Our organs and tissues need a constant supply of oxygen, nutrients and the removal of waste products. This is done through the blood supply system. Blood is “pumped” into organs and tissues through a “pump”, which is the heart. When the heart is healthy and the blood supply system is working properly, then all systems of the body also work in nominal mode. If our pump develops some kind of dysfunction, then the problems will not be local, cardiac, but global - the whole organism will “suffer” as a whole. Therefore, we can say that the heart is one of the most important human organs in everyday life, and even more so in sports practice, since the blood supply needs in sports increase significantly.
Signs of heart strain and its consequences
Dysfunctions of the heart are observed in most cases in the discrepancy between the amount of Oxygen it requires and the amount it receives. When the oxygen content decreases, it is no longer oxygen, but energy starvation. [1] The heart is not able to produce the required amount of ATP and, accordingly, is not able to carry out the required stroke volume of its work. The so-called cardiac overstrain, the symptoms of which will be:
- a sharp decrease in performance,
- weakness, increased sweating,
- shortness of breath, feeling that there is not enough oxygen, cough,
- rapid heartbeat, irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia),
- chest pain, nausea, vomiting.
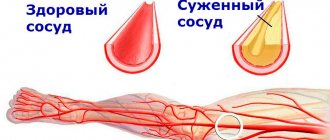
The general state of oxygen deficiency is called hypoxia. The causes of cardiac hypoxia can be various factors. In particular, in clinical practice, the most common diagnosis of cardiac hypoxia is myocardial ischemia, in which the lumen of the coronary vessels supplying the heart muscle decreases, and the cause of this condition in most cases is atherosclerosis of the arteries.
In sports practice, cardiac hypoxia occurs due to an increase in oxygen demand by all organs, primarily muscles. At the same time, the heart begins to experience oxygen deficiency, as a result of which cardiac functionality undergoes changes:
- Firstly, as mentioned above, the production of ATP molecules is reduced. In order to compensate for this dysfunction, the heart increases heart rate. Due to this, the amount of circulating blood increases and the amount of oxygen flowing through this blood also increases. However, heart rate has its own limit; for young and healthy athletes it is 200 beats/min, which is not recommended for other athletes. In addition, high heart rate is a state of cardiac overstrain, which must be clearly controlled in order to avoid irreparable pathological cardiac changes. [2] And this rule must be followed by all athletes, regardless of age and training.
“Secondly, the result of inadequate oxygen supply to tissues will be mitochondrial dysfunction, which will be manifested by phase fluctuations in the activity of mitochondrial enzymatic complexes. [2] This will lead to suppression of aerobic ATP synthesis. At the same time, the rate of formation of free radicals (FR) will increase, and the power of certain segments of the antioxidant system will decrease. A steadily increasing amount of reactive oxygen species (aka RO) and other toxic waste products will lead to the formation of oxidative stress, which is the cause of most cardiovascular diseases.
Diagnosis of angina pectoris
The main role in identifying the type of angina, its functional class and the degree of myocardial ischemia belongs to such functional instrumental techniques as:
- ECG at rest and during an attack;
- ECG during physical activity - stress test;
- echocardiography, c. incl. with load – stress echocardiography;
- daily ECG monitoring (to a lesser extent);
- myocardial scintigraphy against the background of physical or pharmacological stress;
If functional methods reveal signs of high grade myocardial ischemia, then examination of the coronary vessels is necessary.
Coronary angiography or MSCT angiography (computer coronary angiography) is used directly to diagnose damage to the coronary (heart) vessels.
Cardiac pathologies resulting from overexertion
If the overstrain of the heart becomes chronic (permanent), then irreparable changes begin to occur in the heart, in particular:
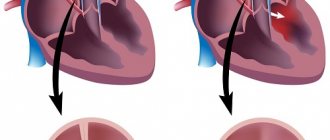
DILATATION OF THE HEART CHAMBERS is a pathological condition accompanied by an increase in the volume of the heart chambers without changing the thickness of the heart wall. [2] Left atrial dilatation often results from a sustained increase in pressure in the systemic circulation due to chronic heavy physical activity. Dilatation is a factor in heart failure because the ejection fraction decreases due to stretching of the heart walls.
MYOCARDIAL HYPERTROPHY is a thickening of the muscles of one or another part of the heart. The most common cause is left ventricular hypertrophy. It occurs in athletes as a result of intense and prolonged physical activity and reflects an irrational path from adaptation to hyperfunction. [2] Cardiac dysfunction, as in the case of dilatation, occurs in a decrease in the ejection fraction, but the reason in this case is a decrease in the volume of the heart due to thickening of the walls. The next problem with hypertrophy is the deterioration of oxygen supply to the heart muscles. Firstly, an enlarged myocardium requires increased blood circulation, but the capillaries that provide increased blood flow develop much more slowly than the muscle cells of the heart.
Secondly, the diffusion time of oxygen from the capillaries to the center of the thickened muscle fiber increases, which leads to changes in oxygen consumption by the hypertrophied myocardium. As a result, lack of oxygen (hypoxia) leads to heart failure, overexertion and arrhythmia. [2]
Myocardial hypertrophy is one of the most common causes of death in sports. The share of such deaths is 33% of all deaths, taking into account non-cardiac (!) causes. [2] The collected statistics show that myocardial hypertrophy above certain values in deceased athletes occurs 17 times more often than in living ones.
ARRHYTHMIA. Normally, the heart beats in a certain rhythm, having in its cycle sequential contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles. If the frequency, rhythm or sequence of excitation and contraction of the heart is disturbed, then this is a state of cardiac dysfunction and is called arrhythmia. 15% of deaths due to cardiac dysfunction are associated with arrhythmia.
What other diseases should be excluded?
Pain under the scapula, localized from the back, can also be a manifestation of pathologies of internal organs, for the diagnosis of which a careful collection of an initial history is of great importance. When contacting a doctor, the patient must describe in detail the existing symptoms, as well as assess the relationship of the pain syndrome with various factors: food intake, physical activity, psycho-emotional state, etc. The most likely causes of pain under the left shoulder blade, as well as their symptoms, are listed in the table below.
Table. Diseases of the internal organs as a cause of pain under the left shoulder blade.
| Organ | Possible diseases | Possible symptoms |
| Heart | Myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, myocardial infarction (necrosis), angina pectoris, arrhythmia. | The most typical manifestations of heart pathologies are changes in the number of heartbeats, shortness of breath, pain in the left side of the sternum, and breathing problems. With a progressive course, arterial instability is observed, signs of hypoxia - oxygen starvation (headaches, dizziness, migraines, hypertension) may appear. |
| Organs of the respiratory system (left side) | Pleurisy, bronchitis, pulmonary tuberculosis, pneumonia. | The leading symptom of respiratory pathologies is cough, but it is important to consider that in some diseases, for example, asymptomatic pneumonia, the cough is of low intensity and can occur in the form of coughing up to 4-6 times a day. In a typical course, the following symptoms are observed: headache, fever, pain in the chest area, which can radiate to the scapula area, sputum or purulent exudate. |
| Spleen | Splenic rupture. | This is a surgical pathology, the symptoms of which depend on the type of rupture. The most characteristic signs include tension in the abdominal wall (breathing is carried out superficially, the abdominal muscles do not take part in the act of breathing) and the forced position of the body adopted by the patient. The classic position for a ruptured spleen is to lie on your left side with your legs brought up to your chest. |
| Stomach (cardia and body of the stomach) | Gastritis, polyposis, stomach ulcer. | The main symptoms of gastroenterological pathologies: stomach pain, nausea, lack of appetite, bitterness and metallic taste in the mouth, stool upset. Pain under the left shoulder blade when the cardiac part of the stomach or its body is affected is of a reflected nature and occurs mainly during exacerbations as radiating pain. |
Symptoms of a heart attack in men and women
Causes of heart strain in sports and methods of prevention
1. It is IMPORTANT to emphasize the main idea here: the main cause of chronic overstrain of the cardiovascular system (CVS) is physical activity of significant volume and intensity. [2] That is incorrect, “greedy” planning of training progress leads to cardiovascular pathology. In the context of bodybuilding, this takes on increased relevance! Due to the fact that one of the main goals of BB is mass gain, other systems of the body, especially the heart, simply do not keep up with the super-intensive growth of mass and in fact pathological adjustments of these organs to the inflated demands of mass appear. Numerous examples of deaths caused by the failure of the cardiovascular system, both among current bodybuilders and among former, but not yet old, bodybuilders, confirm this. Therefore, the main message of this point is that if the goal is to weigh a lot, then this must be done gradually, without extreme weight increases of tens of kilograms!
2. Illness, cold, flu, inflammation...training against the background of illness is strictly not recommended. [1,2] The adaptive forces of the body in such conditions are sharply reduced, oxidative stress is increased, and the load on the heart increases many times over. If you try to maintain training intensity against this background, it will be very easy to get cardiac overstrain. The best option is to take a break, lie down and “get sick.” As a last resort, the intensity of training should be sharply reduced - classes during this period should be considered only as physical therapy (physical therapy).
It is also necessary to strictly monitor chronic diseases. Sports medicine here pays attention to diseases of the oral cavity that can occur in an indirect form, such as tonsillitis, periodontitis, and root cysts. [2] Inflammatory factors from such foci can drain into the blood, reducing both immunity and the activity of myocardial antigens.
3. Psycho-emotional stress. The banal recommendation to be less nervous is, in fact, quite justified in its relevance. Information and communication stress, which creates the background for the development of psycho-emotional disorders, causes overstrain of the psyche and neuroendocrine system, thereby disrupting the regulation of the cardiovascular system. [2] The athlete’s exposure to any traumatic factors must be limited as much as possible.
4. Bad habits. In particular, smoking is one of the most common causes of coronary heart disease. It provokes vasospasm and thus increases blood pressure. The negative effect on the body increases many times over if it is combined with an increase in cholesterol in the blood.
5. Hypertension. This partly echoes the first point and a prerequisite for hypertrophy will be excess body weight. This pathology will be enhanced by problems of insufficient local (capillary) blood supply. Therefore, high-repetition approaches with light weights (such as the Cutting program), as well as cardio training, should be present in training programs to improve local blood supply to the muscles.
Unpleasant sensations in the chest after yoga
By doing yoga, a person becomes more flexible, strengthens the spine and prevents pathologies of most body systems. The cause of pain when performing asanas lies in the chosen tempo or inappropriate posture. If this occurs, it is advisable to immediately consult with an instructor. He will tell you why the unpleasant sensations appeared, adjust the lesson plan and recommend methods of getting rid of the symptoms.
You can prevent heart pain after a yoga workout by changing asanas and reducing physical activity.
Before conducting classes at home, it is advisable to take several lessons from a professional instructor. It will help you avoid common mistakes and show you the correct technique for doing the exercises.
Medicines and dietary supplements for cardiac stress
To reduce the load on the heart and prevent its overstrain, sports pharmacology has a number of medications and dietary supplements, which can be conditionally divided into 4 main groups according to the vector of application of cardioprotection. Some of these drugs may have complex effects and be included in several groups.
1. Drugs that optimize ENERGY PROCESSES IN THE CELL.
These effects are inherent
1A. macroergic phosphates (creatine, riboxin, phosphadene, ATP-long)
1B. inhibitors of lipolytic processes (nicotinic acid, natural antioxidants ceruloplasmin and superoxide dismutase prototypes (panaxod, orgotein, peroxinorm),
1C. enzymes and electron-acceptor substances (D-ribose, cytochrome C, coenzyme Q10, L-carnitine, trimetazidine, meldonium, succinic acid (succinate)).
2. Drugs that increase the RESISTANCE OF CELL MEMBRANES. This is, in particular,
2A. phospholipids (essential), α-tocopherol (Vit.E), probucol, PUFAs (Omega-3-6), β-carotene (Vit.A))
2B. inhibitors of free radical processes (mexidol, flavin, quercetin, rutin, methionine, unithiol, epargriseovit),
2C. phospholipase blockers (cefaransine, chlorpromazine, calcium antagonists, etc.)
3. ANTIHYPOXANTS. These are the means
3A. Improving coronary blood flow and blood transport function. In particular, Arginine, Meldonium, Actovegin, Aerox Oxygen Drops
3B. Improving the processes of energy supply to the cell are the products of the mentioned group No. 1, Meldonium, Creatine, ATP-long, L-carnitine, succinic acid, etc.
4. Means for CORRECTING IONIC FLOWS. Primarily Potassium K+ and Magnesium Mg2+ ions, and the most famous drug here is Panangin (Asparkam)
How the heart reacts to sports stress
At maximum athletic activity, the heart contracts more than two hundred times, pumping more than 30 liters of blood per minute. Trying to ease the colossal cardiac work, the body distributes blood more efficiently, reducing the resistance of the vascular walls, dilating the vessels of skeletal muscles and opening additional collateral vessels, which were previously in a collapsed state. However, even with such a significant compensatory decrease in blood flow, the heart works on the verge of beyond its capabilities.
Under the influence of loads, the heart changes its configuration - it is remodeled to ensure the viability of all organs under intense load. Morphological - biological changes correct the electrophysiology of the myocardium, that is, the emergence of an electrical potential for contraction of the heart chambers and their relaxation. In four out of ten professional athletes, the ECG recording, reflecting the electrophysiological characteristics of the heart, differs from the normal electrocardiogram in the height and depth of the waves.
Over time, but before that, at least two or three years of regular sports activities will pass, the heart will adapt to constant loads that are excessive for the normal body, so that the skeletal muscles are able to develop strength that is inaccessible to an untrained person.