Why does the hand stop moving after a stroke?
A stroke occurs due to an acute circulatory disorder in the brain, in which a portion of it dies. Depending on which part of the brain is affected, a person’s brain function is impaired. Because of this, various organs may stop functioning, including limbs - for example, a hand. Because the nerve pathways cross, the left arm will be affected if the stroke occurs in the right hemisphere, and vice versa.
At the same time, there is another dependence: the closer to the right hemisphere the stroke occurred, the more painful the damage to the limbs is felt. This happens because it is in the right hemisphere of the brain that the nerve centers responsible for the motor activity of the body are located. Therefore, a stroke, after which the left arm fails, usually requires longer rehabilitation.
Both types of stroke - ischemic and hemorrhagic - can cause such lesions and impair the motor activity of the hand. Disturbances can be different: pain, loss of sensitivity and coordination, complete paralysis of a limb.
A set of measures to restore the hand after a stroke
Restoration of hand motor skills after a stroke occurs under the supervision of physiotherapists. The list of measures includes procedures in different areas:
- physical rehabilitation therapy;
- drug treatment;
- psychological counseling.
Physical rehabilitation therapy
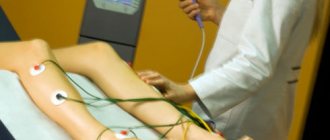
Physical rehabilitation is a critical part of restoring arm movement after a stroke. It involves doctors of various specializations, but primarily physiotherapists, neurologists and rehabilitation specialists. Treatment is aimed at developing and strengthening everyday motor abilities.
The process uses:
- physical therapy and gymnastics
: physical exercises on the arm - from the simplest gradually to more complex, developing fine motor skills; - action and observation therapy
- during these procedures, the patient watches another person performing some actions with his hand (in person or on video), and then repeats after him. The method triggers the work of similar areas of the brain, and this helps restore motor skills of the hand; - mirror therapy method
- within the framework of this rehabilitation technique, a mirror is placed between the patient’s hands in such a way that the image of the movement of the healthy limb creates the illusion of the same normal movement of the affected arm; - tekar therapy
- radio wave exposure to the body to produce endogenous heat. This helps reduce pain and speed up the tissue healing process; - massage techniques
; - acupuncture, modeling
from dough, plasticine or clay; - hydrotherapy methods
: hydromassage baths, contrast and circular showers.
The rehabilitation department has an occupational therapy department and a neuromotor department for the upper limbs. Robotic technologies are used here, including virtual reality. Neuromotor rehabilitation using such high-tech systems is a modern method of restoring hand motor abilities.
The greatest effect is achieved when the doctor competently combines all these methods. In this case, the specialist must first assess the extent to which the patient’s condition allows him to undergo these measures.
Drug treatment
In most cases, rehabilitation of the hand after a stroke requires drug treatment. However, it must be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
There are no universal dosages and regimens; each patient needs his own therapy. To make a decision about which drugs and in what doses the patient needs, the specialist studies all available information about him. In particular, medical history, anamnesis, data on clinical manifestations, results of previous examinations and tests.
The doctor may also change your medication regimen during treatment if he has reason to believe that the current dosage is ineffective or insufficient. The basis is new biometric data, information from the patient’s daily records (“diary of a stroke patient”). First of all, we are talking about the dynamics of blood pressure, heart rate, as well as side effects from medications.
Types of drug therapy that are used to restore limb activity after a stroke:
- intramuscular and intravenous injections
, which are aimed at increasing vascular activity and strengthening neurons. These include Botox injections, which significantly reduce muscle spasticity; - lymphotropic drugs
, which are injected directly into the lymphatic system so that the active substance gets into the arm faster; - analgesics
(to reduce pain in the arm),
muscle relaxants
(to relax the muscles of the limb),
anticoagulants
(to prevent the formation of blood clots),
antidepressants
(to treat depression that has developed due to illness) and other drugs, including antibiotics, vitamins and potent drugs - of necessity.
Psychological counseling
The patient’s internal state greatly influences the process and result of restoring the activity of the arms and legs.
Rehabilitation in a specialized center forces a person to change his usual way of life: he distances himself from society, loses independence and independence even in everyday worries. This cannot but affect the psychological state and leads, at a minimum, to discomfort, and at most to the development of depression.
The patient needs understanding, respect and care, but may also experience anger and powerlessness due to loss of control over his own body. To deal with this, a psychotherapist is needed. He will develop the correct technique for working with the emotional state and select a communication method for the family. The doctor will also prescribe pharmaceutical treatment to the patient if it is necessary and fits into the overall drug treatment plan.
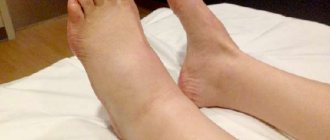
Swelling of the hands
Swelling in the hands can occur in people of any age, from the young to the very old. They often appear due to minor disorders in the body and go away on their own, but sometimes they can be signs of serious diseases. You should be especially wary if the swelling of the hands is asymmetrical: it occurs only on one hand or is much more pronounced on one hand than on the other.
Causes of swelling of the hands and distinctive features of pathologies accompanied by swelling of the hands
Swelling of the hands can appear with superior vena cava syndrome (compression of this large vessel). With this syndrome, swelling may occur in the face, neck, upper torso and arms. The skin of these sections is bluish; the bluishness intensifies even more when the body bends forward. There may also be dilatation of the superficial veins of the neck, torso, and arms. Some patients develop “spider veins” on their chest and back as a result of dilated capillaries. Due to increased blood pressure in the venous system, some patients may complain of bleeding from the nose, throat (esophagus), and headaches. decreased vision, rushes of blood to the head when bending, auditory hallucinations. Swelling of the vocal cords may develop, accompanied by hoarseness.
Neurological diseases can cause swelling in the hands. In patients who have suffered a stroke complicated by paralysis of the upper limbs, capillary permeability increases. In this case, moderate swelling of the paralyzed limbs appears, the nutrition of the skin is quickly disrupted, it becomes thinner, and purulent infections can occur. The same swelling can occur in patients with syringomyelia and polio.
Unilateral swelling of the arms can also occur due to acute thrombosis of the subclavian vein. This pathology may be preceded by a long period of chronic venous insufficiency. It manifests itself as increased fatigue, cyanosis of the hand, and a feeling of heaviness in the hand after physical activity. As a rule, this disease occurs in young men involved in sports and physical labor. Strong physical activity provokes the development of acute thrombosis. And thrombosis itself can be suspected by the rapidly occurring dense swelling of the arm from the shoulder to the hand. Patients feel a feeling of fullness, heaviness and burning in the affected limb. The arm is cyanotic, its circumference is much larger than that of a healthy one. When pressing with a finger on the area of edema, the hole does not remain. Over time, the swelling may subside, and the disease becomes chronic. However, periodically physical activity can provoke exacerbations of the disease and a return of symptoms.
In older people, the most common cause of unilateral swelling of the arms may be compression of the subclavian vein by a tumor. Compared to acute thrombosis of the subclavian vein, the swelling is less pronounced, increases gradually, and, as a rule, there is no pain in the affected arm. Simultaneously with compression of the subclavian vein by the tumor process, compression of the innominate vein may also occur. This is manifested by swelling and cyanosis of half the face and neck.
The cause of swelling of the hands may be inflammatory damage to the lymphatic vessels (lymphangitis). As a rule, it is a complication of a purulent-inflammatory disease of the hand. This pathology is manifested by general symptoms in the form of fever, malaise and local swelling of the arm, redness, and local increase in body temperature. Along the course of the lymphatic vessels, painful compaction-strands are felt. With lymphangitis, there is always regional enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Swelling of the arm in women may occur after breast removal. The main reason for this is impaired lymphatic drainage.
Middle-aged women may experience causeless swelling of the arms and legs. They are more pronounced in hot weather. On the hands and eyelids, such swelling occurs in the morning, and on the legs it is more pronounced in the evening. At the same time, all analyzes and results of instrumental research methods will remain within normal limits.
Taking certain medications - estrogens, mineralocorticoids, vasodilators - can provoke the appearance of hand swelling.
Sometimes swelling in the arms can occur along with swelling in the legs during pregnancy and premenstrual syndrome.
Swelling of the hands can be combined with swelling of the legs, face, and torso and occur as a result of cardiovascular, endocrine, and renal pathologies.
Treatment of hand swelling
You can independently reduce the severity of swelling of both hands with the help of diuretics (for example, veroshpiron). Diuretics such as Lasix and furosemide should not be used (especially for a long time), as they promote the removal of potassium from the body, and this can negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
You can also resort to the help of folk diuretics - drinking watermelon pulp, green tea, burdock root decoction, infusion of cornflower flowers, decoction of lingonberry leaves. If possible, it is necessary to limit fluid intake so that it does not accumulate in the tissues of the hands.
If you have swelling on one arm, then you should not self-medicate. It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor to determine the cause of this disorder and select treatment.
Comments 1
From May 22 to June 3, Dr. Komarovsky will be in Finland!
SDK: Viral croup.
Meeting with a pediatric neurosurgeon - cephalohematoma. Choosing slings and carriers for children. Preparing “orange” cauliflower.