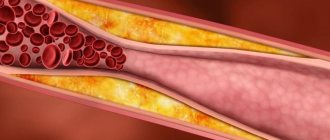
Bradycardia - symptoms and treatment
Since both cardiac and extracardiac diseases can lead to bradycardia, diagnosis is aimed at identifying not only heart diseases.
When talking with the patient, the doctor identifies symptoms that may be associated with bradycardia: fainting, presyncope, episodes of dizziness, shortness of breath and weakness on exercise. The doctor also finds out what medications the patient is taking and what diseases he has suffered.
Standard electrocardiography (ECG) at rest will allow you to evaluate the heart rhythm in the short time during which it is recorded. For clinically significant bradycardia, this is sufficient in situations where disorders accompanied by bradycardia (for example, atrioventricular block or decreased sinus node activity) are constantly recorded.
Another important diagnostic method for assessing heart rhythm throughout the day (and with the advent of multi-day recorders, even for several days) is Holter ECG monitoring. Its diagnostic qualities significantly exceed those of a standard ECG. When performing Holter ECG monitoring:
- estimate the average heart rate during the day, day, night;
- detect significant pauses in the heart rhythm, episodes of sinoatrial and atrioventricular blocks, as well as any cardiac arrhythmias that occur while wearing the ECG recorder;
- compare symptoms and episodes of bradycardia and arrhythmias.
The patient keeps a diary in which he indicates his symptoms and the time of their occurrence, and the doctor, looking at the ECG recording made at these moments, evaluates the connection between the described symptoms and the findings on the ECG. It is this approach that makes it possible to identify the so-called “symptomatic bradycardia,” which is one of the most important indications for installing an electrical pacemaker (pacemaker).
If symptoms presumably associated with bradycardia occur 1-2 times a month, then an external loop recorder is used. The principle of operation of the device is that the recorded data is deleted from memory over time, and the final recording is made only at the moment when the device automatically recognizes the presence of an arrhythmia or the patient himself activates the recording when symptoms occur.
A pharmacological test with atropine will allow one to assess the contribution of the autonomic nervous system to the development of bradycardia in a patient [5].
An electrophysiological study (EPS) in the diagnosis of bradycardia is of less importance, since spontaneously occurring episodes of bradycardia are often diagnosed using Holter ECG monitoring.
non-invasive - using a thin probe-electrode inserted into the esophagus through the nose, electrical stimulation of the heart is performed, and then the time for restoration of spontaneous activity of the sinus node is assessed. This method allows you to assess atrioventricular conduction disturbances.
Invasive EPI involves recording the spontaneous electrical activity of the heart in its various parts and electrical stimulation of the heart through electrodes inserted into the chambers of the heart (atria and ventricles). To do this, you have to pierce the femoral artery or vein and pass the electrode to the heart. However, the diagnosis of bradycardia in most cases does not require invasive EPS. The method is used only when non-invasive methods are not informative and to clarify the issue of implantation of a pacemaker.
In cases where there is reason to believe that blockades develop during physical activity, or there is chronotropic insufficiency of the sinus node (heart rate does not increase with exercise), a stress test under ECG control can be used: the patient walks on a moving treadmill, or pedals a bicycle ergometer, and in parallel, an ECG is recorded, blood pressure is recorded and symptoms are assessed.
Echocardiography is usually performed as part of the examination of almost all cardiac patients and allows one to assess the size of the heart cavities, wall thickness, the condition of the valves and myocardial contractility, and to identify a number of diseases that can lead to bradycardia.
Atropine
special instructions
Use with caution in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, in which an increase in heart rate may be undesirable: atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, chronic heart failure, coronary artery disease, mitral stenosis, arterial hypertension, acute bleeding; with thyrotoxicosis (possible increased tachycardia); at elevated temperatures (may further increase due to suppression of the activity of the sweat glands); with reflux esophagitis, hiatal hernia, combined with reflux esophagitis (decreased motility of the esophagus and stomach and relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter can slow down gastric emptying and increase gastroesophageal reflux through the sphincter with impaired function); for gastrointestinal diseases accompanied by obstruction - achalasia of the esophagus, pyloric stenosis (possibly decreased motility and tone, leading to obstruction and retention of gastric contents), intestinal atony in elderly or debilitated patients (possible development of obstruction), paralytic ileus; with an increase in intraocular pressure - closed-angle (mydriatic effect, leading to an increase in intraocular pressure, can cause an acute attack) and open-angle glaucoma (mydriatic effect can cause a slight increase in intraocular pressure; adjustment of therapy may be required); with nonspecific ulcerative colitis (high doses can inhibit intestinal motility, increasing the likelihood of paralytic intestinal obstruction, in addition, the manifestation or exacerbation of such a severe complication as toxic megacolon is possible); with dry mouth (long-term use may cause further increase in the severity of xerostomia); with liver failure (decreased metabolism) and renal failure (risk of side effects due to decreased excretion); for chronic lung diseases, especially in young children and weakened patients (a decrease in bronchial secretion can lead to thickening of secretions and the formation of plugs in the bronchi); with myasthenia gravis (the condition may worsen due to inhibition of the action of acetylcholine); prostatic hypertrophy without urinary tract obstruction, urinary retention or predisposition to it, or diseases accompanied by urinary tract obstruction (including bladder neck due to prostatic hypertrophy); with gestosis (possibly increased arterial hypertension); brain damage in children, cerebral palsy, Down's disease (reaction to anticholinergic drugs increases).
The interval between doses of atropine and antacids containing aluminum or calcium carbonate should be at least 1 hour.
With subconjunctival or parabulbar administration of atropine, the patient must be given a validol tablet under the tongue in order to reduce tachycardia.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
During the treatment period, the patient must be careful when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration, speed of psychomotor reactions and good vision.
Use by drug addicts
Recreational use of atropine has recently begun to increase.
Today it is quite easy to find a prescription or an illegal drug on the Internet and social networks. Pharmacy drugs are among the cheapest and most accessible, despite the ban and criminal prosecution for distribution without a doctor's prescription. Most often, people who are addicted to atropine are those who have already used or are using narcotic substances. Drug addicts can combine the drug with alcohol, other pharmaceutical drugs, tranquilizers, psychostimulants, opiates, etc. The use of several chemical substances in order to obtain a euphoric effect is called polydrug addiction.
Dual addiction is quite difficult to cure. It is worth noting that it is impossible to get rid of this kind of drug addiction on your own at home. It is necessary to contact a specialized drug treatment clinic. Our rehabilitation center in Rostov-on-Don provides assistance to all drug addicts and their loved ones, regardless of their length of use.
Systematic, regular use of atropine in high dosages leads to serious health consequences for addicts. This is not only a disruption of the central nervous system and depression of cognitive functions, and, accordingly, a person’s intellectual abilities, but also the development of heart and vascular diseases, and disruption of the respiratory system. The addict has problems with communication and socialization. Physical and mental dependence lead to the emergence and development of severe withdrawal symptoms.
Treatment of bradycardia
The selection of therapy depends on the reasons that led to this condition. If bradycardia occurs while taking medications, the doctor will recommend stopping or replacing medications that reduce heart rate.
If the cause relates to extracardiac factors, the cardiologist may schedule a consultation with a related specialist who is responsible for the treatment of the pathology that caused the bradycardia.
In some cases, for strict medical reasons, a surgical operation is prescribed, during which a pacemaker is installed.
Treatment of intoxication
How to cope with poisoning? How is acute atropine intoxication treated? First of all, you need to call the Favorit RC and call the emergency drug treatment service to your home. Doctors will arrive within 30-40 years. However, quite often victims require pre-medical assistance; you can get detailed advice from professionals by calling our clinic’s hotline absolutely free. The patient will also need emergency medical care and then hospital treatment.
How to remove poison from the body without harming the health of the addicted person? First of all, doctors carry out a detoxification procedure. To cleanse the body of toxins as quickly as possible, droppers with adsorbents and a number of medications are used to speed up metabolism and normalize the patient’s general condition. In addition, depending on the degree of intoxication, the following measures are used: gastric lavage (potassium permanganate), induction of vomiting, use of laxatives and diuretics, hemosorption.
Next comes the turn of symptomatic treatment and elimination of physiological disorders in the addict’s health. The drugs are used according to indications and contraindications. In case of severe clinical picture and breathing problems, tracheal intubation and artificial ventilation are used, resuscitation measures include installation of a catheter and administration of the necessary medications intravenously.
In case of atropine poisoning, the victim must be given an antidote: Physiostigmine, Aminostigmine, Nivalin or Galantamine in an individual dosage. These drugs help to quickly get rid of the unpleasant consequences of intoxication and symptoms such as hallucinations.
Choosing a remedy for osteoarthritis: which components are especially important?
When osteoarthritis and the symptoms that accompany it appear or worsen, a logical question arises - which remedy should be preferred in order to slow down the destruction of joints, reduce discomfort and pain. What is the difference between the products presented on pharmacy shelves and what exactly should you look for in their composition?
Osteoarthritis and its treatment
According to ICD-10, the disease is called osteoarthritis. This affects mainly large joints - most often the hip and knee. But this does not exclude the involvement of smaller joints, for example, in the hand area.
A group of drugs used to combat changes in joints due to osteoarthritis are called chondroprotectors. These are components that are used as a building material to renew and improve the structure of cartilage tissue. Cartilage covers the surfaces of the bones that form the joint, cushioning it during movements and ensuring full gliding of moving parts. Damage to cartilage in osteoarthritis leads to disruption of the structure and function of the joints and the appearance of symptoms characteristic of the disease. Taking chondroprotectors helps slow down the development of osteoarthritis, influencing not only the symptoms, but also the trigger mechanisms.
Chondroprotectors come in different forms:
o Solution for intramuscular injection is a prescription drug prescribed by a doctor;
o Tablets or capsules;
o Gels or ointments for external use.
The composition can contain either one active substance or a combination: two or three active components.
Today there are three most studied chondroprotectors:
· NEM® complex – a new generation chondroprotector;
chondroitin sulfate;
glucosamine
Let's take a closer look at these substances.
NEM ®
for joints
The abbreviation NEM ® comes from the English name – Natural Eggshell Membrane, which means “natural eggshell shell”. The complex was the result of innovative scientific development by ESM Technologies LLC (USA). The components are obtained using a specific patented technology of partial hydrolysis with gentle fermentation of the substance.
The NEM® complex is a natural source of substances essential for joints - glycosaminoglycans. They make up the matrix of cartilage tissue. The complex contains chondroitin sulfate, elastin, hyaluronic acid, collagen. These substances ensure the formation of a supporting frame. In addition, the complex contains minerals – magnesium, calcium [8,9].
During the 15-year period of studying the effectiveness of the NEM® complex, 16 experimental and clinical studies were published. They were published in different countries - Italy, USA, Germany, Canada, Turkey [10]. According to scientific works, it has been determined that NEM® has anti-inflammatory [11], immunomodulatory [12] effects, and helps slow down destruction processes [13].
Main effects of the NEM complex®:
· reduction in the level of compounds that provoke the inflammatory process [8];
Reducing the severity of pain in the joints caused by physical activity;
· reduction in the intensity of pain, as well as stiffness due to osteoarthritis [14];
· improvement of flexibility, mobility [15];
· inhibition, reduction in the severity of age-related changes in cartilage tissue in osteoarthritis [16];
During the study of the NEM® complex, its high safety profile was proven [17].
Chondroitin sulfate for joints
The substance that makes up the cartilage matrix, its frame. This is one of the most thoroughly studied chondroprotectors. Its use is included in clinical recommendations for the treatment of osteoarthritis, developed by domestic and European professional associations [1-4]. The body uses chondroitin as a building material necessary to renew cartilage and repair its damage. Due to a sufficient supply of chondroitin, it is possible to maintain the necessary viscosity of the intra-articular fluid and inhibit the activity of enzymes - hyaluronidase, elastase, which destroy the structure of cartilage. Plus, chondroitin has analgesic properties, suppressing the concentration of compounds that provoke inflammation and pain [5,6].
Due to its complex action, taking chondroitin helps [5,6]:
· reduce the intensity of pain and reduce the need for painkillers;
· improve mobility;
· slow down destruction.
In joint products, chondroitin sulfate can be either the sole component or combined with other compounds.
Glucosamine for joints
A natural compound necessary for the production of synovial fluid, especially its components such as proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid. The effectiveness of this substance has been confirmed through numerous studies.
Glucosamine helps [7]:
· reduce the intensity of pain;
· inhibits the activity of destruction processes in cartilage;
· stimulates the synthesis of polysaccharides that are present in the joint fluid under normal conditions.
Often, several components are combined in the complexes: glucosamine, chondroitin and other chondroprotectors, which mutually enhances their effect.
MUCOSAT capsules®*
All three described components are included in the composition of MUCOSAT® capsules. This drug is classified as a new generation of chondroprotectors. The composition of the capsules is supplemented with harpagophytum root extract (also called fragrant martinia) and manganese.
Harpagophytum root extract is a natural anti-inflammatory substance studied by specialists. Its use helps reduce pain and improve mobility [18,19].
Manganese for joints helps protect and renew cartilage, and our body also uses this mineral to produce collagen [20].
MUKOSAT® capsules can be used as an addition to a complex regimen for osteoarthritis and osteochondrosis [21].
The components of the capsules contribute [21]:
· reducing pain and inflammation;
· increased mobility;
· protection of cartilage tissue of joints and spine.
Detailed information, including the regimen and mode of administration, can be found in the instructions for use of MUKOSAT® capsules.
All about MUKOSAT® capsules on mukosat.ru
* BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE SUPPLEMENT. NOT A MEDICINE.
Sources:
*Contains NEM® complex exclusively in Mucosat® capsules
1. Clinical recommendations “Osteochondrosis of the spine”, All-Russian public organization Association of Traumatologists and Orthopedists of Russia, 2021.
2. Kloppenburg M, Kroon FP, Blanco FJ, et al2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of hand osteoarthritis Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019;78:16-24.
3. Olivier Bruyère et al. An updated algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO), Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, Volume 49, Issue 3, 2021, Pages 337-350.
4. Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis. Association of Rheumatologists of Russia. 2016
5. Mezenova T.V. Boosted therapy for osteoarthritis: expanding the boundaries of what is possible. Surgery. Journal named after N.I. Pirogov. 2018;(5): 91-95
6 Fedotova A. V., Mironova O. P. Chondroprotector mucosat in an integrated approach to the treatment of patients with nonspecific back pain. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry. S.S. Korsakov. 2018;118(9):133-137.
7. Lopes Junior, Osmar Valadao, & Inacio, Andre Manoel. (2013). Use of glucosamine and chondroitin to treat osteoarthritis: a review of the literature. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia, 48(4), 300-306.
8. Naumov A.V., Khovasova N.O., Tkacheva O.N. Chondropenia at the forefront of the osteoarthritis epidemic: from aging joints to the clinical manifestation of the disease // Attending physician, 2021. No. 12. P. 69-69.
9. Ruff KJ, DeVore DP, Leu MD and Robinson MA. (2009) Eggshell Membrane: A Possible New Natural Therapeutic For Joint & Connective Tissue Disorders. Results From Two Open-label Human Clinical Studies. Clinical Interventions in Aging 4:235–240.
10. URL: stratumnutrition Access date 04/07/2021
11. Wedekind KJ, Ruff KJ, Atwell CA, Evans JL and Bendele AM. (2016) Beneficial Effects of Natural Eggshell Membrane (NEM) on Multiple Indices of Arthritis in Collagen-Induced Arthritic Rats. Modern Rheumatology, 27(5):838-848.
12. Ruff KJ. Eggshell membrane hydrolyzates activate NF-κB in vitro: possible implications for in vivo efficacy. J Inflamm Res. 2015.
13. Sim BY, Bak JW, Lee HJ, Jun JA, Choi HJ, Kwon CJ, Kim HY, Ruff KJ, Brandt K and Kim DH. (2015) Effects of natural eggshell membrane (NEM) on monosodium iodoacetate-induced arthritis in rats. Journal of Nutrition and Health, 48(4):310-318.
14. Ruff KJ, Winkler A, Jackson RW, DeVore DP and Ritz BW. (2009) Eggshell Membrane in the Treatment of Pain and Stiffness from Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomized, Multicenter, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Clinical Study. Clinical Rheumatology 28:907–914.
15. Brunello E and Masini A. (2016) NEM® Brand Eggshell Membrane Effective in the Treatment of Pain and Stiffness Associated with Osteoarthritis of the Knee in an Italian Study Population. International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7:169-175
16. Eskiyurt et al. (2019) Efficacy and Safety of Natural Eggshell Membrane (NEM®) in Patients with Grade 2/3 Knee Osteoarthritis: A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled, Single-crossover Clinical Study. Journal of Arthritis, 8(4):1000285
17. Ruff KJ, Endres JR, Clewell AE, Szabo JR and Schauss AG. (2012) Safety evaluation of a natural eggshell membrane-derived product. Food and Chemical Toxicology 50:604–611.
18. Ribbat JM, Schakau D. Tratamiento de los dolores crónicos activos en el sistema de locomoción // Natura Med. - 2001. - V. 16, No. 3. - P. 23-30.
19. Chrubasik JE, Roufogalis BD, Chrubasik S. Evidence of the effectiveness of herbal anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of painful osteoarthritis and chronic low back pain // Phytother. Res. - 2007. - V. 21. - P. 675-683.
20. Delmas PD Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. The Lancet. 2002;359(9322):2018–2026. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08827-x
21. Biologically active food additive Mucosat® capsules. Certificate of state registration No.RU. 77.99.88.003.E.001059.03.18 dated 03/15/2018
**ADVERTISING