Excessive blood clotting - causes.
03.09.2021
blood clotting is an important function of the human body, with which it protects itself from excessive blood .
With the formation of blood clots (thrombi), the body repairs damaged blood vessels .
There are complex mechanisms in the circulatory system that are responsible for blood . If the wall of a blood vessel is damaged,
platelets are directed to the damaged vessel and form a blood plug. These activated platelets release chemicals that
which initiate the coagulation process. In some cases, blood clots may form in places where they are not needed, which can lead to various complications.
Certain diseases, genetic mutations, medications, and other causes can cause excessive blood .
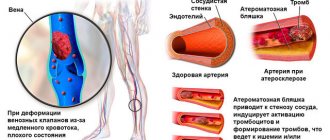
Venous thrombosis
With venous thrombosis, a blood clot forms in the walls of the veins . Most often this happens when a person is stationary for a long time,
and the muscles do not contract to push the blood out of the veins and keep it moving evenly. This stagnant blood the veins begins to form
small clots. These small blood clots can grow and completely block the vein , cutting off circulation in the area.
Bone marrow disorders
In some rare cases, the normal functioning of the bone marrow may be impaired, causing it to become
produce more blood than necessary. Two such conditions are polycythemia vera and thrombocythemia.
Polycythemia is a rare type of disease in which the bone marrow produces more red blood cells than necessary.
These extra red blood cells cause blood to become thicker than normal. Extra red blood cells blood to slow down
its movement through small blood vessels , and blood clots form in some of them. With thrombocythemia, in turn, there is an increased
platelet formation. Their increased quantity can also cause increased blood and frequent thrombosis.
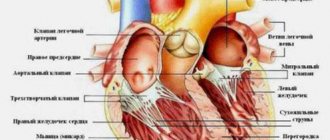
Formation of blood clots in the heart
With ventricular fibrillation, one of the cavities of the heart beats irregularly, which disrupts the functioning of the heart as a whole. For this reason
a certain amount of blood remains in the cavities of the heart for a longer time, which can cause the formation of blood clots.
These blood clots can travel in the blood to different parts of the body and cause stroke and other life-threatening complications.
Antiphospholipid syndrome
This is an autoimmune disorder in which the human body produces antibodies that attack phospholipids in the body.
Phospholipids are a type of fatty substance. Phospholipids are found in all cells of the human body, including
in blood and in the walls of blood vessels . In antiphospholipid syndrome, the antibodies produced cause blood clots to form.
in the walls of arteries and veins . Antiphospholipid syndrome causes a number of miscarriages in women.
Any disease or condition that impairs the integrity of blood vessels can cause increased blood .
Some of them are the most common:
- atherosclerosis
- diabetes
- vasculitis
- obesity
- metabolic syndrome
- smoking
- heart failure.
Published in Cardiology Premium Clinic
Types of laboratory tests for clotting
The content of the article
The blood clotting test includes the following indicators:
- Fibrinogen levels
This substance is a protein produced by the liver. In a healthy person, fibrogen is 2-4 g/l. - Antithrombin III.
This is a hemocoagulation regulator. The antithrombin index is 75-125% in adults, 80-120% in children older than one month, and 30-80% in newborns. - Prothrombin index (PTI)
. The percentage ratio of hemocoagulation time in a particular person with a similar indicator in the control sample. Normally, PTI is 93-107%. - Thrombin time.
In healthy people it ranges from 14 to 20 seconds. During this period, prothrombin must be transformed into thrombin. The results may vary with the use of certain medications, such as aspirin or warfarin. The thrombin time (PT) test shows how well a person's blood clots. - Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
. The indicator is used to monitor the hemocoagulation process in patients prescribed heparin and in the diagnosis of DIC syndrome. Normally, this figure is 29-39 seconds. - Period (time) of bleeding.
Indicates how quickly the blood will stop if the integrity of small vessels is violated. To do this, a puncture is made on the patient's finger and the time is noted. Normally it is 2-3 minutes. - Clotting time.
Determined by the time interval between blood sampling and clot formation. In healthy people, this process takes from 2 to 5 minutes. - D-dimer
. This is a substance formed as a result of the decomposition of fibrin. Normally, this figure should be no more than 250 mcg/l (0.25 mcg/ml).
Diagnostics
The main way to determine the degree of blood viscosity is to conduct a laboratory analysis of its sample. Increased density will be indicated by an increase in the number of blood cells - red blood cells. Another sign is a change in the level of hematocrit - an indicator of the level of leukocytes, platelets and red blood cells in the blood.
Also, if necessary, the child may be prescribed additional examinations if his condition requires it. JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) uses the most modern diagnostic methods:
- magnetic resonance (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) imaging;
- blood chemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- echocardiography;
- daily ECG monitoring.
Preparing for analysis
The test must be taken on an empty stomach. The last meal should be 8-10 hours before blood sampling. The day before, you should avoid eating sweet, fatty, and protein foods. You can drink water as usual. You should also avoid intense physical activity and psychological stress, as this may distort the results of the study.
If the child is taking any medications, it is necessary, if possible, to stop taking them several days before the test. If this is not possible, then you should warn the doctor who will perform the procedure about taking medications.
Treatment
Based on the results of the studies, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment. First of all, parents will be advised to change the baby’s diet if he has already switched to adult food. The child’s diet should contain the following products:
- beet;
- sour berries;
- sunflower seeds;
- olive oil;
- citrus;
- cocoa;
- ginger.
These products help thin the blood. It is equally important to exclude from the menu what, on the contrary, further increases the thickness of the blood. This applies to bananas, smoked products, soda, buckwheat, rose hips and walnuts. The drinking regime must be observed. The child should be given more clean water, green or herbal tea, fruit and vegetable juices.
Drug treatment
The second direction of treatment is taking medications prescribed by a doctor. Typically, these are medications that help thin the blood. The choice of drugs is made taking into account the age of the child, as well as the reason that caused the blood thickening. There is no universal treatment regimen, since the pathological condition can be caused by various reasons. Such drugs break down large protein molecules, thereby preventing blood thickening.
The main treatment is etiological, i.e. aimed at eliminating the disease or condition that provoked the increase in blood viscosity. If the cause is not addressed, then even after a course of thinning medications, the blood will again become thick.
When to see a doctor
Many parents are interested in what to do if their child has thick blood. There is only one answer: if signs of such a pathological condition appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. This is especially important if the child is very young, since he cannot say that he is feeling unwell. If there are symptoms characteristic of increased blood viscosity, parents should make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist with their child.
JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in the center of Moscow employs specialists with extensive experience. They have completed internships in well-known foreign clinics. You can contact a specialist regardless of the child’s age. Our cardiologists work with both newborns and older children.
How to make an appointment with a pediatric cardiologist in Moscow
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow, near the Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya, Mayakovskaya, Novoslobodskaya and Tverskaya metro stations. There are several specialists on staff, so you can make an appointment even on a weekend or holiday. To do this, fill out the online registration form on the website - everything is simple here, just follow the system prompts. You can immediately choose a specialist and any convenient time.
Another option for making an appointment is to contact us at contact number +7. We will help you choose a specialist and a convenient time for consultation. Do not put off visiting a doctor until later, as the child’s future health depends on it.
Symptoms of thick blood in a child
Abnormalities in blood composition can only be accurately identified through laboratory analysis. But some external signs and symptoms allow one to suspect it. Thus, thick blood in a child causes the following manifestations:
- cyanosis of the skin;
- drowsiness and lethargy;
- headache;
- swelling of the limbs;
- severe heaviness in the arms and legs;
- cold extremities;
- dyspnea.
In older children, you may notice a deterioration in concentration, a state of general weakness and apathy. Such sudden changes without any reason should alert parents. Symptoms of thick blood in children in rare cases include watery and burning eyes, complaints of bloating and constipation.