Stroke is an acute disorder of cerebral circulation that causes focal damage to brain cells. The disease has typical neurological symptoms that persist for a long time: painful headaches, paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles or limbs (often one-sided), impaired memory, speech, vision, and coordination of movements.
In the elderly, and especially in old age, strokes are much more severe and pose a direct threat to a person’s life. Whether a patient will be able to return to a full life after suffering a stroke or at least partially restore lost skills depends on a number of factors. In any case, this is a long process, taking months and sometimes years.
Factors influencing recovery time after stroke
Stroke is one of the main causes of disability in old age, most often occurring as a result of untimely medical care or lack of competent rehabilitation. In 80% of cases, the success of recovery after a stroke is determined by the prompt action of medical staff. It is especially important to provide assistance in the first 3-4 hours after the onset of an attack. Rehabilitation must begin as early as possible, because the quality and duration of a person’s future life depend on it.
Other factors also influence the timing of rehabilitation after a stroke:
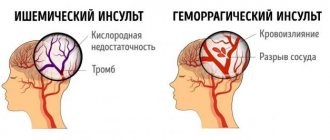
- The mechanism of stroke. There are 2 main types of strokes – ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic occurs in 80% of cases and is caused by a lack of blood supply to any part of the brain. With this type of stroke, if treatment is prescribed correctly and on time, the body has a good chance of recovery. Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by bleeding into the deep parts of the brain. The life prognosis is unfavorable, the probability of death reaches 50-70%.
- The degree of damage to brain tissue. The most serious violations of the basic functions of the body are observed with an extensive stroke affecting large areas of the cerebral cortex. In this case, if the person managed to survive, rehabilitation may take several years, and full recovery may never occur.
- Age and presence of concomitant diseases. The older a person is, the more difficult it is for him to cope with a blow, and in the presence of chronic diseases, especially the cardiovascular system, this often becomes impossible.
- What a seizure. Repeated strokes always increase the risk of death. While it takes an average of 8 months for an elderly person to recover from the first blow, it can take a year or more to recover from the second.
- Psycho-emotional state of the patient. In order to cope with such a serious illness, enormous willpower and desire to live are required, which not every patient has.
Myths about microstroke
Many of us have heard the name “ministroke,” but not everyone knows what it is and why this condition is dangerous.
To begin with, we note that, at the same time, it is necessary to distinguish between this condition and a stroke, and not.
Why?
- A disease that doesn't exist? Experts do not separately identify such a disease as microstroke. In the medical lexicon, this is called transient cerebrovascular accident (TCI);
- "Micro" disease? The prefix “micro” in the word is only misleading: it does not mean at all that there is no need to be afraid of this condition or that there is no need to take urgent measures to eliminate it; rather, on the contrary, it emphasizes the “kinship” with stroke with only one difference - in symptoms. The symptoms of a minor stroke are not as severe as those of a cerebral hemorrhage, and they go away much faster.
- Is it possible to recover? After a mini-stroke, the body can often recover without the help of a doctor, but it is still worth getting examined: even if the symptoms have already disappeared, the specialist should know that they were there. Thus, it is more likely that relapses and strokes will be prevented.
The “micro” in the word does not make this disease insignificant, it only hints that the disease is reversible (unlike a full-blown stroke). Therefore, diagnosis and treatment should be approached with full responsibility. So what myths about microstroke are just myths and should not be believed?
- Minor stroke is a rare disease. Unfortunately, it is not. Every year it affects tens of thousands of people, and many of them, without proper treatment, lead to disability.
- Only old people can get sick. Unfortunately no. This disease increasingly affects people aged 20-30 years. True, a young body usually fights the consequences better than an older person’s body, but that’s another story.
- What can happen cannot be avoided: a stroke cannot be prevented. This is also a myth. There are certain preventive measures that can help avoid encountering this unpleasant disease.
- A microstroke cannot be recognized: the symptoms are too mild. In part, this is not a myth; the symptoms are really mild. But if you have the signs described above, the time-tested exercise “raise both arms up” is suitable - one part fails during a microstroke, so the patient can only raise one arm.
- Micro-stroke, stroke and heart attack are the same thing. If we mentioned the differences between the first two diseases above, then the third differs from both of them in location. A heart attack is located in the heart, while a (micro)stroke is located in the brain.
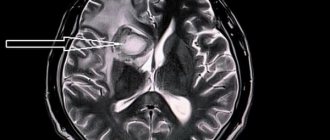
Diagnosis of microstroke at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern medical equipment. European CT and MRI installations make it possible to accurately determine the location of the lesion and its extent. An individual treatment and rehabilitation program is developed for each patient. The recovery period takes place under the supervision of experienced neurologists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors and physiotherapists. A personal approach can reduce the time of hospital stay and reduce the risk of recurrent microstroke.
Periods of rehabilitation after a stroke
Modern medicine recommends starting rehabilitation of a patient who has suffered a stroke in the first hours after the attack, as soon as hemodynamic parameters (heart rate, blood pressure) return to normal. This allows not only to restore lost functions as much as possible, but also to avoid various complications that can aggravate the patient’s condition.
The recovery period can be divided into several main stages:
- acute (first 3-4 weeks after the attack);
- early recovery (first 6 months after an attack);
- late recovery (from 6 months to a year);
- remote (more than a year).
Who does the disease affect?
This disease is getting younger and, if previously it was believed that it only affected older people, now this is not the case. Much depends on the person’s health status, lifestyle and chronic diseases.
Still, patients with the following problems are at risk:
- Atherosclerosis (chronic artery disease);
- Hypertension (pressure surges can trigger a minor stroke);
- Vascular lesions;
- Diabetes mellitus (high sugar content affects the walls of blood vessels);
- Alcohol abuse (the functionality of brain vessels decreases, toxins destroy tissue);
- Congenital and acquired heart diseases.
Busy people suffer a micro-stroke on their feet, that is, they do not pay attention to its symptoms and first signs, trying to maintain their usual activity. This should not be done under any circumstances, since within 24-48 hours there is a high risk of a stroke; the consequences in this case can be disability and even death. Therefore, a minor stroke is an indication for emergency hospitalization of the patient.
Acute stage of the disease
Rehabilitation in the acute period takes place in a medical institution under the guidance of doctors. It is advisable to begin rehabilitation treatment as soon as the patient’s condition stabilizes, optimally 3-4 days after the stroke. The main tasks at this stage are: restoration of simple motor and speech functions, prevention of complications and relapses, assessment of the degree of damage to the body and development of a rehabilitation program.
To restore the motor system, passive gymnastics, massage and treatment by changing body position are used, when the patient’s limbs are placed in various positions to prevent the development of muscle hypertonicity. The return of lost speech skills begins with simple articulation exercises, gymnastics of the tongue, cheeks, and lips. Speech is more actively restored 3-6 months after a stroke, but full recovery requires 2-3 years of work with the patient.
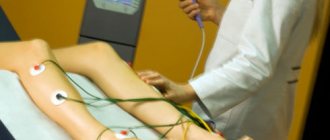
An important condition that accelerates rehabilitation in the acute period is the use of medications and physiotherapeutic pain-relieving procedures - magnetic, electro- and laser therapy.
Rehabilitation after stroke in the early recovery period
The early recovery stage is crucial for the patient and should ideally take place in a sanatorium or rehabilitation center. When deciding to leave the victim at home, you should remember that successful recovery after a stroke is impossible without the active participation of specialized specialists who will have to be invited to the home.
The first three months after the onset of the disease are especially productive and favorable for rehabilitation. At this stage, they move from the simplest exercises to more complex ones - they teach a person to roll over, rise, sit down, and stand up independently. Next, elements of active physical therapy are gradually introduced, physiotherapy, massage, speech work are continued, and complexes are performed to restore vision and eye movements, cognitive functions (memory, thinking, attention).
A common consequence of a stroke is complete or partial loss of vision, dysfunction of the eyelid, presbyopia, when a person cannot distinguish small print or small objects at close range. All these disorders require qualified assistance from an ophthalmologist, who will prescribe either medication or surgical treatment. In mild cases, they can do with therapeutic exercises for the eyes.
To restore attention, memory, and intellectual abilities, there are many exercises: memorization tasks, memorizing poetry, solving riddles, rebuses, putting together puzzles, chess, checkers. However, for complete rehabilitation of cognitive functions, psychological and correctional classes are necessary individually or in groups. Additional stimulation is provided by medications that should be prescribed by a doctor.
Late and remote periods
At a later stage, the body’s potential for rehabilitation after a stroke gradually decreases, but the patient must continue to study and train self-care skills. This period already passes at home, so responsibility for the health and mental state of the patient falls entirely on his loved ones.
You can change your usual exercise therapy complex by adding new exercises and classes with simple exercise equipment, for example, an expander. It is recommended to talk with the patient as often as possible, ask questions, thereby encouraging him to be vocal.
A year after the stroke, the exercises no longer have a pronounced effect, so in the long-term recovery period, the main attention should be paid to consolidating skills and periodic visits to the doctor for follow-up examinations.
Conditions for successful rehabilitation after a stroke
A stroke is a difficult ordeal, especially for older people, who can suffer from it with unpredictable consequences. How long it will take to recover - even doctors cannot answer this question for sure. But in order to shorten the rehabilitation period after a stroke, the patient must provide a number of conditions:
- rehabilitation should take place under the strict guidance of a qualified doctor according to an individually developed program;
- the rehabilitation process must be continuous and comprehensive. This means that it is necessary to work on restoring all body functions simultaneously and sequentially;
- in the home environment, it is necessary to create all the conditions for the successful rehabilitation of the patient: equip the sleeping place with an anti-decubitus mattress, allocate a place for doing therapeutic exercises and purchase the necessary exercise equipment, as well as additional equipment - walkers, wheelchairs, canes, special personal hygiene products;
- provide a balanced diet throughout the entire period of rehabilitation;
- take care to create a favorable home atmosphere, sensitive and caring attitude towards the sick person.
The first symptoms of a microstroke
In terms of symptoms, a microstroke is not very different from a traditional one. The most important difference is the duration of symptoms (usually no more than a few hours) and its intensity (signs are not as noticeable as with a stroke). Symptoms manifest themselves differently, depending on the location of the outbreak (the place where blood circulation is impaired):
- Occipital lobe of the brain (responsible for the perception of visual information): there is visual impairment to complete blindness in one or both eyes;
- Parietal lobe (responsible for tactile sensations): loss of smell, sensation of movement under the skin.
- Temporal lobe (responsible for hearing and memory): short-term memory and hearing loss.
- Frontal lobe (responsible for intelligence and muscle tone): paralysis, mood swings.
The body usually overcomes this condition on its own, and the brain is not seriously damaged.
As already noted, a micro-stroke often hardly manifests itself: the symptoms are very mild, which is why they are so easy to overlook. But it’s still worth paying attention to these first signs of the disease:
- Numbness of the whole body (or one part of it, so it may be impossible to smile or raise both arms);
- Dizziness;
- Severe headache;
- Double vision;
- Unsteady movements, weakness, desire to sit down or lie down.
To diagnose a microstroke at home, you can use the FAST test. It was developed in America for emergency doctors so that they could easily diagnose cerebral hemorrhage. This test is also suitable for a micro-stroke, since the symptoms (facial distortion, weakened arms and incoherent speech) are also present in this case, although they pass much faster. FAST is an abbreviation, but the word itself is translated from English as “quickly” - one of the main rules when diagnosing a disease.
F (face - “face”) - you need to pay attention to the victim’s face: it can be unnaturally skewed.
A (arms - “hands”) - the patient’s hands do not obey: they are weakened, trembling and do not rise up.
S (speech - “speech”) - words are confused, it is impossible to pronounce even a simple sentence without errors.
T (time - “time”) - time: so precious in the case of this disease. It is better to start diagnostics as soon as the first signs appear, because as soon as they pass (with a microstroke this usually takes no more than an hour or two), the patient will feel great again. But for emergency doctors, diagnosing the symptoms will help a lot.
Where to go for help?
It is impossible to provide complete rehabilitation after a stroke in the home environment. Therefore, the most reasonable option for the family of an elderly person who has suffered an attack would be to enter into an agreement with a specialized institution, where he can receive help from highly qualified specialists and undergo a comprehensive rehabilitation program developed taking into account his diagnosis and characteristics of the body.
The Trust boarding house network has been providing care and rehabilitation to stroke victims for the past 5 years. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors and nurses with medical education. The boarding houses have all the conditions for a comfortable stay and full recovery after a stroke:
- Individual rehabilitation programs aimed at adaptation after a stroke and prevention of a recurrent attack.
- Regular medical examination of the patient.
- A full range of rehabilitation procedures: exercise therapy classes, exercises for the rehabilitation of speech and cognitive functions.
- Drug therapy.
- Social and psychological assistance, warm and attentive attitude towards each ward.
- Cozy rooms equipped with functional beds, wheelchairs, orthopedic mattresses.
- Prevention of bedsores and daily hygiene.
- Specialized 6 meals a day, rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Organization of leisure and communication.
By entrusting us with the care of your loved ones, you create decent conditions for life and restoration of their health, thereby reducing the recovery time after a stroke. To find out more details about our programs, leave a request on the website, and we will call you back at a time convenient for you.
Forecast of microstroke
If the disease was diagnosed on time, no serious consequences are observed in patients after a mini-stroke. In young patients, the rehabilitation period can take only a few days; in older patients it usually takes up to a month. If a person begins to pay due attention to his health and follow the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis is favorable, but if not, he should expect a recurrence of the attack, including an increased possibility of a stroke.
During the rehabilitation period, patients may experience the following disorders:
- Men at a young age experience memory loss, erectile dysfunction, frequent headaches, seizures, and mood swings.
- In women, the consequences usually affect the nervous system and are associated with frequent mood swings and even possible depression.
- In the elderly: difficulty in motor activity, decreased vision, epileptic attacks, decreased memory and mental activity, speech impairment, sclerosis.
If the patient does not receive timely treatment, the microstroke may return within two to three days, and 50% of patients subsequently develop an ischemic stroke. In this case, mortality increases from 10 to 40%.