Theory and practice
First aid for cuts and bleeding injuries is taught at school and is included in the camping preparation program. Teaching methods using pictures and posters provide a theoretical understanding of how to stop bleeding.
When actually meeting an injured person, not everyone can stand the sight of blood. Even adults are confused at the sight of a serious condition. Therefore, when preparing, it is important to remember the algorithm for providing assistance.
Children learn more carefully than adults
The table below shows the types of external bleeding and methods of providing first aid for them.
| View | Symptoms | Ways to stop bleeding |
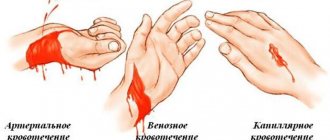
| Capillary | the wound is superficial, blood flows out in slow drops | treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide, apply a bandage of bandage, gauze or a regular handkerchief with moderate pressure on the damaged area. You can use cotton wool to treat the wound, but you should not bandage it. |
| Venous | usually the wound is deep, caused by a cutting or stabbing object, a lot of blood flows out, the color is dark red, the victim is pale | in case of a limb injury, give an elevated position, treat the wound with peroxide, put a napkin on it and bandage it tightly; in case of massive bleeding, the assistant should press on the wound or lower (if the limb is injured) |
| Arterial | the wound is always deep, the result of the action of cutting, piercing means, it can be chopped, blood flows out in a stream, pulsation can be seen, the color is scarlet, the victim is pale, loss of consciousness is possible | While the bandage is being prepared, press the bleeding vessel with your fingers (or palm) above the wound, a tourniquet can be made from available material, a note should be placed under the tourniquet indicating the time of application, the bandage should consist of several layers of gauze in order not only to apply, but to tamponate the vessels; if the injury is in the neck, groin area and the bandage gets very wet, then finger pressure should be continued until the ambulance doctors arrive. |
| Mixed | result of extensive damage, profuse blood loss | any of the above methods are applicable |
The most suitable means for closing the wound surface with the subsequent use of various methods of temporarily stopping bleeding is a bandage from an individual package. It can be purchased at a pharmacy and kept just in case of emergency at home, in the country, or taken on a tourist trip.
The rules for applying a tourniquet and using available materials can be found on our website in the article “How to provide first aid for bleeding”
If possible, apply a heating pad with ice or something cold to the bandage. The victim should be constantly given water to drink. This partially compensates for the loss of fluid.
The table shows places of possible compression of blood vessels
Brachial artery
The closest point lies between the shoulder muscles.
- The victim's hand should be raised or placed behind his head.
- It is more convenient to be behind the patient.
- The vessel is clamped with four fingers from the outside or from the inside.
- The depression between the muscles below the shoulder joint is felt at 1/3 of the shoulder and this place is firmly pressed against the bone.
Pressing the brachial artery from the front (a) and back (b) positions
What is the danger of bleeding
It must be remembered that if bleeding from a finger, a common type of childhood and “kitchen” injuries, can be dealt with on your own, then to eliminate more complex types you need to call an ambulance and not overestimate your knowledge and skills.
When the neck and other large veins are injured, air may be sucked into the vessel. This is how an air embolism is formed, the “bubble” will flow downstream to the right side of the heart. At a volume of about 10 ml, complete atrial tamponade and death occurs.
If a person has a defect in the form of a patent interatrial or interventricular septum, then the air embolus will move to the left side of the heart. Further along the aorta, even being very small, it can reach the cerebral vessels and cause cerebrovascular accident.
Delay in stopping arterial bleeding causes acute anemia. With a blood loss of 1.5 liters, there is a danger to life. Blood carries oxygen to cells. A sharp decrease in oxygen supply (hypoxia) primarily affects brain function. The victim turns pale, the pulse becomes weak and frequent, and sticky cold sweat appears on the forehead. This condition is called shock.
It significantly complicates the recovery period after injuries. Without timely first aid, it leads to death.
Carotid artery
Pressure of the carotid artery is required for bleeding from the vessels of the head, submandibular region, and upper neck. The situation is complicated by the impossibility of applying a circular pressure bandage to the neck, because the victim will suffocate.
Therefore, pressing is carried out on the wounded side with the thumb, when the rest are located on the back of the victim’s head, or with four fingers when approaching from behind. It is important to take into account the direction of the blood through the carotid artery: it is clamped below the site of injury.
In these ways the carotid artery is pressed
The desired point is located in the middle of the anterior surface of the neck muscle. Turn the wounded person's head in the opposite direction and it will be clearly visible. The artery is pressed against the spinous processes of the vertebrae.
Scope of medical care
Treatment of bleeding begins at the First Aid stage. Here the doctor is able to assess the severity of the patient’s condition and use available medications.
The patient must be placed in a supine position. Intravenous drips of saline are started to replace fluid loss and combat shock.
The patient is put on a mask and allowed to breathe an oxygen mixture.
To stop venous bleeding, the doctor removes the primary bandage and tourniquet, reapplies thick sterile gauze and tightly bandages the wound. If bleeding continues, the tourniquet is reapplied. If the site of injury does not allow compression, then transportation to the hospital is carried out under constant pressure by the doctor’s hand.
Drugs with hemostatic properties are administered intravenously (emergency tablets are not applicable): Dicynone, Calcium chloride, Aminocaproic acid, Vicasol. Not all drugs act quickly enough, but during the patient’s delivery to the hospital they will help to thrombose the blood vessels.
In case of massive arterial bleeding, the doctor must clamp the vessel in the wound with a clamp.
An extreme method of finally stopping bleeding can be emergency surgery in a surgical hospital with revision of the wound, search for the damaged vessel and its ligation.
Features of stopping bleeding
There are features of providing assistance depending on the location.
If your nose bleeds
The victim must be seated in a comfortable position. You don't have to tilt your head back. Tampons (turundas) soaked in hydrogen peroxide should be tightly inserted into the nasal passages. Place a cold compress on the bridge of your nose. Tampons can be changed as soon as they get wet. The patient should spit out the blood flowing down the back of the throat.
For frequent recurrent bleeding, Vikasol tablets are prescribed. An examination is carried out by an otolaryngologist. It may be necessary to use electrocoagulation of blood vessels.
If bleeding does not stop from the hole for a long time after tooth extraction
Dentists recommend placing a thick swab with hydrogen peroxide on the wound and pressing it with your teeth.
In case of prolonged bleeding, you should return to the place where the removal was performed. Perhaps there are fragments of bone and roots left in the wound.
Before the proposed extirpation operation, it is necessary to stop taking all blood thinning tablets (containing Aspirin, Warfarin, Analgin).
If blood comes from the ear
Only the outer sink can be inspected. If there are no external injuries, you should put a swab in the ear canal and call an ambulance. The patient should maintain a supine position. The fact is that the symptom of ear bleeding occurs with head injuries and skull fractures. The patient must be examined by a specialist.
In this case, the outer part of the ear is damaged
For pulmonary hemorrhage
If the blood comes from the pulmonary vessels. then it accumulates in the bronchi and causes a reflex cough. For the pulmonary type, foamy blood and coughed up sputum are typical. The patient should be in a sitting position. To relieve cough, you can give a Codterpine tablet. A cold compress is applied to the chest. Patients with pulmonary tuberculosis practice drinking a saturated saline solution (a spoonful of salt per glass of water). The patient must be taken to the hospital to understand the cause of the bleeding.
If the blood comes from the stomach or intestines
Ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines, disintegrating tumors cause damage to blood vessels with acute bleeding. It can “pouring out” in the form of vomit in a dark mass or manifested by liquid black stool.
The patient should not be given anything to drink or eat. As first aid, a cold compress may be applied to the upper abdomen. Urgent transportation to hospital is required.
Hemorrhoidal bleeding from the venous ring of vessels located around the anus is accompanied by other symptoms of hemorrhoids (pain, burning) and is associated with the act of defecation. It is rarely abundant, but lasts for a long time. Rectal suppositories with hemostatic agents are used in treatment.
Uterine bleeding
In girls and women, bleeding from the uterus is associated with disrupted hormonal balance, tumor, heavy menstruation, and ectopic pregnancy. Accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. The woman should be laid down and a rubber heating pad with ice should be placed on her stomach. Dicinon and Vikasol are prescribed internally in courses. An ambulance and delivery to a hospital are required to identify the cause.
Cold causes spasm of uterine vessels and increases thrombosis
Pleural bleeding
Blood leakage into the pleural cavity is possible with rib fractures or chest trauma. No blood comes out. The condition can be suspected by increasing pallor, acute pain in the chest, and difficulty breathing. The victim must be taken to the hospital as quickly as possible.
Is it possible to use folk remedies?
There are known folk remedies that increase blood clotting. But they do not have the emergency effect required to stop bleeding. Therefore, using them for a quick therapeutic effect is useless. In the treatment of chronic bleeding, it is recommended to take a decoction of the leaves of nettle, mint, and shepherd's purse. They are indicated for uterine, hemorrhoidal, and nosebleeds.
Any use of medications or methods in the treatment of bleeding should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Other symptoms
Paleness and shock are signs of internal bleeding
Often internal bleeding associated with damage to internal organs causes shock. Shock is a critical condition of the body caused by acute dysfunction of the cardiovascular system.
Shock can cause conditions of varying severity - from short-term loss of consciousness to coma. Symptoms of shock include:
- Accelerated heartbeat.
- Low blood pressure.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Neurological disorders: headache, drowsiness, lethargy, stupor.
- General weakness.
The presence of other manifestations will help the doctor determine the source of the bleeding. For example, anemia is usually associated with slow, chronic bleeding in the digestive organs. This condition can cause constant weakness, fatigue and shortness of breath.