There is a statistic common to the whole world: every cigarette smoked shortens a person’s life by 5-10 minutes.
Even without medical training, it is not difficult to imagine (and believe) that smoking increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer. Indeed, everything is clear here: cigarette smoke enters the lungs, and so they suffer.
The connection between smoking and heart and vascular diseases is more difficult to imagine, but it is no less close, and the smoker’s risk of getting them and dying for this very reason increases significantly: heart diseases in heavy smokers are 3-4 times more common than lung cancer! And all the deceit lies in the fact that until the last moment a person does not feel the approach of trouble.
- Firstly, smoking stimulates the release of adrenaline, and the need of the heart muscle for oxygen immediately increases sharply. If the coronary arteries are healthy, they will be able to provide the necessary blood flow, and this need will be satisfied, but in a long-term smoker they are rarely healthy.
- Secondly, nicotine (which only first enters the lungs, and then, like all other substances, into the blood) increases the ability of platelets to stick together, that is, the ability of the blood to clot, which leads to the formation of blood clots in the vessels.
- Thirdly, smoking increases the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood much more sharply than one might expect. In this sense, no product can compare with nicotine, even one very rich in cholesterol (for example, egg yolk). Therefore, in a smoker with hereditary or acquired hyperlipidemia, the risk of a heart attack increases several times.
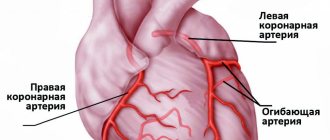
Cardiac ischemia
The combined effects of tobacco smoke and carbon monoxide cause aging of the arteries. They narrow, and as a result, the normal functioning of the heart is disrupted, which leads to the development of coronary artery disease, often progressing to myocardial infarction.
Myocardial infarction
Carbon monoxide prevents the transfer of oxygen from the blood to tissues, including the heart. At the same time, smoking leads to vasoconstriction, and blood transportation becomes even more difficult. If we add to this the fact that inhaled toxic substances from tobacco smoke increase blood clotting, thereby provoking the formation of blood clots, the risk of myocardial infarction increases 4-5 times (compared to non-smokers), and more often in young people, which is explained primarily early start of smoking. People under 40 years of age are most at risk in this regard.
Moreover, all this applies not only to active, but also to passive smoking.
The choice is yours…
Answer
- Victoria Rumyantseva
- Smoking
The effect of smoking on the cardiovascular system
Smoking contributes to the rapid wear and aging of the cardiovascular system, the development of hypertension, coronary heart disease, including myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, obliterating endarteritis, etc. Once in the blood, the toxic substances contained in tobacco smoke are carried through the tissues within 21- 23 seconds (time of complete blood circulation); those. almost instantly poison the entire body.
After smoking 2-3 cigarettes, small blood vessels go into a state of spasm, which lasts 20-30 minutes! For those who smoke a pack of cigarettes a day, the blood vessels are constantly in a state of spasm. As a result, the lumen of small arteries decreases, since nicotine causes a narrowing of blood vessels. As a result, the normal nutrition of many body tissues is disrupted.
When smoking, arteries lose their elasticity, become dense, brittle, and fragile. Over the years, the lumen of smokers' blood vessels narrows more and more, and this can end in disaster.
Constant spasm of blood vessels caused by smoking is a significant factor in the occurrence of hypertension, coronary heart disease and obliterating endarteritis. Under the influence of nicotine, brain vessels also wear out faster, their lumen narrows, and elasticity decreases. Blood flows in smaller quantities, which leads to impaired cerebral circulation and hemorrhages in the brain.
While smoking, the pulse increases by about 20 beats per minute, as the heart works under increased load. In this case, the function of the heart is impaired due to spasm of the small blood vessels that supply the heart muscle. As a result of spasm of the coronary vessels, smokers experience attacks of palpitations, pain in the heart area, and interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
The effect of nicotine on increasing blood pressure has been established. The general narrowing of blood vessels and high blood pressure lead to the fact that the number of smokers with hypertension is much greater than among non-smokers, especially in young and middle age. “Tobacco hypertension” leads to early “tobacco sclerosis” of blood vessels.
Smoking is an important cause of coronary heart disease, as it contributes to the development of the atherosclerotic process.
The main role in the mechanisms of development of coronary heart disease under the influence of smoking belongs to carbon monoxide. Nicotine causes an increase in blood pressure and heart rate, and carbon monoxide causes cardiac failure.
Cardiac vasospasm is the most common complication of smoking. The result of such a spasm can be a myocardial infarction - the death of a section of the heart muscle due to a violation of its nutrition. Death of a large area of the heart muscle leads to death. It is no coincidence that the mortality rate from myocardial infarction among smokers aged 40-50 years is 3 times higher than among those who do not smoke.
Smoking promotes earlier development of atherosclerosis, especially sclerosis of the coronary vessels of the heart, which can lead to angina pectoris (angina pectoris).
Smoking leads to vascular spasms, in particular of the coronary arteries of the heart, manifested by attacks of angina. Due to the development of coronary heart disease, angina pectoris occurs 2 times more often in smokers, and sudden death 4 times more often than in non-smokers.
If you stop smoking when angina attacks occur, the signs of the disease gradually disappear.
Nicotine also promotes fatty degeneration of the heart muscle, reducing the performance of the heart. Often with excessive smoking, dizziness and vomiting are observed, which are explained by spasm of cerebral vessels.
Smoking is the main cause of another very serious vascular disease of the lower extremities - intermittent claudication. This disease is associated with obliterating endarteritis of the arteries of the lower extremities, which can lead to gangrene (death) of the foot and leg and often require their amputation.
Passive smoking, which is the inhalation of smoke coming from a person's cigarette, is also harmful to the health of the heart and blood vessels, as it is also smoking to some extent. It has been proven that secondhand smoke contains almost all the chemical compounds that smokers inhale as a result of smoking. In some cases, secondhand smoke harms people even more than people who smoke and increases the risk of heart attack and death in adults.
Passive smoking is very harmful for children and adolescents, as it tends to increase the risk of developing coronary artery disease in the future. This is because inhaling cigarette smoke increases blood pressure and damages heart tissue, and also reduces levels of high-density lipoproteins, called “good cholesterol,” which reduces the risk of atherosclerosis.
The risk of secondhand smoke is especially high for premature babies who have respiratory distress syndrome, as well as children with asthma.
Cardiologists believe that quitting tobacco smoke is one of the best ways to reduce the risk of heart disease. You should not start smoking, but if this habit is already present, you need to give it up, regardless of your smoking history.
It is also important to avoid secondhand smoke. To do this, it is enough not to visit places where smoking is allowed, and also ask friends and family members not to smoke in the car or in the house.
Quitting smoking significantly reduces the possibility of developing heart disease, in some cases leading to death , reduces the risk of blood clots and the development of atherosclerosis, as well as the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, recurrent heart attack and death as a result of other chronic diseases.
Researchers studying heart disease and the impact of smoking on the development of heart disease have found that in countries that have banned smoking in public places and at work, the number of heart attacks has decreased significantly . Scientists explain this fact as a result of a decrease in active and passive smoking.
Is it worth quitting abruptly?
Conducted studies prove that the human body is completely cleared of the influence of tobacco or other types of smoke (marijuana and cannabinoids) within 1.5 years from the date of cessation of smoking.
Quitting a bad habit becomes more difficult depending on how long you have smoked. A gradual reduction in the number of cigarettes consumed is one of the options to get rid of the harmful factor, but in this case, nicotine continues to affect the blood vessels for some time. But when trying to abruptly refuse, there is no risk of acute reactions from the cardiovascular system.
Unpleasant or painful sensations in the chest area are characterized as withdrawal symptoms caused by “addiction.” Even long-term chronic smokers note a decrease or complete disappearance of heart pain after quitting smoking.
People who are trying to quit smoking are recommended to use an electronic cigarette or a nicotine-free vape while overcoming addiction as a process and set of movements. The mechanism of the device allows you to simulate the smoking process without harm to health, since only flavored vapor is inhaled.
Patients whose heart hurts from an electronic cigarette need to consult a psychotherapist, since such a phenomenon is a sign of a psychosomatic disorder.
How to relieve pain?
Much depends on the cause of the pain, which only a doctor can determine. Accordingly, if painful discomfort occurs, you should immediately consult a neurologist.
, because the problem may be serious (for example, a stomach ulcer or breast cancer). What to do before consulting a specialist? Eliminate the source of pain - quit smoking. If you have already quit, but the pain remains, you need, again, to consult a doctor to find out why this is happening, whether the discomfort is associated with detoxification of the body or with any disease. It is not recommended to take painkillers, as they will provide temporary relief and, unless prescribed by a doctor, can cause even more harm and interfere with an accurate diagnosis.
Why does it hurt and colitis when inhaling after smoking?
Poisons and tars that enter the body along with tobacco smoke displace oxygen , leading to hypoxia (little oxygen in the inhaled air), and then to hypoxemia (“oxygen starvation” of the body). To make up for the deficiency, the heart is forced to increase its beat. Muscle wear accelerates and angina develops.
The disease is accompanied by pain symptoms in the chest area, often on the left. The heart beats strongly, there may be pain in the left shoulder or arm, hand.
It is impossible to cope with this condition on your own. The risk of cardiac arrest increases significantly.
There are other reasons, which we will look at in more detail in the next chapter.
What does the analysis of ALT and AST reveal in smokers?
A blood test for ALT and AST is very informative in diagnosing not only heart diseases, but also other pathologies. These aminotransferases are intermediate enzymes between protein and carbohydrate metabolism, which are found in all tissues of the body, but are released into the blood only when cells are damaged. Due to their specificity and high sensitivity, aminotransferases are effectively used in the diagnosis of various diseases.
The normal AST is 37 U/L in men and 31 U/L in women, ALT is 40 U/L and 35 U/L, respectively. Nicotinic acid entering the smoker’s body distorts the results, so before taking the tests you will have to give up smoking for a while. When diagnosing, not only the AST and ALT indicators are important, but also their ratio, which is called the de Ritis coefficient. In healthy people, it varies between 0.91-1.75, and any deviation indicates a developing pathology.
An increase in ALT indicates liver disease, and a significant increase in ALT indicates liver necrosis caused by hepatitis or cirrhosis. A significant excess of AST over ALT indicates the replacement of healthy liver cells with fibrous tissue. This phenomenon is typical for hepatitis and alcoholism.
A decrease in AST and ALT levels occurs in chronic liver diseases, which result in degenerative changes in the organ.
The advantage of the AST test is that the level of the enzyme in the blood increases 20 times long before the clinical manifestations of a heart attack on the ECG. An increase is also typical for acute coronary insufficiency, angina pectoris, tachyarrhythmia, and rheumatic carditis. A slight increase in AST occurs with hepatitis, liver cancer, cirrhosis, cholestasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, pancreatitis. Any increase in AST may be a signal for a more detailed examination of the patient, even if nothing bothers him.
ALT increases in acute hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, cholelithiasis, and together with an increase in AST indicates organ destruction. Also, a slight increase in ALT gives a signal that viral infections are present in the body. In this case, the patient also experiences an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood.
How to deal with it
To cope with the problem and get rid of it forever, you need to quit smoking. It is definitely worth reducing the overall load on the heart muscle. Under no circumstances should you run, lift weights, or spend a lot of time in the gym.
Many patients complain that their heart periodically hurts; what to do about it, the doctor will tell you. It is worth making an appointment with a cardiologist and undergoing a series of diagnostic measures. If the doctor insists on taking a number of medications, nitroglycerin, for example, you should follow these recommendations.