© Author: A. Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, practicing physician, teacher at a medical university, especially for SosudInfo.ru (about the authors)
MARS (minor anomalies of the heart) are special conditions that are not accompanied by obvious disturbances in the functioning of the organ, but can still manifest symptoms of trouble and even threaten life. Until recently, they were considered a normal option, but as their role in the activity of the cardiovascular system was studied, their apparent harmlessness was questioned. It is now recognized that patients with MARS should be monitored and, in some cases, require drug treatment.
MARS usually manifests as heart murmurs and arrhythmias, but it has been problematic to speculate on the exact cause of these phenomena. With the introduction of ultrasound examination into cardiological practice, the study of the problem of minor anomalies began, and in the 90s of the last century the term MARS itself was proposed. The relevance of the issue is also due to the fact that such defects are found mainly in children and young people, and in order to avoid dangerous consequences, timely diagnosis, observation and treatment are necessary.
Minor anomaly of heart development is associated with defects in the structure of connective tissue . It is generally accepted that this condition is based on dysplasia of connective tissue structures, which occurs in utero as a result of genetic mutations or after birth under the influence of unfavorable external factors.
Connective tissue plays the role of a framework for internal organs, forms the basis of the valve apparatus of the heart and blood vessels, therefore, without its normal formation, various kinds of deviations arise in both the structure and functioning of organs. MARS is often combined with pathology of other organs, where dysplastic changes in connective tissue are also found.
The ambiguity of expert opinion regarding minor cardiac anomalies is caused not only by their diversity and frequent asymptomatic course. As the child grows, the functioning of the internal organs changes, the heart grows, so some abnormalities may disappear on their own, for example, an open oval window can close spontaneously. Along with this, changes such as mitral valve prolapse or an accessory chord in the ventricle lead to some hemodynamic disorders with age, so it is now customary to consider MARS as a pathology rather than as a normal variant.
The presence of minor heart anomalies should be a reason for a comprehensive examination , because if the connective tissue in one organ is not developed quite correctly, then there is a high probability of problems with others. Thus, patients with MARS often suffer from pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (refluxes, intestinal diverticula, diaphragmatic hernias), bronchiectasis is possible in the respiratory system, developmental disorders of the musculoskeletal system are manifested by scoliosis, flat feet, joint hypermobility, and are predominantly diagnosed in women with MARS problems with urination. Combinations of minor anomalies with vegetative disorders in the form of vegetative-vascular dystonia are not uncommon; speech disorders, mental disorders, bedwetting, panic attacks, etc. are possible.
Causes
There can be many reasons for the development of MARS. And almost every individual case in medical practice is individual. But let’s look at the most common situations when MARS develops in children:
- this may be a consequence of various mutagenic effects on the tissue compounds of the fetus in the womb;
- hereditary factor;
- a certain group of diseases affecting the development of chromosomes;
- stress suffered by a woman during pregnancy;
- unbalanced diet of the expectant mother;
- a woman’s use of alcohol and drugs during pregnancy, as well as smoking;
- the presence of infections in a woman who is “pregnant”;
- taking medications during pregnancy.
What if you need pills?
Sometimes there are situations when the doctor will recommend a course of certain medications. The main therapeutic effects are magnesium preparations. This trace element is a component of connective tissue and therefore improves its structure and heart function. The choice of magnesium preparations depends on the age of the patient. There are liquid and tablet forms. Particularly popular are “Magnerot” - in addition it also contains orotic acid, which promotes the absorption and more complete absorption of magnesium, “Magne B6” in the form of syrup or tablets, and “Potassium Orotate”. Usually 1-2 courses per year are recommended.
The second direction of therapy is cardiotrophic - nourishing the heart muscle. These are drugs that improve blood supply and nutrition to the tissue of the heart and other organs, affect metabolism in the body and are active antioxidants. Usually prescribed are “Elkar”, “Ubiquinone” or “Coenzyme Q10”, “Kudesan”, “Cyto-mac”. In addition to these drugs, some vitamins have a similar effect - PP, B2, B1, citric and succinic acids (the drug "Limontar"), biotin. They are prescribed as a multivitamin complex or each separately in courses of 10-14 days twice a year.
In case of infections, the baby is recommended to take preventive courses of antibiotic therapy to prevent heart complications such as endocarditis.
Regular examinations by an ENT specialist and a dentist are indicated to sanitize foci of chronic infection - carious teeth, tonsils, adenoids.
In the presence of arrhythmias, antiarrhythmic therapy is indicated, but it is selected individually in the hospital under the supervision of a physician.
Courses of sedatives are conducted that normalize the functioning of the nervous system, relieve anxiety, increased nervous excitability and treat neuroses.
Symptoms
Note that the diagnosis of MARS in cardiology in a newborn child is practically absent, since there are no clinical signs. More often, such anomalies make themselves felt at an older age. This can happen during the active development of the baby or after any illness. Symptoms for minor anomalies of heart development in children are as follows:
- frequent tingling in the heart;
- regular heart pain;
- the presence of sensations that the rhythm of the heartbeat is lost;
- fast fatiguability;
- frequent weakness;
- dizziness;
- changes in blood pressure parameters.
So how do MARS manifest itself?
In most cases, MARS does not manifest itself in any way, and children are no different from their peers. Less often, the main complaints of children will be intermittent pain in the heart area, arrhythmias, feelings of interruptions in the heart, and surges in blood pressure.
Often heart anomalies are combined with structural anomalies of the nervous, urinary, digestive system, vision, breathing, skeleton or skin; there may be some structural features of other organs - liver, gall bladder, kidneys.
At the beginning of the material, we said that MARS refers to connective tissue dysplasia, and connective tissue is present in all organs and systems in greater or lesser quantities. Therefore, the manifestations will be so-called systemic, that is, at the level of the entire organism. They can range from very minimal to quite pronounced.
A careful examination of the skeleton can reveal elongation of the limbs relative to the body, depression of the sternum, scoliosis (curvature) of the lower thoracic spine, various forms of flat feet, hypermobility (excessive mobility) of the joints. The most common combinations with MARS are polycystic kidney disease, gastroesophageal reflux (reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus), kinking of the gallbladder, megaureter (dilation of the ureter).
In addition, MARS is often accompanied by so-called neurovegetative disorders - the peripheral and central nervous systems work unbalanced. This can manifest itself as enuresis, speech defects, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and behavioral disorders. However, all these combinations in no case lead to severe dysfunction of organs and systems and do not worsen the overall functioning of the baby’s body.
Diagnostics
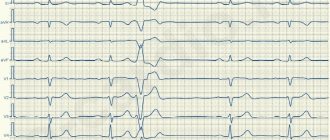
It is possible to diagnose MARS in children. For these purposes, regular ECG testing is recommended. Most often, this diagnosis is made during a routine medical examination. But if there are any signs or suspicions of MARS, it is urgent to do a cardiogram of the child’s heart.
Cardiac ultrasound is often prescribed as a diagnostic measure. This type of examination allows you to most accurately determine pathology, the presence of all kinds of anomalies and their effect on blood flow.
An experienced specialist, while carefully listening to the heartbeat, will be able to notice a systolic murmur, which indicates improper functioning of this organ.
A little anatomy
The framework of all the internal organs of the child consists of special connective tissue - it is formed in utero. Connective tissue gives the organ its characteristic shape, helps it perform functions and prevents it from stretching and deforming under impacts. Connective tissue can be presented in two types - coarse fibrous, an example is cartilage, and soft fibrous - this is a kind of sponge, inside of which there are specific cells of a particular organ.
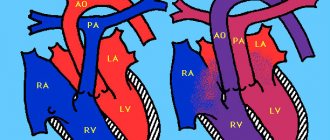
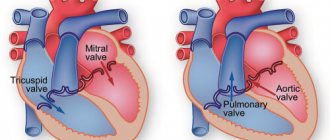
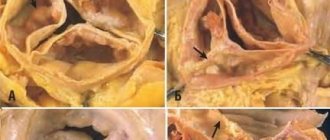
In the structure of the heart, this same connective tissue forms the valves and the heart frame itself, between the fibers of which muscle cells - cardiomyocytes - are located. Due to this, the heart tissue is elastic, but quite strong. In addition, connective tissue also forms the walls of large vessels - the aorta, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary veins and their valves (see figure). Minor cardiac anomalies (or MARS) are one of the manifestations of a condition such as dysplasia (not quite correct development) of this very connective tissue. In this condition, the connective tissue is either too weak or is formed in excess, not in the places where it should normally be. As a result, minor anatomical formations of internal organs, including the heart, appear.
Treatment
If a child is diagnosed with MARS in cardiology, then immediate treatment is required in order to avoid adverse consequences.
Doctors prescribe:
- balanced and proper nutrition;
- full compliance with sleep and rest patterns;
- no load;
- physical therapy classes.
Experts insist that parents completely eliminate the possibility of stress in their child. As for serious physical activities, in most frequent cases they are prohibited.
Where to start therapy?
In order for MARS syndrome to manifest itself minimally or not at all, you need to choose an optimal daily routine, an appropriate load for your age and condition, alternating activities and rest. Many parents believe that a child with MARS needs to sharply limit exercise, which is fundamentally wrong. After consulting with a doctor, for the most part, you can not limit the baby’s movement at all. The heart develops correctly when it is given adequate stress. There is no need for restrictions in activity or excessive effort. If the baby expresses a desire to engage in any kind of sport, first consult with a cardiologist to see if the level of stress that sports activities will provide is possible for him. But ordinary daily activities - walking outside, cycling, running - are quite enough for proper development.
For a child with MARS syndrome, it is important to follow a daily routine, get enough sleep, eat properly, and receive all the nutrients and vitamins required by age. It is important to initially prepare yourself for long-term breastfeeding; this will help the baby get sick less and reduce the risk of heart complications at an early age to a minimum. In addition, it is necessary to introduce complementary foods into the child’s diet correctly and in a timely manner, and subsequently monitor the intake of sufficient amounts of protein foods and foods rich in calcium and magnesium.
Children who have neurological problems and are emotionally unstable benefit from working with a psychologist and sedative therapy. Physiotherapy - various baths, spa therapy, massages - also have a calming and restorative effect.
Such babies are monitored jointly by a pediatrician and a pediatric cardiologist. The timing of inspections is selected individually, depending on the type of MARS and the presence or absence of associated violations. Usually, for most children, non-drug measures or infrequent courses of cardiotrophic (supporting the proper functioning of the heart) drugs are sufficient.
Only isolated cases of MARS may require surgical correction. In such cases, the baby will be referred to a cardiac surgeon to decide on the volume and timing of the operation. There is no need to be afraid of this - open heart surgery is very rarely performed for MARS. Usually these are so-called endoscopic operations - an instrument is inserted into the heart cavity through small punctures or through large vessels and the defect is corrected. Usually, babies stay in the clinic for a short time and after discharge they lead the lifestyle of ordinary children.
Classification of minor cardiac anomalies
MARS anomalies are usually systematized according to their localization in the area:
- Atria and septum between them:
- prolapsed (sagging) pectineus muscles (muscle bundles on the inner surface of the right atrium);
- prolapse (protrusion) of the valve of the inferior vena cava;
- aneurysm (protrusion) of the atrial septum;
- a structural feature of the cardiac septum called a patent foramen ovale (PFO);
- enlarged Eustachian valve (endocardial fold);
- altered trabeculae (tendon formations);
- Pulmonary valve and tricuspid (three-leaf) valve:
- extension;
- prolapse of valves;
- Aortic openings:
- aneurysm;
- violation of the symmetry of the dampers;
- changes in the aortic root;
- Left ventricle:
- additional trabeculae;
- altered chords in the heart and their incorrect position;
- defect of the outflow tract (the area of the heart through which blood enters the arteries);
- aneurysm of the septum separating the ventricles;
- Bicuspid valve:
- prolapse of valve flaps;
- defects in chordal attachment and distribution;
- additional, enlarged, incorrectly located or structurally changed muscles that continue the myocardium of the left ventricle.
Once a diagnosis of MARS has been established, it is necessary to find out whether there are changes in hemodynamics and regurgitation, and to determine the extent of their manifestation. In adult patients, valve prolapse, “irregular” and additional chords in the left ventricle, and excessive trabecularity are more often diagnosed.
Summarize
MARS syndrome is not a death sentence, it is a special condition of the child that requires only observation and minor correction. For mothers and fathers, the presence of such a diagnosis is not a reason to limit the child and panic, it is just a reason to change their lifestyle, adjusting it to the capabilities of the baby. Most MARS do not cause any harm to the baby, and his life is no different from his peers. There is no need to treat such a child as a sick person, much less a disabled person - this is groundless. The main thing that parents need to remember is the doctor’s conclusion: “no hemodynamic disturbances are detected.” This suggests that MARS does not interfere with the baby in any way.
Congenital aortic stenosis
Cardiologists diagnose two types of narrowing of this vessel: subvalvular and valvular. The disorder is a minor congenital heart defect that occurs during fetal development.
The narrowed valve has a characteristic structure: the valve leaflets fuse together, forming a funnel with a hole directed towards the aorta.
The subvalvular narrowing has a different structure: it is a roll of muscle tissue located under the valves in the area of the left ventricle.
The clinical picture depends on the severity of the load on this part of the heart, as well as the degree of stenosis. Severe – leads to LV hypertrophy, in the final stage of the disease heart failure develops.
Patent foramen ovale
The anomaly refers to minor heart defects and is most often normal. The defect does not require treatment, except in cases where there is a pathological discharge of the shunted blood flow from the RA to the left.
The anomaly is eliminated surgically; during the operation, X-ray endovascular occlusion is performed, and the OO is closed using an occluder.
The most dangerous complication of an unoperated large foramen ovale is paradoxical embolism.
Air bubbles travel through the blood vessels to the brain, causing a stroke, so a hole that does not close for a long time and is large in size must be eliminated.
What kind of fabric is this
False left ventricular chord (LVCH) are cords of muscular-connective tissue, usually located inside the left cardiac ventricle, not connected to the valve leaflets. They were first discovered in the cavity of the human heart during autopsy in 1893. Although the author called them an anomaly, he recognized them as a possibility of the norm. A detailed classification of chords appeared already in 1970, where false ones were clearly separated from true ones. In particular, the bias was made on the location of the threads.
Over the course of many years of numerous studies, medical scientists have found that:
- about 20% of cases with the detection of atypical tissues may be accompanied by pathological changes in the functioning of the organ;
- in 19% of cases rheumatic heart disorder was observed;
- the same number of patients had atherosclerotic lesions;
- 12% of those examined were found to have mitral valve disease;
- in 5% of cases cardiomyopathy was detected;
- was present in the same number of patients.
Based on the data obtained, it was concluded that LVHL, as a result of a congenital defect, in particular cases can lead to the development of dysplastic syndrome. Disturbances in the structure of the left cardiac ventricle of this type are more common among the male population of the planet. Appearing during the embryonic development of the fetus, false threads can subsequently be transformed into additional pathways of circulation and impulse conduction. The risk of such formation is especially high when the body is intoxicated, the psycho-emotional state is unstable, and physical exertion is feasible.