What is atmospheric pressure? All bodies in the Universe tend to attract each other. Large and massive ones have a higher force of attraction compared to small ones. This law is also inherent in our planet. The Earth attracts to itself any objects that are located on it, including the gas shell surrounding it - the atmosphere. Although air is much lighter than the planet, it has a lot of weight and presses on everything that is on the earth's surface. This creates atmospheric pressure.
What is atmospheric pressure?
Atmospheric pressure refers to the hydrostatic pressure of the gas shell on the Earth and objects located on it. At different altitudes and in different parts of the globe it has different indicators, but at sea level the standard is considered to be 760 mm of mercury.
This means that a column of air weighing 1.033 kg exerts pressure on a square centimeter of any surface. Accordingly, there is a pressure of more than 10 tons per square meter.
People learned about the existence of atmospheric pressure only in the 17th century. In 1638, the Tuscan Duke decided to decorate his gardens in Florence with beautiful fountains, but unexpectedly discovered that the water in the constructed structures did not rise above 10.3 meters.
Deciding to find out the reason for this phenomenon, he turned for help to the Italian mathematician Torricelli, who, through experiments and analysis, determined that air has weight.
How is atmospheric pressure measured?
Atmospheric pressure is one of the most important parameters of the gas shell of the Earth. Since it varies in different places, a special device is used to measure it - a barometer. An ordinary household appliance is a metal box with a corrugated base, in which there is no air at all.
When the pressure increases, this box contracts, and when the pressure decreases, on the contrary, it expands. Along with the movement of the barometer, a spring attached to it moves, which affects the needle on the scale.
Liquid barometers are used at weather stations. In them, pressure is measured by the height of a mercury column enclosed in a glass tube.
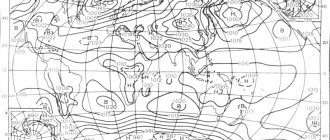
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is not only the opposite of a cyclone. This phenomenon has a different mechanism of occurrence. The wind in both hemispheres of the Earth moves in the opposite direction compared to the cyclone.
Anticyclone
An anticyclone is an area of high pressure. It is characterized by closed isobars - these are lines that mark places with the same atmospheric pressure.
An anticyclone brings stable weather conditions corresponding to the time of year. In summer it is windless, hot weather, in winter it is frosty. Characterized by few or no clouds.
Interesting: Snow: what is it, how is it formed, why is it white, where does it come from, photos and videos
Anticyclones form in certain areas. For example, most often they occur over large bodies of ice: in Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic. Also found in the tropics.
Anticyclones also carry danger and unpleasant consequences. They can contribute to fires and prolonged droughts. When there is no wind for a long time in large cities, harmful substances and gases accumulate, which is especially acute for people with respiratory diseases.
Difference between cyclone and anticyclone
Interesting fact : there are blocking cyclones that form over a certain area and do not move anywhere. At the same time, they do not allow other air masses to pass through. Usually they last no longer than 5 days, but regularly in the European part of Russia anticyclones last for about a month. The last time this happened was in 2015. The result is heat, drought, forest fires.
Why is it measured?
Why does humanity measure atmospheric pressure?
Since atmospheric pressure is created by overlying layers of gas, it changes as altitude increases. It can be influenced by both air density and the height of the air column itself. In addition, pressure varies depending on the location on our planet. This is due to the fact that different regions of the Earth are located at different altitudes above sea level.
By the way, from time to time slowly moving areas of high or low pressure are created above the earth's surface. In the first case they are called anticyclones, in the second - cyclones. On average, sea level pressure readings range from 641 to 816 mmHg, although tornadoes can drop as low as 560 mmHg inside.
Meteopathy
Meteopathy is the body's negative reaction to weather changes. Symptoms range from mild malaise to severe myocardial dysfunction, which can cause irreversible tissue damage.
The intensity and duration of manifestations of meteoropathy depend on age, body composition, and the presence of chronic diseases.
For some, the ailments continue for up to 7 days. According to medical statistics, 70% of people with chronic illnesses and 20% of healthy people have meteopathy.
The reaction to weather changes depends on the degree of sensitivity of the body. The first (initial) stage (or meteosensitivity) is characterized by a slight deterioration in well-being, which is not confirmed by clinical studies.
The second degree is called meteodependence, it is accompanied by changes in blood pressure and heart rate. Meteopathy is the most severe third degree.
With hypertension combined with weather dependence, the cause of deterioration in well-being can be not only fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, but also other environmental changes. Such patients need to pay attention to weather conditions and weather forecasts.
This will allow you to take the measures recommended by your doctor in a timely manner.
How does atmospheric pressure affect the weather?
The distribution of atmospheric pressure across the Earth is uneven. This is due to the movement of air and its ability to create so-called pressure vortices.
In the northern hemisphere, clockwise air rotation leads to the formation of downward air currents (anticyclones). They bring clear or partly cloudy weather with a complete absence of rain and wind to a specific area.
But if the air rotates counterclockwise, then rising vortices are formed above the ground. They are characteristic of cyclones, with heavy precipitation, heavy winds, and thunderstorms. By the way, in the southern hemisphere, cyclones move clockwise, anticyclones move counterclockwise.
University
→ Home → University → University in the media → “Almost every third person reacts to the weather.” Doctors on what to do with weather dependence
You can expect anything from the weather lately. Doctors recommend that weather-sensitive people be on guard. Why weather dependence cannot be considered a universal “excuse” for lazy people, how many Belarusians react painfully to climate vagaries and whether it is realistic to become more resistant to them - GO.TUT.BY was helped to understand by a cardiologist, a psychiatrist and a physiologist.
“Any external changes for the body are stressful, but normally they should not be felt”
Irina Pateyuk, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Let's start with the fact that weather sensitivity and weather dependence are not a disease.
“There is no such diagnosis in the International Classification of Diseases,” states Irina Pateyuk, associate professor of the Department of Cardiology and Internal Medicine of BSMU.
Weather dependence should be regarded as a pathological reaction of the body in response to weather changes. This phenomenon is often encountered by ambulance specialists, hospital emergency departments, therapists and cardiologists.
“The body reacts not only to climate change, but also to any external changes with stress. And this is absolutely normal,” says the specialist. “But the body is designed in such a way that it quickly adapts to external influences, and a person should not normally feel these processes. If your health worsens, it means that adaptation has failed.
Errors in health status can contribute to the development of a pathological reaction to weather changes. As a rule, people who have recently undergone surgery or any infection “respond” to changes in weather conditions. And, of course, those who suffer from chronic diseases. The most vulnerable are heart patients and hypertensive patients, as well as people with diseases of the musculoskeletal system (joint diseases, arthrosis, chronic ailments of the spine). Since the number of chronic illnesses increases with age, older people become “barometers”.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only.
It turns out that increased sensitivity to weather changes is the “prerogative” of people with serious diagnoses?
Irina Pateyuk thinks not. A healthy person who is experiencing psycho-emotional stress or is tired from intense mental work can also react to sudden changes in weather conditions. Hence - drowsiness in the rain and complaints of weakness if it gets colder.
“Hypertensive patients feel changes in atmospheric pressure, people with respiratory pathologies feel changes in humidity”
What kind of disease a person suffers from depends on what parameters he will “respond” to—changes in atmospheric pressure, humidity or temperature.
People with diseases of the cardiovascular system, as a rule, are overly sensitive to changes in atmospheric pressure and changes in geomagnetic fields (magnetic storms).
“The fact is that the nervous and endocrine systems react primarily to changes in atmospheric pressure, and they are both “responsible” for regulating vascular tone,” explains Irina Pateyuk. “Normally, blood vessels quickly restructure in response to changes in external conditions, but when, say, they are affected by atherosclerosis, a malfunction occurs. Blood pressure jumps, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness appear, and the heart rate may be disrupted.
People with respiratory pathologies tend to react to changes in humidity. Air that is too dry (below 40%), saturated with dust, dries out the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract; it does not retain harmful microorganisms well, allowing them to penetrate the bronchi and lungs, and in response - a defensive reaction - the secretion of mucus begins. Too high humidity (over 80%) in the heat can cause swelling of the airways: their patency decreases, as a result, a person does not receive enough oxygen - shortness of breath occurs.
“Almost every third Belarusian reacts to the vagaries of the weather”
The sharper the fluctuations in night and day temperatures, atmospheric pressure, and humidity, the more people will feel it in their own bodies, Irina Pateyuk is sure. According to international studies, almost every third resident of mid-latitudes, which includes our compatriots, is weather dependent.
Clinical observations in Belarus show: on days when significant changes in the geomagnetic field or significant jumps in atmospheric pressure occur, ambulance calls for heart rhythm disturbances increase by 10-30%. Patients are admitted to the hospital with a hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, or cerebrovascular accident.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only.
The connection between the number of exacerbations and complications of the disease during the vagaries of the weather is confirmed by the clinical practice of Irina Pateyuk:
— It often happens that one day, chronic patients who have been observed for 5-10 years, as if by agreement, begin to call or urgently ask for an appointment: the pressure has “soared”, shortness of breath has increased... As a rule, they all unanimously see the reason as , that “the medicine has stopped working”, “I bought a not very good drug”, and tomorrow it turns out that it has become sharply colder. Before changes in the form of rain, snow or extreme heat become visible, the pressure in the atmosphere changes, and cardiac patients immediately sense this.
A cardiologist warns that for people with cardiovascular diseases, a geomagnetic storm or a jump in atmospheric pressure can be fatal:
— A common mistake made by patients is that, feeling relatively well for a long time, they stop taking medications or arbitrarily reduce the dose, for example, instead of taking a pill, they start taking half a tablet. The drug protection of the cardiovascular system is weakened - and a sharp change in atmospheric pressure or fever below forty during the week acts as a trigger for the occurrence of complications.
To prevent weather changes from becoming a blow to the gut, the specialist advises to monitor the weather forecast and, in unfavorable periods, reduce your load as much as possible, be sure to get a good night's sleep and not miss scheduled visits to a specialist to adjust individual therapy.
“Heat can lead to suicidal thoughts”
Alexey Krot, assistant at the Department of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology, BSMU
Alexey Krot, assistant at the Department of Psychiatry and Medical Psychology of the Belarusian State Medical University, states that changing conditions in weather-dependent people is reflected in the psycho-emotional background.
A natural consequence of high air temperature or changes in atmospheric pressure is depression of the functions of the central nervous system. The person is depressed, lethargic, drowsy, lethargic, gets irritated for any reason, has trouble thinking and works less productively. For those prone to depression, the heat can even provoke thoughts of suicide. The reaction to hot weather may be exacerbated in those who live in conditions that disrupt circadian biorhythms and do not allow proper rest. For example, he works hard on the night shift.
Some weather addicts, feeling unwell, desperately try to cheer themselves up with energy drinks or stimulants. But a fifth cup of coffee, an ice-cold shower or ten push-ups, as a rule, saves you for an hour and a half at best, and then has the opposite effect - lethargy and weakness worsen.
Photo is for illustrative purposes only.
“In a state of depression of the nervous system, it is better to avoid intense physical activity and psychostimulants,” says the specialist. — It’s better to prefer a regular walk in a public garden or park, relaxation exercises, and even better, devote some time to this regularly. Since overstrain of the central nervous system is also caused by intense information load, minimize the use of mobile phones, tablets and computers, watch less TV and do not hang out on social networks.
Alexey Krot points out that not every change in the weather affects your well-being. Either sharp fluctuations or parameters of extreme intensity play a role. We are talking about an increase in atmospheric pressure by 8 or more mmHg. Art., a change in air temperature by 7−10 degrees, wind speed by 5 m per second, an increase in humidity over 80%.
“Weather-sensitive people should forget about any sudden lifestyle changes”
Frantisek Vismont, Physiologist, Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Sciences of Belarus, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Anyone looking for effective means of combating weather dependence will most likely be disappointed. Professor František Vismont believes that influencing meteosensitivity is extremely difficult.
“The fact is that meteosensitivity is determined by such an indicator as the reactivity of the body,” he explains. — The more violently it reacts in response to external stimuli, which include temperature changes or a jump in atmospheric pressure, the less stable it is. And reactivity depends on many factors - gender, age, heredity, type of higher nervous activity, constitution, seasonality, functional state of organs and systems, etc. And in order to give recommendations, it is necessary to carefully study all these parameters in a particular person.
Cholerics, for example, are more sensitive to weather changes than phlegmatic people, since the former are characterized by a pronounced reaction to external stimuli. But a young choleric person may be less weather dependent than an elderly phlegmatic person. Tall people with a thin build are more vulnerable to the vagaries of the weather than dense and stocky people. But if an asthenic person is engaged in physical labor, and a hypersthenic person is engaged in mental labor, everything may be the other way around.
Nevertheless, it is possible and necessary to train the body’s resistance to external influences, the professor believes. The methods are not new - hardening, contrast showers, baths and saunas, walks in the fresh air in any weather, morning exercises and other types of moderate physical activity.
“A change of situation, contrasts work as a training of adaptation mechanisms,” says the specialist. - But under one important condition - the loads must be strictly dosed and increased gradually. After all, any adaptation occurs at the expense of the body’s reserve forces, and in weather-dependent people they are already depleted.
So any sudden change in lifestyle for those who are weather sensitive can only be detrimental. Strict diets and travel to countries with exotic climates are contraindicated for them. Otherwise, weather dependence can contribute to the occurrence of diseases.
Photo: Evgeny Erchak, Stanislav Korshunov, Elena Kleshchenok, Dmitry Brushko TUT.BY , May 31, 2018
Share
How does it affect a person?
Each person is pressed by an air column weighing from 15 to 18 tons. In other situations, such a weight could crush all living things, but the pressure inside our body is equal to atmospheric pressure. Therefore, with normal readings of 760 mmHg, we do not experience any discomfort.
If the atmospheric pressure is higher or lower than normal, some people (especially the elderly or sick) feel unwell, have headaches, and note an exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Most often, a person experiences unpleasant sensations at high altitudes (for example, in the mountains), since in such areas the air pressure is lower than at sea level.
Treatment of weather dependence
Increased weather sensitivity pushes people to look for the most effective ways to improve their well-being. It is useful for people who respond to magnetic storms and other atmospheric phenomena to know how to deal with weather sensitivity.
Therapy for magnetic storms
If your health worsens due to magnetic storms, then during this period it is better not to engage in heavy mental and physical work. To make it easier to cope with the period of solar flares, it is useful to get a good night's sleep, spend time in the fresh air more often, do not overindulge in heavy foods and take vitamins. In addition, a few days before the start of a magnetic storm, it is useful to play sports, give up bad habits and switch to a healthy diet.
Therapy for high atmospheric pressure
The answer to the question “How to get rid of weather sensitivity?” is also of interest to people who respond to increases in atmospheric pressure. The same recommendations mentioned above are relevant for them. In addition, it is useful for such people to do light exercises in the morning and take a contrast shower. For breakfast, it is preferable to eat foods rich in potassium (for example, cottage cheese with dried apricots, raisins and bananas). On such days, you should absolutely not overeat, work hard physically, and it is also useful to avoid excessive emotionality.
During periods of high atmospheric pressure, doctors advise going to bed earlier than usual.
Treatment at low atmospheric pressure
First aid for weather sensitivity caused by a decrease in atmospheric pressure is to normalize the blood pressure of a weakened person. As a preventive measure, on such days it is useful to reduce physical activity, and after every hour of work, take 10 minutes to rest. You should start the day with coffee, then drink a lot of fluids, including green tea with honey, and it is useful for heart patients to take special herbal tinctures (with the permission of the attending physician). Before going to bed, you can take a contrast shower and go to bed 1-2 hours earlier than usual.