A urine test is one of the most commonly requested laboratory tests by doctors. The analysis is simple, cheap and fast. You can get the results of a complete urine test within a few hours to find out if everything is fine the same day. Otherwise, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If, for example, a urinary tract infection is suspected, a complete urine test can clearly answer the question of whether an infection has actually occurred. Urinalysis allows rapid and effective diagnosis and initiation of treatment (usually after a longer period of inoculation).
Urine pH - test
A urine test measures several basic parameters that indicate the health of the body. Parameters include the color of the urine being tested, its specific gravity, urine pH, the presence of glucose, as well as protein, bilirubin and ketone bodies. In addition, a general examination is also an assessment of the sediment and the presence of bacteria, squamous epithelium, red blood cells and white blood cells in it.
Several pages could be written about the urine analysis itself and the interpretation of each of the individual parameters. However, this short article will only look at one criterion, namely urine pH. What should the urine pH indicator be, when can it change, at what point should you be concerned, and what does this indicator generally show?
Urine pH standards
The content of the article
As with any test, urine testing has its own standards. The test described in this article determines the pH of your urine.
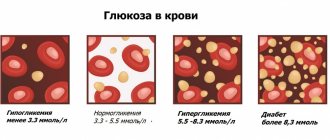
Urine pH ranges from 0 to 7; neutral - the value assumes a urine pH of 7 or alkaline. Then the values start with a urine pH of 7 and end with a urine pH of 14.
In the case of urine pH, it can also be acidic or neutral. In this study, the values that should not be of concern are somewhat limited. They do not have the same range as the entire pH range and only range from urine pH 4.5 to urine pH 8. Reaction ranges are based on the acidity-alkalinity (pH) scale.
But why check urine pH at all and what can be done based on it?
Urine tests, and urine pH in particular, can provide a lot of information, including:
- potential metabolic disorders;
- hormonal disorders (especially in women);
- infections;
- deficiency or excess of potassium is most often associated with current nutrition, but sometimes with serious diseases;
What is the normal pH of water
Due to the rapid pace of modern life, poor nutrition, and poor eating and drinking habits, the pH level in the human body drops. Thus, the acid-base balance shifts towards increased acidity (pH up to 7 implies an acidic environment, and up to 14 - alkaline, respectively, the lower this level, the higher the acidity), which can lead to serious diseases. This problem can be solved by daily drinking mineral water with an optimal level of hydrogen ion activity. That is why it is important to know what pH value is normal for the water you regularly drink.
Take the test
So, what should the pH of water be? Professionals argue that this value should approximately correspond to the normal pH of human blood (7.5). That is why the pH standard for drinking water is calculated from 7 to 7.5. Thanks to clean drinking water with a normal level of hydrogen ion activity, metabolic processes in the body are improved, overall life expectancy increases and oxygen exchange is optimized. Conversely, sugary, carbonated and colored drinks reduce the pH of human blood, which can be immediately noticed by an unpleasant dry mouth.
Therefore, it is best to give preference to water with the “correct” pH value. You can always find this information on the label of any bottle. No filter with fillers and absorbents can replace real natural water with an optimal pH level. Some try to lower the pH of the water and add beneficial properties to the liquid by adding lemon or cucumber juice, however, this does not always have the desired effect. Another well-known method of changing the pH of water is electrolysis, which allows you to obtain alkaline and acidic water in two containers. Alkaline water with a high pH is considered “living”, it is used for treatment, and acidic water is “dead”, which is most often used for washing.
However, such methods are not suitable for daily use. In this situation, there is only one rational solution - to give preference to low-mineral natural water with the acidity level necessary for health.
Read the material on the topic: Is it possible to drink tap water?
Normal urine pH
What is the correct urine pH? It would seem that since a urine pH of 7 indicates a neutral urine pH, a urine pH of 7 is the most desirable and is considered the ideal test result. In fact, a pH of 6.5 is considered the most optimal urine pH. In healthy people without identified metabolic disorders who follow a balanced diet, urine should be slightly acidic. A value below the neutral level is associated with safety. An acidic environment promotes the growth of a low percentage of microorganisms. Both bacteria and fungi do not do well in this environment, so if the urine is slightly acidic, a person may feel safe.
What is pH
The two-letter abbreviation originates in Latin. It stands for “hydrogen power” and means a measure of the activity of charged particles of a given element. To calculate the pH value, the concentration of hydrogen ions is measured. Then the decimal logarithm is taken from the resulting number and multiplied by (-1). The mathematical formula looks like this: pH = -log[H+].
Essentially, the hydrogen index is the ratio of H+ and OH– ions in a liquid, which are formed during the breakdown of water molecules. The ideal ratio is 1:1, i.e. pH=7. Distilled water has this value.
The value of the indicator is directly related to the temperature of the water and its interaction with air. If the pH in a closed vessel is 7, then as carbon dioxide enters the liquid, the value will drop to 5.2.
The pH value is also affected by substances that dissolve in water. The addition of some substances increases acidity, while others decrease it. This phenomenon allows you to evaluate the purity of a liquid, even when visually it does not have impurities.
Slightly low or slightly elevated urine pH
However, sometimes when checking the pH of urine during a general examination, it turns out that the pH is elevated. Generally, small changes such as a urine pH of 7 or a urine pH of 6 are standard and in most cases do not indicate any health threat. Such small changes may be the result of under- or over-hydration of the body. Another explanation is the daily diet.
People who eat more animal products tend to have an acidic urine pH. Vegetarians will have an alkaline urine pH. In neither case is this a particularly dangerous indicator. But it should be remembered that it is best if the diet is varied and does not cause deviations in any of the parameters of our body.
What to do if the pH is lower than normal?
We can regulate our acid-base state using three main mechanisms:
- physical activity and proper breathing;
- choosing certain foods;
- the use of various biologically active components.
If the pH deviates towards the acidic side, it is necessary to increase the content of alkaline foods in the diet. The daily diet of a healthy person should include at least 75-85% of alkalizing foods, and in the diet of a person suffering from acidification, their share should be increased to 90%.
Alkalinizing foods include vegetables and fruits. Freshly prepared vegetable or fruit juices alkalize the blood more effectively. And if you add 1-2 spoons of Eureka BALANCE , you will get a powerful alkalization of the body, and much softer and safer than what happens when you take soda internally.
Low urine pH
What to do if your urine pH is low? Well, the problem can start if urine pH standards deviate significantly from the established norms.
With more acidic urine, the pH of which fluctuates around 4.5-5, we can conclude that these values are incorrect and require consultation with a doctor.
Very low urine pH may indicate kidney disease, including kidney failure. Additionally, improperly regulated diabetes is easy to recognize because it causes acidic urine.
Lung diseases can also be another cause of increased acidity in urine. Emphysema is also characterized by a person's urine having a low pH level.
How to find out your body's pH?
Using pH test strips, you can easily, quickly and accurately determine your pH level.
To make a conclusion about the state of the internal environment of the body, one measurement is not enough. The pH value can change throughout the day depending on the activity of the body, food taken, physical activity, stress, etc. For the readings to be objective, you need to take them several times a day for 4-5 days in a row.
Enter the results obtained into a table, and then a complete picture of urine pH will appear.
Alkaline urine
The problem can also arise if the urine has a pH higher than 7. A urine result of 8 is of course still a value within the normal range, and as mentioned earlier, this value should not mean anything serious either. The influence of a vegetarian diet may also contribute to this value in the overall study. However, usually significant urine alkalinity, that is, a pH between pH 7 and 8, suggests or simply confirms (with additional parameters, such as urine sediment analysis) a urinary tract infection.
An alkaline pH, in addition to urinary tract infections, kidney disease or a diet rich in potassium (hyperkalemia), is also an indication for tests on the functioning of the parathyroid glands and, again, the respiratory system. Although hyperacid urine can be caused by emphysema, excessively elevated pH—that is, increased urine alkalinity—is sometimes a symptom of asthma.
One parameter and many different interpretations help in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases associated not only with the excretory system. A urine test is not only a test performed when a disease or infection of the urinary system is suspected. It gives a general idea of health, and simply changing the pH can help determine what the problem is.
How to quickly and economically measure pH
Litmus indicator paper provides a quick and economical way to measure the pH (hydrogen value) of any necessary liquid and mixtures of liquids (urine, saliva, feces, semen, vaginal acidity, breast milk, solutions, water, drinks, etc.).
Litmus paper is necessary both in the family and for the specialist conducting the patient’s examination, applicable in chemical laboratories, and used for research activities.
In chemistry, there are substances that have the ability to change their color in the presence of acids and alkalis. These substances are called indicators and are used to determine the reaction medium. The environment can be acidic, alkaline and neutral. Filter paper is impregnated with these substances.
Litmus is a coloring substance extracted from certain types of lichen. Its composition is complex. Litmus is a weak acid that is used to soak paper.
How to use indicator paper:
It is necessary to dip a narrow strip of paper into the required solution for two to three seconds. Compare with the supplied color chart and calculate the values.
In a neutral solution at 25°C, pH = 7. In acidic solutions, pH 7, the greater the alkalinity of the solution, the greater its value. Conclusion: the lower the pH, the greater the concentration of H+ ions, i.e., the higher the acidity of the environment, and vice versa, the higher the pH, the lower the concentration of H+ ions, i.e., the higher the alkalinity of the environment.
Indicator paper parameters: pH measurement from 1 to 14. Indicator paper can be in the form of strips, rolls, boxes, tubes, pencil cases, tear-off. Universal indicator paper is used only for approximate determination of pH values over a wide range with an accuracy of about one pH unit or tenth.
PSH - METER - IS IT NEEDED?
To accurately identify the value of this indicator, a pH meter is used in routine methods. The use of indicators to determine the exact value is not practiced due to the subjective determination of color or the low accuracy of the indicator itself. However, the advantage of indicators is their low cost, clarity of analysis, and speed.
Psh meters have various characteristics, on the basis of which its cost is formed, namely, PH measurement range: 0.00 - 14.00, operating temperature, division value: 0.1 pH, accuracy: 0.1 pH. The cost ranges from 15 to 100 dollars.
For soap and cream making, in principle, the cheapest one will do. It has the following characteristics: PH measurement range: 0.00 - 14.00, operating temperature: 0 - 50°C, division value: 0.1 pH, accuracy: 0.1 pH. The PN meter must be calibrated.
If the PN meter is uncalibrated and shows incorrect values, then it needs to be calibrated. An example of calibrating a ph meter 009. However, other models are calibrated using the same principle!
What is needed for calibration? Actually, a psh meter, a slotted screwdriver (included in the kit), a calibration solution and, of course, straight hands, where would we be without them - not a single task can be done without them. I believe that it is enough to calibrate the budget ph meter 009 at one point, having a solution of ph 4.00 or ph 6.8. The solution must be at room temperature! If it is stored in the refrigerator, take it out in advance and shake it well just before calibration.
Place the switched on PN meter into the calibration solution. Wait a minute. There is a screw on the back of the meter; it must be turned clockwise or counterclockwise, depending on the indicator on the display. You must match the values on the display with the pH of your solution! That's actually the whole technological process!
HOW TO USE THE PSH METER
Typically, instructions are included with the device.
Below is an example of instructions for the Miniature pH-meter-tester pH-PAL
- remove the protective cap at the bottom of the housing;
- turn on the device by sliding the top switch to the right;
- immerse the device in the test solution up to the grooved mark;
- stir vigorously for 5-6 seconds. Read the readings after they have stabilized;
- if the electrode was dry, wait a little longer, which will allow the device to carry out temperature compensation;
- After each measurement, thoroughly rinse the electrode with distilled water;
- After completing the measurements, turn off the device and put on the protective cap.
PH STANDARDS
Solutions and liquids with respect to their acidity are considered:
- neutral at pH = 7
- acidic at pH 7
Acidity of urine
If the urine pH level fluctuates between 6.0 - 6.4 in the mornings and 6.4 - 7.0 in the evenings, then the body is functioning normally. The most optimal level is slightly sour, in the range of 6.4 - 6.5. A urine pH value below 5.0 indicates that it is strongly acidified, and above 7.5 indicates that it is strongly alkaline.
The reaction of urine determines the possibility of stone formation: urate - in an acidic environment, oxalate - in a neutral-acidic environment, phosphate - in a more alkaline environment. For example, uric acid stones virtually never occur when the urine pH is greater than 5.5, and phosphate stones never form unless the urine is alkaline. The best time to determine your pH level is 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal.
Check the pH level twice a week 2-3 times a day.
Using indicator litmus paper pH test, you can easily, quickly and accurately monitor the response of urine to changes in the type of diet, the use of medications or dietary supplements. Positive pH dynamics can serve as a criterion for the correctness of the chosen diet or treatment.
The acidity of urine varies greatly depending on the food taken, for example, eating plant foods increases the alkaline reaction of urine. The acidity of urine increases if a person’s diet is dominated by meat foods rich in proteins.
Heavy physical work increases the acidity of urine.
Increased acidity of urine is observed with increased acidity of the stomach. Reduced acidity of gastric juice does not affect the acidity of urine.
The acidity of urine changes in many diseases or conditions of the body, so determining its acidity is an important diagnostic factor.
Saliva acidity:
The acidity of saliva depends on the rate of salivation. Typically, the acidity of mixed human saliva is 6.8–7.4 pH, but with high salivation rates it reaches 7.8 pH. The acidity of the saliva of the parotid glands is 5.81 pH, of the submandibular glands - 6.39 pH. In children, the average acidity of mixed saliva is 7.32 pH.
Optimal measurement from 10 to 12 hours. It is better to measure it on an empty stomach, two hours before or two hours after a meal. Salivation decreases in the evening and at night.
To increase salivation, in order to increase the pH of saliva, it is good if there is a piece of lemon on the plate; it even with visual perception increases salivation. Food should look appetizing, served on beautiful dishes, appetizingly decorated with herbs and/or vegetables, it should, as they say, please the eye! Not only the saliva flows, but also the juices in the body, preparing for the process of digesting food. This is the mental phase of digestive secretion.
Acid gastroesophageal and pharyngolaryngeal refluxes reaching the oral cavity play a leading role in the occurrence of oral pathology. As a result of the ingress of hydrochloric acid, the acidity of mixed saliva decreases below 7.0 pH. Saliva, which normally has alkaline properties, at low pH, especially at values of 6.2–6.0, leads to focal demineralization of tooth enamel with the appearance of erosions of hard dental tissues and the formation of cavities in them - caries. The amount of mucus on the mucous membrane increases, the gums become swollen and inflamed.
When the acidity in the oral cavity decreases, the acidity of dental plaque decreases, which causes the development of caries.
Bacteria in the mouth thrive in the absence of air. Saliva, rich in oxygen, actively prevents their reproduction. Bad breath occurs when the flow of saliva slows down, for example during sleep. Excitement, hunger, pronouncing a long monologue, breathing through the mouth (for example, with a runny nose), stress - dry out the oral cavity, leading to a decrease in the pH of saliva. A decrease in saliva flow inevitably occurs with age.
You can use a slightly alkaline mouth rinse with water with the addition of soda and also take it orally between meals, proposed by Professor A.T. Ogulov. – slightly alkaline pH 7.4-8. Rinsing the mouth with soda water occurs for various inflammatory diseases of the gums and teeth and for general acidification of the body.
You can set the desired pH of water for rinsing or ingestion using litmus indicator paper. There cannot be recipes with the required proportions, because... Each region has its own water, with its own pH. Therefore, it is necessary to have indicator paper on hand.
Vaginal acidity
The normal acidity of a woman's vagina ranges from 3.8 to 4.4 pH and averages 4.0 to 4.2 pH.
Vaginal acidity in various diseases:
- cytolytic vaginosis: acidity less than 4.0 pH
- normal microflora: acidity from 4.0 to 4.5 pH
- candidal vaginitis: acidity from 4.0 to 4.5 pH
- Trichomonas colpitis: acidity from 5.0 to 6.0 pH
- bacterial vaginosis: acidity greater than 4.5 pH
- atrophic vaginitis: acidity greater than 6.0 pH
- aerobic vaginitis: acidity greater than 6.5 pH
Lactobacilli (lactobacillus) and, to a lesser extent, other representatives of normal microflora are responsible for maintaining an acidic environment and suppressing the growth of opportunistic microorganisms in the vagina. In the treatment of many gynecological diseases, restoration of the lactobacilli population and normal acidity comes to the fore.
Sperm acidity
The normal acidity level of sperm is between 7.2 and 8.0 pH. Deviations from these values, in and of themselves, are not considered pathology. At the same time, in combination with other deviations, it may indicate the presence of a disease.
An increase in the pH level of sperm occurs during an infectious process. A sharply alkaline reaction of sperm (acidity approximately 9.0–10.0 pH) indicates prostate pathology.
When the excretory ducts of both seminal vesicles are blocked, an acidic reaction of the sperm is observed (acidity 6.0–6.8 pH). The fertilizing ability of such sperm is reduced. In an acidic environment, sperm lose motility and die. If the acidity of the seminal fluid becomes less than 6.0 pH, the sperm completely lose their motility and die.
The acidity of tears is normal - from 7.3 to 7.5 pH.
Acidity in the stomach.
- The minimum theoretically possible acidity in the stomach is 0.86 pH.
- The maximum theoretically possible acidity in the stomach is 8.3 pH.
- Normal acidity in the lumen of the body of the stomach on an empty stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH.
- The acidity on the surface of the epithelial layer facing the lumen of the stomach is 1.5–2.0 pH.
- The acidity in the depths of the epithelial layer of the stomach is about 7.0 pH. Normal acidity in the antrum of the stomach is 1.3–7.4 pH.
The cause of many diseases of the digestive tract is an imbalance in the processes of acid production and acid neutralization. Long-term hypersecretion of hydrochloric acid or lack of acid neutralization, and, as a consequence, increased acidity in the stomach and/or duodenum, causes so-called acid-dependent diseases. Currently, these include: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum while taking aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, gastritis and gastroduodenitis with high acidity and others.
Low acidity is observed with anacid or hypoacid gastritis or gastroduodenitis, as well as with stomach cancer. Gastritis (gastroduodenitis) is called anacid or gastritis (gastroduodenitis) with low acidity if the acidity in the body of the stomach is approximately 5 or more pH units. The cause of low acidity is often atrophy of parietal cells in the mucous membrane or disturbances in their functions.
Acidity in the intestines:
- Normal acidity in the duodenal bulb is 5.6–7.9 pH.
- The acidity in the jejunum and ileum is neutral or slightly alkaline and ranges from 7 to 8 pH.
- The acidity of small intestine juice is 7.2–7.5 pH. With increased secretion it reaches 8.6 pH.
- The acidity of the secretion of the duodenal glands is from pH 7 to 8 pH.
- The acidity of pancreatic juice is from 7.5 to 9 pH.
- The acidity of colon juice is 8.5–9.0 pH.
In the lower parts of the colon, pH values of acidity gradually increase, reaching a maximum pH value in the region of the rectosigmoid junction.
- The acidity of feces is normally from 6.0 to 8.0 pH.
- The acidity of meconium (original feces of newborns) is about 6 pH.
- The acidity of human breast milk is 6.9-7.5 pH
Blood acidity:
The acidity of human arterial blood plasma ranges from 7.37 to 7.43 pH, averaging 7.4 pH. The acid-base balance in human blood is one of the most stable parameters, maintaining acidic and alkaline components in a certain balance within very narrow limits. Even a small shift from these limits can lead to severe pathology. When shifting to the acidic side, a condition called acidosis occurs, and to the alkaline side, alkolosis occurs. A change in blood acidity above 7.8 pH or below 6.8 pH is incompatible with life.
The acidity of red blood cells is 7.28–7.29 pH.
Normal blood revitalizes lymph cells that can destroy tumor cells. There are many lymphatic cells (eg NK cells, LAK cells) in the human body. Their uniqueness lies in the fact that they are able to distinguish normal cells from diseased and damaged ones, and destroy the latter. This is the function of the human body's immunity. greatest activity of lymphatic cells in destroying diseased cells occurs at pH 7.4. However, usually around the affected cells, there is a more acidic environment, which interferes with the activity of lymphocytes, which work better at a slightly alkaline pH.
By consuming foods that have an alkalizing effect, you can adjust the pH balance within 0.5 units, creating a favorable environment for the action of lymphocytes and the destruction of affected or abnormally constructed cells.
Cancerous tissue has increased acidity, unlike normal tissue, and the body protects it with a fibrous membrane whose pH is alkaline. If you continue to follow the acidic diet, the membrane dissolves and the cancer cells are released.
HOW TO CHECK YOUR BODY’S ENVIRONMENT INDEPENDENTLY
1. Check the pH value - the reaction of saliva and urine on a scale of colored indicator (litmus) paper. If saliva and urine are within the pH range of 5.0-5.7, there is a predisposition to cancer, but this does not mean that the person will get sick. If saliva and urine are within the pH range of 7.0-7.4, you are protected from cancer. 2. You can do a bioimpedance analysis (diagnosis of body composition). By the amount of water in a bound state, you will determine whether you have a shift in the acid-base balance. If an excess of such water is definitely an acidic environment, a deficiency is alkaline.
IF THE BODY IS ACIDIFIC:
Nowadays, this is observed very often in connection with poor nutrition and attitude towards one’s body. Acidification of the body is primarily caused by:
- the predominance in the diet of such products as sugar, meat, chicken, fish, sweets, pasteurized dairy products, flour products and cereals;
- the second factor is the consumption of incompatible foods, for example, proteins with carbohydrates;
- Many preservatives and food additives that modern products are so rich in, especially those with a long shelf life, are also oxidizing agents;
- alcoholic drinks;
- coffee, tea, chocolate, tobacco.
To alkalize the blood, the body uses minerals - calcium, sodium, potassium, iron, magnesium. And this leads to physical weakness, fatigue, decreased mental activity and insomnia, irritability and depression. The leaching of calcium from bone tissue causes a serious disease - osteoporosis.
What to do if the body is acidified:
The daily diet of a healthy person should include at least 75-85% of alkalizing foods, and in the diet of a person suffering from any disease, their share should be increased to 90%. Alkalinizing foods include vegetables and fruits. And it is in this sequence, and not vice versa, since there is an unspoken rule: the closer a vegetable or fruit is to the soil surface, the higher its content of alkalizing macroelements (for example, potassium). Potassium, found in peeled potatoes, basil, dried apricots, and many other vegetables and fruits, helps fight acidification (latent acidosis) and create favorable conditions for the absorption of nutrients and medications. The most useful in this sense are fresh tomatoes, beets, dried apricots, and melons. Freshly prepared vegetable or fruit juices alkalize the blood more effectively. The healthiest ones are carrot, celery and watermelon. Alkaline valences dominate in vegetables and fruits, so their consumption eliminates acidosis.
Your menu should definitely include grated raw beets and carrots, finely chopped cabbage, dill, celery, onions and garlic. It is very useful to eat young green shoots of plants, honey, herbal teas, soy sauce, seaweed, and wheat sprouts.
Once a week, it is advisable to arrange fasting days for yourself, eating only raw vegetables and fruits , or even drinking only juices and purees on one of these days.
Most legumes and cereals, with the exception of buckwheat and millet, increase blood acidity during normal preparation. However, after soaking or sprouting, they acquire an alkalizing effect. Raw nuts and seeds should be soaked half an hour before meals, cereals - 0.5-2 hours before cooking, legumes - overnight.
When the acid-base balance shifts to the alkaline side (as a rule, this can be observed in vegetarians), a lack of water is created in the tissues, the skin becomes dry and dehydrated. There must be a measure for everything.
Physical work and sports slightly shift the body's reaction to the alkaline side.
A person’s mood is of no small importance. A good cheerful mood normalizes the acid-base balance.
Once a week, when the body is acidified, it is advisable to arrange healing days for yourself, eating only vegetables (1.5 kg of vegetables, divided throughout the day), boiled and sometimes raw in the summer, only heat-treated in the autumn-winter) and Be sure to have clean hot water.
If you are sick, you must give up any meat food and broths.
If you are going to have surgery, you need to do it in an alkaline mode of the body, and follow a plant-based diet after the operation.
Please note - alkalizing foods (for example, fruits) consumed with sugar (a strong acidifier) acidify the body (blood).
OXIDIZING AND ALKALIZING PRODUCTS:
The degree of their action will be noted by the number of advantages:
Some foods that acidify the body: sugar! (+++), game (++++), oysters (++++), crayfish (++++), veal (+++), eggs (+++), chickens (+++) , fish (++), mussels (+++), coffee (+++), jam (+++), baked beans (+++), beef liver (+++), lean pork (++) , skinny bacon (++), ham (++), pickled plums (++), green bananas (++), dried peas (++), white flour (++), barley (++), hominy and corn flakes (++), starch (++), peanuts (++), hard cheese (++), white bread (++), boiled lamb (++), stewed lamb (+), black bread ( +), dried beans (+), soft cheese (+), cream (+), beef (+), full-fat bacon (+).
Some foods that alkalize the body: figs (++++), fresh beets (++++), celery (++++), berries (++++), grapefruit (++++), lettuce ( ++++), champignons (++++), fresh tomatoes (++++), dried apricots (++++), fresh apricots (+++), pears (+++), sea buckthorn (+ ++), lemon (if consumed without sugar) (+++), orange (+++), watermelon (+++), melon (+++), prunes (+++), pepper (++ +), fresh beans (+++), currants (+++), cabbage (all types) (+++), pistachios (+++), cucumbers (+++), dandelion (leaves ) (+++), parsnips (+++), plums (+++), peaches (+++), whole milk (+++), kumiss (+++), whey (+++) , ripe bananas (++), apples (++), grapes (.++), cherries (++), raisins (++), dates (++), onions (++), green peas (++ ), radishes (++), almonds (++), carrots (++), potatoes with skin (++), cranberries (+), asparagus (+), lard (+). published
Why is acidification of the body dangerous?
A decrease in pH in the body leads to a decrease in immunity and the appearance of more than 200 diseases, including farsightedness and cataracts, chondrosis and arthrosis, gallstones and kidney stones, and oncology.
When the immune system is weakened and impaired, viruses, bacteria, and fungi begin to multiply rapidly in an acidic environment. With strong immunity, when the blood pH is normal, foreign bacteria and microorganisms will not be able to live and reproduce.
When acid enters, the body releases calcium in large quantities, even in excess. Then the excess calcium must be removed, but the body, unfortunately, does not send it back to the bones, but deposits it in the form of crystals in the joints, on other surfaces of the bones, in the kidneys, and in the gall bladder. Very often, in patients with osteoporosis, there is excess calcium in the blood, but there is none in the bones. The body constantly takes it away.
In the acidic environment of the body, vitamins, minerals and other essential micronutrients are poorly absorbed. Lack of nutrients leads to diseases of all organs and systems.
Excess acid plus lack of sufficient water makes urine thick, acidic and saturated with various salts and poisons, creating ideal conditions for the formation of kidney stones, kidney disease and kidney failure.
Chronic fatigue and weakness, weakening and pain in the muscles occur. And weakness of bones and muscles leads to weakening, disease and destruction of joints.
A constant acidic environment in the mouth destroys teeth and causes gum disease.
When the pH is restored to normal, health is restored, the main thing is not to be late. The body has amazing capabilities for recovery, but it needs conditions and nutrition for this. One of the conditions is a more neutral alkaline environment.
Contraindications to the procedure
The possibility of conducting daily pH -impedance measurements of the esophagus and stomach is determined individually at an appointment with a gastroenterologist at the UNION CLINIC in St. Petersburg. Absolute contraindications include:
- aortic aneurysm;
- severe maxillofacial injuries;
- gastric bleeding and 10 days after it stops;
- strictures (narrowings), diverticula (pathological protrusions), burns of the esophagus;
- nasopharyngeal obstruction;
- severe coronary insufficiency and hypertension;
- severe coagulopathies (blood clotting disorders).