Haptoglobin is a blood plasma protein that captures hemoglobins released during the breakdown of red blood cells and transports molecules that contain iron. An important function of this protein is to ensure economical consumption of iron reserves. In the case of intravascular hemolysis, haptoglobin protects the kidneys from negative effects. In addition, it is produced in response to infection in the body. In inflammatory diseases, protein works as an antioxidant, inhibits the growth of certain bacteria, and reduces cell damage.
In a healthy body, the process of red blood cell renewal constantly occurs. Within 24 hours, approximately one percent of the total number of red blood cells circulating in the bloodstream is destroyed. If the number of destroyed cells doubles the norm, haptoglobin will completely disappear from the serum. The absence of this protein entails the sedimentation of hemoglobin molecules in the kidneys. A large amount of hemosiderin and ferritin is formed. The body strives to remove excess iron through urine. These processes cause kidney dysfunction. In the presence of inflammatory processes, a blood test for haptoglobin
will show an increased level, but it is not related to the concentration of free hemoglobin.
general characteristics
Haptoglobin is a protein of the acute phase of inflammation, synthesized mainly in the liver, as well as in adipose tissue, lungs and binds free hemoglobin released from red blood cells. It is stimulated by inflammatory mediators, with a peak increase observed on days 4–6 and normalizes within 2 weeks after removal of the stimulating factors. With hemolysis of erythrocytes, the level of plasma haptoglobin decreases rapidly, which, in the absence of other causes, is a sensitive marker of intravascular hemolysis. Normally, about 1% of red blood cells are destroyed and removed from circulation per day. An increase in this amount to 2% leads to the complete disappearance of haptoglobin. The haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex is quickly taken up from the circulating blood by reticuloendothelial cells, thereby preventing or minimizing the removal of hemoglobin and iron from the body. Haptoglobin prevents kidney damage, since free hemoglobin is excreted in the urine and toxic concentrations of iron cause renal dysfunction. Haptoglobin plays an important role in the control of local inflammatory processes and is a natural bacteriostatic agent in infections with Fe-dependent bacteria (for example, Escherichia coli). Low levels of haptoglobin are observed during pregnancy and in newborns, as well as during estrogen therapy, including oral contraceptives.
Indications for the study
The test is prescribed if the patient has symptoms of hemolytic anemia. These include the appearance of a yellowish tint to the skin, pallor, darkening of urine, and general weakness. It is also carried out when there is a possibility of hemolysis (for example, in patients with an artificial heart valve, in case of damage to a number of toxic substances, during blood transfusion, hemodialysis). The study is carried out when examining patients with liver pathologies, reduced hemoglobin or the number of red blood cells.
The study is used for:
- establishing the cause of anemia;
- monitoring patients with artificial heart valves;
- diagnosis of intravascular hemolysis;
- liver function assessment;
- identifying acute phase reactions;
- monitoring patients after blood transfusion.
Most often, the test results are used to diagnose hemolytic anemia, and also to assess the degree of their severity.
Interpretation:
- Acute infectious diseases, trauma, necrosis, surgery, sepsis, corticosteroid therapy, biliary obstruction, nephrotic syndrome, malignant tumors, plasmacytoma, diabetes mellitus, collagenosis, Hodgkin's disease, fasting.
- Congenital ahaptoglobulinemia, hereditary spherocytosis, hemolytic disease, autoimmune hemolytic anemia; ineffective erythropoiesis, pregnancy, neonatal period, liver disease (cirrhosis), artificial heart valves, intense sports.
Sample result (PDF)
Interpretation of results
The level of haptoglobin depends on liver function, the presence of inflammation and a number of other factors. It can be affected by many medications.
An increase in the amount of protein is typical for:
- development of a malignant process;
- large-scale tissue damage due to injuries, burns, surgical interventions;
- taking medications containing hormones;
- obstruction of the bile ducts.
Reduced protein levels are observed when:
- development of endocarditis;
- genetic diseases;
- artificial heart valve;
- liver pathologies.
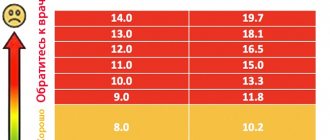
About the normal level of haptoglobin in the blood
Normally, haptoglobin successfully performs its assigned functions. The table shows the age norms for this protein.
| Age | Norm, mg/l |
| Infants up to six months of age | 50 – 480 |
| Children from 6 months and teenagers up to 16 years | 250 – 1380 |
| Adults from 16 to 60 years old | 150 – 2000 |
| People over 60 years old | 350 — 1750 |
The specialized medical literature may provide other normal ranges for haptoglobin. this is because each laboratory has its own reference values. To determine the concentration of haptoglobin, blood serum taken on an empty stomach is analyzed using the immunoturbidimetric method. To identify this glycoprotein, modern high-precision biochemical analyzers are used.
Haptoglobin
A blood test for haptoglobin is a laboratory diagnostic test aimed at determining the level of a specific protein compound, haptoglobin, in the blood plasma of the person being studied. Preparation and direct collection of samples of biological material are carried out according to the general rules for biochemical research. To do this, in the morning on an empty stomach, about 10 ml of blood must be collected by venipuncture. The result is prepared during the working day.
What is haptoglobin?
A complex protein compound of carbohydrates with proteins (globulins) in the blood plasma, which has the ability to bind hemoglobin, is called haptoglobin. This means that its main physiological purpose is to participate in the exchange of hemoglobin and iron in the body. In its pure form, haptoglobin is synthesized in the liver in three phenotypic variants. Circulating freely in the plasma, it captures hemoglobin released after the destruction of red blood cells in the spleen. Thus, this important compound for the body is not destroyed prematurely and is not removed from the body. Important to remember! Haptoglobin is a transport protein that binds free plasma hemoglobin and delivers it to cells that break it down. The iron released in this case is immediately used for the synthesis of new hemoglobin!
Normal haptoglobin level
For haptoglobin, a norm is provided that depends on the age criterion. Commonly accepted reference values in units of measurement - mg/l, are as follows:
- Newborn children (up to a month) – 50-480;
- Children from 3-4 months to adolescence – 250-1380;
- Teenagers over 16 years of age and adults under 60 years of age – 150-2000;
- People over 60 years old – 350-1750.
What does exceeding the norm for haptoglobin mean?
There are two main mechanisms that cause haptoglobin levels to rise above normal levels. This may be hemolysis - excessive destruction of red blood cells in the body, and stimulation of the liver by inflammatory mediators, which results in its excessive activity in relation to the synthesis of haptoglobin. A similar phenomenon occurs when:
- Severe inflammatory reactions in the body;
- Tumor lesions of any localization, especially those accompanied by the spread of metastases;
- Kidney diseases manifested by nephrotic syndrome;
- Rheumatic and other myocarditis, as well as myocardial infarction;
- Autoimmune connective tissue diseases;
- Lymphogranulomatosis. Haptoglobin is one of the group of important criteria for assessing the course of this disease;
- Stagnation of bile (cholestasis).
Why can the haptoglobin level be lower than normal?
The main mechanisms for reducing haptoglobin below normal are as follows:
- Active hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells), which happens with improper blood transfusion, Rh conflict, the presence of artificial heart valves and vascular prostheses, autoimmune diseases. In this case, the liver reserves are simply exhausted due to constant stimulation;
- Liver pathology leading to hepatocellular failure, which causes this organ to lose the ability to synthesize any proteins.
Diagnostic significance of blood tests for haptoglobin
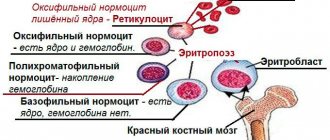
This complex plasma protein binds hemoglobin released when red blood cells are destroyed and prevents its removal from the body. The formation of haptoglobin occurs in the lung and liver parenchyma and adipose tissue. In a healthy person, its amount is 1.2-1.4% of the total protein. Combining with hemoglobin released during the physiological death of red blood cells, it forms a heavily dispersed complex that is not able to penetrate the glomerular apparatus - this prevents the release of heme-containing protein by the kidneys. Its appearance in the urine is observed when the amount of haptoglobin in the blood changes (which is typical for such pathological conditions as liver and kidney damage, the acute phase of the inflammatory process, autoimmune diseases, intravascular hemolysis) or a violation of its ability to bind to hemoglobin.
the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex is accompanied by the release of molecular iron, its connection with the main carrier, the transferrin protein, and delivery to the bone marrow, where the formation of red blood cells occurs. An increase in their breakdown leads to an increase in the flow of hemoglobin into the bloodstream and a decrease in the amount of haptoglobin (hemolysis does not enhance its synthesis). Various reasons lead to the death of red blood cells:
- Genetic defects of components.
- An infectious process caused by hemolytic streptococcus, malarial plasmodium, bacteria of the genus Clostridium.
- Intoxication with lead, dyes, some pharmacological agents and mushrooms, snake venom.
- Transfusion of incompatible donor blood.
- Rh conflict between fetus and mother.
- Presence of artificial heart valves.
- Carrying out hemodialysis procedures.
These factors lead to the development of hemolytic anemia, which is manifested by general weakness, pallor and yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes, darkening of urine, decreased performance, tachycardia (even at rest), shortness of breath, dizziness, and confusion. The release of hemoglobin into the circulating blood provokes kidney damage and the occurrence of pathological changes in their tissues.
To diagnose and assess the severity of hemolytic anemia, practicing clinicians prescribe an immunological test to determine the level of haptoglobin in the blood. Its results are also used to identify liver diseases, intravascular hemolysis and acute-phase reactions that develop during infectious, tumor and inflammatory processes, autoimmune pathologies, burns and frostbite.
Research methodology
To determine the level of haptoglobin in the blood, the method of immunoturbidimetry is used - its principle is to measure the intensity of a certain wavelength of light passing through a cuvette containing a colloidal solution.
The biological material for the study is a sample of venous blood, which is taken in a clinical laboratory center in the morning (from 7.30 to 10.30), on an empty stomach - at least eight hours must pass from the last meal (you can drink still water and Sahara). To obtain reliable research results, the patient must:
- Avoid drinking alcoholic, sweet carbonated and caffeine-containing drinks.
- Limit smoking and physical activity.
- Stop taking oral contraceptives, Dapsone, sulfonamide drugs, estrogens, androgens, Tamoxifen, Methyldopa.
- Avoid overeating and psycho-emotional stress.
Factors that may influence the final data of the study
Obtaining incorrect haptoglobin values may be due to:
- prolonged fasting;
- the use of synthetic hormonal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- pregnancy;
- diabetes mellitus
To prevent medical errors when interpreting study results, the patient should be informed about the medications used and the presence of concomitant chronic pathologies.
With a combination of circumstances that are accompanied by a decrease in the level of haptoglobin in the blood and factors leading to an increase in its concentration, it is difficult to predict the outcome of the disease. For example: during myocardial infarction, an increase in the amount of haptoglobin is observed (this reaction is associated with necrosis of the heart muscle), and then, due to the destruction of red blood cells, it decreases. In this case, additional research will be required.
Description
Synonyms (rus): Analysis for colorectal bleeding
Synonyms (eng): Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT)
Biomaterial: Feces
Indicator(s): Hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex (Hb/Hp) in feces
Method(s): Enzyme -linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Container type and preanalytical features: Sterile stool container with spoon
Hidden blood in stool refers to traces of blood that cannot be detected by the human eye and can only be done through various laboratory techniques. The appearance of even trace amounts of blood in the stool is an alarming sign and indicates the development of a pathological process in the intestines. The greatest caution when detecting hidden blood in the stool should be exercised in relation to colorectal cancer, one of the leading causes of mortality from cancer in our country. In addition, hemoglobin can be detected in feces in conditions such as intestinal ulcers, diverticulosis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and hemorrhoids. A new young immunochemical technique for detecting hemoglobin in stool (FOB, fecal occult blood) is the “gold standard” for screening patients for the presence of occult blood in the stool and has a number of undeniable advantages over older methods. FOB is a highly specific test for human hemoglobin and does not require prior elimination of animal products from the diet before testing. In addition, bleeding is detected, the source of which is in the distal parts of the large intestine, which is most specific for colorectal cancer. It must be taken into account that the test only confirms the presence of bleeding in the large intestine, but does not answer the question of the etiology and localization of the process. Therefore, if a positive result is obtained, a colonoscopy is recommended. To increase the accuracy of the study, simultaneous testing of fecal calprotectin in stool may be recommended.
What does an increase in haptoglobin indicate?
The concentration of haptoglobin increases in the following diseases and conditions:
- Large focal myocardial infarction;
- Active rheumatic carditis;
- Acute phase of the inflammatory process;
- Presence of a tumor;
- Nephrotic syndrome, expressed in severe kidney pathology due to impaired metabolism of lipids and proteins;
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- Rheumatoid polyarthritis;
- Stagnation of bile and disturbance of its excretion;
- Hormonal therapy with corticosteroids.
General information
Hemoglobin is part of red blood cells and is involved in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Red blood cells exist for 120 days, after which they are destroyed. In the vessels, normally only a small part of them is destroyed (the main number of these cells disintegrate in the liver and spleen). Iron from broken cells is used by the body in the formation of new red blood cells. If free hemoglobin is not bound, it enters the kidneys and can damage them.
The destruction of large numbers of red blood cells in the bloodstream leads to an increase in the amount of free hemoglobin. Haptoglobin binds it, and accordingly, the concentration of this protein decreases. However, its synthesis does not increase. Therefore, protein deficiency is an important indicator of intravascular hemolysis.