Everyone knows that blood is a liquid substance that fills the vessels of our bodies. But sometimes you can hear such a seemingly strange phrase as “thick blood.” What does it mean? Some time ago, in the countries of the post-Soviet space, it was very fashionable to “treat” blood thickening with the help of leeches. At the same time, such patients often did not understand what thick blood actually is, whether such a condition is dangerous and how to treat it correctly. Many misconceptions regarding this issue are widespread in our time.
What is “thick blood”
What is commonly called thick blood in simple terms is known to specialists as hyperviscosity syndrome or hypercoagulation syndrome. Such a condition in medicine is considered as a deviation from the norm, which can be contributed by various factors. But in order to fully understand what hypercoagulability syndrome is, you need to have an idea of the composition of the blood.
So, blood consists of the following components:
- cellular part (erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes);
- non-cellular part (plasma, which is also a liquid component);
- ions of macro- and microelements, hormones, enzymes and other substances that are carried throughout the body by blood.
Content:
- What is “thick blood”
- Causes of “thick blood”
- What promotes thickening
- Who's at risk
- Why is condensation dangerous?
- How is the “thickness” of blood determined?
- External signs of thickening
- How to treat
- Blood thinners
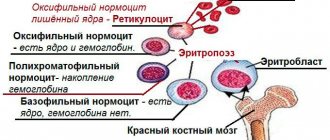
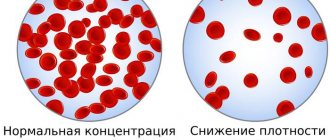
Each of these components is vital for humans. But it is equally important that all components of the blood maintain a certain balance. And such a characteristic as blood viscosity is nothing more than the ratio between plasma and cell mass. If this balance is disturbed, the blood either becomes too thin or thickens. For example, when the body experiences a lack of erythrocytes (red blood cells), they speak of anemia (previously the term “anemia” was used), because the blood becomes unnaturally thin. The opposite effect occurs when there are too many red blood cells. But this is not the only reason for blood thickening.
How to influence the situation
There are several simple ways to bring your blood condition back to normal. First of all, during a consultation with a cardiologist, they will recommend establishing a drinking regime using purified water, juices and fruit drinks. But tea and coffee, which cause a diuretic effect, should be consumed in doses. In addition, it is important to balance the diet by removing excess cholesterol and sugar, which increase viscosity, from the menu. The diet needs to be expanded with vegetables and sea fish, vegetable proteins, fruits - sour and sweet and sour.
Liquefaction also occurs from some herbal infusions - lemon balm, hawthorn, gingko biloba, willow. Seafood, nuts, vegetable oils, raspberries, viburnum and sea buckthorn are also healthy. Be that as it may, paying close attention to your own diet and drinking regime will only be beneficial - it will help prevent heart attack, stroke and other consequences of a dangerous condition!
Causes of “thick blood”
Speaking in the language of specialists, blood thickening leads to a deterioration in its rheological properties. That is, blood flows slower and more difficult. It can become thicker for various reasons. As a rule, this condition is accompanied by:
- violation of hematocrit;
- increased hemoglobin;
- an increase in the number of red blood cells;
- decreased elasticity of red blood cells and their deformation;
- aggregation (sticking together) of red blood cells;
- acceleration of blood clotting (due to an increase in the amount of fibrinogen);
- an increase in the amount of paraproteins (specific proteins that appear in the plasma during myeloma).
Common causes of blood thickening:
- Coagulopathies. This is a group of diseases in which blood clotting occurs. These include autoimmune, genetic and coagulopathies of toxic origin.
- Liver diseases. The liver is involved in the production of proteins responsible for blood clotting. And some diseases can increase or decrease the synthesis of these substances, which affects blood viscosity.
- Oncological diseases. Malignant blood diseases cause an imbalance between the plasma and cellular components of the blood.
- Dehydration. There can be many reasons leading to dehydration. The most common one is not drinking enough water. Diarrhea, severe and prolonged vomiting, taking diuretics, and poor absorption of water by the body also lead to dehydration. But regardless of the reason, the result is always the same - the substance in the vessels becomes thicker.
Which doctor should I contact?
Some medications can cause blood to thicken.
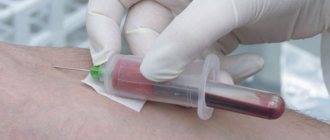
If you experience frequent dizziness, aching headaches, dry skin and other signs of blood thickening, you need to contact a therapist, who will prescribe the necessary tests that reflect the state of its composition - a coagulogram and a general detailed blood test. To find out the reasons for such deviations, consultations with other specialists may be necessary: an endocrinologist, hepatologist, etc. After identifying the causes of blood thickening, appropriate treatment for the underlying disease is prescribed or the cause of changes in its parameters is eliminated.
Blood is the main source of nutrients for our body. It introduces them into tissues and removes from there harmful components that accumulate after the completion of physiological processes. A variety of external and internal factors can change its composition and influence the rheological properties, the effects of which should be stopped.
To determine blood density indicators, you should regularly take a general blood test. The frequency of such monitoring studies performed for preventive purposes is determined by age and the presence of concomitant diseases.
What promotes thickening
High blood viscosity syndrome can manifest itself as an inherited genetic disease. As a rule, such people have a tendency to more active thrombus formation. More often, hypercoagulation syndrome is secondary in nature, that is, it develops under the influence of external or internal factors.
Risk factors:
- Aging. As most people age, the blood vessels become stiffer and more calcified, which impairs the flow of blood through them. Upon reaching the age of 50, it is recommended to monitor blood rheology, and for this purpose, medications are prescribed to maintain its fluidity.
- Overweight. Obesity is accompanied by metabolic disorders in the body, due to which the blood can become more viscous, and atherosclerotic changes are observed in the vessels.
- High cholesterol. Lipoproteins always increase the proportion of the thick component.
- Smoking. Cigarette smoke contains substances that increase the risk of blood clots and affect the density of the substance in the blood vessels.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcoholic drinks contribute to rapid and severe dehydration of the body. Scientists have calculated that the ratio of alcohol consumed and the liquid it removed from the body is 1:4. Therefore, if the hydrobalance is not restored in time, the share of the liquid part in the vessels decreases.
- Bed rest for a long time. Post-surgery, as well as some health problems, may force a person to remain in bed. Over time, inactivity leads to impaired blood flow and stagnation of blood, which ultimately causes blood to thicken.
- Severe hypothermia or burns. Extreme temperature effects lead to severe stress, dehydration, and impaired hematopoietic function, which also increases the risk of hypercoagulation syndrome.
- Organ transplantation, surgery on blood vessels or their injury, installation of implants (valves, dialysis shunts, venous catheters, etc.). Any impact on the heart or vessel walls leads to the formation of irregularities, and this increases the risk of increased blood clot formation.
- Inflammation. Any inflammatory process, especially if it is chronic, provokes an increase in the number of leukocytes, fibrinogen, proteins and cholesterol. When there are too many of these components, the blood becomes viscous.
- Physical inactivity. Experts use this term to describe a sedentary lifestyle. The causes of thickening in sedentary people are associated primarily with impaired blood flow in the vessels.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives. Hormone-based drugs often lead to increased thrombus formation, which changes the density of the substance in the vessels.
- Pregnancy. As the fetus matures, the uterus increases in size and puts pressure on the pelvic vessels. This leads to blood stagnation and excessive blood clot formation.
- Toxin poisoning. Poor environmental conditions, eating food contaminated with heavy metals, and radiation can also contribute to hyperviscose syndrome.
- Microorganisms. Most diseases caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi and some parasites are accompanied by fever and the accumulation of toxic substances in the body. And this is another factor that causes thickening of fluid in the veins. In this case, the degree of thickening depends on the nature and intensity of exposure to the toxin or parasite.
- Stress. During stress, the body releases hormones that cause vasoconstriction, causing blood circulation to slow down. If the stressful condition is chronic, the blood tends to thicken.
THICK BLOOD IS A SOURCE OF INCREASED DANGER!
We talked about this with Denis Sokolov, a cardiologist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic), candidate of medical sciences, member of the Acute Cardiovascular Care Association (ASSA) .
Denis Vladimirovich, “thick blood” is a philistine concept. How does it sound in medical language? — In medical practice, this condition is called increased blood viscosity and depends on the ratio of the amount of formed elements and blood plasma. Human blood consists of formed elements (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets) and a liquid part (plasma). Normally, the proportion of formed elements is no less than 40 and no more than 45%. If this amount increases, we are talking about increased blood viscosity.
Does “thick blood” threaten human health or life? - Threatens. The fact is that increased blood viscosity negatively affects the condition of the heart, blood vessels and all internal organs, because in the presence of such a condition, there is a risk of blood clots.
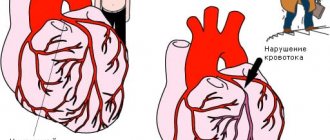
The main complication caused by increased blood viscosity is the formation of clots (thrombi) in the bloodstream. They block movement through the deep veins and vessels of the limbs, internal organs, and brain. As a result, increased blood viscosity can cause a number of diseases - ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, thrombosis of the veins and arteries of the lower extremities, and a number of internal organs. It is very dangerous. After all, acute disorders of coronary and cerebral circulation, pulmonary thromboembolism become causes of death if a predisposition to thrombosis is not detected in a timely manner and treatment is not started.
Are there any known causes that lead to increased blood viscosity? And who is at risk? — Such reasons are known, there are several of them. For example, dehydration often leads to increased blood viscosity. It occurs when a person does not drink enough water during intense physical activity and a hot climate. Diarrhea, vomiting, poisoning, and a number of somatic diseases also provoke dehydration and blood thickening.
Chronic diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, in which increased synthesis of blood cells occurs, is another risk factor for blood thickening.
Metabolic disorders in the form of macroglobulinemia (a malignant hematological disease), diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome (manifested by impaired metabolism of fats and carbohydrates), obesity are also a trigger for increased blood viscosity. This group of causes also includes amyloidosis, in which a special, “abnormal” protein—amyloid—begins to be synthesized in the body. It is deposited in all tissues and organs, disrupting their functioning.
Increased blood viscosity is also diagnosed with increased spleen function and many oncological diseases.
People of what age, lifestyle and occupation are more likely to have “thick” blood? — The risk of high blood viscosity increases in older people. This is understandable: over the years, chronic diseases accumulate and metabolism slows down. Obese people are also at risk. People who work in hot weather conditions and in rooms with high air temperatures also have a high risk of blood thickening.
Can medications cause blood clotting? - Yes, this is possible. Blood thickening can occur due to uncontrolled use or overdose of diuretic drugs (furosemide, torsemide, spironolactone), because this leads to dehydration of the body.
Women have a specific risk factor - the use of oral contraceptives. The point here is that the estrogenic component present in such contraceptive drugs stimulates the activity of the blood coagulation system. In this regard, when taking contraceptives, blood clotting increases significantly.
There is evidence that drugs for the treatment of erectile dysfunction also provoke blood clotting.
What to do, stop taking much-needed medications? - Of course not. You just need to pass all tests and undergo examinations prescribed by your attending physician both before their appointment and during the appointment period. And strictly adhere to the rules for taking medications, avoiding their overdose.
Are there any manifestations of “thick” blood that should alert a person? — Signs of increased blood viscosity may include dizziness, noise in the head, headache with a feeling of heaviness, blurred vision, and numbness in the fingers. This may be accompanied by nausea, sleep disturbances, confusion, poor appetite, tingling shins and dry mouth.
Frequent infectious diseases should also be of concern. Indeed, due to blood thickening, blood circulation in the internal organs is disrupted, which, in turn, leads to a deterioration in the digestive function of the intestines and a deficiency of nutrients. The result is the body's instability to viral and bacterial pathogens.
Increased blood viscosity can be accompanied by dry skin, brittle nails, as well as thinning and hair loss. This again occurs due to insufficient blood supply to the tissues and impaired microcirculation.
Cold extremities are another manifestation. This is explained by the fact that with increased viscosity, blood circulation worsens. And this interferes with normal blood flow.
What specialty should you consult with in connection with the problem of “thick” blood? - To begin with, see a therapist, family doctor or general practitioner. The treatment of high blood viscosity itself must be comprehensive and carried out with the participation of a medical specialist. In particular, a cardiologist, and in some cases a hematologist.
What tests need to be done to detect increased blood viscosity? — To diagnose increased or decreased blood viscosity, the patient must undergo a clinical blood test, which will reveal the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and other indicators. Another mandatory test is hematocrit .
What kind of analysis is this? - Hematocrit readings accurately reflect the volume of blood contained in red blood cells (erythrocytes). In addition, the analysis reflects the cell size of red blood cells. Normal hematocrit values depend on the person’s gender and age. So, for an adult man it is 40-48%, for an adult woman - 36-46%, for a newborn child - up to 60%, for children under 13 years old - up to 38-40%. If the values are increased by at least 0.55%, then patients are diagnosed with high hematocrit .
What other tests need to be performed? — In some cases, the clinical laboratory uses the determination of the duration of bleeding and the determination of blood clotting. Clotting time describes how quickly blood clots form, the ability of platelets to stick to each other, and also gives information to the doctor about how long it will take for the body to seal the leak if the integrity of the vascular walls is compromised.
It is also necessary to perform a coagulogram . This study is a comprehensive laboratory assessment of hemostasis. And hemostasis is a complex of physiological processes that stop blood loss in the event of damage to the vascular wall, as well as maintain blood in a liquid state.
How is too viscous blood treated? — To reduce the number of formed elements and reduce blood viscosity, the patient requires special therapy, including treatment of the pathology that provoked this condition. In addition, the patient is prescribed a diet and specific medications. There is no specific treatment regimen. Treatment tactics always depend on the patient’s clinical picture. The general principles of combating high viscosity include correction of metabolic processes, prevention of blood clots, and treatment of neoplasms of hematopoietic tissue.
What medications are used to reduce blood viscosity? — Medications that reduce blood viscosity and reduce thrombus formation include antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants . Such as acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel, warfarin, abigatran, rivaroxaban, apixaban, heparin and many others. etc. These drugs are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician and are taken strictly according to indications on an individual basis. Self-prescription may lead to negative consequences. For example, aspirin-based medications are highly effective in normalizing blood consistency, but are prohibited for use in patients with abnormal gastrointestinal tract functions - gastritis, peptic ulcers. Since these drugs negatively affect the mucous membrane of internal organs.
Is excessive blood thinning, in turn, dangerous? — Of course, excessive blood thinning is dangerous, because... it can cause bleeding. And those, in turn, can become a serious threat to life.
Is it important to adhere to a certain type of diet to thin the blood?
- Necessarily. So, you need a special diet with sufficient fluid intake. It will reduce blood viscosity. In addition, the following products help reduce increased blood density:
- berries (blueberries, cherries, strawberries, white and red currants, gooseberries, cranberries);
- fruits - oranges, lemons, peaches, apples;
- vegetables - cucumbers, tomatoes, beets;
- spices - garlic, ginger, pepper, cinnamon;
- dark chocolate, cocoa, coffee.
Is it possible to use folk remedies to thin the blood? — With the doctor’s permission, you can try auxiliary treatment using folk remedies, taking into account the healing properties of some herbs and plants. For example, yellow sweet clover herb, hawthorn berries, valerian root, lemon balm, narrow-leaved fireweed, etc. have blood-thinning properties.
Flax oil has good thinning and antithrombotic properties. The product helps to establish metabolic processes, remove excess cholesterol, and prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
What is better - to prepare medicinal herbs yourself or buy them in a pharmacy chain? — Independent preparation of medicinal herbs requires special knowledge. Therefore, it is easier and better to buy herbal remedies at the pharmacy. It’s not for nothing that they are called medicinal. And all medicines are sold in pharmacy chains.
And further. If you decide to take medicinal herbs on your own, be sure to notify your doctor. The fact is that the simultaneous use of herbs and medications often has either an activating effect on the body, or, on the contrary, a leveling effect.
Can leeches help thin the blood? — In some cases, hirudotherapy is used. And as an adjuvant, leeches can help. Leeches, by injecting saliva containing many different enzymes (including hirudin), can improve the properties of blood and reduce its viscosity. In addition, the use of leeches has a mechanical effect on the body, which consists in reducing the amount of blood at the site of its attachment, which leads to a decrease in pressure and redistribution of fluid in the body.
But hirudotherapy does not help everyone. This method also has contraindications. Therefore, you can use it strictly according to your doctor’s recommendations.
What can you recommend to prevent “thick” blood? — The first thing you need to do is establish the correct drinking regime. Much is known about the dangers of dehydration. Lack of water affects not only the functioning of organs and systems, but also the viscosity of the blood. It is dehydration that often causes the development of hyperviscosity syndrome. To prevent it, it is recommended to drink at least 30 ml of clean water per 1 kg of weight daily. If for some reason a person does not drink plain water, but replaces it with tea, juices or compotes, then the volume of liquid consumed should be higher.
Smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages contribute to significant blood thickening. That is why people with “thick” blood are advised to give up these bad habits.
Regular physical activity is indicated. You need to move more, walk in the fresh air. Swimming and cycling are also suitable.
Prevention and treatment of chronic diseases is also necessary. Especially associated with the bronchopulmonary system, metabolic disorders, diabetes insipidus and diabetes mellitus, obesity, and improper functioning of the spleen.
And, of course, you need to eat right. After all, there are foods that provoke blood thickening. In particular, these are meat broths, sausages and smoked meats, jelly, white bread, cream, lentils, bananas and pickles.
Medicinal herbs should also be used with caution. For example, St. John's wort, valerian, nettle and yarrow can also provoke “thick” blood.
It is summer now. Is heat dangerous for those with “thick” blood? — Hot weather is a significant risk factor for blood thickening. It is especially dangerous for people in the risk groups I mentioned above. That is why it is so important, if possible, to avoid going outside in the heat, stay in a cool room and replenish fluid loss with sufficient drinking regimen.
Is donation harmful or beneficial for those whose blood is too thick? — If there are no contraindications to becoming a donor, become one! This way you will benefit not only people in need, but also yourself. After all, scientists have proven that blood viscosity after bloodletting decreases by 20–30%. And this is very good!
Who's at risk
Any of the above factors can cause blood thickening. But also people suffering from the following diseases are at increased risk:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pancreatitis;
- food poisoning;
- varicose veins;
- hypoxia;
- myocardial infarction;
- thrombophilia;
- atrial fibrillation;
- heart failure;
- stroke;
- diabetes;
- antiphospholipid antibody syndrome;
- amyloid dystrophy;
- leukemia;
- myeloma;
- bone marrow cancer;
- polycythemia;
- adrenal dysfunction.
The development of hypercoagulability syndrome is facilitated by long-term use of diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as drugs containing estrogen or phytoestrogen.
Blood thinners
The most common foods that reduce blood viscosity include ginger, cranberry, garlic and lemon. Seafood, vegetables and fruits, fish, and herbs have a slightly weaker effect.
- Ginger. The root of this plant has healing properties. It is used as a food seasoning mainly in powdered or raw form. It has a rich chemical composition, in which the most important place in terms of blood thinning belongs to natural antioxidants and lipids. For reception, you can prepare tea from half a teaspoon of grated ginger, which is infused in one liter of boiling water. This is the daily dose. You should not exceed it due to the high activity of ginger, which is contraindicated when taking most cardiac and blood-thinning medications, severe damage to the liver and kidneys, the presence of sources of bleeding, increased temperature, and also in hot weather.
- Cranberry. A wonderful berry with wonderful properties, one of which is reducing blood viscosity. The berries of this plant are mainly used, both fresh and dried. You can take whole fruits, or you can include them in juices, fruit drinks, and infusions. It is acceptable to prepare teas and compotes containing only cranberries or their combination with other ingredients. The only contraindication for use is gastritis and gastric ulcer with high acidity due to the high content of acids in its composition.
- Garlic. Refers to products with strong blood-thinning properties. It is used raw and as a seasoning for food products. Eating one clove of garlic per day has a very good anti-clotting effect. Contraindications for use may include gastritis, hemorrhoids, heart disease, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Lemon. One of the few products that has no contraindications for use. Lemon fruits have beneficial properties. At the same time, both its pulp and peel are active. Only the seeds have toxic properties. You can take lemon in any form with the addition of honey, tea or plain water.
- Cayenne pepper. Red hot pepper can greatly thin the blood due to its high level of salicylates. It can be crushed and added as a seasoning to food. Cayenne pepper can also lower blood pressure and improve circulation.
Why is condensation dangerous?
Blood viscosity often increases in pregnant women. In this case, this process plays a natural role of protection against possible bleeding and miscarriage. Also, the fluid in the vessels of women becomes thicker immediately before childbirth. This is how nature protects the expectant mother from severe blood loss. But excessive thickening during pregnancy can be dangerous both for the woman (promotes thrombosis, thrombophilia, varicose veins, leukemia) and for the fetus (damage to the vascular bed).
As for newborns, their blood is much thicker than that of adults. But that shouldn't be a concern. The baby needs time to adjust to life in a new environment. In the first hours after birth, hemoglobin in the baby’s body can reach 200 g/l. But already in the first few days of life, these numbers will begin to decline. Almost half of the hemoglobin will be destroyed in the first day and the thickness of the baby’s blood will decrease.
It’s a different matter for adults whose blood has become thick for various reasons. They should not expect the indicators to return to normal on their own. This condition can be dangerous to health.
Often, thickening is accompanied by increased formation of blood clots, which can clog blood vessels, preventing normal blood flow. If a blood clot blocks a vessel in the heart or brain, a heart attack or stroke may occur, possibly with death.
If the substance has become viscous, but the number of platelets has decreased, this condition leads to circulatory problems in the body and increases the risk of bleeding. In some cases, hypercoagulability syndrome accompanied by a reduced platelet count is a symptom of cancer.
If increased viscosity is not treated, this condition can provoke hyperosmolar coma and intracerebral hemorrhage, which has a high risk of death.
A little about thrombosis
Against the background of increased viscosity, a blood clot can form at any time, and under such circumstances it will look like a natural physiological process, for example, against the background of dehydration. When platelets come close to each other, they undergo friction and stick together into entire conglomerates. Thrombosis often causes strokes. Therefore, doing an electrocardiogram, even with enviable regularity, is not enough: it is important to keep the viscosity situation under control.
How is the “thickness” of blood determined?
To measure thickening, specialists use a device called a viscometer. It measures the speed of movement of the substance in the vessels, and then compares this indicator with the speed of movement of distilled water. For measurements, blood and water are taken in equal quantities at identical temperatures.
It is considered normal if blood flows 4-5 times slower than water, and its relative density (depending on the number of red blood cells) remains within the range of 1.050-1.064 g/cm3. This value determines the amount of salts, proteins and formed elements in the plasma.
Hematocrit (the volume of red blood cells in 1 liter of blood) differs depending on gender and age. For women, the norm is 37-47%, for men - 40-54%, for newborns - approximately 20% more than for adults, and 10% more than for older children.
As for laboratory viscosity indicators directly, the norm is considered to be from 4 to 5.5. This parameter directly depends on the number of red blood cells in the plasma: the more there are, the stronger the viscosity.
In addition to the viscometer, immunoelectrophoresis (determines what proteins are in the plasma) and immunochemical study (counts the number of proteins) are also used to diagnose blood thickening.
Apple vinegar
Many consider this product an indispensable aid for maintaining health, systematically using it according to a proven scheme. We can say for sure that apple cider vinegar is hard to harm the body. Therefore, its use can be considered a relatively safe activity. Many of its positive effects on the body have been recorded, one of which is a decrease in blood viscosity.
The mechanism of this action can be explained by its slightly acidic reaction caused by natural beneficial components. Their entry into the body helps eliminate toxic acidic compounds, which are replaced by the active components of apple cider vinegar. At the same time, metabolic acidosis in the blood is eliminated, which helps it acquire more liquid properties compared to the initial level. Naturally, to achieve such an effect, it is necessary to systematically take the substance, which can easily replace the daily use of tablets with the same effect.
Proper intake of apple cider vinegar should be done in the morning. This is a very important condition, since at this time the body is most capable of discharging oxidized products. The recipe for preparing an aqueous solution consists of a glass of warm water and two teaspoons of apple cider vinegar. A single daily dose is sufficient. The duration of the course is from 2-3 months to a year with 10-15 day breaks every 2 months. The only contraindication is gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer with increased stomach acidity.
More details:
The benefits and harms of apple cider vinegar and its treatment
External signs of thickening
The most accurate indicators of this condition can be determined exclusively by laboratory analysis. However, there are a huge number of signs that may indirectly indicate that the fluid in the vessels flows more slowly.
People with high blood viscosity may experience the following symptoms:
- aching headaches;
- fainting state;
- dizziness with loss of coordination;
- fast fatiguability;
- drowsiness;
- in places of cuts, blood flows unnaturally slowly;
- muscle weakness;
- heaviness and pain in the legs;
- "pins and needles" sensation, numbness, burning, tingling in the legs and arms (paresthesia);
- noise in ears;
- increased sensitivity to low temperatures;
- dry skin;
- cyanosis (cyanosis) of certain areas of the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth and eyelids;
- increased anxiety;
- sleep disorders;
- tendency to depression;
- constipation
Often hyperviscose syndrome occurs in parallel with chronic fatigue, candidiasis or irritable bowel syndrome.
Juices for blood thinning
Drinking juices significantly reduces blood viscosity. Various fruit and vegetable juices are ideal for these purposes. Their positive effect on the coagulation system is determined by the high content of vitamins and microelements responsible for the balance between the coagulation and anticoagulation systems. In addition, water, which is found in significant quantities in any even the most concentrated juice, replenishes the fluid deficiency in the body. Daily consumption of one glass of fruit juice is enough for positive changes in the hemostatic system.
As for specific types of juice, they can be very diverse, containing components of one or more fruits. It is desirable that they are not canned, but freshly squeezed.
Reduces blood clotting very well
against the background of systematic intake of orange, cranberry, lemon, carrot, apple, peach, pineapple, pomegranate, banana-strawberry, currant and various other types of juice.
It is worth mentioning separately the exceptional benefits of tomatoes and their pulp. This juice can be drunk in large quantities. In addition to the anticoagulant effect, it is an excellent antioxidant. The same effect is characteristic of fruits and berries from which juices are made: gooseberries, raspberries, blackberries.
Only freshly squeezed juices have a healing effect on the body! Store-bought juices will only harm your health.
Turkey Cream Soup Recipe
Not everyone likes such thin soups with a uniform consistency. But they are ideal for people with a tendency to form blood clots, with a diseased liver and pancreas. This is a popular blood thinning diet recipe that will replace the first course during lunch.
Ingredients needed:
- broth in which two turkey legs were boiled;
- remove meat from boiled legs;
- a couple of potatoes, boiled in broth until tender;
- medium-sized carrots, pre-boiled;
- salt, garlic and ginger - to taste.
Grind all ingredients to a smooth puree using an immersion blender or food processor. Puree soup tastes good only immediately after preparation. When reheated, it loses its taste properties.
Diseases that develop against the background of blood stagnation
As a result of prolonged stagnation, diseases develop that have to be treated with medication and, in some cases, surgery.
The following pathologies are observed in women:
- Adnexitis, inflammation of the appendages;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Miscarriage;
- Infertility.
In men, the diseases are as follows:
- Prostatitis;
- Varicocele;
- Impotence.
One of the most common ailments is hemorrhoids, and almost everyone notices a deterioration in their emotional state.