Call the clinic +7 928 828 4001
Prices for services
| Service | Price |
| ECG | 500 ք |
| Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) | 2000 ք |
| Consultation with a gynecologist | 1350* ք |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | 500 ք |
| CARDIOTOCOGRAPHY | 500 ք |
| Cardiotocography | 500 ք |
| Consultation with a cardiologist-arrhythmologist | 1350* ք |
The presence of what symptoms is a reason to visit a cardiologist-arrhythmologist?
- Arrhythmia, which includes a slow or rapid heartbeat or skipped beats;
- Pain in the heart area. This symptom does not always specifically indicate heart problems, but it is still worth checking with a cardiologist-arrhythmologist;
- Weakness and fatigue that occur for no apparent reason;
- Unreasonable irritability;
- High sensitivity to temperature changes;
- Weak potency;
- Menstrual irregularities;
Who should you turn to for help when your heart beats unevenly?
Every person has had cases in his life when his heart beat unevenly. Every third patient at an appointment with a cardiologist complains of heart rhythm disturbances. They can be different - rare and frequent, long-term and short-term. But in any case, the patient feels them and worries about his health. Calmly! Arrhythmologists are guarding your rhythm. Who are they and how can they help patients with arrhythmia, we asked Maria Sergeevna Kharlap, cardiologist-arrhythmologist, candidate of medical sciences, employee of the Arrhythmological Ministry of Health of Russia.
Hello, dear Maria Sergeevna. Please tell us what kind of doctor this is – an arrhythmologist?
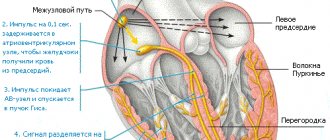
An arrhythmologist is a specialized specialist, initially a cardiologist or cardiac surgeon, who deals with the electrical activity of the heart, studies and corrects the electrical conduction system of the heart.
Patients come to us with any rhythm disturbance. We conduct diagnostics to understand why a person’s heart is beating abnormally. If necessary, we carry out treatment - medicinal or interventional, using a special catheter inserted into the heart through a vein.
Tell us in more detail about the mechanism of arrhythmias.
Our heart cannot beat without electrical activity. First, an electrical impulse is generated and transmitted to the myocardium, which contracts. And the heart carries out its main function - it supplies organs and tissues with blood.
The electrical conduction system is made up of special cells responsible for electrical activity. It is located inside the heart.
Disturbances in the process of formation and conduction of an electrical impulse cause arrhythmia.
Does any arrhythmia require treatment?
No. Some rhythm disturbances may be normal and do not require treatment. Depends on various factors, including the nervous system and environmental influences.
But there are also dangerous, life-threatening arrhythmias.
Arrhythmologists help to figure out in what cases medical care is needed.
What are these dangerous arrhythmias?
There are a number of arrhythmias that are associated with a rare heart rhythm. Electrical activity fails and assistance from an external source is required. In this case, the patient is implanted with a device that stimulates the functioning of one or more chambers of the heart, depending on the diagnosis.
The device is placed under the skin, under the pectoral muscle, and the electrodes are passed into the heart through the venous system and remain there for life. During pauses in the heart's work, they perform stimulation, simulating the heart's own electrical activity.
Does the operation of such devices need to be monitored?
Yes, definitely. In the future, such patients should come for a consultation with an arrhythmologist to check the operation of the devices. We use special programmers for this.
Sometimes patients are implanted with complex devices that have the ability not only to deliver electrical impulses, but also an electrical shock in the event of a dangerous, life-threatening arrhythmia. Such devices are supplied with remote monitoring and a home monitoring system, which allows the doctor to remotely read the activity of the device and control its operation.
Can the patient come to your appointment on his own or does he need to see a cardiologist first?
Yes, the patient can come on his own if he has complaints about rhythm disturbances. But it is better if he first undergoes a diagnostic examination.
What tests can you order?
Ideally, the patient comes with an already registered electrocardiogram. An ECG reflects the electrical activity of the heart at a specific period of time. We are especially interested in ECGs when you feel unwell. But complaints do not always last long enough for the patient to get to the clinic.
For such patients, we recommend purchasing a home ECG recorder. This, of course, is not a full-fledged ECG, but the device records the rhythm at the time of the complaint and helps us in diagnosis.
In our clinic, we can also prescribe 24-hour 12-lead monitoring to record an ECG. It allows you to study arrhythmia in more detail. But there are situations when nothing bothers the patient on the scheduled day of the study. Then we prescribe multi-day monitoring.
Maria Sergeevna, tell us what are the advantages of the Arrhythmology Ministry of Health of Russia?
Our most important advantage is experience. Our arrhythmology service was created at the Center 8 years ago. But in fact, my colleagues and I have been studying cardiac rhythm and conduction disorders for more than 20 years.
We were lucky that we stood at the very beginning of the formation of arrhythmology in Russia. This area, especially interventional treatment of cardiac rhythm and conduction disorders, is a young field of medicine. The first opportunity to evaluate the electrical conductivity of the heart from the inside, using catheter technologies and implanted devices, appeared about 30 years ago.
In the late 90s, my colleagues and I, then employees of other institutions, began our professional activities as cardiologists and cardiovascular surgeons specifically in the field of studying arrhythmias.
Almost all employees of our Arrhythmology Center have European certificates in cardiac electrophysiology. Our experience has been accumulated both in Russia and among leading arrhythmologists and electrophysiologists abroad.
Another advantage is our experience in the study of cellular electrophysiology and molecular genetic methods. For example, I am a specialist in the field of molecular genetics of arrhythmias; using genetic methods it is also possible to clarify the cause of disturbances in the electrical activity of the heart. Some arrhythmias have a hereditary etiology.
Together with pediatric cardiologists, I supervise families with various familial forms of cardiac rhythm and conduction disorders.
This allows us to monitor arrhythmias in the early stages and take control of the disease.
Our experience allows us to differentiate arrhythmias, separating dangerous from safe.
We have also been teaching young specialists in the field of cardiac electrophysiology for several years, which speaks in favor of our professional experience. And there is the opportunity to conduct hands-on training in the operating room.
What treatment methods do you use in your work?
Our arrhythmology service consists of an outpatient and inpatient unit. We have our own operating rooms, modern and fully equipped. They have X-ray units for visualizing parts of the heart during interventional treatment, and systems for mapping - determining the exact localization of the source of arrhythmia.
To eliminate the source of the arrhythmia, cauterization or freezing of the area of increased electrical activity can be used. We also perform left atrial appendage occlusion for non-drug prevention of thromboembolic complications in atrial fibrillation, implant cardioverter defibrillators, and successfully use other latest technologies for the treatment of arrhythmias.
You can make an appointment at the Arrhythmology Center by calling: +7(495)790-71-72
How is diagnosis carried out by a cardiologist-arrhythmologist?
Diagnosis of diseases treated by a cardiologist-arrhythmologist is usually carried out using the following tests and studies:
- ECG - atropine tests;
- Phonocardiography;
- ECG;
- ECG in a state of physical activity;
- ECG - monitoring for 24 hours;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- General urine and blood tests;
- Diagnostics for atherosclerosis;
- Analyzes for the degree of development of cardiac risks, such as high cholesterol and others;
What does a cardiologist treat?
In addition to helping people treat vascular and heart pathologies, cardiologists are also involved in the development and implementation of rehabilitation measures for patients who have already suffered an acute form of a particular disease.
In their practice, doctors in this specialty most often encounter the following diseases:
- Heart defect (acquired during life or present from birth);
- Ischemic heart damage;
- Heart failure caused by various reasons;
- Angina pectoris, which develops against the background of insufficient blood supply to the heart;
- Damage to the blood vessels and muscles of the heart that occurs against the background of inflammation of one or another area (carditis);
- Arrhythmias, including: bradycardia, tachycardia, partial heart block;
- Aneurysms of the aorta and other arteries;
- Heart attacks and conditions preceding them;
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis.
This is not a complete list of pathologies that are within the competence of a cardiologist, but they are the most common. Any heart or vascular disease requires mandatory consultation with a specialist and proper treatment. Therefore, you should not put off visiting a cardiologist if you have even the slightest doubt about the health of your heart and blood vessels.
Read more: Causes of heart disease and help for it
Symptoms that should alert you: TOP reasons to go to the doctor
Be sure to make time for a visit to the clinic if you notice:
- pain in the chest area
- shortness of breath
- rapid heartbeat or changes in its rhythm
- high blood pressure
- blueness of the nose, fingers
- regular causeless deterioration in health, accompanied by sweating
Never self-medicate! You can only prevent heart disease: proper nutrition, getting rid of bad habits, regular moderate physical activity. If a problem does arise, entrust the fight to a specialized specialist.
How is the initial appointment and diagnosis carried out?
No special preparation is required to see a cardiologist. It is enough to take with you your medical history and examination results for the last six months. The scope of the initial consultation includes:
- Anamnesis collection . The specialist finds out what symptoms bother the patient, when they occur (for example, after physical activity, at night), whether there have been problems with the cardiovascular system in the past, whether there are bad habits, allergic reactions.
- Examination of the patient . The doctor examines the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes, which makes it possible to identify possible circulatory disorders (for example, blueness of the lips, tip of the nose), and the chest area (visible deformation occurs in heart pathologies).
- Palpation . Tissues in the heart area are palpated, and the intensity and amplitude of contractions of the heart muscle are determined.
- Percussion . The organs located in the chest area (lungs, heart, large blood vessels) are tapped and their sizes are determined.
- Auscultation . The sounds of the heart and blood vessels and heart rate are listened to using a phonendoscope.
To obtain a complete clinical picture, an ECG (electrocardiography) is performed. 3 pairs of electrodes are placed on the skin in the heart area and 2 more pairs on the forearms and ankles. The device then records the electrical activity of the heart and displays it in the form of an electrocardiogram.
Important! When going to the cardiologist, wear comfortable underwear so that the doctor can diagnose and you do not feel discomfort.
Risk group: who needs cardiologist supervision
Preventative visits to a cardiologist are necessary even for young people under 35 years of age who do not have health problems. To control the situation, one visit every 2 years is enough. Men and women over 40 years of age should come for a consultation with a specialist once a year. From this age, the course of some chronic diseases worsens, heart ailments appear, and the risk of stroke or heart attack increases significantly.
The cardiac risk group includes people suffering from:
- diabetes mellitus;
- obesity;
- renal failure;
- pulmonary diseases.
Every six months, people whose close relatives have suffered from severe heart and vascular diseases, who have suffered a hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, stroke and other acute conditions should come for examination and diagnosis.
Please note! If you smoke, drink alcohol frequently, eat poorly, exercise little, or become very fat, be sure to make an appointment with a cardiologist for prevention, as you are at risk.
My heart hurts: which doctor should I contact?
A doctor by heart is called a cardiologist. This is a general specialist who deals with diagnosis and treatment. There are also narrower specializations. For example, a doctor who treats the heart for inflammatory processes is a cardiorheumatologist. A cardiac surgeon deals with surgical interventions required, for example, for defects.
The professionalism of this doctor determines how successful the treatment will be, whether it will be possible to correctly and timely identify the cause of the problem and begin adequate therapy. Only a professional with many years of experience can cure you, restore your health, and perhaps significantly prolong your life.
Additional diagnostic methods
If a cardiologist refers you for additional examinations, this means that you need to clarify the diagnosis so as not to make mistakes when determining further treatment tactics. The doctor will explain why they are needed, what disease they can confirm/refute.
Laboratory research:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood test for ALT and AST, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, GGTP;
- test for glucose levels, creatinine, urea, cholesterol, triglycerides, neopterin;
- blood test for genetic markers of cardiovascular pathologies and markers of autoimmune myocardial damage;
- cardiac profile (for high blood pressure, angina pectoris, tachycardia, bradycardia, vascular atherosclerosis, after stroke and heart attack).
Instrumental studies:
- 24-hour Holter heart monitoring (special electrodes are attached to the chest area, and a recorder is attached to the torso using a belt, after which the patient lives a normal life for 24 hours, and heart rate data is recorded and processed by a computer);
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring;
- echocardiography (an ultrasound sensor is installed in the heart area and its structure and blood flow are examined in the current mode and Doppler mode);
- coronary angiography;
- X-ray of the chest organs (if heart failure, tumors, aortic aneurysm, congenital heart defects are suspected);
- myocardial scintigraphy (carried out with intravenous administration of a radiodrug, the radiation of which is recorded by a gamma camera);
- duplex scanning of vessels (arteries and veins) of the upper and lower extremities;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys (for arterial hypertension);
- sphygmography;
- magnetic resonance imaging with contrast;
- computed tomography of the heart;
- positron emission tomography.
Laboratory tests are taken in the morning on an empty stomach. Half an hour before blood sampling, you should not smoke or play sports. Some instrumental examination methods (especially with contrast) require prior consultation with a diagnostician.