Diseases of the retina and choroid can occur in acute and chronic forms. Chronic diseases include dystrophies and degenerations (central and peripheral), angioretinopathy of various natures, inactive and subactive phases of chorioretinitis.
Therapy for these diseases comes down to regular use of medications prescribed by an ophthalmologist. As a rule, it is recommended to take comprehensive courses twice a year, which include up to five types of drugs from several groups. Thus it turns out: 2 months of treatment, followed by a four-month break. It is better to combine one of the annual courses of therapy with local treatment - subconjunctival and parabulbar injections, and leave local instillations for the second annual course.
Drugs prescribed for annual courses of treatment are divided into the following groups: retinoprotectors, angioprotectors, anticoagulants, stimulants, absorbents, improve microcirculation, vasodilators, vitamins and drugs that activate tissue respiration. At the same time, one drug may have several specific properties and be in different groups. And drugs from the same group can have completely different effects on the body. For example, vasodilator drugs sometimes lower blood pressure, do not change it in any way, and in some cases they increase it. In this regard, the schemes of therapeutic courses are built taking into account the individual characteristics of a particular patient. To avoid polypharmacy, it is always better to choose 2 or 3 drugs that are completely suitable for the patient and will have the necessary complex effect on his body.
Tissue respiration stimulants
For this purpose, the enzyme preparation Cytochrome C , which is produced from the heart muscle of cows. The active substance is a participant in the act of tissue respiration and can accelerate oxidative reactions. Known as one of the components of Katachrom drops.
The drug is prescribed as an intramuscular injection of 5 ml. Before starting the course, a test is performed, the frequency of daily injections is 1 or 2. The duration of treatment is up to 20 days.
A test is required before each treatment course. With its help, the individual sensitivity of the patient is determined. As a test, 0.1 ml of Cytochrome C is injected into the skin and observed for half an hour. If redness, itching or allergic rashes occur, individual intolerance is indicated and the appointment is cancelled.
Angioprotectors
These are substances that help normalize the permeability of vascular walls, reduce swelling of vascular tissue, and accelerate metabolic processes in the vascular wall. The angioprotective effect is fully possessed by: vitamin P, anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, as well as the following medications.
Doxium, the main substance of which is a special form of calcium dobesylate, necessary for strengthening the walls of blood vessels. This drug is needed to increase capillary resistance, improve blood microcirculation, and stimulate drainage function in lymphatic vessels. It thins the blood and slightly reduces platelet aggregation, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of the retinal tissue. Does not have any effect on microaneurysms and does not significantly penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
The tablet form of the drug is prescribed at the rate of 0.75-1.0 g per day, which is 3-4 tablets, which are drunk after meals. The course of treatment is quite long and can last a year or a year and a half.
Among the negative aspects of taking the drug, experts note dyspepsia and allergic skin rashes. This is a reason to reduce the dose or completely cancel it. Not prescribed during pregnancy.
Ascorbic acid is a drug for normalizing the permeability of the capillary wall, improving redox reactions, and regulating carbohydrate metabolism. In addition, ascorbic acid helps reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, accelerate tissue regeneration, and stimulate the production of steroid hormones. This property of the drug is very important if a course of steroid therapy is necessary.
Prescribed in injections or tablets. Dosage for tablets: 0.05-0.1 g up to 5 times daily, with intramuscular administration of a 5% solution - 2.0 ml No. 20-30. Intravenous injections in the same dose are also possible, although it must be taken into account that in the case of thrombosis, thrombophlebitis or increased blood clotting, they are contraindicated.
Flavonoid Rutin is a drug that reduces capillary fragility and permeability (especially in combination with ascorbic acid). Together with it, it is a participant in redox reactions and slows down the action of hyaluronidase.
The daily dose of Rutin is usually 0.1 g, prescribed in combination with ascorbic acid. Ascorutin tablets are mass produced, including rutin with ascorbic acid and glucose. The therapeutic course involves taking them 4 pieces per day. It has no contraindications or side effects.
Troxevasin (venoruton) is a drug with an action close to rutin. Regulates capillary permeability, fights swelling and tissue inflammation. In capsules, prescribed one at a time with meals, for a course of 2-4 weeks.
Divascan is a hemostatic drug that reduces microvascular permeability. Available in tablets, which are prescribed one three times a day. Patients with diabetic retinopathy or intraocular hemorrhages are recommended to take without interruption for at least two years.
Dicynone (etamsylate) is a substance that increases the content of high molecular weight mucopolysaccharides in the capillary wall, which increases their stability and normalizes permeability. The drug has the property of improving microcirculation, normalizing platelet adhesion, and has a hemostatic effect without promoting the formation of blood clots.
Prescribed orally or intramuscularly. The daily dose in tablets is 1.5-2.0 g, duration of administration is 2-3 months. IM injections are prescribed for 10-14 days; they can be combined with subcutaneous administration of this drug at a dose of 0.5 ml.
To prevent bleeding during surgical interventions, Dicynon is administered intramuscularly before and after surgery if there is a risk of postoperative bleeding.
The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with thrombosis and embolism. There are no side effects.
Prodectin (parmidin) is an angioprotector drug whose action is aimed at restoring microcirculation. It helps reduce platelet aggregation, activates fibrinogenesis, and improves the condition of the vascular endothelium. Prodectin has a pronounced anti-sclerotic effect and accelerates the disappearance of signs of intoxication.
Its intake is 4 tablets daily (1.0 g), for a course of up to 6 months.
Side effects include nausea, occasionally allergic skin rashes, and headache. When the dosage is reduced or the drug is discontinued, all phenomena disappear. Contraindications for use are liver disease.
Emoxipine helps reduce blood viscosity, reduce the permeability of vessel walls, and resolve hemorrhages. It is a retinoprotector and antioxidant, protects the retina from the negative effects of bright light (laser coagulation, sunburn). It is prescribed for hemorrhages, retinopathy, complicated myopia, retinal dystrophies, thrombosis of its veins, light or radiation burns of the eyes, and glaucoma. It is also a component of complex treatment for laser coagulation.
Prescribe one injection into the eye (subconjunctival, retrobulbar, parabulbar) of a 1% solution in a dosage of 0.5 ml every day for 10-15 days. If necessary, the course of treatment is extended to 30 days and repeated several times a year. Sometimes the drug is used in the form of eye drops.
Its side effects may include: itching, burning, pain, related to allergic reactions. They are relieved by using corticosteroids. Sometimes during injections, compaction of the orbital tissue is observed, which subsequently resolves on its own.
To assess the platelet component of hemostasis, the number of platelets in the blood is counted. Platelet pathology is the cause of bleeding in almost 80% of cases. Thrombocytopenia is its most common manifestation. Thrombocytopenia should be diagnosed in cases where the platelet count is less than 150 × 109/L. The duration of bleeding is an important screening test, the main advantage of which is that it allows you to simultaneously qualitatively assess the number of platelets in the blood, their adhesive and aggregation functions, the functional properties of the blood vessel wall, as well as a pronounced deficiency of plasma coagulation factors (for example, factors VIII and IX, the deficiency of which is the cause of hemophilia A and B). Prolongation of bleeding time reflects a violation of hemostasis due to thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopathies (impaired platelet functions - adhesion and aggregation), disorders of the vascular wall, or a combination of these factors. Prolongation of bleeding time with a normal number of platelets in the blood suggests a violation of their functions. This is the main value of the test, because... To assess the adhesive and aggregation properties of platelets in laboratory conditions, complex and expensive equipment (aggregometer) is required. When platelet function is not impaired, bleeding time remains normal even when the platelet count drops to 100.0 x 109/L. Below this level, the bleeding time gradually increases in a linear relationship with the platelet count. Spontaneous bleeding occurs if the platelet count falls below 50.0 x 109/L; fatal bleeding is almost inevitable if the platelet count drops to 5.0 x 109/L. The duration of bleeding increases under the following conditions:
- Severe thrombocytopenia;
- Impaired platelet function - thrombocytopathies, which can be congenital (Bernard-Soulier syndrome) and acquired (pernicious anemia, acute and chronic leukemia, multiple myeloma, long-term use of aspirin);
- Marked decrease in plasma coagulation factors;
- If the resistance of the capillary wall is impaired (lack of vitamin C, defects in capillary contraction - microangiopathies).
A shortening of bleeding time has no diagnostic significance and is most often the result of a technical error during the test or indicates an increased spasticity of the capillaries. It is impossible to assess the susceptibility to thrombus formation using the bleeding duration test. An increased number of platelets in the blood - thrombocytosis, carries with it the risk of increased coagulation and is manifested by thrombosis. In clinical situations, the risk of thrombosis becomes real if the platelet count reaches 1000.0 x 109/L.
Study of platelet aggregation functions Aggregation processes are studied using an aggregometer, which reflects the progress of aggregation graphically in the form of a curve; ADP, adrenaline and collagen are often used as aggregation stimulators.
Disorders of platelet aggregation in various diseases (according to the results of studies using an aggregometer)
| Type of thrombocytopathies | Aggregation stimulator and aggregation disorder | ||||
| ADF | collagen | adrenalin | ristocetin | ||
| primary wave | secondary wave | ||||
| Thrombasthenia | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Norm |
| Essential atrombia | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Norm |
| Aspirin-like defect | Norm | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Norm |
| Bernard-Soulier syndrome | Norm | Norm | (+,-) | (+,-) | Norm |
| Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Pathology | Norm |
| von Willebrand disease | Norm | Norm | Norm | Norm | Reduced pathological |
Note: (+,-) – has no diagnostic value.
Platelet pathology is the cause of bleeding in almost 80% of cases. Thrombocytopenia is its most common manifestation. Thrombocytopenia should be diagnosed in cases where the platelet count is less than 150 × 109/L. There are acute and chronic thrombocytopenia. The latter is diagnosed when its duration exceeds 6 months. Individuals with platelet levels above 50×109/L rarely experience bleeding. However, a decrease in platelets below 100×109/L can accompany serious pathology. In this regard, the cause of each case of thrombocytopenia must be clarified. With thrombocytopenia, severe thrombocytopathies and von Willebrand factor (VWF) deficiency, the bleeding time is significantly prolonged. Bleeding is associated with insufficiency of the adhesive-aggregation function of platelets - a violation of the formation of a platelet plug in damaged vessels. This may be due to either a significant decrease in the number of platelets in the blood, or their dysfunction, which is most often based on the absence or blockade of receptors on the platelet membrane that interact with stimulators (agonists) of aggregation of these cells (VWF, adrenaline, ADP, fibrinogen, arachidonic acid and prostaglandins), or the absence in platelets or a violation of the release from them of granule components containing these aggregation stimulants. Modern hematology analyzers display thrombocytometric curves (histograms of platelet distribution by volume). There is a connection between the size of platelets and their functional activity, the content of biologically active substances in platelet granules, the tendency of cells to adhere, and changes in platelet volume before aggregation. The presence of predominantly young forms of platelets in the blood leads to a shift of the histogram to the right; old cells are located in the histogram on the left, since as platelets age, their volume decreases. An increase in the content of young forms of platelets is observed during blood loss and indicates enhanced regeneration. An increase in the content of old forms, vacuolated platelets, forms of irritation and a decrease in the content of mature platelets are characteristic of various inflammatory processes, intoxications, and malignant neoplasms.
Thrombomodulin is an integral membrane protein, a thrombin receptor located on endothelial cells of blood vessels and involved in the anticoagulation system. It determines the speed and direction of the hemostasis process, actively limits and regulates blood clotting. The endothelium, forming thrombomodulin, blocks active coagulants secreted by the liver and found in the blood plasma, primarily the most active coagulation factor, thrombin. Bound thrombin is excluded from the blood coagulation system. Thrombin, having joined thrombomodulin, acquires new qualities: together with the anticoagulant proteins C and S (protein S cofactor), it forms an antiplatelet and antithrombotic complex, which prevents coagulation and inhibits fibrinolysis. Thus, the thrombomodulin-protein C system performs an anticoagulant function. Moreover, thrombin, modified by interaction with thrombomodulin, loses the ability to convert fibrinogen into fibrin and cause platelet aggregation. When the vascular wall is damaged, thrombomodulin is “separated” from the endothelium and enters the blood. Its increase in the blood is observed in patients with prethrombotic conditions, vasculitis, etc. The degree of increase in thrombomodulin in the blood has diagnostic and prognostic significance. Thrombomodulin is significantly reduced in some diseases, such as atherosclerosis, which can increase blood clotting and increase the risk of thrombosis.
Factor B illebrand is a complex multimeric adhesive glycoprotein, a carrier-stabilizer of the procoagulant protein F VIII:C, which is an adhesion protein in the processes of hemostasis. Von Willebrand factor can bind collagen and possibly other endothelial structures and mediates platelet adhesion to the subendothelium through binding of the platelet surface receptor glycoprotein Ib. Von Willebrand Factor-mediated platelet adhesion occurs most intensely at high shear rates, i.e. in the arteries. VIII-vWF is also a carrier of F VIII - antihemophilic globulin A. Von Willebrand factor in healthy people prevents the growth of blood clots in blood vessels by activating the formation of plasmin. Elevated levels of von Willebrand factor activity are an indicator of endothelial damage in vascular disease, which may be significant for hypertensive vascular complications. Von Willebrand disease is a congenital hemorrhagic diathesis. In its mild form, this disease is the most common hemorrhagic disorder in men, with an incidence of 1:100. This is a disease of a heterogeneous nature, caused either by defects in protein structure or by a decrease in the concentration of von Willebrand Factor. Classification of the disease is based on the clinical picture, history and laboratory results, including clotting time and determination of antigen and von Willebrand factor activity. Determining the level of Von Willebrand Factor helps in the differential diagnosis of two main types of disease: type 1 and type 2. Determining the type of disease is important, since the choice of patient management tactics depends on it.
Fibronectin is a receptor for fibrin-stabilizing factor. Promotes platelet adhesion by participating in the formation of a white blood clot; binds heparin. By joining fibrin, fibronectin thickens the blood clot. Under the influence of fibronectin, smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts increase their sensitivity to growth factors, which can cause thickening of the muscular wall of blood vessels (narrowing of diameter).
Drugs that promote resorption
Chymotrypsin is a drug that helps break down blood clots, exudates, and fibrin. Prescribed as intramuscular injections of 5-10 mg in saline solution, lasting 20-30 days.
Fibrinolysin is a drug with high activity against fresh blood, so if the hemorrhage has occurred recently, treatment begins with it. It is prescribed as a sub injection in combination with fibrinolysin and heparin for 10-15 days. If necessary, chymotrypsin can be used after this. If the hemorrhage occurred a long time ago, it is not advisable to administer Fibrinolysin.
Another drug in this group, Lidaza, is contraindicated in recent hemorrhages. And in case of long-standing hemorrhage, it can provoke it again, therefore it is also contraindicated.
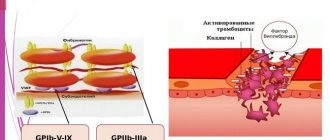
What is “platelet aggregation”
Platelets are colorless blood cells whose function is to protect the body from blood loss. When body tissues are damaged, platelets immediately rush to the site of injury and block it, preventing excessive blood loss. This blocking occurs due to the fact that platelets instantly stick together and form a block that closes the wound. This blocking process is called platelet aggregation. The process occurs in two stages:
- Blood cells stick together
- Later they adhere to the walls of the vessel, forming a blood clot or thrombus.
When the body is healthy, this function is protective. But if pathological changes occur in the body, the formation of blood clots can disrupt nutrition in vital organs and tissues.
Anticoagulants
Heparin , as an active substance, has a multicomponent effect: absorbable, lipotropic, anticoagulant. It is prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections according to the following scheme: the first 4 days, 4 daily injections, the next 4 days, 3 injections, then 4 days, 2 injections and another 4 days, 1 injection.
The dosage is up to 5000 units. The drug is not used in large doses as complications are possible.
Iodine preparations are prescribed to increase the fibrinolytic activity of the blood. In addition, they reduce the content of b-lipids and cholesterol. Prescribed orally 5-10 drops in milk twice or thrice a day, or in the form of pills with a dosage of 0.0005 g. The course of treatment is at least one month, carried out intermittently for many years.
Antiplatelet agents
Curantil is a drug that slows platelet aggregation, which prevents the formation of blood clots in blood vessels. It has a vasodilating effect, slightly lowers blood pressure, reduces peripheral resistance, and improves cerebral circulation.
Prescribed as an antiplatelet agent to prevent the occurrence of thrombosis after operations and for blood clots in the central retinal vein. The antiaggregation activity of Curantil is close to that of acetylsalicylic acid. However, this drug is better tolerated and does not have ulcerogenic properties.
Curantil is prescribed orally at a dose of 25 mg three times a day for a long period.
There are side effects of taking the drug, although they are very rare. These include: redness of the face due to a vasodilator effect (short-term), increased heart rate, allergic rash. Not prescribed for widespread atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries.
Acetylsalicylic acid is an anti-inflammatory drug with antithrombotic action and the ability to inhibit platelet aggregation. The drug is used for thrombosis of retinal vessels to prevent the formation of clots.
Prescribed orally 0.125 g or 1/4 tablet after meals once a day. Can be used for a long time.
Tiklid (ticlopedine) has the ability to suppress the aggregation of erythrocytes and platelets, activates the synthesis of prostacyclin and prostaglandins E1 and D2, and improves microcirculation. It is used for retinopathy - diabetic and post-thrombotic.
Tiklid is taken orally 0.25 g with food twice a day for a long time (up to 6 months or longer) under the control of blood composition and liver function.
When taken, diarrhea and epigastric pain may occur. Phenomena of hemorrhages, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis are also possible.
The drug is not prescribed simultaneously with anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents. It is contraindicated in cases of increased risk of bleeding, stroke, exacerbation of stomach ulcers, liver disease, pregnancy and lactation.
Explanation of the platelet aggregation test
In the platelet aggregation test, indicators of 25–75% indicate good hematopoiesis. This means that tissues and organs are normally supplied with oxygen, and there are no blood clots.
Platelet rate
| Age | Indicator, x 10^9/l |
| Newborn | 100–420 |
| Child under one year old | 160–320 |
| 1–4 years | 150–300 |
| 15–18 years old | 180–340 |
| Men over 18 years old | 180–400 |
| Women over 18 years old | 150–380 |
Vasodilators
Cinnarizine (stugeron) has an antispasmodic effect, reduces the reaction of blood vessels to vasoconstrictors. The drug improves microcirculation, thins the blood, and increases tissue resistance to hypoxia. Cinnarizine also has antihistamine properties; reduces the excitability of the vestibular apparatus, thereby suppressing nystagmus. Does not significantly affect systemic blood pressure.
The drug is taken orally after meals, 2 tablets twice a day. The duration of treatment can vary from several weeks to several months.
Side effects of the drug include dry mouth, drowsiness, and possible gastrointestinal disorders. Cinnarizine enhances the effects of alcohol and sedatives. There are no contraindications.
Sermion is a drug with antispasmodic activity against retinal vessels. It is used for diabetic retinopathy, corneal dystrophies, ischemic lesions of the optic nerve.
Take 10 mg orally before meals three times a day. Treatment is long - several months.
If phenomena such as hypotension, gastrointestinal disorders, dizziness, drowsiness or sleep disturbances, skin itching, redness of the face or skin of the upper half of the body occur, the dosage should be reduced or the drug discontinued.
Cavinton (vinpocetine) is a drug with vasodilating properties and a direct relaxing effect on smooth muscles. It improves blood flow, promotes glucose utilization, thins the blood, reduces platelet aggregation, and to a small extent reduces blood pressure levels.
Prescribed orally 2 tablets after meals twice a day. The course of admission is 60 days.
Not prescribed for patients with severe ischemia and cardiac arrhythmias, or pregnancy. Contraindicated in case of low vascular tone and labile blood pressure.
Nicotinic acid - the drug has an antipellagritic effect, normalizes cholesterol levels in the blood, affects fat and carbohydrate metabolism, dilates blood vessels, inhibits the sympathetic and stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system.
The drug is taken in tablets twice or three times a day, 0.02-0.05 g. In addition, it can be prescribed as injections of 1-2 ml intramuscularly for 10-15 days.
For ophthalmological pathologies, nicotinic acid is practically not prescribed as an independent drug. However, it is very often part of the used complexes: Xanthinol nicotinate, Nikoverin, Nikoshpan.
Nigexin is a drug with a vasodilator effect without lowering blood pressure levels. Prescribed for a course of up to 6 weeks, 0.25 g three times a day.
Complamin - has a vasodilating effect on peripheral vessels, improves peripheral blood circulation and microcirculation in the vessels of the retina.
The tablets are taken without chewing after meals, 2-3 pieces at a time. For patients with acute myocardial infarction, severe heart failure and bleeding, Complamin is not prescribed. When taking, caution should be exercised by people with stomach ulcers and labile blood pressure.
Trental (agapurine, pentoxifylline) is a drug with vasodilating properties, which improves the supply of oxygen to eye tissue. It improves blood microcirculation and its rheological properties, thins the blood and affects the elasticity of red blood cells.
It is taken in the form of tablets, which I take without chewing after meals. The daily dose is 4 tablets (0.4 g).
Taking the drug may be accompanied by side effects: nausea, redness of the face, dizziness.
In patients with recent retinal hemorrhages, massive bleeding, severe vascular sclerosis, or heart attack, the drug is not used.
Antisclerotic drugs
Miscleron has the ability to reduce the level of lipids and uric acid in the blood, increase its viscosity and fibrinolytic activity, and reduce platelet aggregation. Due to this, it is widely used for diabetic retinopathy, as well as other conditions associated with hyperlipidemia.
It is recommended to take the drug three times a day, 2 capsules during or after meals. Courses of treatment usually last 20-30 days, followed by an equal break; it is advisable to take 4-6 such courses per year.
Taking Miscleron may be accompanied by: gastrointestinal disorders, skin itching, muscle weakness and pain, weight gain due to water retention. Long-term use of this drug can cause intrahepatic cholestasis and cholelithiasis. Therefore, many European countries abandoned its production.
The drug should not be taken by people with liver and kidney diseases, as well as during pregnancy and lactation. Prescribed with caution to diabetics.
Methionine is a drug containing essential amino acids. Its lipotropic effect is aimed at removing excess fat from the liver. In addition, it has the property of activating hormones, vitamins and enzymes, and neutralizing toxic substances. Methionine is used for toxic liver damage, prescribed for diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis (to reduce blood cholesterol levels and increase phospholipid levels).
It is taken 2 tablets (0.5 g) before meals 3-4 times daily, lasting from 10 days to a month. Sometimes, the course of treatment is longer: 10 days of taking pills, 10 days of rest.
An unpleasant consequence of treatment with Methionine is vomiting, which requires its discontinuation.
References
- Trubacheva OA, Petrova IV, Kologrivova IV, Gusakova AM, Schneider OL Mechanism of collagen-induced platelet aggregation in patients with impaired carbohydrate tolerance or type 2 diabetes mellitus in combination with arterial hypertension. The Siberian Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2019;34(4):112-117. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.29001/2073-8552-2019-34-4-112-117.
- Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of platelet function disorders.” Vasiliev S.A., Berkovsky A.L., Melkumyan A.L., Suvorov A.V., Mazurov A.V., Kozlov A.A. Federal State Budgetary Institution Hematological Research Center, Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Moscow, 2013.
- Clinical laboratory diagnostics, National guidelines, Volume 1, Dolgov V.V., Menshikov V.V., 2012, pp. 761-765.
- Kozlovsky V. I., Kovtun O. M., Seroukhova O. P., Detkovskaya I. N., Kozlovsky I. V. Research methods and clinical significance of platelet aggregation. Focus on spontaneous aggregation // Vestnik VSMU. 2013. No. 4.
- Puri RN, Colman RW.ADP-induced platelet activation.Crit Rev BiochemMol Biol. 1997;32(6):437-502. doi: 10.3109/10409239709082000. PMID: 9444477.
Stimulant drugs
Phibs is a biogenic stimulant produced from distilled mud from estuaries. Prescribed in the treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, myopia, vitreous opacities.
It is administered in the form of subcutaneous injections of 1 ml, the course of treatment is 30 injections.
ATP is a substance that regulates the energy metabolism of cellular reactions, mainly during the synthesis of RNA and DNA. Thanks to its action, the processes of alteration and exudation are stopped and redox reactions are stimulated. Subconjunctival administration of ATP results in its accumulation in the eye tissues without complications.
It is prescribed subconjunctivally in 0.2 ml or intramuscularly in 1-2 ml. Course of treatment: 15 subconjunctival injections or 25 intramuscular.
Peat is a derivative of distilled peat. Indications for its use, dosage and course of treatment are similar to the drug FiBS.
Aloe extract is a very effective drug in the treatment of a number of eye diseases: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, progressive myopia, vitreous opacities, etc.
It is prescribed as a subcutaneous injection in a dosage of 1 ml.
Not indicated for patients with severe cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, acute gastrointestinal disorders, severe kidney diseases. And also for older people.
What does platelet aggregation disorder lead to?
If the aggregation process is disrupted, this can lead to negative consequences. So, if the activity of colorless blood cells is increased, this can lead to a stroke or heart attack. And if platelet production is reduced, this can lead to large blood loss: a person suffers from frequent bleeding that does not stop for a long time, leading to exhaustion and anemia.
It is in order to prevent these consequences that platelet aggregation analysis is performed. Indications for testing are:
- Frequent bleeding (nasal, uterine)
- Poorly healing wounds.
- Bruises that appear from the slightest injury.
- Constant swelling.