01 Aug 2021 at 10:37 MRI of the heart in Tushino 7910
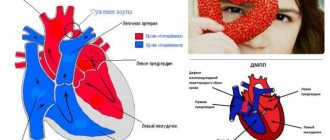
“Aneurysm of the aorta of the heart - what is it?” Many patients in whom a specialist has just discovered this disease ask a similar question. An aortic aneurysm is a widespread or limited dilation of the largest vessel in the human body. With this disease, the diameter of the aortic lumen exceeds the norm by two or more times. Aortic aneurysm is one of the most dangerous heart diseases.
Causes of an enlarged heart
The weight of an average man’s heart is 332 grams, a woman’s – 253. It is considered normal if the weight of the organ varies within these limits.
As for the sizes, they are usually correlated with a person’s fist. For an organ to function normally, it is very important that all its parts (atria, ventricles) are normal, or more precisely, the thickness of their walls, length and width as a whole.
What to do if fluorography (x-ray, ultrasound) showed that the heart is enlarged and dilated?
How dangerous is it to literally have a big heart? And as a result of what can the organ become larger? Let's figure it out in order.
The most important reasons why the heart is larger than normal in a fluorography image include:
- great physical activity;
- diseases.
In people who engage in heavy physical labor every day, as well as in professional athletes, the heart also works harder: it is forced to beat more often and pump blood faster.
This leads to the fact that there are often more heart muscle cells and they grow. As a result, the weight of the organ and its size increase.
If physical activity in the future is moderate, an enlarged heart for this reason does not pose a health risk.
If a person subjects his body to excessive stress for a long time, then it is possible to develop a pathology such as a hypertrophied heart, which is already fraught with serious complications and even life-threatening.
The reason that the heart is enlarged in size can be diseases of the cardiovascular system (coronary diseases: for example, hypertension, coronary disease) and the heart itself (viral, inflammatory diseases), as well as heart defects.
So, if there is a defect and the organ is unable to function normally in order to properly supply the entire body with blood, the organ can enlarge.
The mechanism of development of expansion of the borders of the heart
The pathogenesis of cardiomegaly depends on the cause. Most often, left ventricular hypertrophy occurs in people with metabolic syndrome, coronary artery disease, or arterial hypertension.
When oxygen supply is low, the heart muscle contracts more strongly than usual and gradually increases in size. Roughly the same thing happens with hypertension.
In this case, the heart does not have time to pump blood quickly enough due to its high pressure, so the organ requires more effort. The mechanism of development of cardiomegaly differs in stenosis and valve insufficiency.
In the case of these pathologies, the blood does not completely flow into the adjacent chamber or vessel (aorta, pulmonary artery) and causes stretching of one of the parts of the heart. With long-standing defects, both the ventricle and the atrium enlarge.
In some cases, hypertrophy of the entire organ may occur. Right ventricular failure occurs with pulmonary pathologies and liver diseases.
Coronary diseases
Hypertension is the most common cause of heart enlargement.
This is explained by the fact that due to increased blood pressure, the organ is forced to pump large volumes of it and work in enhanced mode.
This causes the heart muscles to enlarge and the organ itself to expand.
If a person has ischemia, the heart muscle cells constantly do not receive enough nutrients, as a result of which they degenerate, and connective tissue appears in their place.
The latter, unlike muscle tissue, is not capable of contraction; as a result, the organ cavities become deformed and increase in size.
What to do if an x-ray showed that the organ is enlarged, and the cause of this phenomenon is a disease of the cardiovascular system?
The answer to this question is simple and obvious - treat the root cause and return the organ to normal limits.
If a patient is diagnosed with hypertension, he is usually prescribed pharmaceuticals that lower blood pressure. The latter helps restore the normal size of the organ.
A patient with hypertension or coronary artery disease who has been diagnosed with an enlarged heart must take medications.
The fact is that despite the increased size of the organ, a large heart performs its most important function - pumping blood - much worse, which means that human organs and systems do not receive the nutrients they need - heart failure develops, and the whole body suffers.
That is, returning the organ to its normal size helps prevent heart failure, which in some cases can simply save a person’s life.
Forecast
It depends on what exactly caused the enlargement of the heart:
- With arterial hypertension, the prognosis is favorable. If you take the medications prescribed by your doctor on time, your heart will soon return to normal and will no longer enlarge.
- In case of ventricular septal defect – relatively favorable.
- For dilated cardiomyopathy – unfavorable. Full recovery occurs only after transplantation. However, it is not always possible to find a donor for a heart transplant. In addition, the risk of postoperative complications is high.
- In hypertrophic cardiomyopathy – relatively unfavorable. With an asymptomatic course of the disease, patients die before the disease is detected. With proper therapy, the risk of death is reduced.
- Metabolic cardiomyopathy has a favorable prognosis. When metabolism is established, complete recovery occurs.
- With aortic stenosis without treatment, life expectancy ranges from 1 to 4 years from the onset of symptoms. If the operation is performed in a timely manner, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
- If mitral stenosis is left untreated, 50% of patients die within 5 years of the first symptoms appearing. After surgery, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
- In case of Ebstein's anomaly, it is relatively favorable. The risk of sudden death is 3–4%.
- For myocarditis – favorable. Complete recovery occurs after 4–8 weeks in 90% of cases, after a year – in 10% of cases.
- For exudative pericarditis – favorable. All operated patients recover.
- In case of amyloidosis – unfavorable. The maximum life expectancy is 5 years from the date of diagnosis.
class=»fa»>If the operation is not performed in time, there is a risk of developing aortic valve insufficiency, severe rhythm disturbances, left ventricular dysfunction and sudden death. If the patient is operated on, the heart will no longer bother him.
Non-coronary diseases
Another fairly common cause of an enlarged heart is inflammatory processes affecting muscle tissue (carditis), primarily rheumatic carditis.
So, if a person has suffered a serious infection such as tonsillitis or scarlet fever, complications (rheumatism) can also affect the most important organ that transports blood.
In this case, the muscle loses its elasticity, and the ventricles are overstretched, as a result of which the size of the organ can increase several times, and its functionality, accordingly, will decrease several times.
In this regard, timely treatment of rheumatic carditis is very important. To date, drugs have been developed to completely eliminate streptococcal infections and prevent overstretching of the heart.
If therapy is not followed, the person may die. In addition, being a carrier of streptococcus, the patient infects others.
Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease that affects the internal cavity of the heart and its valves.
Endocarditis in an advanced stage causes expansion of the organ, loss of muscle elasticity and ability to contract. The disease requires immediate treatment.
Myocarditis is a consequence of viral infections, accompanied by arrhythmia and shortness of breath, and heart failure may occur. Video:
In this regard, a patient with myocarditis needs immediate medical attention and supportive care.
Chronic alcohol consumption can cause cardiomyopathy and cardiac dystrophy, as a result of which the heart cavities expand and the heartbeat rhythm changes significantly.
Also, patients with alcoholism, as a rule, have high blood pressure - another factor that contributes to the modification of the heart muscle.
If a person recovers from alcoholism and stops drinking alcohol, and if he has hypertension, takes blood pressure-lowering medications, after some time the organ will restore its normal size.
Thus, if a fluorography image reveals an increase in the size of the heart, you should immediately contact a specialist, find out the cause of the pathological changes and, if necessary, begin therapy: the problem is solvable in most cases.
Treatment of myocardial hypertrophy
To carry out qualified treatment, it is necessary to diagnose the disease, as well as determine its nature and course features. Based on these data, the optimal treatment method is selected. In most cases, treatment of myocardial hypertrophy consists of taking the drug verampil with beta blockers. The complex use of medications can reduce the symptoms of the disease, as well as normalize the general condition of the patient. As an additional therapy, it is necessary to follow the prescribed diet, and also stop smoking and drinking alcohol. In addition, it is necessary to reduce the amount of salt and consumed foods with the highest fat content. During treatment, physical activity should be moderate.
In particularly severe cases, surgical intervention is required. In this case, the specialist removes the hypertrophied part of the muscle. During treatment, the patient's condition is monitored using an ECG.
Rehabilitation
As you know, after treatment or surgical intervention, full rehabilitation is required. Therapeutic diet is an integral part of the rehabilitation process. In this case, you need to eat up to 6 times a day in small portions. Flour products should be limited; fatty and smoked foods should also be excluded from the diet. The level of physical activity needs to be reduced. Full rehabilitation allows the patient to recover much more quickly after treatment.
Make an appointment Make an appointment and get a professional examination at our center
Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment for cardiomegaly
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
The heart is one of the most important organs of the human body. One of the most dangerous symptoms of diseases that affect not only the cardiovascular system, but also other organs, is an enlarged heart (cardiomegaly). This can manifest itself in different ways: in one case, the patient has symptoms characteristic of diseases of the heart muscle, in another, he lives for a long time and does not even suspect the presence of pathology.
Pathology treatment methods
Taking into account the degree of the disease, the doctor selects medications that help improve the functioning of the heart muscle. List of drugs:
- anticoagulants - “Heparin”, “Angioks”;
- diuretics - Trifas, Lizax, Furosemide;
- beta blockers – “Anaprilin”, “Digoxin”;
- angiotensin blockers - Eprosartan, Losartan.
The traditional method of treatment should not be excluded. Freshly prepared juices help well: carrot, cranberry, onion, birch. Beekeeping products work well: propolis, honey.
Causes of pathology
The most important organ that ensures the vital functions of the entire body consists of 4 chambers: two ventricles and two atria. There are two sections of the heart - right and left, each of which includes an atrium and a ventricle. Normally, the boundaries of the heart change throughout life. People who play sports experience an increase in its size, which is considered a completely natural process and does not cause any cause for concern.
The weight of a man's heart is 332 grams, a woman's - 253 grams. An enlarged heart is observed when the myocardium grows and (or) expands its cavity. Most often, the organ enlarges to the left, which is observed in many diseases: hypertension, stagnation of blood in the systemic circulation, heart defects. Enlargement of all parts of the organ is dangerous. This condition is called “bull’s heart”, and only surgical intervention can improve a person’s quality of life.
The reasons influencing the enlargement of the organ are:
- Hypertonic disease. An increase in pressure leads to changes in the cardiovascular system: vascular tone increases, the thickness of the muscle layer increases, and the systemic circulation suffers.
- Coronary heart disease: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction. Oxygen starvation of the organ tissues occurs with the death of their cells and replacement with connective tissue, which leads to an increase in the size of its left section.
- Rheumatic heart disease. It is a consequence of tonsillitis (frequent tonsillitis). Rheumatic disease is manifested by an inflammatory process occurring in the tissues of the organ. As a result, the valves suffer and defects form.
- Myocarditis.
- Renal dysfunction.
- Alcohol abuse. The most common example is alcoholic cardiomyopathy.
- Smoking.
- Acute pericarditis (inflammation of the serous membrane).
- Congenital heart defects.
The presence of pathology in close relatives is considered a risk factor, therefore, under certain conditions, the disease can manifest itself in other family members. A common cause of changes in the heart muscle is an increase in pressure (above 140/90 mm Hg), which has a detrimental effect on the state of the cardiovascular system and in some cases leads to an enlargement of the organ up to the “bull heart”.
Congenital heart disease is of great importance. Today, it is treated in the first years of life, but there are also forms that are discovered only at an older age. An example is non-closure of the interventricular septum. The left ventricle contains oxygen-rich blood (arterial), and the right ventricle contains carbon dioxide (venous).
Normally, the blood does not mix, but with pathology of the interventricular septum, blood flows from the left ventricle to the right. There are different variations in the size of the defect. Improper distribution of blood within the organ leads to its enlargement.
Treatment of aortic aneurysm
A cardiac aortic aneurysm, the diameter of which exceeds 5 cm, is subject to surgical treatment due to the fairly high risk of its rupture. Surgery is performed under conditions of hypothermia and artificial circulation. In addition, surgical intervention is performed if the specialist observes too rapid growth of the aneurysm. The surgical mortality rate of this disease is about 15%. Contraindications to surgery are present if the patient suffers from severe heart disease.
Rehabilitation after treatment
During rehabilitation, it is important to follow a diet (eat as little fatty foods as possible, include apples, garlic, strawberries, and legumes in the diet). In addition to proper nutrition, it is very important to avoid stressful situations, control blood pressure, and monitor your weight (it should not exceed the norm). After the surgical intervention, an individual daily routine is drawn up for the patient. It is necessary to set aside time for rest. In this case, the patient undergoes regular examination by the attending physician.
Symptoms of the disease
Manifestations of cardiomegaly are purely individual. In some cases, symptoms do not occur at all, and a person learns about the expansion of the organ’s boundaries by chance, for example, during fluorography or a doctor’s examination. If the pathology makes itself felt, its manifestations are not much different from the symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular system. But there are cases when the pathological process develops so rapidly that a “bull’s heart” quickly forms.
Signs include:
- Pain behind the sternum.
- Dizziness, loss of consciousness for no reason.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Shortness of breath with slight exertion.
- Arrhythmia (change in rhythm).
- The appearance of edema (especially in the lower extremities in the evening).
- Cough not associated with respiratory diseases.
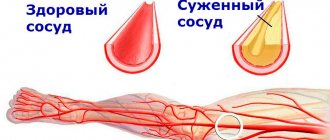
Expanding the size of such an important organ of the cardiovascular system entails very dangerous consequences. If the heart rhythm is disturbed, there is a risk of cardiac arrest. The occurrence of noise should be monitored by a doctor, because it indicates a change in the structure of the valves. An enlarged heart affects the quality of the entire cardiovascular system. Over time, there will come a point when the organ cannot pump the required amount of blood, so the risk of developing heart failure increases over the years. If the problem is ignored, then you can get a serious complication - “bull heart” (an increase in the size of the organ to critical).
Prevention
Lifestyle changes will help not only prevent the development of the disease, but also improve the condition of an already enlarged ventricle. Since hypertrophy is common in people suffering from obesity, maintaining an ideal body mass index will be the best prevention of the disease.
It is also worth limiting the amount of salt in your diet to normalize blood pressure. If hypertrophy is suspected, it is recommended to drink alcohol in moderation, and if treatment is prescribed, then it is better to avoid strong drinks altogether.
Despite the fact that one of the reasons for an enlarged ventricle of the heart is heavy physical activity, you should not give up sports. Regular physical exercise, such as walking, Pilates, yoga, will not only do no harm, but, on the contrary, will strengthen the heart.
If a diagnosis of hypertrophy has already been made, it is necessary to ask a physiotherapist to select the optimal exercise program. 30 minutes of moderate physical activity will strengthen weakened heart muscle and prevent its enlargement. A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will allow you to forget about problems with the left ventricle for a long time.
Diagnostics
Bringing together the symptoms of the disorder, functional diagnostics, and other methods help to establish the disorder:
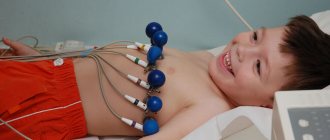
- ECG for determining EOS, interpretation of indicators, norms and deviations
- Ultrasound;
- Holter monitoring;
- ECG;
- X-ray;
- coronary angiography.
Thanks to these studies, it is possible to visually assess the organ and its parts, determine the size of the enlarged cavity, and establish the cause of the insufficiency.
Using electrocardiography with a load in the form of a bicycle track or an exercise bike, it is possible to determine at what point myocardial ischemia appears.
The doctor prescribes a daily test if he suspects that the patient has an arrhythmia disorder; the person is fitted with a device for a day that records the contraction of the heart.
Angiocoronary angiography is a study of blood vessels, allowing one to see their condition and circulatory disorders. The image allows you to determine the expansion of the shadow of the organ, which indicates hypertrophy.