Medicine is a very multifaceted science, filled with many interesting terms. Many of them have one or more synonyms, which may sound completely different, but mean the same concept. One of them is ROE. The decoding of this abbreviation sounds like the erythrocyte sedimentation reaction. That's what doctors called her before. Out of habit, older generation doctors still use this term today. This introduces certain misunderstandings among patients who do not know the basics of medical terminology, and even more so, the correct assessment of such an indicator.
What is this indicator
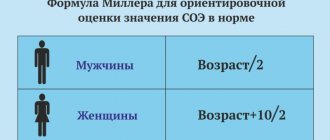
The erythrocyte sedimentation reaction (ERS) is one of the indicators of a general clinical blood test. Its modern name is ESR, which refers to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is based on determining the ability of erythrocyte cells to settle under the influence of gravity when they are placed in a narrow glass capillary simulating a vascular lumen. The value of the ROE indicator depends on how quickly this happens. It is measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h), which indicates how many millimeters the red blood cells have settled while remaining in an upright position for an hour.
Symptoms of androgenetic alopecia in women
The success of treatment for androgenetic alopecia in women is closely related to the extent of the damage. Doctors at the HFE Clinic recommend contacting them at the first signs of the disease, and in the case of hereditary baldness, in advance, before hair begins to fall out quickly. But an important feature of this type of disease is its inconspicuous onset. Many patients turn to doctors at the moment when the bald spot is clearly visible and only a transplant can help. The first signs are missed - women consider the large number of hairs remaining on the comb to be a seasonal phenomenon or explain it as improper care.
The process of the appearance of noticeable bald spots takes a long time: several years may pass from the onset of the disease to the moment when panic begins. But there are several symptoms that show that the pathology has already begun and it’s time to see a doctor:
- hair becomes thin, hair volume is lost, strands grow slowly or break off;
- On the parting, thinning of the strands is noticeable. The hairs at the parting site become thin and fluffy, and the parting visually expands. The same thing happens with the strands at the temples;
- Dandruff and dry scalp appear. At the next stage, dandruff disappears, replaced by seborrhea;
- In appearance, the hair becomes less vibrant, brittle, dull, and the strands feel dry to the touch. At the seborrheic stage, the picture changes: the strands always look unkempt, as if they haven’t washed their hair for a long time;
- the structure of the hairs changes. Strong long hair is replaced with short, fluff-like strands.
The development of the disease is especially noticeable on the top of the head, at the parting site. First, vellus hairs appear on the parting, through which the scalp is visible, then they fall out, and a bald spot forms. The disease can also affect eyebrows and eyelashes. But on the body and face, on the contrary, unwanted hair may appear.
You should consult a doctor in the first stages of the disease, especially if fortified and strengthening masks and shampoos do not bring results. The sooner the doctor makes a diagnosis, the higher the chance of delaying the visible signs of androgenic alopecia.
Conducting research
To determine ROE, no special techniques or equipment are needed. The indicator is studied as part of a general blood test, for which capillary blood is taken from a finger according to a method familiar to everyone. Determining ROE is one of the easiest stages of clinical analysis, since it does not require any manipulation of the blood after collection. It is simply left in a glass capillary for one hour. After this time, they look at what level the boundary of blood separation into light and dark layers is located. The height of the light layer in millimeters is used to determine the resulting erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Physiological norms and pathological changes
Standard ROE indicators have a fairly wide scope and depend on gender, age, diet and other factors that can naturally influence its value. The differentiated rate of ROE is given in the table.
| Adult men | Adult women | Aged people | Newborns | Infants | Children under 10 years old | Normal for teenagers | |
| Girls | Boys | ||||||
| 1-10 mm/h | 2-15 mm/h | 15-20 mm/h | 3-4 mm/h | 3-10 mm/h | 4-12mm/h | 2-15 mm/h | 1-10 mm/h |
Deviations in ROE in blood tests can be represented either by its increase or decrease. In such cases, it is more correct to say that ROE is accelerated or slowed down.
Important to remember! In most cases, you have to deal with situations in which ROE is elevated. This phenomenon is a typical indicator of immune-inflammatory reactions in the body, which change the properties of red blood cells, making them partially defective!
How to prepare for a blood test for ESR?
In order for the result of the procedure to be as reliable as possible, you need to prepare for it. It is a well-known fact that you need to donate blood on an empty stomach - and this is usually not forgotten. However, this is not the only recommendation. You also need:
- Temporarily, for 1-2 days before taking the test, give up alcohol;
- Refrain from fatty and spicy foods the day before;
- Do not smoke at least 2-3 hours before the procedure;
- Avoid physical activity immediately before blood collection.
You should also tell your doctor about the medications you are taking. Some medications can affect test results.
What does ROE depend on?
The ability of red blood cells to settle without the participation of the blood coagulation system depends on two factors:
- Structure and number of erythrocyte cells;
- Plasma composition.
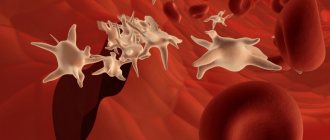
Healthy red blood cells have a negative charge on their surface. This allows them to circulate freely in the riverbed, pushing away from each other. When immune cells and mechanisms are activated in the body, this leads to an increase in the amount of immunoglobulins and fibrinogen in the plasma. On the one hand, they increase the density and viscosity of the plasma, and on the other, they change the surface charge of red blood cells. The natural consequence of such changes is the formation of large and heavy erythrocyte conglomerates in the vessels, which are able to settle much faster under the influence of gravity.
The situation changes exactly the opposite if the blood plasma becomes thicker. Red blood cells in such an environment are not able to settle, being in a suspended state. The higher the density of the plasma, the less opportunity there is for sedimentation, even for erythrocyte accumulations.
The adhesion of red blood cells to each other is the main mechanism for increasing RER during immune-inflammatory reactions in the body
Causes of androgenetic alopecia in women
There are several reasons why women develop male pattern alopecia:
- by inheritance.
The baldness gene is passed on through the maternal line. Therefore, if one of the representatives of the older generation in the family is faced with this disease, then you need to especially carefully monitor the condition of your hair and consult a doctor even before its first signs appear. Preventive therapy will help delay the onset of symptoms to later years;
- hormonal disbalance
. Increased hair loss is associated with an increase in the hormone dihydrotestosterone in the female body. This hormone makes hair follicles unviable, causing hair strands to fall out and the follicles to no longer produce new ones;
- pregnancy
. During this period, the female body is rebuilt, all energy goes into bearing a child, and hormonal levels are disrupted. In most cases, after the birth of a child, the amount of hormones returns to normal, and the hairstyle becomes voluminous and beautiful again. But sometimes only therapy helps prevent androgenic alopecia;
- internal diseases -
disorders of the endocrine system, gastrointestinal tract, liver;
- scalp diseases;
- taking certain medications.
Long-term use of antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hormonal drugs, antidepressants can affect the loss of follicle viability;
- prolonged exposure to stress.
Stress negatively affects all body systems, including hair follicles.
Another cause of androgenetic alopecia in women is a strict diet. During strict restrictions, nutritional balance is disrupted. The body does not receive enough vitamins and microelements important for the development and growth of vegetation. As a result, while acquiring a beautiful body, a woman loses her beautiful hair. Nutritionists warn about this, recommending women not to prescribe diets for themselves. It is better to consult a doctor who will select the right diet based on the balance of the necessary vitamins and microelements.
Androgenetic alopecia is caused by improper hair care. Hair often becomes brittle and falls out from constant use of styling products: drying with a hot hairdryer, daily use of curling irons or hair straighteners. Perm, low-quality dyes or too frequent hair coloring also lead to hair loss.
Physiological factors influencing the indicator
Acceleration of ROE, as a norm, can be perceived in the following situations:
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding;
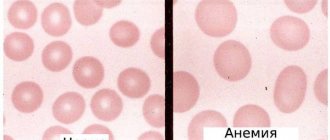
- Anemia;
- While taking hormonal contraceptives;
- Diet or fasting;
- Obesity and high cholesterol;
- The period after vaccination or recovery from infectious diseases;
- The temperature regime in the conditions where the study was carried out was more than 27˚C;
- Taking vitamins;
- In children and the elderly.
The following can slow down ROE:
- Increased number of red blood cells or other cellular components of the blood (polycythemia, erythremia);
- Hereditary changes in red blood cells in the form of small sizes and irregular shapes;
- Prem non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Severe heart failure;
- The temperature regime in the conditions where the study was conducted was less than 22˚C.
Causes of pathological increase in indicator
ROE is an indicator whose increase does not occur immediately after the development of pathology in the body. Such a reaction can be registered only after a few days. An increased ROE can be recorded for a long time after recovery from the disease, which is quite logical, since pathological red blood cells must be gradually replaced with normal ones.
High ROE in the following diseases:
- Inflammatory process: Acute and chronic sinusitis, otitis, tonsillitis;
- Menignoencephalitis;
- Pleuropneumonia, bronchitis, tracheitis;
- Myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle);
- Carious-destructive changes in teeth;
- Inflammatory processes of the digestive system (hepatitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, appendicitis, enterocolitis);
- Inflammatory processes of the organs of the excretory system (paranephritis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, cystitis);
- Pathology of the genital organs of an inflammatory nature (orchitis, endometritis, adnexitis);
- Inflammation of bones and joints (reactive and specific arthritis, osteomyelitis).
- Any viral infections (herpes, measles, rubella, hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, infectious mononucleosis);
A slowdown in ROE can be recorded very rarely and indicates blood thickening due to intoxication or dehydration.
Important to remember! When assessing increased ROE, first of all, all possible causes of physiological acceleration of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are excluded. A slight deviation from the norm can be considered physiological. Pronounced fluctuations always speak in favor of immune-inflammatory changes in the body or malignant neoplasms!
Age-related changes in the female body after 60
| CHUZ "RZD-Medicine" Vikhorevka" |
The health of a woman after 60 years largely depends on herself. In order to stay healthy and vigorous for as long as possible, it is necessary to monitor the main indicators of the body’s activity and constantly engage in health improvement. This includes a healthy diet, an active lifestyle, weight control and, if necessary, rehabilitation courses.
Age-related changes in the female body after 60
At 60, a woman is postmenopausal. Her hot flashes and changes in blood pressure (BP) stopped, her mood stabilized, and her overall health improved. But against this background, new problems arise related to age-related changes. All problems are surmountable, you just need to be aware of them and adhere to the generally accepted recommendations of specialists for their correction.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis in women begins late; the most dangerous age in this regard begins after 55-60. The first signs of angina pectoris appear in the form of attacks of acute short-term pain in the heart. The condition is dangerous because blocking the access of arterial blood to the heart muscle (myocardium) can lead to necrosis of its area (myocardial infarction). And the same process in the vessels feeding brain tissue leads to the development of ischemic stroke.
Arterial hypertension
Changes in blood pressure due to hormonal changes at this age are almost no concern. Stably high blood pressure may appear - a threat of developing arterial hypertension and associated hemorrhagic strokes (bleeds in the brain).
Mineral metabolism disorders
Osteoporosis develops: bone tissue, with estrogen deficiency, intensively loses calcium. Bones become brittle and prone to fractures. A fracture of the femoral neck is especially dangerous at this age: the bones hardly heal, and many older people become disabled after this.
A lack of potassium and magnesium negatively affects the condition of the heart muscle: angina attacks intensify and heart rhythm disturbances appear.
Decreased immunity
Immunity (general and local - skin and mucous membranes) is reduced due to metabolic disorders. After 60 people are more likely to suffer from colds, and the risk of acute infections turning into chronic infectious and inflammatory processes increases. Decreased immunity also contributes to the development of tumor processes.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine and joints
Metabolic disorders lead to the destruction of cartilage tissue first, and then the bones of the spine (osteochondrosis) and joints (osteoarthrosis) are injured and destroyed. All this is accompanied by pain, first when moving, and then by other disorders. Cervical osteochondrosis, complicated by compression of the vertebral arteries carrying blood to the brain, is especially dangerous. Cervical migraine and fainting appear.
Diabetes
The disorder begins due to the fact that tissues cannot absorb glucose. Type 2 diabetes mellitus develops. If it is not compensated for, severe dehydration develops. Due to glucose deficiency, all types of metabolism and the functioning of internal organs are disrupted. The formation of new cells (including immune cells) is disrupted, and atherosclerosis progresses.
Excess body weight
Age-related changes in fat metabolism and a general slowdown in metabolic processes in women contribute to the development of obesity, which negatively affects the entire body. Maintaining a normal weight is one of the main tasks after 60.
Genitourinary organs
The problems are associated with the increasing dryness of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs, which causes thinning of the mucous membranes and suppression of their barrier functions: they are easily injured and do not prevent the penetration of infection. Sometimes this is accompanied by weakness of the sphincter muscles - a circular muscle that prevents involuntary urination. As a result, a woman suffers from urinary incontinence, cystitis, infectious and inflammatory processes of the external genital organs, which, with insufficient general immunity, can spread to the internal genital organs.
Thyroid dysfunction
The thyroid gland in women after 60 gradually reduces the secretion of its hormones, and a tendency to develop hypothyroidism appears. It manifests itself in increased dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, an increase in body weight and a gradual decrease in mental abilities.
How to stay healthy at 60
Health at 60 years old must be constantly maintained at the required level. In order for a woman to stop noticing her age, she needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, adhere to proper nutrition and monitor her weight and basic indicators of the functioning of the body for the timely detection of serious diseases.
The psychological attitude is also very important: you need to remember about age-related changes in your body, but you should not forget about the joys of life. An optimistic attitude helps improve the quality of life.
Regular medical examination is mandatory
Every woman over 60 years of age must undergo an annual medical examination. Medical examination includes examinations by a therapist and specialists, examination of key indicators, changes in which indicate serious disorders in the body. If you carry out medical examinations regularly, you can promptly notice small changes and correct them with the help of diet, therapeutic exercises or drug therapy. This will allow you to stay healthy for a long time.
What tests need to be taken and the norms of indicators
Some vital signs of the body are of great importance during the aging period. They give an idea of how physiologically this process occurs. Small periodic fluctuations in indicators do not play a big role. Sustainable change is important.
Blood sugar
Normally it is 3.3 - 5.5 mmol/l. This indicator needs to be monitored. If there is a suspicion of diabetes mellitus (constant thirst and frequent excessive urination), then blood sugar testing should be done outside of medical examination.
Blood cholesterol
Cholesterol levels can tell a lot about the threat of developing or progressing atherosclerosis. This disease does not threaten everyone; it is mainly associated with family history. But you need to control your cholesterol levels. Three types of cholesterol are studied: total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and NSAID cholesterol. LDL and HDL are lipoprotein (protein-fat) complexes that transport cholesterol from the liver to tissues that need it vitally for metabolism.
Cholesterol is the same everywhere, but the complexes are different: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) is a “leaky” carrier; it loses cholesterol during transportation, which is deposited on the walls of blood vessels in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. It is LDL that is most abundant in the blood. HDL (high density lipoprotein) carries cholesterol without loss, this cholesterol enters into metabolic processes and prevents the development of atherosclerosis. But it is not enough, which is why it is so important to consume foods that maintain high levels of HDL in the blood (vegetable oils).
Cholesterol standards:
- general - 4.45 - 7.7 mmol/l;
- as part of LDL - 2.59 - 5.80 mmol/l;
- as part of HDL - 0.98 - 2.38 mmol/l.
Pressure
Blood pressure is one of the most important health indicators. After 60, changes in blood pressure are rare; pressure stabilizes at 130/80 mm Hg. But these are average numbers, they are individual for each woman: the norm may be 140/85 and 110/80. You should focus on your well-being. A rise in lower (diastolic) pressure and a decrease in pulse pressure (the difference between upper and lower) are dangerous. If your lower blood pressure is consistently above 90 and you are experiencing headaches, you should consult a doctor to maintain your health.
Normal ESR in the blood
ESR or erythrocyte sedimentation rate is an indicator, an increase in which reflects the presence of an inflammatory process or a malignant tumor in the body. The generally accepted standard for ESR is 2 – 15 mm Hg. But there are also age standards. After 60 years, you can have a much higher upper level of ESR, as physiological changes in the body and chronic diseases accumulate. Each individual case of high ESR should be dealt with individually.
Blood creatinine
Creatinine is a residual product of protein metabolism formed in the liver, pancreas and muscle tissue. Its daily content in blood and urine is constant and corresponds to the volume of skeletal muscles. An increase in creatinine in urine indicates kidney disease, injuries or diseases of the muscular system, and dehydration. A temporary increase in this indicator can occur when taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, or eating large amounts of animal proteins (meat, fish, dairy products).
Standards for women over 60:
- blood creatinine: 38-70 (µmol/l)
- daily excretion of creatinine in urine: 7.1-15.9 mmol/day. (0.8-1.8 g);
- residual nitrogen: 14.3 - 28.6 mmol/l.
Hemoglobin is normal after 60
Another important indicator is hemoglobin. This iron-containing protein carries oxygen to tissues, so a decrease in its content in the blood will affect the condition of all organs and tissues. The age norm of hemoglobin is 117 – 160 g/l, which is slightly higher than after 50 years. The increase in the norm is associated with the absence of menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding after 60 years.
TSH and its norm in elderly women
The pituitary gland is the main endocrine gland that regulates the work of other glands by secreting its hormones. The pituitary gland itself is under the same control of the hypothalamus.
At the age of 60 years and older, the thyroid gland significantly reduces the secretion of its thyroid hormones (TG) - thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Therefore, the pituitary gland works hard, producing the maximum amount of thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH), which stimulate the production of thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
The condition of hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) is very harmful to the body, especially to the brain, as it leads to the development of dementia. Therefore, it is important to monitor the levels of TG and TSH in the blood. The first indicator will be reduced, and the second will be overestimated compared to other age categories.
TSH norm: 1 – 10 mU/l. Exceeding the norm even in the absence of symptoms of the disease indicates the presence of subclinical (asymptomatic) hypothyroidism.
Intraocular pressure and its norm
Aging is often accompanied by an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) and impaired outflow of intraocular fluid. If you do not pay attention to unpleasant symptoms for a long time, optic nerve dystrophy occurs with the development of blindness. Symptoms of increased IOP are: headache, pain in the eyeballs, blurred vision, flashing “floaters” before the eyes, deterioration of lateral vision.
But low IOP is also bad; it can lead to a significant decrease in vision. Symptoms: rare blinking, sunken eyeballs, decreased vision.
The normal IOP ranges from 10 to 23 mm Hg. Art.
How to maintain health and beauty after 60?
After 60, a woman feels better than at fifty-five, when she was still bothered by hot flashes and changes in blood pressure. The changes taking place are more dangerous, although they do not cause such unpleasant sensations. But all these changes in the body can be corrected, trying to keep aging within physiological limits and suppressing the development of pathological processes.
Hormonal background
After 60 years, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can stimulate the growth of malignant tumors, the risk of which is quite high at this age. The hot flashes have already passed, and there is no urgent need to fix any problems. Therefore, gynecologists-endocrinologists prescribe HRT with caution, trying to replace it with hormone-like substances contained in plants and animals.
Phytohormones are found in soybeans, hop cones, red clover, and licorice roots. Recently, many medications and dietary supplements with these substances have been produced: Estrovel, Feminal, Klimadinon, Klimadinon Uno, Qi-Klim. You can also use homeopathic remedies - Remens, Klimaxan, etc.
Cytamines, biologically active substances obtained from animal organs and tissues, act similarly to phytohormones. An example of a dietary supplement with cytamines is Ovariamine.
You can activate your general metabolism, which will lead to an improvement in hormonal levels, by taking special vitamin and mineral complexes for older women.
Osteoporosis
Advice from a specialist on the prevention of osteoporosis:
- eating foods high in calcium, such as: dairy products, eggs, sardines, shrimp, sesame seeds, cabbage, almonds, chocolate;
- strengthening skeletal muscles that support the musculoskeletal system; muscles protect bones from fractures;
- taking medications and vitamin-mineral complexes that contain calcium - Calcium D3 Nycomed, Kalcemin, etc.
Genitourinary system
Problems with the genitourinary system can increase due to dry mucous membranes. Expert advice: a way out may be to use topical medications with hormones (vaginal suppositories and Ovestin cream). To strengthen the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, special gymnastics complexes are prescribed.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a serious problem in older people. Therefore, you should limit or not consume sweets at all; baked goods are a source of simple carbohydrates. Fatty animal products should also be limited - they can also produce glucose. By following such a diet, diabetes in the initial stages is compensated. If blood sugar does not decrease, hypoglycemic drugs such as metformin (Siofor, Glucophage) are prescribed.
Physical exercise
High physical activity at 60 is contraindicated, but physical activity and feasible sports or gymnastics are vital. It is important to alternate physical activity with rest. Evening walks are very useful: they not only strengthen muscles, but also help you fall asleep quickly.
Cosmetology
It is worth taking care of your face and body, as they determine a woman’s appearance, her age and state of health. To achieve the desired result, you need to adhere to the following expert advice:
- cleanse your face daily, removing decorative cosmetics with special milk;
- clean with a scrub once a week;
- use age-appropriate nourishing creams; Apply day cream with photoprotective properties in the morning, and night cream in the evening; Do not apply the cream in a thick layer; if you do this before bed, swelling may appear on your face in the morning;
- Apply nourishing masks to the skin of the face and neck twice a week; ready-made nourishing masks for your age can be bought in the store; you can also use folk remedies;
- use age-appropriate cosmetic serums in courses;
- Visit a beauty salon 1 – 2 times a year to conduct courses of cosmetic procedures.
Sexual life of women over 60 years of age
Sex life at sixty should continue. Studies have shown that in most cases, married couples at this age retain sexual desire and sexual activity. This strengthens the muscles of the pelvis and perineum (prevention of prolapse of the internal genital organs) and makes life brighter.
The health of a woman in old age requires constant support. But this does not mean that you need to do only examination and treatment. And in your declining years, life should be bright, happy and full of pleasures.
Address: Vikhorevka, st. Komsomolskaya, 1a Contact numbers.