The danger of atrial fibrillation attacks for the heart
The danger of attacks directly depends on the form of atrial fibrillation.
If the attacks can be stopped, that is, they can be eliminated, this must be done. Of course, it is better to choose a treatment so that paroxysms occur as rarely as possible. However, gradually, in most cases, the paroxysmal (attack-like) form of atrial fibrillation becomes permanent. In this case, another treatment is necessary - aimed at slowing down the pulse and preventing blood clots. When an attack (paroxysm) of atrial fibrillation develops, the patient has an increased likelihood of thromboembolic complications, primarily stroke, as well as myocardial infarction.
This is because the sudden onset of chaotic heartbeats disrupts the normal flow of blood into the heart and causes platelets to deposit on its inner walls. These cells form clots, which break off and travel to large arteries, such as the brain.
The faster the attack is stopped, the less the risk of complications of atrial fibrillation.
Why is arrhythmia dangerous?
If we are talking about sinus tachycardia or bradycardia, the patient most often experiences severe discomfort during unexpected attacks: dizziness, rapid or slow heartbeat, nausea, fear. There is also general weakness and malaise.
These symptoms seriously affect your well-being, but are not life-threatening, and with the right regimen and treatment lead to complete recovery. Paroxysmal arrhythmia, which disrupts blood circulation and is an indicator of the presence of heart disease, requires a more serious attitude. Extrasystole can be deadly and indicate myocardial infarction or other serious pathologies.
Specifics of the work of the heart muscle
To understand what to do in case of arrhythmia, you need to understand the work of the heart muscle and the reasons why its functioning fails.
In a healthy person, the number of heartbeats varies from 60 to 90 beats per minute.
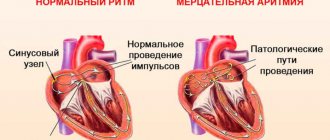
Contraction of the heart muscle occurs under the control of the sinus node, from where impulses are sent to both ventricles of the heart. This further stimulates blood pumping.
Due to many reasons, blood flow can be disrupted, that is, contractions of the heart go beyond the control of the sinus node and arrhythmia occurs.
With a low heart rate, when the readings are less than the permissible values, bradycardia is diagnosed. Over 90 heart beats per minute means the onset of tachycardia.
During an attack of arrhythmia, which appears suddenly, and the number of contractions exceeds 140 contractions per minute, paroxysmal tachycardia appears.
- Electrocardiogram for atrial fibrillation - preparation, rules of conduct, analysis of results
Doctors identify several types of manifestations of cardiac arrhythmia:
- Flickering. The most dangerous manifestation of tachycardia, which is characterized by chaotic contraction of the heart muscle, reaching up to 600 beats per minute. Help for atrial fibrillation should be provided immediately, as otherwise a heart attack may develop.
- Sinus. It occurs against the background of neuroses and chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system. Characterized by different intervals between muscle contractions.
- Extrasystolic. It manifests itself as an irregular alternation of stopping contractions followed by sharp jerks.
If the patient first encounters manifestations of arrhythmia, he needs to undergo diagnostics at a medical institution, since the type of heart contraction disorders is determined by the doctor after a detailed examination using an ECG.
It is important!
In the case of low blood pressure, it is prohibited to self-prescribe medications to eliminate arrhythmia, since they have the property of reducing it even further.
Diagnostics
Symptoms of suspected arrhythmia need to be carefully checked. Alarming signs include not only rapid heartbeat, but also sudden cardiac arrest, pressure changes, weakness, alternating with drowsiness.
If you experience the above symptoms, it is time to see a doctor and undergo a full diagnosis. You should contact a cardiologist - first of all, he will begin to check the thyroid gland and identify possible heart diseases.
Many methods have been developed to diagnose arrhythmia. An electrocardiogram must be recorded - it can be short or long. Sometimes doctors provoke an arrhythmia to record readings and more accurately determine the source of the problem. Thus, diagnostics are divided into passive and active. Passive techniques include:
| Echocardiography | An ultrasonic sensor is used here. The doctor receives an image of the heart chambers, observes the movement of the valves and walls, and specifies their sizes. |
| Electrocardiography | Electrodes are attached to the patient's chest, arms and legs. The duration of the contraction phases of the heart muscle is studied and the intervals are recorded. |
| Daily ECG monitoring | This diagnosis is also called the Holter method. The patient carries a portable recorder with him at all times. This happens within 24 hours. Doctors receive information about heartbeats during sleep, rest and activity. |
In some cases, passive research is not enough. Then doctors induce arrhythmia by artificial means. Several standard tests have been developed for this purpose. Here they are:
- exercise stress;
- mapping;
- electrophysiological study;
- Tilt table test.
First aid for arrhythmia at home: what to do?
If an attack occurs for the first time, you need to call an ambulance as quickly as possible for the reason that identifying the type of arrhythmia on your own is very problematic. Help at home while waiting for a paramedic involves the following actions:
- Pre-medical support begins with ventilation of the room. In case of shortness of breath, it is better to place the patient in a semi-sitting position, unbutton his shirt buttons or remove items of clothing that interfere with normal breathing.
- It is worth measuring your pulse and blood pressure.
- In some cases, changing positions (from lying to sitting, and vice versa) can prevent an impending attack.
- While waiting for a team of emergency doctors, you can use manual therapy methods as the safest ones. Every few seconds it is necessary to apply gentle pressure on the eyelids. Also, emotional support and the creation of a comfortable, relaxing atmosphere are extremely important for the patient.
What to do if you have cardiac arrhythmia? It is not recommended to take drugs with antiarrhythmic effects without a doctor's permission. As a last resort, it is permissible to take a Valocordin (Corvalol) tablet or another sedative prescribed by a cardiologist. Emergency care for atrial fibrillation will be much more effective if you provide the doctor with the following information:
- Data on heart rate measurements and blood pressure levels (recorded in mm Hg), which should be recorded daily in a separate notebook or notepad.
- Factors preceding the onset of an attack (stressful situations, alcohol consumption, withdrawal of a particular drug).
- The patient’s complaints before and during the attack, features of well-being after the heart rhythm was restored.
In case of a very low pulse, the patient's head is thrown back to facilitate the flow of oxygen. Fainting requires artificial respiration or chest massage, which must be performed by a person with certain training. This technique often helps: the patient’s face is placed under a stream of cold water or lowered into a reservoir. In this way, it is possible to achieve a reflex reduction in the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle, which makes it possible to stop the attack. In case of bradycardia, the patient is recommended to take a supine position so that the legs are higher than the level of the head.
If the first prehospital care for arrhythmia does not bring positive results, the gag reflex should be provoked by irritating the larynx area with the fingers. Thanks to such stimulation, it is possible to stabilize the heart rate even in the absence of vomit. If there is shortness of breath or swelling, which often accompanies atrial fibrillation, it is worth helping the patient sit up. In critical situations, when breathing or heartbeat stops, emergency pulmonary-cardiac resuscitation is performed. For certain types of arrhythmias, the following treatment is suggested:
- For extrasystole, potassium preparations, sedatives and medications containing toxic atropine are used mainly. If attacks become more frequent, the patient requires hospitalization with a course of intravenous administration of Lidocaine and intensive therapy for the disease that provoked the occurrence of arrhythmia.
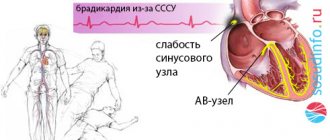
- In the case of sinus bradycardia, they usually resort to vasodilator drugs, such as Actovegin and Zufillin. If complications occur, the patient may need a pacemaker.
- An attack of paroxysmal tachycardia requires massage of the eyeballs, artificial induction of vomiting and pressure on the abdominal area. If the above methods do not have the desired effect, the patient may need urgent hospitalization.
When atrial fibrillation worsens, it is worth lowering the ventricular rate, for which they resort to electrical pulse therapy, Quinidine, Digoxin, as well as medications from the group of anticoagulants (one of the most effective representatives is Coumadin).
In the case of asystole, atrial and ventricular flutter, they often resort to urgent cardiac massage, the use of calcium chloride, lidocaine injections, temporary cardiac stimulation or surgery.
Certain medications for arrhythmia, which include coagulants and other potent drugs, have a number of serious side effects, including internal bleeding. Therefore, they should be prescribed exclusively by the attending physician, based on the results of biochemical tests, ultrasound examinations and the individual characteristics of the patient.
- How to provide first emergency aid for atrial fibrillation?
Prevention of complications
Rhythm disturbances are dangerous due to the possibility of blood clots forming and breaking off. The most unfavorable in this regard is atrial fibrillation.
To avoid thromboembolic complications, the following drugs are used:
- Anticoagulants (reduce blood clotting):
- with a direct mechanism of action (heparin and heparinoids);
- with indirect (hydroxycoumarin and phenylindanedione derivatives).
- Antiplatelet agents (reduce the ability of platelets to stick together):
- acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin), Clofibrate, Anturan, Dipyridamole.
The drug regimen is selected by the attending physician based on the number of risk factors present in the patient.
Forms of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation) can occur in several variants (forms):
- paroxysmal form: usually the patient has a normal sinus rhythm, but periodically it “breaks down” and an attack of irregular heartbeat develops, usually rapid;
- persistent form: the patient’s usual rhythm is atrial fibrillation, but sometimes due to unknown reasons, his normal heartbeat is restored for some time;
- permanent form: only an irregular heartbeat is recorded, sinus rhythm is not restored.
And also, depending on the average pulse frequency, tachysystolic, normo- and bradysystolic forms of atrial fibrillation are distinguished.
Tachysystolic form - an increase in the average heart rate of more than 100 per minute.
Normosystolic form with heart rate from 60 to 100 beats,
Bradysystolic form is a decrease in heart rate of less than 50 - 60 per minute.
In the paroxysmal course of MA, attacks usually have a high heart rate.
Restoration of sinus rhythm
Doctors believe that any paroxysm (attack) of atrial fibrillation, even if it has no symptoms, must be stopped. That is, restore normal heart rhythm (also called sinus rhythm). This is achieved with the help of so-called cardioversion, which is carried out in two ways - electrical or medicinal. The causes of atrial fibrillation and the duration of the attack are the main factors that influence the choice of cardioversion method.
Options for stopping an attack of atrial fibrillation in medical institutions:
- Electrical cardioversion. The essence of the procedure is to try to convert the pathological heart rhythm to normal using a cardioverter-defibrillator. The manipulation is painful for the patient, so before it he is given analgesics and sedatives. An electrical discharge applied to the heart causes it to stop for a short time, after which there is hope that it will begin to work in a normal rhythm.
- Medical cardioversion. This concept refers to the use of antiarrhythmic drugs that can restore normal sinus rhythm. Medical cardioversion is usually performed in the intensive care unit.
The most commonly used is procainamide, which is administered intravenously. Recently, amiodarone and propafenone have been frequently used. The popularity of these drugs is associated with ease of use (administered orally), as well as high efficiency. As a rule, a single dose of these drugs is sufficient to restore the rhythm. When using amiodarone, sinus rhythm is restored within 5 hours, and with propafenone - 2.5 hours.
After the heart rhythm is restored, upon discharge, the doctor will recommend further use of antiarrhythmic drugs to prevent attacks of atrial fibrillation. And also before and after cardioversion, anticoagulants, drugs that prevent the formation of blood clots, are prescribed for several weeks. This is usually warfarin.
About what symptoms of arrhythmia should alert the patient and minimally invasive methods of treating arrhythmia:
General rules for first aid
The rules for providing first aid for the treatment of paroxysm of atrial fibrillation are carried out differently depending on several characteristics of the attack:
- blood pressure level;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- duration of the attack;
- heart rate;
- primary or repeated paroxysm.
Depending on this, emergency doctors either try to restore sinus rhythm or reduce the heart rate, while simultaneously preventing the formation of blood clots. For this purpose, medications are used, and, if necessary and conditions exist, electropulse therapy is used.
What you can and cannot do at home during an attack
If an attack of irregular heartbeat develops, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Before the medical team arrives, you can:
- give the patient a semi-sitting position;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
- invite the patient to breathe with his stomach, wipe his face with a handkerchief dipped in cold water;
- give 20 - 30 drops of Corvalol in half a glass of water;
- prepare for the arrival of the team: organize its meeting, prepare medical documents, previous ECGs, think about transporting the patient to the ambulance (such a need may arise, but the duties of the ambulance personnel do not include carrying the patient);
- reassure the patient, tell him to call the doctors.
When detecting an attack of MA before the arrival of the ambulance, you cannot:
- Diet for atrial fibrillation: permitted and prohibited foods, sample menu
- give the patient medications before the ambulance arrives, including nitroglycerin;
- massage the eyeballs or the area of the carotid arteries;
- waste time measuring blood pressure without preparing for the arrival of medical personnel;
- collect things for hospitalization (this will be the time while the doctor examines the patient, relieves the attack, etc.; hospitalization is not always required);
- worry and panic.
How to stop an attack of MA on your own (a pill in your pocket)
Some patients whose diagnosis of “paroxysmal atrial fibrillation” has been established for a long time, and attacks occur less than once a month, can learn to independently stop such paroxysms. This tactic is called “pill in the pocket.”
It is used in intellectually intact patients who can adequately assess their condition. The “pill in your pocket” strategy should not be used if the next attack of arrhythmia caused any new symptoms:
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- facial asymmetry and so on.
In such cases, you should not stop the paroxysm on your own, since these symptoms may be a sign of the development of a heart attack or stroke.
If paroxysmal fibrillation proceeds as usual, the patient can take the drug propanorm at a dosage of 450–600 mg.
The patient should consult his cardiologist in advance about in what cases and in what dose to take this medicine. It is better if the first dose of propanorm is taken in a hospital, under the supervision of medical professionals.
conclusions
Paroxysm of arrhythmia occurs with the active use of compensatory capabilities.
This happens with physical or emotional overload, exacerbation of the disease. You can relieve an attack of arrhythmia at home by ensuring complete rest, sometimes using light sedatives. For sinus tachycardia, vagal tests will be effective, while ventricular fibrillation requires resuscitation measures. The diagnosis of arrhythmia is confirmed by an electrocardiogram.
Disruption of blood flow can lead to the formation of a clot in the heart cavity (detected by ultrasound), its rupture and thromboembolic complications. For prevention, anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents (Warfarin, Xarelto, Dabigatran) are used as continuous medications.
Types of arrhythmias, their symptoms and signs
The most common disorders of the automatic functioning of the sinus node are:
- Sinus-type arrhythmia, which is an abnormal heart rate and is diagnosed mainly in young patients.
- Bradycardia. Characterized by a slowing of the myocardial rhythm.
- Tachycardia (sinus), which is characterized by a rapid heartbeat of 100 beats per minute and above. A failure occurs most often due to emotional arousal or increased physical activity. It can be triggered by VSD, anemia, heart failure, myocarditis or thyrotoxicosis.
- In the case of atrial asystole, the functioning of the sinus node is almost completely suppressed.
With atrial fibrillation, which is considered one of the most dangerous, the heart rhythm is irregular, with the beat frequency varying between 110-160 beats per minute. Flickering manifests itself in paroxysmal or persistent form, while the patient may not experience significant discomfort or only feel an increased heart rate. Such problems often accompany coronary artery disease, thyrotoxicosis or mitral valvular disease.
Extrasystole is characterized by premature contractions of the heart muscle, which usually occur in people who do not complain about their own health. In such cases, extrasystolic pathology does not require any therapeutic measures. However, if it is observed more than several times within one minute, accompanied by dizziness, loss of coordination and other negative symptoms, you should contact a qualified cardiologist.
A separate group includes disorders of neurogenic origin. In such cases, the normal functioning of the heart is interfered with by the nervous system, which acts on the heart muscle in a diverse manner: the parasympathetic (vagus) nerve in a state of increased tone has a slowing effect on the rhythm, and an increase in the tone of the sympathetic nervous system leads to a rapid heartbeat. The cause of such a failure may be excessive consumption of fatty and fried foods, alcohol, as well as regular consumption of caffeine, smoking and a sedentary lifestyle.
There are many types of arrhythmia, caused by various reasons and having a number of distinctive features. The most common symptoms are:
- Sinus tachycardia is characterized by a rapid heart rate above 95-100 beats per minute. Most patients experience: general lethargy, shortness of breath, increased heart rate and a “broken” state.
- Paroxysmal tachycardia is characterized by a regular rhythm with a rapid heartbeat of 130 beats per minute. Accompanied by frequent urge to urinate, pain in the chest area, increased sweating and fainting.
- Atrial fibrillation is diagnosed by an irregular heart sound and a heart rate greater than 150 beats per minute. It is considered a sign of serious problems with the cardiovascular system and can be caused by various defects.
- In the case of blockade or fluttering of various compartments, dilation of the pupils and temporary cessation of breathing are observed.
In addition to the symptoms described above, an attack of arrhythmia is most often accompanied by general weakness and pressing pain, localized in the left side of the chest and “radiating” to the neck, jaw or arm. Patients often complain of increased anxiety, sometimes reaching the point of panic. Many people do not feel an attack, and the rhythm disturbance only becomes apparent after visiting a doctor's office and undergoing a diagnostic examination.
While some symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia do not pose a serious threat to health and may disappear on their own over time, others only aggravate the disease that caused them and lead to its rapid development.
Myocarditis is often a harbinger of atrial fibrillation, and repeated extrasystole can lead to a diagnosis of coronary insufficiency.
Causes and symptoms
Manifestations of arrhythmia are conventionally divided into 2 groups:
- Benign manifestations, the manifestations of which do not require treatment, go away on their own after eliminating the causes that caused them, and do not pose a threat to human life and health;
- Malignant – serious conditions that are most often caused by diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Arrhythmia of the first group is caused by the following factors:
- Excessive consumption of coffee and strong tea;
- Stressful situations and intense physical activity;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Long-term and uncontrolled use of medications or dietary supplements;
- Menopause.
Changes in heart rate of the second category provoke the following diseases:
- General intoxication;
- Chronic heart diseases;
- Pathologies of the nervous system;
- High pressure;
- Diabetes;
- Disorders of the thyroid gland;
- Heredity.
First aid for arrhythmia of the second group must be provided correctly and immediately, since it provokes a heart attack and can lead to the death of a person.
With arrhythmias, symptoms are not always clearly expressed. Thus, many people are not even aware of problems with heart contractions, and the disease is discovered in them by chance. Quite often this happens at low pressure.
Some patients experience some deterioration in well-being, which has the following symptoms:
- Manifestation of pain in the chest area;
- Increased sweating, weakness, loss of strength;
- Severe dizziness that may lead to loss of consciousness;
- Panic sensations of fear of death, lack of air.
These symptoms are especially pronounced at low pressure, the indicators of which must be taken into account when providing emergency care for arrhythmia.
In addition to these general symptoms, each type of arrhythmia has its own specific manifestations.
Thus, a type of atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal tachycardia, is characterized by paroxysmal manifestations with a sharp increase in heart rate. During paroxysm (as sudden changes in condition are called), the patient experiences panic attacks, which are accompanied by pressure surges and increased sweating. When systolic pressure is low, diastolic pressure increases.
During the manifestation of extrasystole, a person feels characteristic “somersaults” of the heart, and then it freezes.
Emergency care for arrhythmia is provided before the arrival of the medical team by witnesses of the attack.