Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Cardiovascular diseases — Symptoms of cardiovascular diseases
The main function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood to all tissues and cells of the body. The circulatory system is represented by the heart and a closed network of blood vessels - arteries, veins, capillaries, which penetrate all tissues and organs of the body.
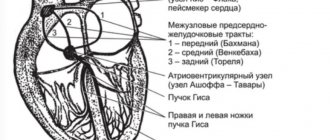
The heart consists of muscular chambers (atria and ventricles) that move blood through the vascular system and a series of valves in the desired direction. The heart's self-regulating electrical system sets the heart rate and coordinates the sequence of contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles.
The cardiovascular system ensures uninterrupted blood circulation through a closed system of blood vessels, without which it would be impossible to maintain a constant internal environment. Together with blood, oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other vital components are delivered to each cell of the body; the cells are cleansed of toxins and metabolic products, the accumulation of which would lead to the death of both an individual organ and the body as a whole.
It becomes clear that a violation in any part of a complex structure, such as the cardiovascular system, will lead to a breakdown of all functions of the body, which can result in death. That is why cardiovascular diseases are recognized as the most dangerous in the world.
As the pathological process progresses, the heart ceases to perform its functions, and other organs and systems of the body begin to suffer.
Symptoms of CVD
Cardiovascular diseases are numerous, have different origins and mechanisms of development. The main causes of cardiac pathologies are infectious and inflammatory processes, congenital developmental defects, damaging environmental factors (intoxication, hypothermia), metabolic disorders, and autoimmune reactions.
A peculiarity of the development of cardiovascular diseases is that they can occur hidden for a long time. Early signs of CVD, such as unmotivated weakness, fatigue, heaviness in the legs at the end of the working day, discomfort and discomfort in the chest, are not considered by people as symptoms of the disease that are worth paying attention to. Poor sleep, nausea not associated with food intake, clammy sweat, exercise intolerance, and headaches may indicate the appearance of heart problems.
Common cardiovascular diseases include:
- Atherosclerosis.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Inflammatory heart diseases.
- Violations of excitability and automatism of the myocardium.
- Heart defects.
Diagnosis of pain in the heart area when inhaling
What to do when I breathe and my heart hurts? Contact specialists at the KDS Clinic. Medical workers will conduct a comprehensive examination, diagnose the disease even at an early stage, and prescribe effective and affordable treatment. Pain in the heart area when inhaling indicates impaired functioning of the internal organs. We are talking not only about the cardiovascular system, but also about neighboring organs that can load the heart, thereby causing discomfort. If the patient feels a sharp nagging pain, he should change his position and take painkillers.
If these symptoms occur regularly, it is worth getting tested. Visit a cardiologist and TB specialist. He will direct the patient to undergo tests, including stool, urine, biochemistry and blood tests. With the help of tests, the condition of all indicators of the body will be diagnosed. The patient may be referred for an electrocardiogram, radiography and ultrasound diagnostics. If we are talking about lung disease, then auscultation of the lungs will be performed at a medical institution. To diagnose the cardiovascular system, the patient remains in the hospital where he undergoes a Holter examination. Over the course of several days, doctors observe changes in the patient’s condition and study the dynamics.
If you feel pain in the heart area when you inhale, do not worry and go to the clinic as soon as possible, where they will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis using modern equipment. In most cases, surgery will not be required. Even in advanced cases, doctors will find an effective solution to the problem. When your heart hurts when you inhale, make an appointment with a specialist by number.
Signs of cardiovascular diseases
There are a number of clinical manifestations that suggest pathology associated with the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Pain and discomfort in the chest
Pain is the most common symptom indicating a disorder in the normal functioning of the heart. The nature of chest pain varies: from mild squeezing (numbness, burning) to severe acute squeezing.
Angina is characterized by compressive pain in the heart radiating to the arm, neck, and shoulder blade with a gradually increasing amplitude. The attack is provoked by physical activity, emotional stress, and resolves after taking nitrosorbide.
Severe intense chest pain that does not go away after taking nitroglycerin, accompanied by sweating, palpitations and fear of death, may indicate the development of acute myocardial infarction. One of the causes of a heart attack is damage to the coronary arteries by atherosclerosis. The pain of a heart attack can be so sharp that a person may lose consciousness with the development of painful shock: blood pressure drops, pale skin appears, and cold sweat appears.
Excruciating pain in the chest, radiating to the back of the head, back, and sometimes to the groin area, is a symptom indicating an aortic dissection or aneurysm.
A dull aching pain in the heart area without a tendency to radiate, against a background of elevated temperature, of varying intensity: sometimes intensifies, sometimes weakens - indicates inflammation of the heart sac - pericarditis. The pain intensifies with movement, coughing, or pressing on the chest.
Signs of pulmonary embolism depend on the location and size of the clot. A person experiences chest pain that radiates to the jaw, shoulder, neck, and arm. Weakness, tachycardia, cough, shortness of breath occur. Hemoptysis may occur.
A short stabbing or dull pain in the heart area, occurring regardless of physical activity, without disturbance of breathing or heartbeat, is typical for patients suffering from cardiac neurosis. In the clinical picture of neurosis, in addition to cardiovascular disorders, signs appear that indicate a functional disorder of the nervous system: weakness, increased fatigue, absent-mindedness, poor sleep, tremors of the extremities.
Palpitations and a feeling of irregular heartbeat
Rapid heartbeat is not always a sign of heart disease; it can be physiological in nature, for example, after exercise, emotional excitement or after eating a large amount of food.
On the other hand, tachycardia as a symptom appears in the early stages of the disease. When there are heart rhythm disturbances - arrhythmias, a person has a feeling that the heart either “jumps out” of the chest or freezes for a certain period of time.
A disruption of the heart rhythm can occur in the form of a sharp non-simultaneous excitation of different muscle fibers of the myocardium, and this causes the cessation of the orderly contraction of the heart muscle - atrial fibrillation.
Supraventricular tachycardia is characterized by attacks of rapid heartbeat that can last from a few seconds to several days. Prolonged attacks are accompanied by weakness, sweating, fainting, increased intestinal motility, and excessive urination.
Ventricular tachycardia is less common and leads to disruption of the blood supply to organs and heart failure.
With heart block, irregular contractions, loss of individual heart impulses, and a significant slowing of the pulse are observed - bradycardia. Due to a decrease in cardiac output, signs of ischemia develop: drop in pressure, dizziness, fainting.
Dyspnea
A feeling of shortness of breath or shortness of breath occurs with heart failure, when the heart is not able to work at full capacity and does not pump the required amount of blood through the blood vessels. Heart failure can be the result of atherosclerotic vascular disease (deposition of fatty plaques on the inner wall of the arteries), acute myocardial infarction, heart defects, and high blood pressure. In the initial stages, shortness of breath is a concern only after physical exertion; as the pathological process progresses, it appears even at rest.
Severe shortness of breath is accompanied by rapid heartbeat, acrocyanosis - blue discoloration of the skin of the nose, lips, and fingers. The patient cannot lie down, takes a forced position (half-sitting), his legs are cold. With the development of pulmonary edema, a severe cough and foamy sputum mixed with blood appear.
Cardiac dyspnea should be distinguished from shortness of breath of a psychogenic nature (anxiety, fear, panic attacks).
Edema
The appearance of edema is a manifestation of venous stagnation in the systemic circulation. They first appear in the afternoon on the feet and ankles. After a night's sleep, swelling usually subsides.
Further accumulation of fluid in the body leads to the appearance of edema in the hips, lower back and abdominal wall.
As the edematous syndrome progresses, fluid begins to accumulate in the abdominal cavity, and the volume of the abdomen increases. The patient complains of heaviness in the abdomen, especially in the right hypochondrium due to liver stasis and hypertrophy.
If blood circulation in the abdominal cavity is impaired, dyspeptic disorders occur in the form of poor appetite, nausea, vomiting, intestinal spasms, flatulence, and stool disorders (alternating diarrhea with constipation). Kidney function may deteriorate and diuresis may decrease.
In especially severe cases, swelling can spread to the subcutaneous tissue of the chest, arms and face. The hands become numb, and symptoms of paresthesia (crawling sensations) develop.
Change in skin color
Pale skin often accompanies vasospasm, some heart defects (aortic valve insufficiency), and severe forms of rheumatic carditis.
Cyanosis (blueness) of the lips, nose, cheeks, earlobes, fingers of the extremities - the result of prolonged tissue hypoxia is observed in advanced stages of pulmonary heart failure. The cause of cyanosis is darkening of the blood due to slower blood flow and insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood in the pulmonary circulation as a result of stagnation. Dark blood, shining through the skin and giving them a bluish tint.
Headaches and dizziness
These symptoms are often present in diseases associated with damage to the cardiovascular system. The main reason for this reaction of the body is insufficient blood supply to the brain structures. Oxygen deficiency causes hypoxia; in addition, brain cells suffer from intoxication with decay products formed during the metabolic process, which are not taken up by blood from the brain in time.
Jumps in blood pressure can cause headaches or attacks of dizziness. Long-term hypertension causes irreversible structural changes in the myocardium (hypertrophy), in which the heart muscle quickly wears out and cannot cope with its work. Against this background, heart failure develops when the pumping function of the myocardium is disrupted and the blood supply to all organs and systems of the body deteriorates.
Inflammatory diseases of the cardiovascular system
These include: myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the muscular lining of the heart. Caused by various infectious agents. Manifested by pain in the heart, shortness of breath, swelling, palpitations, arrhythmias. As complications, it can cause heart failure or vascular thromboembolism.
Endocarditis is inflammation of the inner lining of the heart. The consequence of the inflammatory process is the formation of heart defects. Symptoms are determined by the type and stage of the disease.
Pericarditis is damage to the outer lining of the heart. Typical signs are constant chest pain, cough with dry pericarditis. The appearance of effusion between the layers of the pericardium (exudative pericarditis) is an unfavorable sign, as complications such as suppuration of the exudate or cardiac tamponade are possible.
Pain in the heart when taking a deep breath, causes
Every second person wonders why my heart hurts when I inhale? The appearance of this symptom is influenced by several factors that are worth paying attention to. Among them is pneumothorax. When taking a deep breath, the heart hurts if the patient develops pneumothorax. This is a diagnosis in which a large amount of air penetrates into the pleural cavity. Often, upon diagnosis, a patient develops a complication, even with effective treatment.
The disease is caused to develop in two cases:
- Traumatic pneumothorax. Air enters the lungs during a fall, injury, or injury.
- Damage to lung tissue. The lungs begin to function incorrectly, which is what causes pneumothorax.
The pain of pneumothorax is cutting and pulling. It gets worse when laughing, when inhaling and when talking. Associated symptoms include depression, fear, arrhythmia, changes in blood pressure, cough, general weakness, and pallor. If neglected and untreated, it leads to tuberculosis, lung tumors and other complications.
Most often occurs in males in adulthood. Pneumothorax also appears when flying to high altitudes, when diving to depths and serious injuries.
- Intercostal neuralgia. Intercostal neuralgia occurs when pinched nerves are irritated and can also cause severe pain in the heart. The nature of the pain is sharp and pulling. The patient feels unpleasant sensations constantly, they intensify. The pain is localized in the heart and ribs. Stops when taking painkillers or changing position. Intensifies with breathing, coughing and sneezing. Sometimes accompanied by sharp tingling and burning in the ribs. With intercostal neuralgia, there are no cardiac symptoms other than pain in the heart. Blood pressure and pulse are within normal limits. This disease is not dangerous if treated on time. More often observed in mature people. Medication treatment using injections and droppers is attributed.
- Precordial syndrome. With precordial symptoms, heart pain is the main symptom. The nature of the pain syndromes is acute and sharp. Lasts for two minutes and stops. After this, the patient is again disturbed. When breathing, the discomfort intensifies. Sometimes the aching pain lasts for several hours and only stops when taking painkillers. Precordial syndrome most often appears at the age of twenty. It is not life-threatening during treatment and with timely assistance. Treatment in a hospital is necessary to monitor the patient’s condition and monitor dynamics. In untreated cases, the patient is prescribed drug treatment at home with bed rest.
- Dry pleurisy. We are talking about inflammation of the pleura. It also causes pain syndromes in the heart area. Pleurisy appears when ribs are broken, bruises and other injuries. Unpleasant sensations appear when inhaling, when changing posture and when moving. Does not pose a danger to human life. The causes of pleurisy include pneumonia, benign and malignant tumors, bronchial asthma, abscess, heart attack and other diseases. Tuberculosis can also be a concomitant diagnosis.
Diagnostics
After an in-person examination, collection of anamnesis and communication with the patient, the doctor creates an examination plan. It includes:
- pulse measurements;
- blood pressure monitoring for 7–14 days;
- auscultation of the heart;
- neurological tests;
- general blood analysis;
- electrokariogram (ECG);
- Ultrasound of the heart (EchoCG);
- X-ray of the chest organs (survey and targeted when suspicious areas are detected);
- FGDS;
- MRI or CT scan with or without contrast agent;
- endoscopy;
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast;
- X-ray diagnostics or MRI of the spine.
Such an examination will create a complete picture of the disease. Based on the data obtained, treatment is prescribed.
Actions for pain syndrome
If an attack of pain occurs for the first time, and its cause is unknown, the first and most important thing to do is not to be nervous, take a comfortable sitting position and take something soothing. Try to analyze the reason that caused the pain in your heart. In the case of cardiac pathology, most often this can be due to severe physical activity or serious stress. The pain should go away within 10-20 minutes. If the pain is unbearable, lasting more than 5-10 minutes, you should immediately take a nitroglycerin tablet and urgently call an ambulance.
Quite often, chest pain occurs due to neuralgia of the intercostal nerves. This is partly facilitated by hypothermia, nervous strain and chronic stress. The pain intensifies when turning the body, changing position, and it becomes difficult to breathe. In this case, it is best to take a comfortable position, wrap yourself in a blanket and take a sedative. But if the pain is severe and continues after the measures taken, it is better to call an ambulance. Do not delay visiting the doctor in any case, since only a specialist can correctly diagnose and select treatment.
Causes of heart attack in teenagers
Heart attacks in minors are a rare disease. In most cases, a teenager becomes a victim of a heart attack for the following reasons:
- An underlying congenital heart disease that has gone undetected.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (enlarged heart muscle cells), an inherited disease.
- Kawasaki disease (inflammation of blood vessels), which is also inherited.
- Pericarditis (inflammation or irritation and swelling surrounding the heart), myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle).
- Excess weight, which leads to type II diabetes and increased blood pressure and “bad” cholesterol levels.
- Smoking, a major risk factor for heart attacks.
- Congenital heart abnormality (problems in the structure of the heart).
What to do first
To alleviate the condition yourself, you need to do the following:
- stop physical work, try to calm down;
- open a window to let in fresh air or go outside;
- put something cold on your forehead (a wet napkin or towel, a bottle of water);
- relax, take a comfortable position;
- breathe deeply, with quick inhalations and slow exhalations;
- you can try to reduce your heart rate by coughing;
- You need to hold your breath for a few minutes and tense your abdominal muscles;
- induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue;
- immerse your face in cold water;
- apply strong and sharp pressure at the angle of the lower jaw;
- take drops (Corvalol, valerian or Valocordin);
- if a person has difficulty breathing, you need to give him an oxygen bag;
- if the condition does not improve, call an ambulance.
If there is not enough air and your heart rate increases, you need to consult a therapist or cardiologist. Perhaps the patient will be referred to another specialist, since these symptoms are not always characteristic of cardiac diseases.
Sedatives will help you calm down and reduce your heart rate.