Drug poisoning is a fairly common situation. Many people have an already formed habit of reaching for medications for any ailment, bypassing a doctor’s appointment. This problem is associated with the impossibility of obtaining medical care in a short time, and with the over-the-counter dispensing of many medications in pharmacies. Typically, the reasons for taking medications without a prescription from a specialist are headaches, gastrointestinal tract disorders, spasms, back and joint pain.
Poisoning occurs due to a number of factors:
- exceeding the recommended dosage;
- uncontrolled use of the prescribed drug. For example, taking a dose for several days at a time;
- taking a combination of incompatible drugs - two drugs, and/or alcohol incompatible with the drug;
- use of expired drugs;
- errors in choosing a medication.
Drug intoxication can lead to dangerous consequences for life and health. Therefore, for any ailments that appear while taking medications, consult a doctor immediately.
Drug poisoning. Uncontrolled use of medications is a common cause of poisoning.
Symptoms of drug intoxication
Symptoms of drug poisoning can be very different; the manifestations are mainly determined by the type of drug. A distinctive feature of drug poisoning is its detrimental effect on the central nervous system. Common symptoms include weakness, lethargy, decreased reaction time, or severe psychomotor agitation. Cases of loss of consciousness are known in practice.
One of the common symptoms includes severe headaches. They can even be triggered by hormonal agents, especially if the patient has a predisposition to periodic headaches. When taking hormones, compensatory mechanisms are disrupted, which normally maintain the absence of symptoms. This occurs when taking a large dose of drugs containing caffeine, nitrates, hydralazine, bronchodilators, etc.
An overdose of antibacterial drugs is often accompanied by negative manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract: diarrhea, abdominal pain, increased gas formation. For example, an overdose of penicillin antibiotics leads to rash, vomiting, and convulsions. Excess chloramphenicol can cause heart failure.
Symptoms of poisoning with drugs used to normalize cardiovascular function include:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- spasms and bradycardia;
- gagging.
An overdose of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs affects the central nervous system: depression of consciousness, lethargy, lethargy, sleep disturbances, etc. are observed. The use of large amounts of antihistamines (decongestants, antiallergic) drugs can provoke weakness, dilated pupils, hallucinations, and psychomotor agitation.
Poisoning with tranquilizers is dangerous due to disturbances in heart rhythm, suppression of central nervous system function and respiratory disorders, convulsions, severe tremors of the limbs, and hallucinations. The patient's speech may be incoherent and slurred.
It is important to understand that manifestations depend not only on the presence of a particular active substance in the blood, but also on its concentration. Even traditionally beneficial components, such as vitamins, can be harmful and lead to the need for detoxification. What one person can easily endure, another will endure with a whole range of unpleasant manifestations.
What is a cough?
Coughing is a defense mechanism that clears the airways of irritants and germs. It can safely be called a useful reaction of our body: after all, it protects the trachea and bronchi from pathogenic infections and foreign bodies.
Most often, a cough may indicate a cold, but it is important to understand that severe coughing attacks can be symptoms of dangerous processes in the body and serious, and sometimes chronic, diseases. In one case or another, the cough has its own characteristics, and it is its character that helps make an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor in time to determine the cause of the symptom.
First aid
Often, a person who finds himself next to a patient does not know what exactly caused the intoxication and what to do in case of drug poisoning. In some cases, the first symptoms can be noticed only a few hours after taking the drugs. But there are several general rules for providing first aid. They are relevant for all severe cases:
- immediately call an ambulance;
- if a person is unconscious, but there is normal breathing and heart rate, it is necessary to lay him on his side;
- If a person is conscious and less than half an hour has passed since taking the medicine, it is necessary to give him a large amount of water and artificially induce vomiting. To do this, you need to press on the root of the tongue. If you do not know what poisoned a person, there is no need to induce vomiting;
- · After vomiting, give the patient a sorbent.
Drug poisoning. First aid for poisoning.
If a person is in serious condition, breathing slows down, the pulse is difficult to palpate, and artificial respiration must be performed. Remember that inaction can have fatal consequences.
It is necessary to show the emergency medicine packaging to the emergency doctors and describe the person’s condition. If you know that a person took alcohol along with the medicine, also tell the doctors about this.
Dry cough
A dry cough originates in the upper respiratory tract. It comes in fits and starts - often unpredictable and uncontrollable. The process is accompanied by a “barking” sound. However, the attacks do not bring relief.
The cause of a dry cough can be inflammation of the throat mucosa and soreness. However, a prolonged cough only irritates the mucous membrane more, forming a “vicious circle.” Also, a dry cough occurs when the bronchi do not secrete enough mucus to effectively remove germs from the body.
If you have a severe and prolonged dry cough due to a cold, your doctor may recommend a drug that stops the cough reflex (Omnitus, Sinekod). And to facilitate the discharge of sputum, special means that stimulate expectoration (Bronchicum TP, Gerbion, licorice root syrup) may be recommended.
With proper diagnosis and treatment, the dry cough is replaced by a wet one, the infection and germs are removed from the body along with sputum, and the inflammation goes away.
Treatment of drug intoxication
The basis of treatment is drug withdrawal. Neurological symptoms are of great importance in diagnosing the condition. The drug and its breakdown products are eliminated through all excretory organs: intestines, kidneys, saliva, sweat glands. The main routes of elimination are the kidneys and liver. Toxins are eliminated from the kidneys quickly enough and are eliminated in the urine. The situation is more complicated with drugs that are eliminated through the gastrointestinal tract.
From the liver cells, the breakdown products of the drug enter the bile and end up with it in the intestines, where they can be reabsorbed and delivered to the liver. This process is called enterohepatic circulation of substances. In some cases, harmful substances are excreted from the intestines along with feces. Circulation can result in toxins remaining in the body for quite a long time. This creates a high load on the liver, provokes the activity of liver enzymes and unpleasant symptoms.
But the entry of drugs and their breakdown products into the stomach, as well as their further movement through the intestines, does not pass without a trace. Peristalsis is disrupted, mucous membranes are irritated, and an imbalance of bacteria occurs. For example, many antibiotics have a detrimental effect on the intestinal microflora. Frequent, prolonged use or an inadequate dose can lead to intoxication. You can speed up their removal with the help of sorbents.
It is important to understand that many mild symptoms of intoxication are an attempt by the body to independently remove excess substances. There is no need to interfere with these processes if they proceed in moderation. It is best to provide conditions under which natural cleansing will occur. For example, with moderate vomiting, you should not resort to the use of antiemetic drugs. You should sound the alarm if your temperature rises above 38.5 °C, uncontrollable vomiting that interferes with fluid intake, signs of dehydration and frequent diarrhea.
Treatment of drug poisoning is carried out using several methods:
- gastric and intestinal lavage (according to indications);
- intravenous infusions to accelerate the elimination of toxins, replenish lost fluid due to diarrhea and vomiting. This technique is appropriate for acute forms of intoxication, in a hospital setting;
- prescribing enterosorbents for internal use to bind and remove toxic substances;
- use of enzyme preparations and diuretics according to indications;
- the use of probiotics and prebiotics to restore normal intestinal microflora;
- vitamin therapy and antioxidant treatment to neutralize free radicals.
For chronic intoxications, outpatient treatment is allowed. But it is important to consult a physician to find out the exact cause of poisoning, adjust the dosage of regularly used medications, or choose an alternative.
In the future, you can cope with the elimination of toxic substances with the help of plenty of drinking, a gentle diet, and enterosorbents. One of the effective drugs to combat intoxication is Fitomucil Sorbent Forte. The product contains a plant sorbent, inulin - a prebiotic that promotes the growth of its own beneficial microflora, as well as live bacteria. The drug accelerates the elimination of harmful substances and improves motility of the gastrointestinal tract. It has a gentle effect on the gastrointestinal tract and does not cause bloating or abdominal pain.
Moist cough
With a wet cough, sputum is easily released from the bronchi. It originates in the depths of the chest and after each coughing the patient feels relief. The process is accompanied by bubbling sounds and wheezing. Typically, an attack of wet cough occurs in the morning after sleep and when the body position changes.
Often, a wet cough can be a symptom of a viral infection. When treating it, it is recommended to use drugs not for cough, but, on the contrary, for it. If the sputum is too viscous and difficult to clear, the doctor may prescribe mucolytic drugs (“ACC”, “Ambrobene”) - they dilute the sputum and facilitate its removal from the lungs, so the body quickly clears itself of the infection and gets better.
Mistakes in cough treatment:
- It is not recommended to take mucolytic drugs for dry cough. If there is no sputum yet, then such a medicine can only do harm.
- You cannot take anti-cough medications if the cough is wet - the sputum must be removed from the body, as it contains pathogenic bacteria.
- During illness, it is extremely important to remember to drink as much fluid as possible and maintain optimal humidity in the room.
Remember that cough is a symptom of a number of diseases. Consult your doctor to choose the right treatment regimen!
Is it necessary to stop taking a medicine that causes a cough?
The question of canceling treatment is decided on an individual basis. The appearance of a cough in the early stages of hypertension is an unfavorable symptom. It indicates developing vascular diseases and limits the range of medications that can be used to treat the underlying disease. If you continue therapy with the same drug, the side effects will become stronger.
If there are any signs of poor tolerability of the drug, it is better for the patient to seek help from a doctor. The best option is to replace the drug. However, this must be done correctly, after additional examination and identification of all the features of the course of hypertension. Independent selection of funds is fraught with a number of complications and aggravation of the patient’s condition.
Periodic pauses in therapy also lead to adverse consequences. Destabilization of pressure indicators and the development of a crisis are possible. In this case, the patient will have to go to the hospital. Severe changes are fraught with acute, life-threatening complications.
What medications provoke the syndrome?
So, what medications are there for hypertension that cause cough? Today it is known for sure that it is provoked by medications that belong to the following groups:
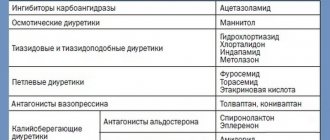
| Types of medicines | Names of drugs as an example |
| Beta blockers | |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers | |
| ACE inhibitors |
As experts note, a strong cough reflex is most often stimulated by medications that belong to the enalapril class of ACE inhibitors.