Causes
Depending on what caused the development of inflammation, the following types are distinguished:
- Bacterial (infectious). Occurs due to exposure to microorganisms such as coccus, tuberculosis and other bacteria. Possible consequences of late treatment and late treatment: impaired renal function, heart disease, spread of inflammation to nearby organs.
- Immune. The antigen complex deposited in the heart walls provokes the development of the disease. It is this type of inflammatory process that most often develops with rheumatism and chronic connective tissue diseases.
- Traumatic. Develops as a result of injury or malignant neoplasm.
- Reactive. The development of inflammation occurs as a result of myocardial infarction, radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer.
2. Reasons
There are several main factors that can cause inflammation of cardiac structures:
- infections, and the pathogenic agent can be both bacteria and viruses. Infectious and inflammatory processes of the heart are extremely dangerous (even fatal) due to their complications: the formation of acquired heart disease, the development of severe renal failure, etc.;
- metabolic disorders (metabolic disorders);
- toxic damage;
- combined infectious and allergic reactions;
- systemic autoimmune diseases;
- injuries;
- oncopathology.
The last two factors in the vast majority of cases lead to pericarditis.
As for toxic or infectious-allergic inflammation, a particular (and quite common) case is bacterial invasions - waste products of pathogenic microorganisms can cause both intoxication and an acute allergic reaction from the muscle tissue of the heart.
Visit our Cardiology page
Symptoms of inflammation development
Each disease has its own symptoms. The following signs are the reason to seek help from specialists at SANMEDEXPERT clinics:
- Endocarditis. This is the cause of deformation of the valve leaflets and the formation of heart disease within six months or two years. Inflammation can be rheumatic or infectious. In the latter case, the symptoms are more pronounced: profuse sweating, chills, fever, rash, nausea, kidney damage, decreased hemoglobin, muscle pain.
- Myocarditis. The mild form is characterized by shortness of breath and increased heart rate even with minor physical exertion. Heart rhythm disturbances, enlargement of the heart muscle and liver are signs accompanying severe forms.
- Pericarditis. There are dry and exudate forms of inflammation. In the first case, patients complain of dull pain in the cardiac region. In the second, inflammation is manifested by shortness of breath even at rest, heaviness in the area of the heart muscle. In the chronic form, there is an increase in blood pressure, an increase in liver size, swelling of the lower extremities, and ascites.
3. Symptoms, diagnosis
Taking into account the above, it is obvious that the clinical picture, the pace and nature of development, subjective and objective manifestations of inflammatory processes of the heart are determined by many factors (cause, localization, etc.) and therefore vary over a wide range.
Thus, endocarditis can begin with symptoms of fever, chills, febrility, various kinds of rashes and characteristic changes in skin color. With infective endocarditis, the shape of the terminal phalanges and nails may change (“drumstick symptom”). Severe complications from the kidneys, liver, blood vessels, etc. are common.
Myocarditis can develop asymptomatically or with minor symptoms in the form of asthenia, arrhythmia, shortness of breath, chest pain, and in infectious myocarditis - general fever or other malaise.
With pericarditis, it is generally difficult to identify typical, specific symptoms. There are various types of pain and discomfort in the heart area, angina pectoris, a characteristic dry cough, loss or, conversely, weight gain for no apparent reason.
With any variants and localizations of cardiac inflammation, especially if treatment is not started immediately, heart failure develops to varying degrees of severity. The diagnosis is established clinically and on the basis of a number of instrumental and laboratory studies (ECG, ultrasound, clinical tests, etc.). Based on the characteristic changes in the cardiogram and cardiac “acoustics”, the characteristics of the development of the disease state and the results of additional diagnostic procedures, an experienced cardiologist can determine the specifics of the lesion and prescribe adequate, most effective treatment in each individual case.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Diagnosis and treatment
Due to the fact that inflammatory heart diseases are one of the causes of the development of heart disease, after the first symptoms appear, you should immediately contact experienced doctors at the SANMEDEXPERT clinic.
Diagnostic methods used:
- Laboratory research
- Electrocardiography
- Echocardiography
- X-ray
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is admitted to the hospital. The intensity and course of treatment depend on the severity of the inflammatory process:
- In mild cases, a ward regimen, a special diet with a limited amount of salt and water, and medication are indicated.
- The average form requires strict bed rest and dietary rules.
- In especially severe cases, surgical intervention is prescribed.
The duration of treatment depends on many factors, the main one of which is the timeliness of treatment. Be attentive to your health!
4.Treatment
Therapy for inflammation of the heart muscle, as well as symptoms, depends on the causes, pace, severity of the pathological process, as well as the presence of concomitant diseases (especially infectious foci that require immediate treatment) and the general somatic condition of the patient. Treatment is etiopathogenetic in nature, i.e. is aimed at eliminating the immediate causes - if and to the extent possible.
Thus, for infectious lesions, antibiotic, immunostimulating, and restorative treatment is prescribed; in the presence of an allergic component, antihistamines and desensitizing drugs are prescribed. According to indications, antiarrhythmic therapy is prescribed, measures are taken to relieve symptoms of acute heart failure, prevent and/or treat complications. If necessary, specialists from related fields (infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, allergist, etc.) are involved in the diagnostic and treatment process.
Accordingly, the prognosis is also purely individual; In this regard, the timeliness of seeking specialized help is important. Today, the possibilities for its effective provision are very wide, and in many cases, inflammation can be eliminated completely, without any consequences or significant complications, however, in more severe situations, the outcome may be disability or even death of the patient.
Therefore, at the slightest symptoms of cardiac dysfunction, especially those progressing against the background (or after) of an acute viral or bacterial infection, it is necessary to be examined by a cardiologist.
Prevention
There are two types of preventive measures:
- Primary. It is aimed at comprehensively strengthening the immune system by maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle, hardening procedures and timely treatment of foci of infection (caries, sinusitis, and so on).
- Secondary. After completing the course of treatment and discharge, the patient is registered with a dispensary for constant monitoring and prevention of relapses. A change in work regime is necessary, since a person needs to work in a comfortable environment with a minimum amount of physical activity.
Inflammatory heart diseases
| Inflammation of the heart | 111 |
| Endocarditis | 1555 |
| Myocarditis | 2130 |
| Pericarditis | 1243 |
The inflammatory process can affect various membranes of the heart. In this regard, they distinguish:
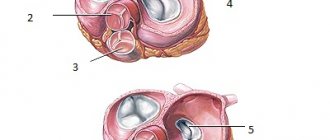
- Endocarditis – damage to the internal connective tissue membrane, endocardium;
- Myocarditis – inflammation of the heart muscle;
- Pericarditis - the outer connective tissue membrane, the pericardium, is inflamed, represented by two layers, external and internal;
- Pancarditis is inflammation of all three linings of the heart.
Why do inflammatory heart diseases occur?
The main reason is the direct effect of viral infection (herpes virus, cytomegalovirus), bacterial (staphylococcus, streptococcus), and in rare cases, fungal in nature. Sometimes the introduction of an infection (mainly streptococcal) triggers the so-called. an autoimmune mechanism in which the heart muscle is damaged by circulating immune complexes consisting of microbial toxins and antibodies to them. The autoimmune pathway is characteristic of cardiac pathology in systemic collagenoses - rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus.
In addition, inflammatory lesions of the heart lead to:
- Allergic reactions;
- Certain medications;
- Chest injuries;
- Conditions after cardiac surgery;
- Severe burns;
- Gout;
- Tuberculosis;
- Chronic renal failure.
- Frequent and recurrent acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, sore throats
How does heart inflammation manifest?
Inflammation of the heart by :
- Increase in heart size. The heart expands in all directions - the so-called. bull's heart.
- A decrease in myocardial contractility - mainly with myocarditis.
- Formation of valve defects in the form of valvular insufficiency or stenosis. More often observed with endocarditis.
- Accumulation of liquid effusion in the cavity between the pericardial layers.
- Heart rhythm disturbance.
The severity of all these manifestations is not the same in each individual clinical case. But together they mutually burden each other and lead to heart failure.
In addition to general weakness and dizziness, it is accompanied by pale skin and shortness of breath. Sometimes the temperature rises to subfebrile levels. In advanced stages of heart failure, swelling appears in the legs, the liver enlarges, and free fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory heart diseases in the clinic at Barclay LLC MED-City
During diagnosis, a wide range of studies is used: ECG, ultrasound of the heart, Holter monitoring, immunological tests. Treatment is aimed at eliminating not only the cause, but also the consequences of heart inflammation - heart failure.
If you experience discomfort in the heart area, be sure to consult a specialist. You can make an appointment right now by calling + 7-495-979-99-82; +7-495-978-78-67
Drugs to prevent heart disease
Healthy heart
It is impossible to treat the heart or prevent problems with it in isolation from the whole organism. Yes, the heart is the most important organ that works throughout life and ensures blood circulation in our body. But for its normal operation, it is necessary to provide it with optimal operating conditions. The heart itself is a muscular organ. This means that to contract muscle cells (cardiomyocytes), oxygen, nutrients, and removal of metabolic products are required. The coronary vessels surround the heart muscle and supply it with blood.
For coordinated work with other organs, it is connected with them through the nervous system and hormones circulating in the blood into one whole. We run and our heart beats faster, but at night, on the contrary, it slows down. Blood viscosity and its quantity also affect the functioning of the heart. The condition of the arteries and veins also determines whether it is easy or difficult to pump blood. Even physical activity can help in its work. Thus, the muscles of the foot and lower leg can rightfully be considered a “second heart”, since their contractions when walking help overcome the force of gravity and return blood upward through the vessels.
The work of the parts of the heart themselves must be coordinated with each other. Full contractions of the ventricles and atria should alternate with periods of relaxation when the muscle “rests”.
How the disease develops
Our body has a large margin of safety against damage and the ability to adapt even if some of the mechanisms “break down”. That is, the disease does not appear immediately. Atherosclerosis is considered one of the main causes of heart problems. It leads to damage to the walls of blood vessels and a gradual narrowing of its lumen. These processes continue for many years and can proceed completely unnoticed. This means that when any symptom of problems with the heart or blood vessels appeared, the body stopped coping with them. It is impossible to predict in advance where an atherosclerotic plaque will grow in a coronary vessel, on the wall of the heart valve or in the arteries of the brain. It can also break away from the wall of the vessel and clog any narrow artery with the blood flow. In this case, could there be a “magic pill” that, by taking it, can “clean” blood vessels or cure the heart? Unfortunately no. After all, even after coronary artery bypass surgery there are no guarantees that this will not happen again.
Risk factors
It turned out that the presence or absence of risk factors plays a major role in the prevention of problems with the heart and blood vessels. The same ones that accumulate their potential for many years, and then “suddenly” are realized in the form of heart attacks and strokes.
Risk factors:
- Arterial hypertension
- Hypercholesterolemia
- Smoking
- Insufficient consumption of vegetables and fruits
- Excess body weight
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Physical inactivity
It is these factors that act for many years that lead to irreversible changes. Only by eliminating them and replacing them with the opposite ones can effective prevention of heart disease be carried out. If we talk about hereditary predisposition, then they will play even more importance.
For those people who already have heart problems, secondary prevention is necessary to avoid a recurrence of the acute situation. It also involves eliminating risk factors. But it also adds treatment and control of existing diseases.
Prevention
In addition to lifestyle changes, nutrition, and physical activity, various medications can be used to prevent heart disease. The purpose of their use is to reduce risk factors if this could not be done without drugs. In practical medicine, a doctor cannot force a patient to quit smoking, eat less and move more; the person must do this himself. You can start taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor, after undergoing tests and studies, since each drug has contraindications, and their combinations can increase side effects. Compliance with the treatment regimen will help correct current problems that directly affect the risk of heart attacks and strokes:
- Arterial hypertension
- Arrhythmias
- Cardiac ischemia
- Atherosclerosis
- "High" cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obesity
Drugs
Statins . Taking statins helps fight hyperlipidemia and prevents the development of atherosclerosis. Helps stabilize the surface of cholesterol plaques, which prevents the formation of blood clots. Taking these medications is necessary for life with periodic monitoring of biochemical blood tests for liver function. Therefore, before taking them, you should make every effort to correct your lipid profile first through diet. Some of the modern and studied statins are Crestor and Mertenil.
Antihypertensive drugs
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors Diroton, Prestarium A, Hartil
- Angiotensin receptor blockers Valsacor, Aprovel
- Beta blockers Concor, Betalok
- Calcium antagonists Verapamil, Normodipine
- Diuretics Hypothiazide, Arifon-retard
There are many groups of drugs with this effect. Their selection is made only by a specialist, since they may have additional effects on slowing heart rate when interacting with other drugs. Also, a combination of 2 several groups may be more effective. The bottom line is that even a decrease in pressure by only 5-10 mmHg. already reduces the risk of disaster.
Antiplatelet agents . Help prevent the formation of blood clots and improve blood flow. Must be prescribed by a doctor, as they can lead to bleeding. Aspirin is most often prescribed. Curantil, Clopidogrel, Pentoxifylline can also be used.
Antianginal drugs . Helps cope with attacks of ischemic pain during angina attacks. The most famous drug is Nitroglycerin
Metabolic drugs. Not all drugs in this group have a broad evidence base, but are also used in practice. They are designed to improve metabolic processes in cells and protect them from ischemia. These include Preductal (trimetazidine), Mildronate, ATP, cocarboxylase, Neoton.
It is also necessary to effectively treat diabetes mellitus, as it provokes the progression of atherosclerosis.
Prevention can only be effective in combination, and medications only provide support where our efforts and the body’s capabilities are exhausted.
Literature:
PREVENTION OF CHRONIC NON-INFECTIOUS DISEASES. PRIMARY AND SECONDARY PREVENTION OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES. Recommendations 2013
Clinical recommendations. Arterial hypertension in adults. Russian Society of Cardiology 2019