or carrot with a dull knife, then most likely the vegetable will not cut, since the surface area of the knife is now larger, which means the pressure is less.
In the SI system, pressure is measured in pascals, or newtons per square meter.
Relationship between air density and altitude. Peculiarities
How does atmospheric pressure near the Earth's surface change with altitude? This question has already been answered by the picture above. The higher the altitude, the lower the air density. As long as we are close to the surface of the earth, the change in air density is imperceptible. Therefore, for each unit of height, the pressure decreases by approximately the same value. The two expressions we wrote down earlier should be perceived as correct only if we are located close to the Earth’s surface, no higher than 1-1.5 km.
Atmosphere pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the air pressure at a given location. It usually refers to the pressure of a column of air per unit surface area. Changes in atmospheric pressure affect weather and air temperature. People and animals suffer from severe pressure changes. Low blood pressure causes problems of varying severity in humans and animals, from mental and physical discomfort to fatal diseases. For this reason, aircraft cabins are maintained above atmospheric pressure at a given altitude because the atmospheric pressure at cruising altitude is too low.
The aneroid contains a sensor - a cylindrical corrugated box (bellows) connected to an arrow, which rotates when the pressure increases or decreases and, accordingly, the bellows compresses or expands
Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude. People and animals living high in the mountains, such as the Himalayas, adapt to such conditions. Travelers, on the other hand, should take the necessary precautions to avoid getting sick due to the fact that the body is not used to such low pressure. Climbers, for example, can suffer from altitude sickness, which is associated with a lack of oxygen in the blood and oxygen starvation of the body. This disease is especially dangerous if you stay in the mountains for a long time. Exacerbation of altitude sickness leads to serious complications such as acute mountain sickness, high altitude pulmonary edema, high altitude cerebral edema and extreme mountain sickness. The danger of altitude and mountain sickness begins at an altitude of 2400 meters above sea level. To avoid altitude sickness, doctors advise not to use depressants such as alcohol and sleeping pills, drink plenty of fluids, and rise to altitude gradually, for example, on foot rather than by transport. It's also good to eat plenty of carbohydrates and get plenty of rest, especially if you're going uphill quickly. These measures will allow the body to get used to the oxygen deficiency caused by low atmospheric pressure. If you follow these recommendations, your body will be able to produce more red blood cells to transport oxygen to the brain and internal organs. To do this, the body will increase the pulse and breathing rate.
First medical aid in such cases is provided immediately. It is important to move the patient to a lower altitude where the atmospheric pressure is higher, preferably to an altitude lower than 2400 meters above sea level. Medicines and portable hyperbaric chambers are also used. These are lightweight, portable chambers that can be pressurized using a foot pump. A patient with altitude sickness is placed in a chamber in which the pressure corresponding to a lower altitude is maintained. Such a chamber is used only for providing first aid, after which the patient must be lowered below.
Some athletes use low pressure to improve circulation. Typically, this requires training to take place under normal conditions, and these athletes sleep in a low-pressure environment. Thus, their body gets used to high altitude conditions and begins to produce more red blood cells, which, in turn, increases the amount of oxygen in the blood, and allows them to achieve better results in sports. For this purpose, special tents are produced, the pressure in which is regulated. Some athletes even change the pressure in the entire bedroom, but sealing the bedroom is an expensive process.
Dependence on air temperature
Air temperature is one of the key factors in the formation of atmospheric pressure. When heated, air expands, becomes denser and at the same time lighter. As a result, atmospheric pressure decreases. If we talk about cold air, then it becomes, on the contrary, heavier, increasing atmospheric pressure. Therefore, when we talk about air temperature, we need to understand that a change in this indicator simultaneously entails a change in air pressure.
To understand how this movement (primarily the replacement of air) occurs through temperatures, we can consider circulation into the premises. The air, heated by the battery, rises up to the ceiling. It stays there for some time, cools down and goes down. Then it gets back into the battery, heats up and rises again. This happens in a closed cycle.
Spacesuits
NASA's reusable transport spacecraft Atlantis is on display at the Kennedy Space Center.
Pilots and astronauts have to work in low-pressure environments, so they wear spacesuits that compensate for the low pressure environment. Space suits completely protect a person from the environment. They are used in space. Altitude-compensation suits are used by pilots at high altitudes to help the pilot breathe and counteract low barometric pressure.
Health Hazard
Changes in atmospheric pressure are dangerous for weather-sensitive people, as well as sudden changes (rapid diving to depth, climbing mountains, or a sharp increase/decrease in pressure) for ordinary people.
Possible complications from fluctuations in atmospheric pressure:
- disturbance of psychological balance in an irreversible direction (schizophrenia, depression, psychosis);
- development of stroke due to increased intracranial pressure;
- development of heart attack in people with heart pathologies;
- irreversible impairment of mental activity due to lack of oxygen;
- development of asthma due to impaired oxygen metabolism and bronchial activity;
- formation of blood clots with subsequent blockage of blood vessels;
- as a result of decreased immunity, infection with a dangerous infection with the development of subsequent complications;
- deterioration of the condition of blood vessels with the likelihood of developing varicose veins or their rupture;
- irreversible changes in the quality of vision and hearing. Possibly to the point of complete blindness and deafness.
Fainting is also dangerous, since the result of a fall from loss of consciousness can be fatal.
Hydrostatic pressure
Hydrostatic pressure is the pressure of a fluid caused by gravity. This phenomenon plays a huge role not only in technology and physics, but also in medicine. For example, blood pressure is the hydrostatic pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels. Blood pressure is the pressure in the arteries. It is represented by two values: systolic, or the highest pressure, and diastolic, or the lowest pressure during a heartbeat. Devices for measuring blood pressure are called sphygmomanometers or tonometers. The unit of blood pressure is millimeters of mercury.
Digital blood pressure machine, also called a sphygmomanometer
The Pythagorean mug is an interesting vessel that uses hydrostatic pressure, specifically the siphon principle. According to legend, Pythagoras invented this cup to control the amount of wine he drank. According to other sources, this cup was supposed to control the amount of water drunk during a drought. Inside the mug there is a curved U-shaped tube hidden under the dome. One end of the tube is longer and ends in a hole in the stem of the mug. The other, shorter end is connected by a hole to the inside bottom of the mug so that the water in the cup fills the tube. The principle of operation of the mug is similar to the operation of a modern toilet cistern. If the liquid level rises above the level of the tube, the liquid flows into the second half of the tube and flows out due to hydrostatic pressure. If the level, on the contrary, is lower, then you can safely use the mug.
At-risk groups
Pressure (atmospheric) can cause problems even in healthy people if the mercury level rises or falls by more than 3 points within 1-3 hours. After the atmospheric pressure returns to normal, your health will stabilize.
The diagnosis of weather dependence is diagnosed more often in the following groups of people:
- men and women of advanced age. Their body can no longer quickly adapt to changes in atmospheric pressure;
- women during pregnancy. During this period, the body’s forces are aimed at maintaining pregnancy and developing the fetus. As a result, pregnant women feel even small pressure drops;
- children under 3-5 years old. Their body is still learning to respond to weather changes;
- teenagers during hormonal changes. During this period, the body is sensitive not only to pressure fluctuations, psycho-emotional balance is disturbed and the immune system is weakened;
- menopause period. The body again undergoes hormonal changes and is sensitive to any changes inside and outside;
- people with kidney diseases. This disease causes a violation of the water composition in the body, which causes increased sensitivity to pressure fluctuations;
- allergy sufferers and asthmatics. Weather dependence is caused by decreased immunity;
- patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system and those suffering from changes in blood pressure;
- people with chronic pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- patients with psychological disorders;
- people with chronic ENT diseases.
People living in big cities with poor environmental conditions are more susceptible to feeling pressure changes than residents of rural areas.
Pressure in geology
Quartz crystal illuminated by laser pointer
Pressure is an important concept in geology. Without pressure, the formation of gemstones, both natural and artificial, is impossible. High pressure and high temperature are also necessary for the formation of oil from the remains of plants and animals. Unlike gems, which primarily form in rocks, oil forms at the bottom of rivers, lakes, or seas. Over time, more and more sand accumulates over these remains. The weight of water and sand presses on the remains of animal and plant organisms. Over time, this organic material sinks deeper and deeper into the earth, reaching several kilometers below the earth's surface. The temperature increases by 25 °C for every kilometer below the earth's surface, so at a depth of several kilometers the temperature reaches 50–80 °C. Depending on the temperature and temperature difference in the formation environment, natural gas may form instead of oil.
Diamond tools
Natural gemstones
The formation of gemstones is not always the same, but pressure is one of the main components of the process. For example, diamonds are formed in the Earth's mantle, under conditions of high pressure and high temperature. During volcanic eruptions, diamonds move to the upper layers of the Earth's surface thanks to magma. Some diamonds fall to Earth from meteorites, and scientists believe they formed on planets similar to Earth.
Synthetic gemstones
The production of synthetic gemstones began in the 1950s and has been gaining popularity recently. Some buyers prefer natural gemstones, but artificial stones are becoming more and more popular due to their low price and lack of hassles associated with mining natural gemstones. Thus, many buyers choose synthetic gemstones because their extraction and sale is not associated with human rights violations, child labor and the financing of wars and armed conflicts.
One of the technologies for growing diamonds in laboratory conditions is the method of growing crystals at high pressure and high temperature. In special devices, carbon is heated to 1000 °C and subjected to pressure of about 5 gigapascals. Typically, a small diamond is used as the seed crystal, and graphite is used for the carbon base. From it a new diamond grows. This is the most common method of growing diamonds, especially as gemstones, due to its low cost. The properties of diamonds grown in this way are the same or better than those of natural stones. The quality of synthetic diamonds depends on the method used to grow them. Compared to natural diamonds, which are often clear, most man-made diamonds are colored.
Due to their hardness, diamonds are widely used in manufacturing. In addition, their high thermal conductivity, optical properties and resistance to alkalis and acids are valued. Cutting tools are often coated with diamond dust, which is also used in abrasives and materials. Most of the diamonds in production are of artificial origin due to the low price and because the demand for such diamonds exceeds the ability to mine them in nature.
Some companies offer services for creating memorial diamonds from the ashes of the deceased. To do this, after cremation, the ashes are refined until carbon is obtained, and then a diamond is grown from it. Manufacturers advertise these diamonds as mementos of the departed, and their services are popular, especially in countries with large percentages of wealthy citizens, such as the United States and Japan.
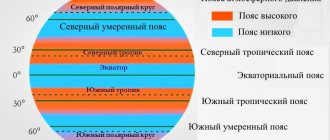
Pressure distribution across belts
Considering climatic zones, we noted that they are distributed on Earth according to the belt principle. For atmospheric pressure, which, as we have already found out, also strongly correlates with air temperature, a clear zonality can also be traced on our planet. At the equator, where the sun shines most intensely, there is a belt of low pressure. From the equator, warm air moves through the winds to moderate latitudes. During this movement, the air cools and becomes heavier, sinking down. Therefore, a zone with high pressure is formed in the region of 30 latitudes.
The next zone of high atmospheric pressure forms in the area of the south and north poles. The reason is that the air temperature here is always quite low, and snow and ice also actively repel the sun’s rays. Considering the topic of winds, we said that air masses move from the poles towards the equator. Therefore, cold air, gradually moving towards the equator, becomes warmer, forming a belt of low atmospheric pressure in the region of 60 latitudes.