Definition
Hiccups are periodically occurring involuntary myoclonic contractions of the diaphragm with possible involvement of the intercostal muscles (usually unilateral). The contraction results in a sudden inhalation followed by closure of the glottis, which is accompanied by a characteristic sound.
Duration
Short-term – up to 48 hours; long-term – from 48 hours to 1 month; intractable – more than 1 month.
Prevalence
Prolonged, difficult-to-control hiccups are quite common in patients with advanced cancer.
Anatomy and pathophysiology
The physiological mechanism of hiccups remains unclear. The hiccup reflex arc includes:
- afferent pathways: phrenic and vagus nerve pathways, sympathetic nervous system;
- diffuse “hiccup center”: midbrain, brain stem, proximal cervical spinal cord (C3 – C5);
- central neurotransmitters: dopaminergic and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA);
- efferent pathways: diaphragmatic, vagus and intercostal nerve pathways, conducting signals that cause contraction of the diaphragm.
Classification and causes
Hiccups occur due to a reflex motor act involving the diaphragm, which is located on the border of the chest and abdominal cavities.
Outwardly, it looks like a membrane involved in breathing. Due to contractions of the diaphragm, air flows from the environment into the lungs and back. The work of this organ is controlled by the vagus and phrenic nerves. When they are irritated, a nerve impulse appears that goes to the cerebral cortex, signaling the need to contract the diaphragmatic muscles. This causes an extraordinary sharp exhalation through a narrow glottis. This accelerated air flow is the cause of the characteristic sound.
Based on duration, hiccups are divided into:
- episodic, which lasts no more than 10-15 minutes,
- persistent with the presence of symptoms for 2 days,
- intractable lasting more than 2 months.
Short-term hiccups are normal. It occurs due to poor nutrition, quick snacks, bloating, eating very cold or hot food, stress, and excessive swallowing of air.
With pathological hiccups, it is divided according to the location of the lesion. Central occurs after an acute cerebrovascular accident, with tumors, injuries or inflammation of the brain. Peripheral is associated with damage to the phrenic nerve and its branches. It occurs when it is compressed by scar tissue, with hiatal hernia (HH), tumors of the stomach or pancreas.
The same symptoms are caused by diseases of the heart and blood vessels - myocardial infarction, significant rhythm disturbances. The phrenic nerve is involved in lung diseases - pneumonia, bronchitis.
The use of certain medications, significant concomitant diseases such as diabetes, various intoxications: alcohol or smoking, metabolic disorders such as hypocalcemia also lead to the appearance of hiccups.
general characteristics
A sudden attack of hiccups may be preceded by overeating, fast food with poor chewing of hard and dry foods, swallowing air, and drinking highly carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
In young children and sometimes in adults, hiccups are triggered by hypothermia. Some patients begin to hiccup after taking muscle relaxants, barbiturates, benzodiazepines and other medications. Often the symptom appears for no reason and goes away on its own within a few minutes. At the time of an attack, a person experiences jerky muscle contractions in the epigastric region, accompanied by protrusion of the anterior abdominal wall and a strangled sound. Due to the closure of the glottis, breath holding occurs for a short period of time. A special feature of hiccups is the impossibility of conscious control. With intense hiccups, moderate pain is sometimes noted behind the sternum, in the lower parts of the chest. An attack of hiccups is characterized by rhythmic muscle contractions at approximately equal intervals.
Prolonged, especially pathological hiccups often have a debilitating effect and may be accompanied by irritability, emotional instability, increasing asthenia, vegetative manifestations - sweating of the palms, paleness or redness of the skin, a decrease in the temperature of the skin of the distal extremities. For episodes that repeat several times a day or several days a week, last more than an hour and are combined with other disorders (heartburn, pain, shortness of breath, etc.), you should seek medical help.
Diagnostics
There are many reasons for the occurrence of this symptom, so you first need to conduct a thorough diagnosis of the patient, find out where the lesion is located or whether it is a physiological process.
An important role in finding the cause of hiccups is played by the medical history, objective examination data, as well as laboratory and instrumental examination methods. The patient needs to be told how long he has been bothered by the existing symptoms, possible features of their occurrence, whether he consulted a doctor or whether breathing was restored on his own.
Additionally, the doctor will prescribe:
- general and biochemical blood test,
- if necessary, ECG, X-ray or CT scan of the chest,
- FGDS, MRI of the brain,
- lumbar puncture if a neuroinfection is suspected.
These studies will be enough to identify the lesion and establish the cause of hiccups.
Hiccups after a stroke
- Santi
23.04.2007 — 12:14
Hello! Please help me with advice, maybe someone has already had this situation. My father had a stroke six months ago, the right side was affected, but he later returned to normal, his arms and legs work, his speech is not affected. But the fact is that after the stroke he began to hiccup, he hiccups constantly, the hiccups may stop, but only for a while. then it starts again. Our Ivanovo doctors say that this is the first case in their practice. The stomach is normal, the lungs too. We tried everything or almost everything, it doesn’t help. He is in a lot of pain, we don’t know what to do, please help!!!!
I have never seen anything like this, but theoretically the mechanism of such a lesion during a stroke is quite clear.
Description:
Causes of Hiccups:
Hiccups are very common. It occurs in men and women with equal frequency, and occurs mainly in the evening. Hiccups are very common in pregnant women.
Most people experience brief bouts of hiccups periodically. In most cases, it starts for no apparent reason, lasts for a while, and then stops. Sometimes it is due to the following factors:
1. Sudden excitement or emotional stress.
2. When overeating, eating quickly, drinking carbonated drinks, swallowing air.
3. Sudden change in temperature (very hot or cold food, drinks, cold shower, etc.).
4. Alcohol.
5. Smoking.
Persistent hiccups that last more than 48 hours can be caused by more than 100 underlying medical conditions. Some are common, such as acid reflux, and some are quite rare. In addition to hiccups, other symptoms characteristic of the underlying disease are also observed. In some cases, persistent hiccups have no obvious cause. Factors that can lead to persistent hiccups are:
- some medications - steroids, tranquilizers, painkillers containing opiates (for example, morphine) and methyldopa;
- changes in the blood, for example, from alcohol, high blood sugar, or lack of calcium or potassium in the blood;
— concomitant pathology of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathology of the organs of the neck, chest or abdominal cavity. For example, sore throat, pneumonia. tumors in these parts of the body.
- some heart diseases;
- Hiccups sometimes occur in the later stages of cancer.
Treatment for Hiccups:
Treatment Short attacks of hiccups in most cases do not require treatment, and the attack of hiccups usually goes away soon.
Popular methods to stop hiccups:
- blockage of the airways for a short time. This can be done by placing your fingers on your ears and closing your nostrils. In this position, take a sip of water from a glass;
- Drink ice water slowly;
- eat a piece of lemon or something sour;
— hold your breath or breathe into a paper bag.
- Pull your knees to your chest and/or lean forward, hugging your chest.
You can use a technique called the Valsalva maneuver: try to perform movements similar to those of exhalation with the vocal cords closed.
If hiccups persist for more than 48 hours, or if you have frequent, short bouts of hiccups, you should consult a doctor. If the doctor determines the need for drug therapy, chlorpromazine or haloperidol may be prescribed, which can relax the muscles of the diaphragm. For stomach problems such as acid reflux or stomach distension: anti-acid drugs (omeprazole, ranitidine, etc.) and others (eg metoclopramide). Baclofen is a medicine that helps relax muscles. Gabapentin may also help because... is able to reduce the supply of impulses to the diaphragm. Ketamine, a substance for intravenous anesthesia, can be used when other methods are ineffective. Intravenous injections of metoclopramide can treat hiccups that occur after anesthesia. Midamizole and other tranquilizers can help control hiccups and relieve the stress they cause.
For persistent hiccups, some procedures may be used:
1. Acupuncture.
2. Hypnosis.
3. Blockade of the phrenic nerve, which consists of its intersection. The need for the procedure must be carefully analyzed, because there is a high possibility of complications.
For hiccups that continue despite treatment, a phrenic nerve block is sometimes used. This involves interrupting the innervation to the diaphragm (phrenic nerve), for example by injecting a local anesthetic near the nerve. However, this treatment must be carefully analyzed: it carries risks because the phrenic nerve plays an important role in breathing.
Therapy methods
If the hiccups are episodic, go away on their own, and the patient has no other accompanying symptoms, then in this case no medical intervention is performed.
You can use a number of physiological methods to get rid of hiccups. All of them are aimed at breaking the pathological reflex arc. Such activities often help - breathe into the bag, hold your breath, lightly press on the eyeballs, bring your legs to your stomach, lightly press on your chest. The symptoms go away within a couple of minutes if you hold a piece of ice or lemon in your mouth.
In another situation, depending on the cause, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment. Muscle relaxants, antidepressants, antiarrhythmics, and other drugs aimed at the etiological treatment of the disease can be used as drug therapy.
In cases of significant hiatal hernias with complications or tumor damage to the brain or digestive tract, surgical intervention may be required.
Treatment
Non-drug
It is recommended for use before the use of medications; it is prescribed purely individually. The most common types of non-drug therapy are the following.
Changing the diet : reduce the single volume of food taken with an increase in the frequency of intake.
Use of mint infusion : helps relax the sphincters, should be freshly prepared, not used together with prokinetics that increase the tone of the muscles of the stomach and intestines and the lower esophageal sphincter.
Nasopharyngeal stimulation techniques:
- rinse your nose with cold water;
- suck cold water through a straw, swallow or suck small pieces of ice;
- swallow 1 teaspoon of dry granulated sugar;
- quickly drink two glasses of water;
- gargle with water;
- suck on lemon slices;
- swallow pieces of dry bread;
- inhale saline solution through a nebulizer;
- stretch your neck;
- massage the soft palate for 1 minute;
- stretch out your tongue with your fingers;
- press hard on your tongue.
Preventing irritation of the diaphragm : bend forward, pressing your knees to your stomach.
Stimulation of the C5 dermatome (interrupts stimulation of the hiccup neural arch):
- patting or scratching the back of the neck;
- placing a cold, safe metal object behind the collar (for example, a key);
- cold compress on the face.
Breathing manipulations:
- holding your breath;
- causing sneezing or coughing;
- frequent deep breathing (hyperventilation);
- breathing into a paper bag (hypoventilation);
- “Valsalva maneuver” (forced exhalation with the nose and mouth closed). Should not be carried out if you have a cold, because... the infection can penetrate into the middle ear cavity, and in patients with heart disease (increases blood pressure). Use caution in patients with pulmonary emphysema, primary/secondary tumor lesions of the lungs, so as not to provoke pulmonary hemorrhage.
Medication
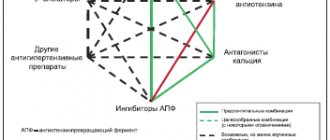
Treatment for hiccups is determined by the cause of its occurrence. In palliative care, hiccups are most often caused by several causes; as a rule, an integrated symptomatic approach is used for treatment (see Diagram 1, Appendix 1).
Table 1 shows the medications and dosages used in the treatment of hiccups. The route of administration of drugs is oral (inside), unless otherwise indicated.
Prevention and prognosis
You can prevent the occurrence of physiological hiccups by observing the following rules.
It is necessary to eat breakfast, lunch or dinner slowly, chewing thoroughly, which will prevent excessive swallowing of air. You should also not eat dry, too cold or hot food. It is necessary to undergo regular examination by a doctor so as not to miss any disease. Avoid hypothermia or dehydration. Follow the principles of a balanced diet.
In terms of ability to work and life, the prognosis is favorable. Hiccups are not a threatening condition, unless we consider the intractable form. However, it can disrupt sleep and daily activities, cause dehydration, chronic fatigue, lead to weight loss, and starvation.
Stroke and its consequences
To understand why a person hiccups after a stroke and how to deal with it, you also need to know what a stroke is.
So, a stroke is an acute disorder in the blood circulation of the brain, which leads to damage to certain areas of the main organ in the human body. This leads to a host of severe complications affecting the musculoskeletal and nervous systems.
There are two types of stroke:
- Ischemic is the most common, in which complete or partial obstruction of a vessel in the brain occurs. The consequences of violation of this form are tissue distortions, necrotic transformations, etc.
- Hemorrhagic is a rarer and more dangerous pathology caused by a violation of the integrity of the vessel, that is, its rupture with subsequent hemorrhage. In this case, the severity of brain damage is much higher, as is the likelihood of death.
Hiccups during a stroke manifest themselves under a huge number of factors, because significant damage is caused to the brain. The more extensive the brain damage, the higher the likelihood of these manifestations occurring.



![Rice. 1. ACCOMPLISH study: the effect of the combination of ACE inhibitor* amlodipine and ACE inhibitor hydrochlorothiazide on the risk of primary endpoint events (CVE) [14]](https://expert35.ru/wp-content/uploads/ris-1-issledovanie-accomplish-vliyanie-kombinacii-iapf-amlodipin-i-iapf-330x140.jpg)