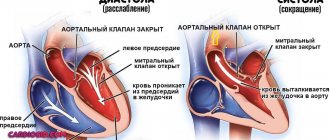
Types of arrhythmia in children
Taking into account the characteristics of heart rhythm deviations, childhood arrhythmia is divided into four key types:
- Tachycardia. Accompanied by increased rhythm. The heart rate normally increases with physical activity, elevated temperature, and stress. But if such a condition does not depend on external factors, it is considered a pathology. Tachycardia indicates a malfunction of the heart muscle and leads to its rapid wear.
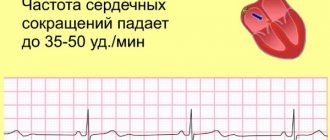
- Bradycardia. Characterized by a rhythm that is too slow. The contraction frequency decreases to 30-50 beats per minute. Pathological bradycardia may not interfere with circulation and cause no symptoms. But if the rhythm drops below 40 beats per minute, the baby experiences fainting, chronic weakness and dizziness.
- Extrasystole. It is distinguished by the presence of contractions outside the rhythm. It occurs when an extraordinary impulse appears between normal heart contractions - an extrasystole. Extrasystoles can be multiple or single, appear according to a certain rhythm or randomly. Rare single extrasystoles are not dangerous and do not require treatment. However, with frequent group extraordinary impulses, diagnosis and treatment of the pathology is necessary.
- Atrial fibrillation . Random rapid contraction of different parts of the atria, which causes an acceleration of the pulse. This type of arrhythmia occurs most often in childhood. The pathology is quite dangerous and, if left untreated, causes heart failure.
Methods for treating bradyarrhythmia
Only after a comprehensive examination does the doctor select a treatment method. For moderate forms of the disease in children and adolescents, a special diet and correction of the daily routine are recommended. A vitamin complex with magnesium, potassium and Omega-3 amino acids strengthens the heart muscle and immunity, helping the child cope with the stress of school and section.
If the heart rate is 40–50 beats, a therapeutic course in a hospital is recommended. The child is given special medications to eliminate hormonal imbalance or infectious inflammation due to pericarditis. In the organic or toxic form, treatment of the underlying cause is required.
Drug therapy
If the heart rate is slow, drugs are administered to normalize the heartbeat.
These are special cholinergic protectors that stimulate myocardial function without sudden surges in blood pressure:
- Metacin. Taken intravenously or subcutaneously 2–3 times a day, 0.5–1 mg. For a child, the daily dose should not exceed 6 mg.
- Atropine. When the heart rate decreases to 20–25 beats, the medicine is administered at a dose of 300 mcg every 6 hours. During an attack of bradyarrhythmia, a one-time dosage of 10 mcg per 1 kg of baby’s weight is used.
- Amiodarone. Improves coronary blood flow, used in the form of tablets or injections. For children, the dose is up to 10 mg per day. Course duration is up to 2 months.
To stimulate signal conduction from the sinus node, it is recommended to take beta-agonists:
- Ephedrine (Norepinephrine, Adrenaline);
- Izadrina;
- Alupenta (Eufillina).
For neurological problems that provoke attacks of bradyarrhythmia, doctors select sedative medications. When treating children, preference is given to herbal remedies with minimal risk of complications: Glycine, Pantogam, Citral.
Surgery
If drug therapy does not help stabilize the heart rhythm, surgery is performed. A common method is radiofrequency cardiac ablation, or RFA.
With its help, the cardiac surgeon cauterizes the area of the muscle that causes the signal to slow down or removes excessive tissue growth on the wall of the sinus node. As a result, the incorrect path of impulses is interrupted, the frequency enters the normal range of 65–75 beats.
Before the operation, the child in the hospital undergoes a comprehensive examination for blood clotting time, viral hepatitis, and receives consultation with an otolaryngologist.
The cauterization procedure is as follows:
- Anesthetic and sedative drugs are injected into the femoral artery for anesthesia.
- Through a vein, the doctor passes a thin probe from sensors directly to the inflamed area of the heart.
- Using a visual intravascular sensor, the surgeon determines the point of impact.
- After cauterization, a change in heart rhythm is observed for 10–15 minutes, after which the probe is removed and the patient is sent for rehabilitation.
The operation has minimal complications: there are no painful incisions, healing and recovery time is reduced. Already on the first day the baby can get up, move and eat. On days 3–5 he is discharged for home treatment.
A more traumatic method is to install a pacemaker. The miniature device becomes an artificial pacemaker, replacing the function lost by the heart. The device is permanently implanted into the child and is adjusted individually.
The procedure for installing a pacemaker is carried out by experienced cardiac surgeons and includes the following steps:
- Electrodes are inserted into the device through a puncture in the vein. They will pass through large vessels directly to the device.
- A subcutaneous pocket no larger than 5 cm in size is formed in the armpit, into which the pacemaker is placed.
- The connection occurs through the lateral vein of the arm.
- The electrodes are additionally attached to the endocardium using reliable hooks.
- Additionally, the device is tested and the results are recorded in a computer program.
The operation to install a pacemaker lasts at least 3 hours. The child receives antibiotics for 3–5 days to prevent rejection of the implanted device. Complete rehabilitation takes no more than 10 days.
Recipes for folk remedies
At the initial stage of the disease, drug treatment and traditional methods can be combined. Some plants contain beneficial substances that stimulate the functioning of the heart muscle and saturate tissues with mineral compounds and phytoncides. The most accessible recipes at home:
| Hawthorn decoction | In a clean container you need to brew 2 tbsp. l. herbs, pouring 0.5 liters of boiling water over it. This tea calms the child after an attack and restores sleep. |
| Calendula tea | Dried flowers are crushed, brewed at the rate of 250 ml of hot water and 2 tsp. plants. The product should be drunk 2 times a day for up to 10–14 days. |
| Honey with dried fruits | In a clean bowl, chop 200 g of dried apricots, prunes and walnuts, mix with 0.5 liters of natural honey. The composition is given to the baby 3 times a day in a spoon after meals. The vitamin mixture saturates with magnesium, potassium, amino acids, supporting heart function. |
With an integrated approach, sinus bradyarrhythmia is treatable. Many children “outgrow” the disease by the age of 16–18 and get rid of shortness of breath and muscle weakness. Modern methods make it possible to completely relieve a child from the consequences of the disease and reduce the risk of dangerous complications, disability or death by 90%.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia in a child
The symptoms of heart rhythm disturbances have different specifics and differ in children of different age groups.
Arrhythmia in a newborn baby can manifest itself through:
- pale, bluish skin;
- baby anxiety for no apparent reason;
- refusal to eat, breastfeed, or bottle;
- shortness of breath;
- slight or no weight gain;
- problems sleeping, crying.
Arrhythmia in a child aged 6 years and older very often has no symptoms. In such cases, pathology is detected during a routine medical examination. Only sometimes do children exhibit characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- excessive fatigue;
- poor body response to physical activity;
- causeless fainting, dizziness;
- pale skin;
- apathy or increased excitability;
- poor appetite;
- pain in the heart area.
Causes of arrhythmia in children
Children's nervous, autonomic and immune systems have not yet entered a stable stage of maturity. It takes years before the sinus node, which is responsible for normal rhythm, begins to generate the correct electrical impulses for the rhythmic contraction of the heart chambers. Only in adolescents the heart begins to beat at the same rhythm as in adults - 60-80 beats per minute.
The most common causes of cardiac arrhythmia in children are:
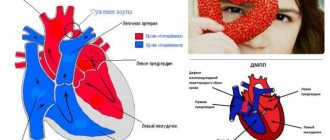
- heart defects and anomalies (congenital or acquired);
- inflammatory cardiopathologies (myocarditis, endocarditis, etc.);
- severe course of infectious or viral diseases and their complications (angina, hepatitis, diphtheria, intoxication, pneumonia, typhoid fever);
- arterial hypertension;
- failures of nervous regulation of rhythm (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- mitral valve prolapse;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- malignant diseases of the brain;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- anemia;
- hereditary diseases;
- difficult course of labor, prematurity;
- rapid development of the child’s body, in which the cardiovascular system does not keep pace with the growth of bone and muscle structures Source: Skudarnov E.V., Baranova N.V., Antropov D.A., Dorokhov N.A. Structure and etiological factors of cardiac arrhythmias in newborns Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics No. 3, 2021, p. 183.
How dangerous is the disease?
In most cases, cardiac arrhythmia in a child has a favorable prognosis and is benign. However, for any form of the disease, it is extremely important to monitor the baby’s health, regularly conduct preventive examinations and, according to the doctor’s decision, undergo treatment.
In the absence of competent and timely treatment, the pathology can cause serious complications in the future. The long course of the disease has a detrimental effect on the functioning of the heart and leads to dangerous consequences.
Arrhythmia can cause heart failure and cardiomyopathy, which carry the risk of early disability and even death. Increases the risk of developing arterial hypotension and myocardial ischemia. A prolonged attack of tachycardia can provoke cardiogenic shock or acute heart failure with pulmonary edema.
In addition, the long-term chronic course of the pathology significantly worsens the child’s well-being. The quality of life is gradually decreasing, and constant fatigue and apathy only increase over the years Source: Dubovaya A.V. Modern approaches to assessing the quality of life of children with arrhythmias Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2016; 61:5, pp. 75-81.
Diagnostics
Doctors identify several acute time periods when the possibility of developing pathology becomes especially acute. Often, arrhythmia in a child develops in infancy, at 4-5 years, at 7-8 years, at 11-12 years and in adolescence. Growth spurts occur during these age intervals. Therefore, carrying out preventive diagnostics and cardiac examination at this time is of particular importance, even if the symptoms of the disease do not manifest themselves.
Only a pediatric cardiologist or arrhythmologist can identify the deviation and establish a diagnosis. Initially, you should consult with a specialized specialist who:
- will study the medical history of a small patient;
- will conduct a full examination, palpation, percussion and auscultation;
- will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
To identify the disease and record the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes:
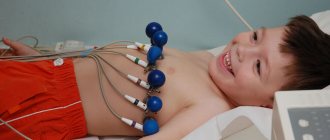
- Electrocardiography (ECG) is a method of studying the heart that allows you to record the electrical activity of the heart. With its help, the doctor identifies rhythm deviations and determines the frequency of muscle contraction.
- Daily ECG monitoring is a study of cardiac activity that takes place throughout the day. Compared to ECG, this method is more accurate. Allows you to record the dynamics of the rhythm during different periods of the child’s life: activity and sleep.
- Stress tests – analysis of heart activity during physical activity of varying intensity. Prescribed for suspected cardiac arrhythmia in a child 3 years of age or older.
The diagnostic results allow the cardiologist to diagnose the disease. Additionally, the doctor can prescribe procedures that will help identify the causes of the pathology:
- Echocardiography (EchoCG) is the study of the heart using ultrasound. With its help, you can detect the organic prerequisites for the development of arrhythmia: defects, neoplasms, etc.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) is the study of the electrical activity of the brain. It is prescribed if there is a suspicion of a connection between the pathology and abnormalities in the functioning of the brain.
- Radiography is a study using x-rays. Allows you to detect the preconditions for arrhythmia that are not directly related to the work of the heart: diseases of large vessels, pathologies of the spine, etc.
Diagnostics and treatment at NEARMEDIC
In most cases, to make a diagnosis, NEARMEDIC cardiologists prescribe standard electrocardiography, Holter (24-hour) monitoring - HM ECG. If there are initial changes on the ECG, pharmacological tests are recommended. In a number of doubtful cases, the doctor prescribes EPI - an electrophysiological study, which helps to develop treatment tactics and determine the electrophysiological indications for pacemaker implantation.
Mild sinus dysfunction does not require treatment. You can limit yourself to monitoring the patient’s condition and conducting non-drug therapy: quitting smoking and alcohol, avoiding taking certain medications. To avoid irritation of the sinocarotid area, it is not recommended to wear tight scarves and ties that put pressure on the neck. Physical therapy classes and swimming are shown.
The most effective treatment for bradyarrhythmia, regardless of its classification, is cardiac pacing. The patient undergoes a mini-operation - a pacemaker is implanted that generates electrical impulses. The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
Treatment of cardiac arrhythmia in children
After completing the examination, the doctor examines the results of diagnostic procedures and makes a diagnosis. Only after this, the specialist develops an individual treatment plan, taking into account the type and degree of development of the disease, its duration, the presence or absence of concomitant pathologies, the cause of the development of arrhythmia, the age and general health of the patient, as well as many other factors.
Complex treatment of arrhythmia in children involves taking drugs with a different spectrum of action: vascular, neurometabolic, antiarrhythmic. Antioxidants and cell membrane stabilizers are also used. The doctor determines the type of medication, dosage and duration of use individually.
In addition to drug therapy, preventive measures are also prescribed. Parents receive recommendations that will help speed up recovery and stabilize the child’s cardiovascular system:
- reduction of stress, emotional changes;
- healthy sleep and daytime rest;
- proper diet, which excludes fatty foods;
- normalization and maintenance of healthy body weight;
- monitoring cholesterol and blood glucose levels;
- regular preventive examination Source: Balykova L.A., Nazarova I.S., Tishina A.N. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children Practical Medicine No. 5 (53), September 2011, pp. 30-37. .
Diagnostic measures
Measuring your pulse daily can help detect irregular heart rhythms. If a decrease is observed for more than 7–10 days, it is better to consult a pediatrician or cardiologist for advice.
For a comprehensive examination, the following diagnostic methods are recommended:
- Taking an anamnesis, interviewing parents (doctors are interested in the presence of a genetic predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system).
- Daily monitoring of rhythm and blood pressure using a special device (Holter technique).
- Electrocardiogram.
- Ultrasound of the heart or echocardiography.
- MRI of the chest in severe forms of the disease.
- Analysis of thyroid hormones.
- Doppler of the arteries and vessels of the brain in the neurogenic form.
A clinical blood test helps identify hidden inflammation, shows anemia and other disorders. Diagnosis is carried out without hospitalizing the child to the hospital.
Treatment of children's ari
Our medical centers provide comprehensive diagnostics and treatment of cardiovascular pathologies in young patients. By contacting SM-Clinic, you can be sure that:
- the child will be treated by qualified cardiologists;
- if necessary, related specialists will be involved in the therapeutic process, who will provide an integrated approach;
- the baby will be examined in a modern diagnostic center with advanced equipment that provides highly accurate results and eliminates the possibility of receiving erroneous data;
- consultations and other procedures will take place at a clearly appointed time, without queues or tedious waiting.
Sign up for a consultation by phone or fill out the feedback form, and we will contact you to confirm your appointment.
Sources:
- Balykova L.A., Nazarova I.S., Tishina A.N. Treatment of cardiac arrhythmias in children. Practical Medicine No. 5 (53), September 2011, pp. 30-37.
- Pavlova N.P., Maksimtseva E.A., Artemova N.M. Arrhythmias in children. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention No. 18, 2021, pp. 118-119
- Dubovaya A.V. Modern approaches to assessing the quality of life of children with arrhythmias. Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2016; 61:5, pp. 75-81
- Skudarnov E.V., Baranova N.V., Antropov D.A., Dorokhov N.A. Structure and etiological factors of cardiac arrhythmias in newborns. Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics No. 3, 2021, p. 183
Types of bradycardia
At the first examination, a pediatric cardiologist in Saratov will help determine the main type of bradycardia in order to prescribe treatment and supportive procedures in the future. It is customary to distinguish the following types:
- Physiological - especially popular among athletes and does not harm the body. It is often called moderate bradycardia because it is caused by a well-trained heart.
- Absolute - an anomaly in which violations are observed under various circumstances.
- Relative - diagnosed in children under certain stable factors: crying, fever, sports or emotional stress.
Bradycardia in children is often caused by congenital heart disease. The main threat is that if the working rhythm is disrupted, the heart does not pump the required amount of blood, which means that the required amount of oxygen does not reach the brain. Pediatric cardiology in Saratov will select the most effective and supportive therapy for your health. The child will be less tired, will be able to do more physical exercise, and over time may even learn suitable sports.