The terms “arterial hypertension” and “hypertension” are often perceived as synonymous words. Many people think that both diagnoses mean the same thing - high blood pressure. However, this is not entirely true.
One of these terms actually means high blood pressure, and the second is the name of a disease that can cause high blood pressure. In order not to confuse two similar names, let's look at the differences between the diagnoses of hypertension and hypertension.
Unfortunately, some patients and their relatives, having collected a lot of useful information about diseases, feel the desire to engage in treatment personally. However, this is strictly prohibited.
To perform such serious functions, it is necessary to have fundamental knowledge and a wide range of useful skills and abilities. Observation and treatment should be carried out by a doctor - a qualified specialist with experience.
Why is hypertension dangerous?
The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels, providing all the body's cells with oxygen and nutrients. When blood vessels become clogged or lose their elasticity, the heart begins to work harder and increases the pressure inside the vessels.
Against the background of the disease, if not treated in a timely manner, serious pathologies such as acute heart failure, hypertensive crisis, stroke, and myocardial infarction can occur.
The difficulty of hypertension is that it often remains virtually asymptomatic for years and the person does not know about the existence of the disease. Symptoms are often observed - headache, fatigue, memory loss, dizziness, high blood pressure, to which a person simply does not pay attention. This may indicate the beginning of the development of the disease.
Main features
Often high blood pressure (hypertension) is diagnosed after the age of 45-50 years. If a person is attentive to himself, he notices painful changes and may suspect an increase in blood pressure. But sometimes people are unaware of hypertension because they do not know its symptoms. This lasts until the first hypertensive crisis, when the pressure jumps sharply to the upper values.
A gradual increase in blood pressure may last for several months. Therefore, you need to know the symptoms of high blood pressure in order to diagnose the disease in time and begin treatment.
We list the main signs of high blood pressure (hypertension):
- Headache - surrounds the head with a “hoop” - spreads to the back of the head, temples and forehead;
- Redness of the facial skin;
- Feelings of pressure on the eyes from the inside;
- Swelling of the eyelids and face in the morning;
- Noise in ears;
- "Floaters" before the eyes.
If elevated blood pressure persists for some time, this causes changes in the functioning of the cardiac system. Heart pain appears, heart rhythm is disturbed, shortness of breath is possible.
Small blood vessels are also damaged. With chronic high blood pressure, they cannot withstand pressure, become depleted, and rupture. Vision, hearing, and tactile sensations deteriorate.
Hypertension is accompanied by chronic hypertension. Therefore, the signs of hypertension and hypertension are the same (headache, redness, swelling, spotting and noise). High blood pressure is the main symptom by which one judges the presence of hypertension and begins an examination.
Causes of hypertension
- Excess weight. People who are prone to obesity are several times more likely to suffer from heart disease. Also, excess weight causes increased levels of calcium and sodium in the blood, disruption of normal kidney function and diseases of internal organs. This, in turn, is an additional factor for the development of hypertension.
- Arterial sclerosis. Due to the presence of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels, normal blood circulation stops. The heart has to work harder to increase the pressure in the blood vessels.
- Stressful situations. During stress, blood pressure increases due to the release of the hormone adrenaline into the blood. By acting on the heart, adrenaline causes it to beat faster, throwing more blood into the vessels.
- Bad habits. Smoking, drinking alcohol, fatty and heavy foods increase pressure in blood vessels, form vascular spasms and lead to their damage.
- Age. Over the years, a person's heart wears out. The risk of developing hypertension increases with age if you do not pay due attention to your health. It is necessary to undergo preventive examinations and give up bad habits, if any. High blood pressure often develops in people over 35 years of age.
- Genetic predisposition. If first-degree relatives (father, mother, siblings, grandparents) suffer from hypertension, the risk of developing the disease increases.
- Sedentary lifestyle. At a low level of stress, metabolism slows down, the nervous system and other body systems are weakened, and immunity is reduced. The risk of developing hypertension increases by 50%.
MEDICAL CENTER
- home
- Information
- Articles
- Arterial hypertension.
>
>
>
Arterial hypertension
Arterial hypertension (hypertension, hypertension) is the most common chronic disease in adults associated with increased blood pressure. This disease cannot be completely cured, but it can be kept under control. Unfortunately, there are no clear external signs by which you could understand that the pressure is rising again. Therefore, timely diagnosis and regular visits to the doctor are necessary.
What is arterial hypertension?
Arterial hypertension (arterial hypertension) is persistent increased hydrostatic blood pressure in the arteries of the systemic circulation. Normally, pressure numbers can fluctuate depending on a person’s condition: increase during physical or psycho-emotional stress, decrease during sleep. However, the pressure returns to normal numbers from 100/60 to 140/90. If these numbers are higher, arterial hypertension occurs.
Arterial hypertension requires special attention and control, because Hypertension is a leading risk factor in the development of strokes, myocardial infarction, vascular and kidney damage, vision loss and other dangerous diseases.
Why does arterial hypertension occur?
The causes of arterial hypertension remain unknown in 90% of cases. In this case, the doctor speaks of primary or essential hypertension. Hypertension (essential hypertension) occurs as a result of increased activity of biological mechanisms that cause narrowing of arterial vessels. Essential arterial hypertension accounts for 90-95% of cases of hypertension. In other cases, secondary, symptomatic arterial hypertension is diagnosed, which is the result of another disease or a side effect of medications used.
Some researchers believe that hypertension is caused by hormonal imbalance, salt reabsorption in the kidneys, or/and the presence of vasoconstrictor substances in the blood.
Some lyrics
The total length of blood vessels in the human body is about 111,000 kilometers. Each heartbeat means that 60-80 grams of oxygenated blood flows from the ventricle of the heart into the aorta, the largest artery.
If the human vascular system is compared to a tree, it turns out that the aorta is the trunk of this tree. It branches into many arteries, which in turn are divided into many small arterioles. The arterioles, in turn, carry blood to the capillaries, which supply oxygen and nutrients to every cell of the human body.
In order to move blood along all these branches, it is necessary to expend a certain amount of energy and strength. The force that acts on the walls of blood vessels during blood flow is what we call pressure. Thus, pressure regulation is influenced not only by the work of the heart, but also by these small arterioles. They are able to both relax to reduce pressure and contract if it needs to be increased.
Blood pressure varies for all people and depends on their activity. For example, if you are resting, then your heart does not need to work quickly. During physical activity, large volumes of blood are required to supply muscles with oxygen, and blood pressure increases.
In another situation, for example, if you suddenly rise from a horizontal position, the pressure will immediately increase to ensure a steady supply of oxygen to the brain.
Blood pressure is usually lower from 1:00 to 5:00 am, rises sharply from 6:00 to 8:00, then remains virtually unchanged during the day and evening, and decreases from 11:00 to 12:00 at night. Blood pressure also varies with age. In children, normal pressure readings can be 70/50, and in older people - more than 120/80.
Signs of arterial hypertension
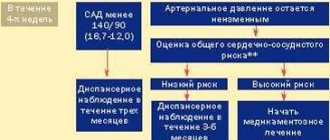
Arterial hypertension is divided into three degrees of severity, depending on blood pressure indicators:
- I degree: 140-159/90-99 mmHg;
- II degree: 160-179/100-109 mmHg;
- III degree: more than 180/110 mm Hg;
Initial arterial hypertension in most cases does not manifest itself in any way, and therefore this disease is often called the “silent killer”. It received this name because very often a person does not even suspect that he has high blood pressure, and only learns about it when complications occur, often fatal, such as a stroke or myocardial infarction. Such asymptomatic manifestations of hypertension can last up to several years or even decades. This suggests that even if you do not have any external signs of illness, this does not mean that you need to refuse regular diagnostics of your health.
In some cases, hypertension manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- dyspnea;
- visual impairment;
- noise in the check;
In some cases, with arterial hypertension, a hypertensive (or, as they say, hypertensive) crisis . This is a condition in which there is a sharp increase in blood pressure and disruption of blood circulation in the internal organs. During a hypertensive crisis, symptoms of impaired blood supply to the brain and heart are observed:
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- loss of performance, fatigue;
- redness of the face, chest;
- “goosebumps”, “floaters” before the eyes (associated with narrowing of the vessels of the optic nerve, as well as the retina. This can sometimes even lead to temporary blindness);
- insomnia, anxiety, fear;
- headaches, especially in the back of the head and temples (mainly associated with vasoconstriction of the soft tissues of the head);
- tinnitus, deafness (associated with narrowing of the vessels of the hearing aid);
- shortness of breath (may indicate ischemic events in the heart, when there is a violation of blood flow in the coronary arteries);
- chest pain;
- neurological disorders;
- dizziness;
- nausea and even vomiting (associated with increased intracranial pressure);
Factors that increase the risk of developing arterial hypertension:
As already mentioned, essential hypertension is the most common type of hypertension, although its cause is not always identified. However, some characteristic relationships have been identified in people with this type of hypertension. For example, essential hypertension develops only in groups with high salt intake , more than 5.8 g per day.
With age , the walls of large arteries become more rigid, and because of this, vascular resistance to blood flow increases, therefore, pressure increases, so age is also a factor.
The genetic factor is considered to be the main factor in the development of essential hypertension. However, the genes responsible for the occurrence of this disease have not yet been discovered.
A large number of patients with essential hypertension have arterial pathology: there is a loss of elasticity of the smallest arteries - arterioles.
Obesity is also a risk factor for essential hypertension. People who are obese are 5 times more likely to develop hypertension compared to those who are of normal weight.
In general, risk factors include the following:
- age;
- hereditary predisposition;
- gender (men are more likely to suffer);
- smoking;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- excessive salt intake;
- lack of physical activity, obesity;
- excessive exposure to stress;
- kidney diseases;
- increased level of adrenaline in the blood;
- congenital heart defects;
- regularly taking certain medications;
- complications of pregnancy (late toxicosis);
Thus, we can conclude that in most cases you yourself are able to prevent the development of hypertension by leading a healthy and active lifestyle . It is also recommended to regularly measure your blood pressure at home and visit your doctor at least once a year (to monitor your general condition and the effectiveness of the therapy). Get examined using professional diagnostic equipment, and our specialists will help you take good care of your health.
Types of cardiac hypertension
There are many classifications of the disease, which are based on the patient’s appearance, blood pressure level, causes of increased blood pressure, and the nature of the disease. However, doctors everywhere use a classification based on the severity of the disease.
Hypertension 1st degree
– is also called the preclinical stage. This is the mildest form of hypertension, in which blood pressure reaches 140/90 mmHg. mercury column. Mild headaches, decreased performance, and general fatigue are observed. While the patient is at rest, the pressure normalizes.
Hypertension 2 degrees
– moderate stage, at which the pressure increases to 180/110 mm. rt. Art. formation of atherosclerotic plaques, hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart, and increased concentration of creatinine are observed.
Hypertension 3 degrees
– pressure rises to 220/115 mm. rt. Art. in this case, the risk of complications is high. With this degree of development of the pathology, the blood supply to the internal organs is disrupted. Stage 3 disease can manifest itself as renal failure, hemorrhage from the eyes, and blindness.
Blood pressure indicators for hypertension
The main manifestation of hypertension is a long-term and persistent increase in blood pressure (BP).
There are systolic (or upper) blood pressure, which shows the level of blood pressure at the moment the heart contracts, and diastolic (lower), which shows the level of blood pressure at the moment the heart relaxes.
Normal blood pressure levels are considered to be 120-134/80-84 mmHg, but data may vary due to emotional shocks, physical activity, changes in air temperature, etc. These fluctuations are normal; they reflect the body’s naturally programmed reaction to changes in living conditions. However, constantly elevated blood pressure in the absence of obvious reasons for this is a significant reason to take care of your health.
Arterial hypertension is indicated by a stable increase in blood pressure (systolic - above 140 mm Hg, diastolic - above 90 mm Hg when measured at a doctor’s appointment; 135/85 mm Hg and above - when measured independently) , confirmed by repeated measurements. To establish a diagnosis of arterial hypertension, two measurements with elevated blood pressure in the absence of physical and emotional stress are sufficient.
How to diagnose the disease?
When the first symptoms of hypertension appear, consult a cardiologist. He will conduct an examination and refer you for tests:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood test for hemoglobin;
- urine test for protein and glucose;
- electrocardiography;
- echocardiography;
- chest x-ray;
- biochemical blood test to detect cholesterol, urea, glucose and calcium levels;
- phosphates and uric acid;
- CT scan;
- ultrasonography.
Based on the results of the tests, the attending physician will determine whether hypertension is present, the stability of the increase in pressure, the degree of development of pathological changes in the internal organs, and the cause of the increased pressure.
Treatment of hypertension
The method of treatment depends on the degree of development of the disease. In the first preclinical stage, normal blood pressure levels can be maintained without the use of medications. The patient needs to balance their diet, give up bad habits, lead an active lifestyle and normalize their sleep and work patterns.
When treating stage 2 hypertension, the doctor prescribes a medication for long-term use and with a minimum number of contraindications, combined with moderate activity and giving up bad habits. The drug is prescribed by a cardiologist after examining the patient. The drugs must be taken continuously as this can cause a stroke or heart attack.
Therapy of stage 3 hypertension is carried out with the help of 1-2 drugs from different drug groups in combination with an active lifestyle and stabilization of nutrition and sleep patterns.
- diuretics with a diuretic effect are prescribed for salt and water retention in the body;
- to normalize blood circulation - ACE inhibitors;
- calcium antagonists - to reduce the oxygen demand of the heart muscle;
- beta blockers for atrial fibrillation or other concomitant pathologies.
Therefore, when determining therapeutic therapy, the doctor must know the patient’s entire medical history, take into account contraindications, lifestyle and physical characteristics (body weight, height).
Hypertension is treated in Krasnoyarsk at the medical level. We have experienced cardiologists who will conduct a complete examination and examination, friendly medical staff and high-quality equipment. To make an appointment with a specialist or find out more detailed information, leave a request on the website or by calling the clinic 201-03-03.
Which doctor treats hypertension
A cardiologist treats hypertension. Also, treatment of hypertension can be carried out by a general practitioner (general practitioner or family doctor), who often detects high blood pressure when contacting him with complaints of poor health.
Drug therapy
Medicines should be selected by a doctor, who does this taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient.
Lifestyle change
First of all, you need to:
- stop smoking;
- eliminate or reduce alcohol consumption;
- try to reduce weight to normal;
- reduce salt intake to 5 g/day;
- provide regular physical activity. The most beneficial are walking, swimming and therapeutic exercises;
- increase your resistance to stress;
- optimize nutrition (eat more greens, fruits, foods with a significant content of potassium, calcium and magnesium, and, conversely, reduce the consumption of vegetable fats and protein foods). You should eat regularly.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.