Herbal medicine or herbal treatment is a common method for various diseases. Many effective recipes are approved by official medicine and are successfully used as an auxiliary treatment. Maintenance therapy for diabetes mellitus is carried out with the help of herbs, vegetables, grains and cereals.
To avoid harming yourself, before using traditional medicine, you should consult an endocrinologist and herbalist. Experienced specialists will tell you which plants lower blood sugar and help you choose an individual course. You should not start treatment on your own. Despite their relative safety, herbal remedies have contraindications and are not suitable in all cases.
Prerogative aspects of plant treatment
The advantages of herbal medicine include:
- Availability of raw materials. Ingredients for preparing medicines can be easily purchased at a pharmacy or grown in a garden plot.
- Multifunctionality. Due to their natural composition, plants not only lower blood sugar well, they enrich the body with minerals and vitamins and help restore immunity. The products normalize the functioning of the digestive system, cleanse the blood, promote the removal of toxins, and restore the functioning of the renal apparatus.
- Naturalness. Grown or purchased raw materials are not subjected to chemical treatment and do not contain synthetic impurities.
Most folk remedies have minimal restrictions on use based on the gender and age of the patient. The use of folk remedies is not replacement therapy, but only an addition to drug treatment prescribed by a doctor. Systematic consumption of herbs and plants helps normalize glucose levels, which helps control the course of diabetes and prevents the risk of complications.
The effect of plants on the diabetic body
Plants used in diabetic practice are classified into several groups, depending on their effects:
- Natural adaptogens. Increases the body's resistance to harmful external influences and stabilizes hormonal levels.
- Diuretic herbal remedies. Increase the rate of glucose removal from the body.
- Hypoglycemic biguanides. Plants similar in action to the antidiabetic drug Metformin. They reduce sugar by accelerating the processes of transport and utilization of glucose.
- Inulin-containing plants. Natural sources of insulin and stimulators of endocrine pancreatic function.
- Plants with active trace elements (zinc and chromium). They lower the level of glucose in the blood plasma, enhance the effect of insulin, and increase the body's protective reactions.
The combined use of plants from different groups is allowed after prior consultation with a doctor.
Herbs for diabetes
Life for diabetics is neither sugar nor honey. Regular injections, eating based on the glycemic index of foods, frequent visits to the clinic - this is not a complete list of all the problems. Herbal remedies for diabetes are not a complete therapy, but as an additional remedy they will help keep glucose levels under control. Let's look at them in more detail.
Buy omik (root) on our website
Plants that lower sugar levels
Some herbs can lower glucose concentrations because they have insulin-like properties. For you, we have compiled a list of plants that will help with diabetes:
- Nettle regulates carbohydrate metabolism and reduces the concentration of sugar in the lymph.
- Omic is prescribed to diabetics to regulate blood glucose levels. The root of this plant also contains coumarin, which prevents the formation of blood clots.
- Schisandra seeds are recommended for diabetes to maintain overall body tone.
- Golden root is used to eliminate the symptoms of diabetes and restore the body's strength after illness.
- Carrot grass improves metabolism and lowers sugar levels. To treat diabetes, tea is prepared from this plant. It cleanses the blood and has antitumor properties.
- Bean flaps regulate protein and carbohydrate metabolism, stimulate the production of hormones and enzymes that break down sugar. The pods contain the active compound glycokinin, which has an effect similar to insulin: it lowers the concentration of glucose in the blood plasma.
- Flax seeds affect the functioning of the pancreas, stimulating the secretion of insulin. They also cleanse blood vessels of cholesterol deposits and regulate lipid metabolism, which is especially important for overweight diabetics.
- Ginkgo leaves are often prescribed for diabetes and vascular diseases to avoid complications.
- Wintergreen is used as part of an infusion to reduce the amount of glucose in the blood. Important: it is used only for mild forms of the disease!
- Wintergreen is used to prevent diabetes.
Attention!
Taking any herb for diabetes should be discussed with your doctor first! He can prescribe decoctions of one of the listed plants or prescribe a series, astragalus, and other dietary supplements.
Plants that replace sugar
Diabetics are extremely careful with foods containing a lot of fast carbohydrates. For this reason, they courageously refuse flour products and confectionery, but sometimes you really want something sweet!
Medicinal plants will help sweeten the pill. Some of them have a sweet taste, but do not increase blood glucose levels. Among these plants are polysaccharides, which are used in the production of sweeteners. These herbs are recommended to drink instead of tea for diabetes. But, unfortunately, their list is not so long:
- Stevia is the most popular herb for diabetics with a sweet tooth. Stevia leaves have very few contraindications. This herb is very sweet, but it does not increase glucose levels.
- Licorice also has a sweet taste, but is not often prescribed for diabetes. The fact is that the plant has many contraindications, which include heart, kidney and blood diseases. It is best to make infusions from licorice root with the addition of rose hips.
- Elecampane has a sweetish taste. It also helps reduce the symptoms of diabetes: eliminates thirst, reduces the urge to urinate.
- Jerusalem artichoke is used in complex therapy of diabetes.
Interesting fact
Stevia leaves are the raw material for most industrial sweeteners.
Medicinal herbs
Herbal infusions and decoctions must be used for a long time. There will be no immediate effect to eliminate hyperglycemia from drinking a decoction or infusion. Only regular treatment will help stabilize the condition of a diabetic. The most common herbs that lower blood sugar are:
Galega (rue or goat's rue)
Flowers, roots, shoots and leaves are suitable for preparing medicine. Galega neutralizes glucose like artificial insulin and helps remove it from the body along with toxins.
The hypoglycemic effect of galega and chicory helps keep sugar levels stable
Burdock
Roots and leaves are used. It has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect on the digestive system. It has a beneficial effect on the weakened pancreas and stimulates the flow of bile.
Chicory (roots)
Contains a natural polysaccharide belonging to the group of prebiotics - inulin, essential oils, biflavonoids (substances with active vitamin P), organic acids. In the body it acts on glucose like medical insulin.
Sage
Has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Reduces the load on the pancreas. When consumed on an empty stomach, it reduces sugar levels.
Nettle
Contains vitamin PP, which regulates blood sugar. Helps reduce bad cholesterol levels and improves the condition of blood vessels.
Dandelion
The roots of the plant have a choleretic and calming effect. The above-ground part contains glycosides, vitamins A, C, B2, E, and minerals. Helps improve appetite and normalize metabolic processes.
Hellebore or kupena
All parts of the plant are used in folk medicine. Long-term use of the decoction for non-insulin-dependent diabetes helps to effectively reduce sugar. The first type of disease can be treated with purchased medicine only with the permission of a doctor.
Cuff
Normalizes blood flow by cleansing blood vessels. Has a diuretic effect. Contains: phenol carbonic acids, cahetins, phytosterol, vitamins and microelements.
St. John's wort
It has a therapeutic effect on the organs of the hepatobiliary and digestive systems, stabilizes metabolic processes. Decoctions and infusions of herbs that reduce sugar can be single-component or in the form of mixtures.
Berry bushes
Wild and garden berries have a low glycemic index (that is, they are slowly absorbed into the blood and have virtually no effect on glucose levels). For diabetes, the menu includes the berries themselves and leaves of shrubs as a source of vitamins.
Herbs for the pancreas
- Cowberry. Contains carotene, pectin, tannins, tannin, vitamins and minerals. Acts as an insulin catalyst and diuretic.
- Kalina. The plant is based on invert sugar, which does not require insulin for delivery to the body's cells. The berries are rich in plant organic alcohols, tannin, organic acids, and vitamins.
- Blueberry. The combination of glycosides, vitamins, tannins and minerals in the plant allows you to regulate sugar levels, maintain the health of the pancreas, and relieve swelling. The beneficial effect on the blood vessels of the visual organs helps prevent rhinopathy (one of the complications of diabetes).
- Black currant. Saturates the body with vitamins, pectin, microelements. Activates metabolic processes, helps eliminate toxins, stimulates the immune system.
Wild berries are an indispensable component in a diabetic’s menu.
Combining herbs and berries intended to lower blood sugar enhances the effect of their use. You can prepare the medicine yourself or purchase a ready-made anti-diabetes mixture at the pharmacy. The most common herbal combinations include:
- burdock root + blueberry leaves;
- dandelion (roots and leaves) + dried blueberry berries and leaves;
- blueberry (leaves) + nettle + rue;
- goat's rue + agrimony + cucumber + bean leaves + blueberry fruits + centaury;
- flax seeds + St. John's wort + linden blossom + dandelion root;
- dandelion leaves + nettle + goat's rue + viburnum bark + blueberry and lingonberry leaves;
- centaury + licorice root + calamus root + galega.
Not all diabetics tolerate combined medications equally. Therefore, it is better to check with your doctor which herbs and in what combination to use.
Healthy recipes for diabetics
Now let's talk about what folk remedies will help make life easier with diabetes. Among them there are infusions and decoctions that lower glucose - they are drunk in small quantities. You can also brew special tea, in which you do not need to add sugar or honey.
Infusion of bean leaves to lower sugar
Very often, when treating diabetes with herbs, it is recommended to use bean leaves. Decoctions are prepared from them, but we recommend making an infusion that retains maximum nutrients. We are publishing a recipe especially for you:
- chop 5 tbsp. l. bean wings;
- pour the powder into a thermos;
- pour hot water (2 cups);
- leave for 12 hours;
- strain.
This infusion can be taken up to 5 times a day, 50 ml. The course of treatment is 1 week.
Flax decoction, lowering blood glucose
If you have flax seeds, you can make an excellent sugar stabilizer. Just follow the recipe:
- 1 tbsp. l. Grind the seeds in a blender;
- place flaxseed flour in a small enamel saucepan;
- pour in 250 ml of boiling water and turn on the gas;
- when it boils, simmer over low heat for 5 minutes;
- let sit covered until cool, then strain.
It is better to take the healing decoction warm, dividing it into 2 doses.
Sweet stevia tea
And, of course, we can’t help but share with you a recipe for those with a sweet tooth! After all, many diabetics love sweets, but they are not allowed. But you can drink stevia tea, since it does not affect blood sugar levels at all and at the same time satisfies the taste buds of diabetics. The recipe is simple:
- 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water over stevia leaves;
- leave for half an hour covered;
- strain.
Important!
You can drink stevia tea no more than 3 times a day, provided that you are not allergic to this plant!
Thus, medicinal herbs will be an excellent help for diabetics. Some plants will help lower blood glucose, while others will satisfy the need for sweets. Health to you, dear readers!
Legumes and cereals
This category of plants is used to reduce sugar in the form of specially prepared medicines and as components for preparing diabetic diet dishes.
- Fenugreek. Effectively lowers the level of glycated hemoglobin, normalizes blood pressure, and maintains the performance of the cardiovascular system. Contains: manganese, selenium, zinc, magnesium, B vitamins, plant glycosides, pectin, amino acids and tannin.
- Green beans. Cleanses the body of toxins and waste, improves hematopoiesis, increases the tone of blood vessels, improves metabolism.
- Oats. Eliminates “bad” cholesterol and normalizes heart function. Thanks to the content of vitamins, minerals, starch and fiber, it regulates digestion and the presence of glucose in the body.
- Flax seeds. Rich in Omega-3,6,9 polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins B, C, E, K, D, A. They cleanse blood vessels of cholesterol plaques, promote the restoration of pancreatic cells, improve metabolic processes and metabolism.
- Amaranth or amaranth. It is not a true cereal. Contains squalene, which ensures natural regulation of metabolic processes (lipid and steroid) and proper absorption of glucose. Has antioxidant properties.
Cereals are an ideal breakfast for a diabetic patient. In addition to their ability to regulate glucose, they give the body a long-term feeling of fullness.
Oatmeal stimulates the hepatobiliary system, protects the stomach, improves digestion, reduces sugar and cholesterol
Top 10 Foods to Lower Blood Sugar
Broccoli
When chopping or chewing broccoli, a substance called sulforaphane is formed. The compound has potent antidiabetic effects and reduces markers of oxidative stress. The best way to increase the availability of sulforaphane is to eat lightly steamed broccoli or add mustard seed powder to cooked cabbage. [6, 7]
Sauerkraut
Fermented vegetables contain probiotics, minerals and antioxidants. They increase insulin sensitivity and prevent the development of hyperglycemia. [8]
Pumpkin and pumpkin seeds
Rich in fiber and antioxidants, pumpkin is used as a traditional cure for diabetes in Mexico and Iran. The benefits are provided by the polysaccharides included in its composition. The seeds contain a lot of healthy fats, proteins, and by eating 65 g of pumpkin seeds after meals, you can reduce your sugar levels by 35%. [9, 10, 11]
Seafood
Fish (salmon, sardines) and seafood are a valuable source of proteins, omega-3, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The substances slow down digestion, increase the feeling of satiety, prevent hyperglycemia after meals and promote weight loss. [12, 13]
Nuts and nut butter
Eating peanuts and almonds on an empty stomach and after meals throughout the day as part of a low-carbohydrate diet reduces glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). To get the effect, it is enough to eat 56 g of nuts daily. [14, 15]
Oats and oat bran
Whole grains and bran contain a lot of healthy soluble fiber. More than 15 studies have confirmed that oats significantly lower HbA1c when consumed before high GI foods. [16, 17]
Flax seeds
Fiber and healthy fats are of great benefit - to reduce HbA1c, just drink 200 g of 2.5% fat yogurt mixed with 30 g of flax seeds daily. The effect is confirmed by 25 controlled studies. [18, 19]
Beans and lentils
Magnesium and protein contained in legumes lower blood sugar after meals. And soluble fiber and resistant starch slow down digestion and heal the intestines. [20]
Avocado
Avocado fruit is rich in healthy fats, fiber, vitamins and minerals. It protects against the development of metabolic syndrome - disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism that pose a serious health risk. [21]
Calais
It's not for nothing that curly kale is called a superfood - the flavonoids it contains, including quercetin and kaempferol, can protect against hyperglycemia and improve insulin sensitivity. To get the effect, it is enough to eat 7-14 grams of kale with a high-carbohydrate meal. [22]
Additional ways to lower blood glucose
A few simple lifestyle changes can improve the condition of people with type 2 diabetes and sometimes eliminate the need to take medications.
5 Natural Ways to Lower Blood Sugar Levels:
- 1 low-carbohydrate breakfast no later than 1.5 hours after waking up - skipping breakfast suppresses the beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin;
- 2 maintaining hydration - water thins the blood and helps the kidneys flush out excess glucose;
- 3 increased physical activity - daily walking and moderate exercise 2-3 times a week reduces the risk of stroke and heart disease, improves the body's sensitivity to insulin and helps convert glucose into energy;
- 4 stress control - cortisol reduces sensitivity to your own insulin and to injections, so it is important to learn to relieve stress in natural ways (walking, breathing practices, meditation);
- 5 Sleep at least 7-9 hours a night – Lack of sleep increases stress, releases cortisol and increases hunger hormones, making it difficult to maintain a healthy diet.
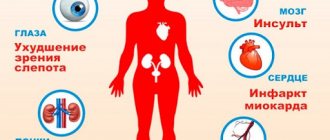
Low blood glucose concentrations can be life-threatening, but high blood glucose concentrations are insidious and easier to ignore. It may take years before a person becomes aware of the disease. By then, latent diabetics have damaged small blood vessels in the eyes, kidneys, heart and nerves, contributing to complications such as vision problems, frequent urination and nerve pain.
According to statistics, about 70% of people with prediabetes develop type 2 diabetes, so the disease has reached epidemic proportions among adults and children around the world. [23] Fortunately, this transition is not inevitable—you can control your diet and maintain an active lifestyle. It is easier to prevent this condition than to treat serious complications.
Information sources
- The Effects of Mental Stress on Non-insulin-dependent Diabetes: Determining the Relationship Between Catecholamine and Adrenergic Signals from Stress, Anxiety, and Depression on the Physiological Changes in the Pancreatic Hormone Secretion, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. gov/pmc/articles/PMC6710489/
- Blood sugar regulation as a key focus for cardiovascular health promotion and prevention: an umbrella review, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6709577/
- Impact of Diet Composition on Blood Glucose Regulation, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24219323/
- The prevention and control of the type-2 diabetes by changing lifestyle and dietary pattern, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3977406/
- Ancient Wheat Diet Delays Diabetes Development in a Type 2 Diabetes Animal Model, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5397290/
- Sulforaphane Prevents Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Blocking Serine Palmitoyltransferase 3-Mediated Ceramide Biosynthesis, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6566605/
- Supplementation of the Diet by Exogenous Myrosinase via Mustard Seeds to Increase the Bioavailability of Sulforaphane in Healthy Human Subjects after the Consumption of Cooked Broccoli, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29806738/
- Impact of botanical fermented foods on metabolic biomarkers and gut microbiota in adults with metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review protocol https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6678017/
- Extraction and purification of pumpkin polysaccharides and their hypoglycemic effect, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28153462/
- Anti-Diabetic Effects and Mechanisms of Dietary Polysaccharides, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6680889/
- Addition of pooled pumpkin seed to mixed meals reduced postprandial glycemia: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30055778/
- Nutritional Strategies to Combat Type 2 Diabetes in Aging Adults: The Importance of Protein, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6724448/
- High intake of fatty fish, but not of lean fish, improved postprandial glucose regulation and increased the n-3 PUFA content in the leucocyte membrane in healthy overweight adults: a randomized trial, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov /28606215/
- A Randomized Controlled Trial to Compare the Effect of Peanuts and Almonds on the Cardio-Metabolic and Inflammatory Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6267433/
- Effect of tree nuts on glycemic control in diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled dietary trials, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25076495/
- The Metabolic Effects of Oats Intake in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4690088/
- Effect of Consuming Oat Bran Mixed in Water before a Meal on Glycemic Responses in Healthy Humans—A Pilot Study, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037511/
- The Effect of Flaxseed Enriched Yogurt on the Glycemic Status and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized, Open-labeled, Controlled Study, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6826058 /
- Flaxseed supplementation on glucose control and insulin sensitivity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 25 randomized, placebo-controlled trials, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29228348/
- Glycemic Response to Black Beans and Chickpeas as Part of a Rice Meal: A Randomized Cross-Over Trial, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5691712/
- A randomized 3×3 crossover study to evaluate the effect of Hass avocado intake on post-ingestive satiety, glucose and insulin levels, and subsequent energy intake in overweight adults, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24279738/
- Intake of kale suppresses postprandial increases in plasma glucose: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5103670/
- Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4478580/
Attention! The information is for informational purposes only and is not intended to make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment. Always consult a specialized doctor!
Authors: Anna Shelestun, Tatyana Eliseeva Ask a question
Rating:
9.8
/10
Votes: 22
Usefulness of material 9.7
Reliability of information 9.7
Formatting of Article 10
Herbs in the form of spices
The diet of diabetics welcomes the presence of spices that can lower blood sugar. These include cinnamon. Activates the functioning of the digestive system, acts as a natural antispasmodic, improves appetite, inhibits glucose absorption, and reduces cholesterol levels.
Oregano or oregano. The vitamin and mineral composition of the plant resists decreased immunity. Essential oils improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Oregano has a pronounced hypoglycemic effect. With regular consumption of it, a stable decrease in blood sugar levels is observed. All spices have a pronounced, concentrated taste, so they must be consumed with caution.
What else is used?
To reduce sugar, vegetables that have hypoglycemic properties should be included in the diet menu:
- Jerusalem artichoke or earthen pear. It is a natural source of insulin and a stimulator of endocrine pancreatic function. It is recommended to eat small portions half an hour before the main meal. In addition, you can add to salads or bake in the oven (the beneficial properties of the plant are preserved during heat treatment).
- Momordica or bitter gourd. A rare but very useful plant with fruits resembling cucumbers. Helps eliminate “bad” cholesterol, restore metabolic processes, improves vision, helps in the fight against excess weight, and activates insulin production. Momordica juice is used as a medicine.
Vegetables should make up the majority of the diet of diabetic patients, regardless of their effect on glucose levels.
Recipe examples
All herbal infusions are usually brewed the same way. Herbs and berries are taken in equal proportions and mixed together. A tablespoon of the mixture must be brewed with a glass of boiling water and left for a quarter of an hour to 30 minutes. It is recommended to drink the infusion on an empty stomach in order to prepare the body for eating and, accordingly, the intake of glucose. Cereals and beans are prepared differently:
- Oats. Pour one glass of uncrushed whole grains into a liter of boiling water and cook in a steam bath for at least a quarter of an hour. Leave for 30 minutes, filter. It should be consumed for a month, three times a day before meals.
- Flaxseeds. Grind flax seeds in a coffee grinder. Pour five grams of powder into a glass of boiling water. Leave for three quarters of an hour, add a teaspoon of lemon juice. Drink a full serving once a day.
- Green beans. The plant is pre-dried in air. Brew two tablespoons of raw materials with 1/4 liter of boiling water in a thermos. Leave for 8 hours, filter and squeeze. Drink half a glass a quarter of an hour before meals.
As an antidiabetic agent, you should buy natural Ceylon spice, and not its Chinese relative cassia, which has a different chemical composition and properties
Leaves of berry bushes are added to herbs or brewed as tea. Berries are best consumed fresh. In winter - dried or frozen. Chicory is an excellent substitute for coffee, but does not increase blood pressure or impair cardiac function. Diabetes mellitus is a serious disease, but if all medical recommendations are followed, the disease can be controlled. Traditional medicine helps the patient maintain a decent quality of life and prevent complications.
Cooking and eating
Boiled and baked products, less often - fried and stewed. Meals 6 times a day: 1st breakfast, 2nd breakfast, lunch, afternoon snack, dinner and at night.
Allowed
Bread and flour products: rye, protein-bran, protein-wheat, wheat from 2nd grade flour, on average 300 g per day
Soups: vegetable, cabbage soup, borscht, beetroot soup, okroshka, weak low-fat meat, fish and mushroom broths with vegetables and permitted cereals, potatoes and meatballs
Meat, poultry: lean beef, veal, pork (trimmed, meat), lamb, rabbit, chickens and turkeys after boiling, dietary sausages and sausages, tongue, liver – limited
Fish: low-fat types, canned fish in its own juice or tomato
Dairy products: milk and fermented milk products, semi-fat and low-fat cottage cheese, limited sour cream, unsalted and low-fat cheese
Eggs: 1-1.5 pcs. per day soft-boiled, white omelettes
Cereals: porridge from buckwheat, barley, millet, pearl barley, oatmeal, legumes
Vegetables: cabbage, zucchini, pumpkin, lettuce, cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, with restrictions: green peas, potatoes, carrots, beets. Can be eaten raw
Fruits, sweet dishes: fresh fruits and berries of sweet and sour varieties in any form, jellies, mousses, compotes, candies and cookies with xylitol, sorbitol or saccharin. Limited honey
Sauces and spices: low-fat sauces based on weak meat, fish and mushroom broths, vegetable broth. Limited: pepper, horseradish, mustard
Drinks: tea, coffee with milk, juices from vegetables, low-sweet fruits and berries, rosehip decoction Fats: unsalted butter and ghee, vegetable oils for dishes
Must be excluded
Products made from butter and puff pastry, cakes, strong, fatty broths, milk soups with semolina, rice, noodles, fatty meats, duck, goose, smoked meats, most sausages, fatty fish, salted fish, canned fish in oil, caviar , salty cheeses, cream, sweet curd cheeses, rice, semolina, limit pasta, salted and pickled vegetables, grapes, raisins, bananas, figs, dates, jam, candies, ice cream, grape and other sweet juices, carbonated drinks and lemonades , animal and cooking fats, alcoholic beverages. Daily sugar intake is determined by your doctor and usually depends on the dose of insulin.
Download and print:
Diet No. 9
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.