What are the positive effects on the body?
- Plasmapheresis reduces the amount of harmful substances circulating in the plasma;
- Cleanses the blood and all tissues of the body;
- Improves blood supply to all organs and systems by purifying the blood and removing cholesterol plaques;
- Activates brain function;
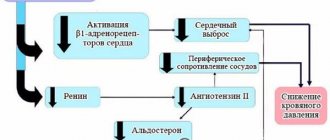
- The work of the heart is normalized, which stops attacks of angina pectoris;
- Improves the functioning of the liver and kidneys, resulting in the timely removal of toxins and harmful substances from the body;
- Strengthens the immune system;
- Improves skin structure;
- Promotes weight loss.
Blood glucose
Blood glucose determination is one of the most widely used tests in clinical laboratory diagnostics. Glucose is determined in plasma, serum, and whole blood. According to the Laboratory Manual for the Diagnosis of Diabetes presented by the American Diabetes Association (2011), it is not recommended to measure serum glucose when diagnosing diabetes because the use of plasma allows samples to be quickly centrifuged to prevent glycolysis without waiting for clot formation.
Differences in glucose concentrations between whole blood and plasma require special attention when interpreting results. The concentration of glucose in plasma is higher than in whole blood, with the difference depending on the hematocrit value, therefore, using a constant factor to compare blood and plasma glucose levels may lead to erroneous results. According to WHO recommendations (2006), the standard method for determining glucose concentration should be the method for determining glucose in venous blood plasma. The concentration of glucose in the plasma of venous and capillary blood does not differ on an empty stomach, but 2 hours after a glucose load the differences are significant (Table).
| Glucose concentration, mmol/l | ||||
| Whole blood | Plasma | |||
| venous | capillary | venous | capillary | |
| Norm | ||||
| On an empty stomach | 3,3–5,5 | 3,3–5,5 | 4,0–6,1 | 4,0–6,1 |
| 2 hours after OGTT | <6,7 | <7,8 | <7,8 | <7,8 |
| Impaired glucose tolerance | ||||
| On an empty stomach | <6,1 | <6,1 | <7,0 | <7,0 |
| 2 hours after OGTT | >6,7<10,0 | >7,8<11,1 | >7,8<11,1 | >8,9<12,2 |
| SD | ||||
| On an empty stomach | >6,1 | >6,1 | >7,0 | >7,0 |
| 2 hours after OGTT | >10,0 | >11,1 | >11,1 | >12,2 |
The glucose level in a biological sample is significantly affected by its storage. When storing samples at room temperature, glycolysis results in a significant decrease in glucose content. To inhibit glycolysis processes and stabilize glucose levels, sodium fluoride (NaF) is added to the blood sample. When collecting a blood sample, according to a WHO expert report (2006), if immediate separation of plasma is not possible, the whole blood sample should be placed in a tube containing a glycolytic inhibitor, which should be kept on ice until plasma is isolated or analyzed.
Indications for the study
- Diagnostics and monitoring of diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system (pathology of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland);
- liver diseases;
- obesity;
- pregnancy.
Features of sample collection and storage.
Before the study, it is necessary to exclude increased psycho-emotional and physical stress.
Preferably, venous blood plasma. The sample should be separated from the formed elements no later than 30 minutes after blood collection; hemolysis should be avoided.
Samples are stable for no more than 24 hours at 2–8 °C.
Research method.
Currently, enzymatic methods for determining glucose concentration - hexokinase and glucose oxidase - are most widely used in laboratory practice.
Increased values
- DM type 1 or 2;
- pregnancy diabetes;
- diseases of the endocrine system (acromegaly, pheochromocytoma, Cushing's syndrome, thyrotoxicosis, glucoganoma);
- hemachromatosis;
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- cardiogenic shock;
- chronic liver and kidney diseases;
- physical exercise, strong emotional stress, stress.
Reduced values
- Overdose of insulin or hypoglycemic drugs in patients with diabetes;
- diseases of the pancreas (hyperplasia, tumors) causing disruption of insulin synthesis;
- deficiency of hormones with counter-insular effects;
- glycogenosis;
- oncological diseases;
- severe liver failure, liver damage caused by poisoning;
- gastrointestinal diseases that interfere with the absorption of carbohydrates.
- alcoholism;
- intense physical activity, feverish conditions.
Artificial blood substitutes
A great achievement in medicine is the discovery and use of artificial blood substitutes, i.e., liquids, the administration of which can in some cases replace a blood transfusion, and in others temporarily delay it. Of course, blood cannot be completely replaced by either plasma or any of the blood-substituting solutions, because they do not contain oxygen carriers - red blood cells.
However, the use of certain blood substitutes can bring a sick or wounded person out of a severe state of shock, even with large blood loss. This eliminates the immediate threat to his life. Blood transfusion, if still required, may then be postponed.
Blood substitutes: plasma and its components
The best natural blood substitute is plasma, the liquid part of the blood, rich in proteins and containing substances that help stop bleeding. In shock conditions without blood loss or in bleeding with little blood loss, plasma transfusion can have a full therapeutic effect.
Plasma collected under conditions of strict sterility is stored for a long time without deterioration. Dried in a special way, it can be stored for months and even years. Before transfusion, it is diluted with distilled water.
Blood plasma
It has become possible to prepare and purposefully use individual plasma proteins that have a specific effect inherent in each of them.
Albumen.
The most valuable drug for protein nutrition of tissues and organs. It maintains the so-called colloid osmotic pressure, which retains fluid in the bloodstream. This is due to its anti-edematous effect.
By attracting tissue fluid into the bloodstream, albumin increases blood pressure if it drops for some reason (for example, during shock). Albumin solution is a highly effective protein preparation for traumatic and surgical shocks.
It is very useful when there is a lack of protein in the body. Protein deficiency can be a consequence of many diseases leading to loss of protein in urine, sputum, pus, burn fluid, or due to impaired absorption of food proteins (diseases of the gastrointestinal tract) or from a disorder of protein metabolism (liver disease).
How does BLOOD SERUM differ from PLASMA?
The cells of our body are washed by a certain amount of bodily fluids, or humors. Due to the fact that these fluids occupy an intermediate position between human cells and the external environment, they ensure the survival of cells and play the role of a so-called shock absorber during sudden external changes, in addition, they are an effective means of transporting nutrients and waste products in the body.
An important role in the human metabolic process is played by blood, which consists of the liquid part of blood plasma and formed elements suspended in it:
- leukocytes - white blood cells that perform protective functions;
- erythrocytes - red blood cells containing hemoglobin (red respiratory pigment);
- platelets - blood platelets necessary for blood clotting.
Formed elements make up 40–45%, plasma – 55–60% of the total blood volume. This ratio is called the hematocrit ratio, or hematocrit number. In some cases, the hematocrit number includes only the volume of blood that accounts for the formed elements.
Blood plasma is a solution that consists of:
- water (90-92%) and dry residue (10-8%);
- organic and inorganic substances;
- formed elements (blood cells and plates);
- dissolved substances: proteins (albumin, globulins and fibrinogen); inorganic salts that are dissolved in the form of anions (sulfate, chlorine ions, phosphate, bicarbonate) and cations (potassium, magnesium, sodium and calcium); transport substances derived from digestion (amino acids, glucose) or respiration (oxygen and nitrogen), metabolic products (urea, carbon dioxide, uric acid) or substances absorbed by the lungs, skin and mucous membranes.
Plasma constantly contains all microelements, vitamins and intermediate metabolic products (pyruvic and lactic acids).
Lymph, blood, tissue, pleural, spinal, joint and other fluids form the internal environment of the human body. They originate from blood plasma and are formed through the process of plasma filtration by passing through the capillary vessels of the human circulatory system.
Plasma protein contains fibrinogen, which appears due to changes in the physicochemical state during blood clotting. Fibrinogen has the ability to pass from a soluble to an insoluble form, converting into fibrin and forming a clot.
Blood serum is a clear, yellowish (or light yellow) liquid separated from a blood clot after blood has coagulated outside a living body. From the blood serum of animals and people immunized with certain antigens, it is possible to obtain immune sera used in the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of various diseases.
The serum can be either red due to hemolysis - this is the process of destruction of red blood cells with the release of hemoglobin into the environment surrounding the red blood cells, or icteric - due to increased values of bilirubin (a pigment that is contained in the blood and excreted with bile, due to which it is called bile pigment).
Blood serum is used for preventive, diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. To obtain it, it is necessary to place sterilely collected blood in a thermostat for 30–60 minutes, remove the clot from the wall of the test tube with a Pasteur pipette and place it in the refrigerator for several hours (preferably for a day). The settled blood serum is aspirated or drained using a sterile Pasteur pipette into a sterile test tube.
Conclusions:
- Blood plasma is the liquid part of the blood that remains after the removal of formed elements. In a suspended state, it contains formed elements - blood cells and platelets (or blood cells).
- Blood plasma in its composition is a very complex liquid biological medium, which includes vitamins, carbohydrates, proteins, various salts, lipids, hormones, dissolved gases and intermediate metabolic products.
- Blood serum (or blood serum) is the liquid fraction of clotted blood.
- Blood plasma is obtained by precipitation of formed elements, and serum is obtained by introducing coagulants (substances that promote blood clotting) into the blood plasma.
- Blood serum differs from plasma in the absence of a number of proteins of the coagulation system, such as fibrinogen and antihemophilic globulin, therefore it does not coagulate in the presence of coagulase, incl. microbial
WHAT MEDICAL EXAMINATION SHOULD BE PASSED TO BECOME A DONOR
All necessary tests are usually done directly at blood transfusion stations. A certain amount of blood donated by a donor is taken for testing. Determined: blood type and Rh factor; general blood test data (hemoglobin, leukocytes, erythrocytes, ESR, etc.); as well as markers of pathogens of blood-borne (blood-borne) infections: human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B and C viruses; the causative agent of syphilis.
If desired, in 1-2 days the donor can come with a passport to the Station and receive the results of his tests. Results are reported only in person and confidentially. If signs of infection are found in the blood, only the person who donated the blood and the doctor will know about it. And the doctor will advise where you can go to find out your health situation.
In addition to a blood test, a potential donor undergoes a medical examination, during which the doctor measures blood pressure, temperature, pulse, and asks about his health. Before the blood donation procedure, each potential donor fills out a special “donor questionnaire” in which he answers questions about his state of health and previous diseases.
The final decision on admission to blood donation is made by a transfusiologist, who also evaluates the psychoneurological status of the donor and can reject him if he is suspected of using drugs, alcohol, or leading an antisocial lifestyle.
Globulins
The remaining plasma proteins are classified as globulins, which are large in molecular weight. They are produced in the liver and in the organs of the immune system. Main types:
- alpha globulins,
- beta globulins,
- gamma globulins.
Alpha globulins bind bilirubin and thyroxine, activate the production of proteins, transport hormones, lipids, vitamins, and microelements.
Beta globulins bind cholesterol, iron, vitamins, transport steroid hormones, phospholipids, sterols, zinc and iron cations.
Gamma globulins bind histamine and participate in immunological reactions, which is why they are called antibodies, or immunoglobulins. There are five classes of immunoglobulins: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE. Produced in the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, and bone marrow. They differ from each other in biological properties and structure. They have different abilities to bind antigens, activate immune proteins, have different avidity (rate of binding to antigen and strength) and ability to pass through the placenta. Approximately 80% of all immunoglobulins are IgG, which have high avidity and are the only ones that can cross the placenta. IgM is synthesized first in the fetus. They are also the first to appear in the blood serum after most vaccinations. They have high avidity.
Blood composition
Fibrinogen is a soluble protein that is produced in the liver. Under the influence of thrombin, it is converted into insoluble fibrin, due to which a blood clot is formed at the site of vessel damage.
Difference Between Plasma and Serum
The main difference between Plasma and Serum is that Plasma contains a blood clotting agent whereas Serum does not contain blood clotting factors. Plasma is the clear and yellowish liquid part of the blood, whereas Serum is the liquid part of the blood after coagulation.
Contrary to popular belief, serum and blood plasma are not the same thing, and therefore the terms cannot be used interchangeably. In this article, we'll look at what plasma and serum are and the main differences between them.
Content
- Overview and main differences
- What is Plasma
- What is Serum
- Separation of Blood Plasma and Serum
- What is the difference between Plasma and Serum
- Conclusion
What is Plasma
Plasma is the liquid part of blood, which is 90% water and makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. Its main function is to transport proteins, nutrients, hormones and antibodies, among other things, throughout the body. As it spreads throughout the body, cells also release their waste into the plasma.
Blood composition
In addition to water, plasma also contains albumin, fibrinogen, globulin, hormones, nutrients, amino acids, and nitrogenous waste products. Typically, plasma helps regulate body temperature and blood pressure. Plasma has a long shelf life and can last up to a year.
What is Serum
Simply put, serum is plasma without clotting factors and blood cells. During the process of removing clotting factors (achieved by centrifugation), the protein fibrinogen is converted into fibrin. Fibrin is an insoluble protein that is used to repair damaged tissue by forming a clot in a wound that impedes blood flow.
Obtaining blood serum
It is noteworthy that the whey has a short shelf life and can be stored for only a few months. It is used to identify problems related to cholesterol, blood sugar and blood pressure.
Separation of Blood Plasma and Serum
The composition of serum and plasma can be separated by centrifugation. Notably, each component can be separated due to its different size, weight and density. EDTA Heparin, which is an anticoagulant, is needed to separate blood components such as white blood cells and red blood cells from the plasma. However, the whey separation process is relatively complex.
What is the difference between Plasma and Serum
| Plasma | Serum |
| This is the clear or straw-colored part of the blood. It is slightly alkaline. | This is the extracellular part of the blood. |
| Structure | |
| Blood cells with salts, glucose, lipid and protein. | Electrolytes, antigens, antibodies, proteins and hormones. |
| Components | |
| Water and blood clotting factor.a | Proteins such as globulin and albumin. |
| Fibrinogen | |
| Fibrinogen is present. | Fibrinogen is absent. |
| Cell location | |
| The cells are suspended. | Blood clotting usually keeps the cells attached. |
| Separation method | |
| They are separated through a process of twisting before rolling. | They are separated through a process of twisting after rolling. |
| Anticoagulant use | |
| Anticoagulants are necessary. | Anticoagulants are not needed. |
| Easy to store | |
| Plasma can be stored for a year. | The serum can be stored for several months. |
| Density | |
| 1.025 g/ml. | 1.024 g/ml. |
| Purpose | |
| It serves as an important medium for transporting excretory products. | It is one of the main sources of electrolytes |
| Function | |
| Helps regulate blood pressure and body temperature. | Serum is used to diagnose cholesterol, sugar, protein, hCG, etc. |
Conclusion
Serum and plasma are the liquid part of the blood, which contains at least 90% water. Plasma is the clear, straw-colored part of blood before coagulation, and Serum is the undiluted part of blood. Plasma contains clotting factor and serum, while serum contains the rest of the blood. The main difference between Plasma and Serum is that Plasma contains a blood clotting agent whereas Serum does not contain blood clotting factors. Serum contains electrolytes, hormones, antigens, antibodies and proteins such as globulin and albumin. On the other hand, plasma includes suspended blood cells, glucose, salts, proteins and lipids. It also contains water and clotting factors.
Modern market of plasma technologies
The main difference between serious professional plasma devices and portable devices for home and salon use is the presence of control over the depth and degree of skin damage. This is an extremely important aspect that allows you to obtain a predictable result and reduce the risks of unwanted side effects.
The number of new devices using plasma capabilities is increasing every year. There are even portable devices that allow you to use plasma energy in salons and at home. However, it should be noted that they set exposure modes in which it is not possible to change either the strength, depth, or treatment time, which raises questions regarding their effectiveness and safety.
At the same time, developers of professional devices, on the contrary, focus their efforts on improving devices and creating more controlled technologies that allow them to obtain the expected and stable results. For example, Neogen PSR (Energist, UK) is the direct “successor” of Portrait PSR, which has improved pulse delivery technologies.
Devices are appearing that incorporate the latest scientific advances in the use of plasma. Among them, it is worth highlighting the Plasma BT device (Seoulin Medicare, Korea), which is already presented on the Russian market. This is a new generation device that uses not only the already well-known thermal effects of plasma exposure, but also the recently discovered properties of cold plasma.
Plasma BT is equipped with two separate nozzles that generate plasma with different characteristics and therefore different effects on the skin ( Fig. 8 ).
Rice. 8. Plasma BT device
- Plasma Surgical - for thermal effects leading to tissue sublimation. The nozzle allows you to deliver plasma in the form of single pulses or a series of pulses of different frequencies, as well as a continuous flow ( Fig. 9 ).
Rice. 9. Damage generated by different modes of the Plasma Surgical Plasma BT handpiece
Moreover, for each mode it is possible to change the energy, and therefore the depth and area of influence.
A patented design of Plasma BT is the presence of a special guide clamp that controls the distance between the plasma-emitting needle and the skin ( Fig. 10 ).
Rice. 10. Plasma Surgical Plasma BT nozzle with a needle-shaped tip and a needle in a special clamp
This allows treatment to be carried out from an optimal distance (0.5 mm) and the formation of homogeneous lesions over the entire surface of the skin. Is used for:
- skin tightening (including for the so-called non-surgical blepharoplasty) ( Fig. 11 ) [16];
Rice. 11. Patient, 42 years old, before (left) and 3 weeks after blepharoplasty using the Plasma BT device (pulse mode, 40 Hz, level 2). Reducing the size of the skin fold opened the upper eyelid by 25% in the right eye and 46% in the left eye, resulting in a 14% widening of the palpebral fissure in both eyes. There were no serious side effects, the swelling resolved after 2 days, and small scabs at the points of injury fell off after 3 days [according to the doctor]
- eliminating wrinkles;
- removal of pigment spots;
- eliminating scars;
- removal of formations on the skin.
- Plasma Poration (plasma shower) - generates cold plasma, which has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, and also stimulates the renewal of skin cells and extracellular matrix components. In addition, a separate area of application is to increase the transdermal delivery of active ingredients to the skin without damaging it ( Fig. 12 ).
Rice. 12. Increasing the permeability of the skin barrier using a plasma shower
Is used for:
- skin rejuvenation;
- acne treatment;
- improving the penetration of various active substances into the skin.
An illustrative example of the effectiveness of using a plasma shower for transdermal delivery of active substances is given in the article by Dr. Beatriz Molina, medical director and owner of Medlkas clinics (UK), leading specialist at Galderma UK [17]. She describes a case of poor circulation during non-surgical rhinoplasty after the injection of hyaluronic acid filler into the tip of the nose.
Because hyaluronidase injections were quite painful for the patient, Dr. Molina used a Plasma Poration tip—3 minutes of nasal treatment followed by topical application of 1,200 and 750 U of hyaluronidase for the first two days after symptom onset, respectively.
Following this, she used a nozzle for transdermal administration of an injectable form of hyaluronic acid for biorevitalization (3 procedures). All adverse events resolved without any complications, which confirms the effectiveness of using a plasma shower for delivering large molecules to the skin ( Fig. 13 ).
Rice. 13. Successful experience of using the Plasma Poration attachment for transdermal administration of hyaluronidase and hyaluronic acid for biorevitalization
Difference between plasma and serum
Many people know that plasma and serum are related to blood. But not everyone has deeper knowledge on this issue. Let's consider what the declared substances are and how they fundamentally differ.
So, one of the fluids that performs its important functions in the body is blood. Obedient to the beats of the heart, it constantly moves, transporting various substances to their designated places. In addition to transportation, blood is responsible for many other aspects. Solving a large number of problems, this substance is quite complex.
A significant part of the blood consists of the so-called formed elements. They are represented by a certain number of leukocytes, platelets and bodies called erythrocytes. All mentioned components exist in a liquid medium, which is plasma. This substance can be observed at the top of the settled blood in the form of a light layer, while heavier particles settle down.
Plasma itself is also a combination of many components, each of which has a clear purpose. The basis here is water. Some types of proteins, vitamins, and nutrients are dissolved in it. In addition, mineral compounds, excreted metabolic products and other various elements are found in the plasma.
As we can see, we are talking about a rich substance that is naturally found in the blood, which always functions in the body. At the same time, serum can only be obtained outside the body. It is produced on the basis of plasma. The latter contains fibrinogen, a protein component responsible for blood clotting.
Serum remains after fibrinogen is removed using certain techniques. The resulting fraction is usually yellowish, but may also have a reddish tint due to the presence of certain particles. The value of such a liquid lies in its stability. Whey that is not subject to coagulation is stored for a long time. At the same time, its composition remains uniform, without unnecessary clots.
At the same time, the practical significance of the serum lies in the fact that it is rich in antibodies, which pathogens are afraid of. This blood processing product is indispensable in the manufacture of drugs that perform not only a therapeutic, but also a preventive function. A similar composition is used in the process of diagnosing diseases, for conducting various studies, as well as for some other purposes.
Blood plasma: today and tomorrow
Plasma eliminates protein deficiency and increases blood oncotic pressure, promoting increased diuresis and elimination of edema; serves as an excellent addition to the complex therapy of infectious-toxic shock, hepatic coma, hemorrhagic syndromes, etc.
Products from the processing of donor blood plasma are high-tech modern therapeutic drugs, the timely use of which saves the lives and health of many people.
Donated blood plasma is a complex mixture of proteins (about 500), the medicinal properties of many of which have been established. However, the shelf life of blood products is limited, and their production requires a long time. The need for these drugs is very high.
Currently, it has become possible to obtain and use individual plasma proteins that have a specific effect - albumin, fibrinogen, fibrinolysin (plasmin), etc. Methods for removing (inactivating) hepatitis viruses, HIV, etc. from plasma are being actively developed. Using genetic engineering methods, scientists are working to obtain artificially synthesized blood plasma proteins, which will ultimately eliminate the need for donors.
Prepared by Alexandra Demetskaya
“Pharmacist Practitioner” #07–08′ 2013