Enzymes are a large group of substances that are involved in the processing of compounds. The main task is to speed up biochemical reactions. As follows from the nature of the named group of structures. That is, they act as so-called catalysts.
Amylase is an enzyme that is involved in the breakdown and processing of starch molecules, which makes it possible to quickly convert it into different types of saccharides.
Another name for the substance is diastase. It is produced by the salivary and pancreas glands.
There are several main types of connection.
Among them:
- Alpha amylase. The most important in the human body. Participates in the digestive process. Also in carbohydrate metabolism as such. Therefore, it acts as a key structure in metabolism. Along with other substances that exist separately.
- Beta amylase. Not found in the human body. It is the main one in plants and fungi. It promotes the same metabolic processes, albeit those that occur in the organisms of other forms of life. In particular, plant-based. Otherwise, the essence is approximately the same as in humans.
- Gamma amylase. It works on the same principle as the alpha variety. But it is also not synthesized in the human body. Therefore, it plays a secondary role in the topic under consideration.
As for the indications for analysis, the substance is examined in several cases:
- Suspicion of diabetes mellitus.
- Inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
- Digestive disorders.
- Past infectious diseases. Especially in the field of gastrointestinal structures.
What is amylase, how important is this compound and in what cases does it deviate from the norm?
What is amylase?
Amylases (alpha-amylase) are a group of enzymes that serve to break down complex carbohydrates inside the pancreas, which is an exocrine gland.
The enzyme is synthesized by acinar cells and then passes through the pancreatic ducts to reach the digestive tract. Amylases are also produced by the salivary glands, small intestinal mucosa, ovaries, placenta and liver. Pancreatic and salivary isoenzymes are detected in the blood at high concentrations by examination.
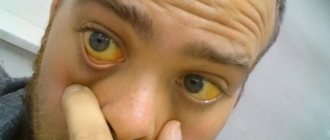
Under normal conditions, amylase is present in small amounts in the blood and urine, however, when the cells of the pancreas have some problem, such as pancreatitis or when the pancreas is blocked by a stone, or in rare cases by a tumor, the enzymes enter the blood circulation more easily, so their concentration increases as in blood and in urine (amylase leaves the body through urine).
Amylase testing is often used by doctors to diagnose pancreatitis. Pancreatic amylase testing (amylase P isoenzyme) is most useful for laboratory diagnosis of acute pancreatitis.
Total serum (blood) is still the most widely used method for diagnosing acute pancreatitis and is accurate to 95% (accuracy of a diagnostic test refers to its ability to provide true values).
Normal values
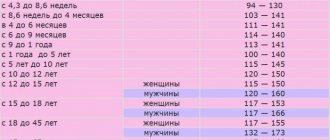
Total amylase by age
- 0-30 days (newborn): 0-6 units/l;
- 31-182 days: 1-17 units/l;
- 183-365 days: 6-44 units/l;
- 1-3 years: 8-79 units/l;
- 4-17 years: 21-110 units/l;
- after 18 years (adults): 26-102 units/l.
Pancreatic amylase by age
- 0-24 months: 0-20 units/l;
- 2-18 years: 9-35 units/l;
- after 18 years: 11-54 units/l.
(Please note that reference intervals may vary between laboratories, so for blood and urine tests please refer to the intervals listed on the report).
What are the reasons for increased amylase?
Reasons that cause an increase in the amount of alpha-amylase in the blood (increased blood amylase is considered to be numbers above 105 units/l for alpha-amylase and above 50 units/l for pancreatic amylase):
- Acute or chronic pancreatitis . With inflammation of the pancreas, the secretion of amylase by cells increases several times
- Cyst, tumor or stone in the lumen of the pancreas . A change in the structure of the gland causes compression of the glandular tissue and its secondary inflammation, which increases the secretion of amylase (amylase level reaches 150-200 units/l).
- Parotitis . Inflammation of the salivary glands also causes increased secretion of amylase.
- Peritonitis . With peritonitis, all organs of the abdominal cavity, including the pancreas, are subject to irritation and inflammatory changes. Such changes increase the activity of pancreatic cells, which leads to increased amylase levels in the blood test.
- Diabetes . Diabetes mellitus causes systemic metabolic disorders, including carbohydrate metabolism. Thus, not all amylase produced by the body will be rationally spent on converting starch into oligosaccharides, which will lead to an increase in its amount in the blood.
- Kidney failure . Since amylase is excreted from the body through the kidneys, insufficient kidney function will cause a delay and increase in the amount of enzyme in the blood. The reasons for the decrease in the amount of amylase in the blood are considered to be figures less than 100 U/L for alpha-amylase.
- Hepatitis in acute or chronic form . With hepatitis, carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted, which entails an increased load on the body's enzymatic systems, including amylase. For a certain time, the pancreas produces a sufficient amount of the enzyme, but subsequently begins to slow down the process of amylase synthesis, which will be reflected in its low amount in a blood test.
- Pancreatic tumors . Some tumors cause degeneration of pancreatic tissue, which makes amylase secretion impossible.
- Also, as a result of injuries, falls from a height and poisoning, amylase secretion may be impaired, either to a greater or lesser extent.
In our clinic, you can consult a gastroenterologist and undergo all the necessary tests, including ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Pancreatic amylase is one of the types of amylase that is produced by the pancreas.
Synonyms Russian
P-amylase isoenzyme, pancreatic alpha-amylase, P-amylase, P-type amylase.
English synonyms
Pancreatic alpha-amylase, pancreatic AML, P-type amylase, P-type alpha-amylase, amylase isoenzymes, amylase isoforms.
Research method
Enzymatic colorimetric method.
Units
U/L (unit per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress and do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Amylase is a digestive enzyme that can break down carbohydrates.
The largest amount of amylase is found in the salivary and pancreas glands.
Amylase, which is produced in the pancreas, is pancreatic amylase (P-type) and is part of pancreatic juice. From the pancreas, pancreatic juice containing lipase passes through the pancreatic duct into the duodenum, where it helps digest food.
Amylase of the salivary glands - salivary amylase (S-type) - digests food starch in the oral cavity.
Normally, a small amount of amylase circulates in the blood. In this case, about 60% is salivary amylase (S-type), and the remaining 40% is pancreatic amylase.
When damage to the pancreas occurs, as in pancreatitis, or if the pancreatic duct is blocked by a stone or tumor, pancreatic amylase (P-type) begins to leak into the bloodstream in large quantities. There is no increase in salivary amylase activity.
Small amounts of amylase are also produced in the ovaries, intestines and skeletal muscles.
What is the research used for?
- An increase in the activity of pancreatic amylase in the blood without a change in the activity of salivary amylase confirms the pathology of the pancreas. For example, in acute pancreatitis, its activity in the blood can increase to 90% of the total amylase activity.
- For the diagnosis of pancreatitis in the postoperative period, when the activity of total amylase is increased.
- If pathology of the salivary glands, ovaries or bronchi is suspected.
When is the study scheduled?
- When the diagnosis of “acute” or “chronic pancreatitis” is confirmed.
- If you suspect a disease of the salivary glands and ovaries.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Age | Reference values |
| 1 – 10 years | |
| 10 – 18 years | |
| > 18 years old |
Interpretation of the results of the analysis for pancreatic amylase is carried out taking into account the assessment of the total amylase activity in the blood or urine. If the total amylase activity is increased and the activity of pancreatic amylase is decreased, then damage to the pancreas is unlikely and pathology of the ovaries, intestines, bronchi or other organs must be excluded.
Reasons for increased pancreatic amylase activity
- Acute pancreatitis. In this disease, the activity of pancreatic amylase can be significantly higher than normal and constitute a larger percentage of the activity of total amylase. However, in some patients with acute pancreatitis, amylase may increase slightly or even remain normal. In general, amylase activity does not reflect the severity of pancreatic damage in pancreatitis. For example, with massive pancreatitis, sometimes the death of most of the cells that produce this enzyme occurs, so its activity may not be changed.
- Chronic pancreatitis. With it, amylase activity is initially moderately increased, but then may decrease and return to normal as damage to the pancreas worsens.
- Decompensation of diabetes mellitus is diabetic ketoacidosis, both due to high sugar levels and due to the concomitant involvement of the pancreas in the pathological process.
- Trauma to the pancreas.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Blockage (stone, scar) of the pancreatic duct.
- Acute appendicitis, peritonitis.
- Perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer.
- Acute cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Ruptured aortic aneurysm.
- Macroamylasemia is a condition where amylase binds to large proteins in the serum and therefore cannot pass through the glomeruli, accumulating in the blood.
Reasons for decreased pancreatic amylase activity
- Decreased pancreatic function.
- Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) of the pancreas is a severe hereditary disease associated with damage to the exocrine glands (lungs, gastrointestinal tract).
- Removal of the pancreas.
What can influence the result?
- Captopril, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives, furosemide, ibuprofen, and narcotic analgesics can increase amylase activity.
- Chronic renal failure sometimes leads to increased activity of pancreatic amylase.
- Elevated cholesterol can cause decreased activity of pancreatic amylase.
What to do if amylase is low?
Low levels of the enzyme are much less common than high levels. Such changes in the analysis are typical for pancreatic failure, cystic fibrosis, severe liver damage (liver failure), pancreaectomy (removal of the pancreas).
Increased blood cholesterol levels can lead to low pancreatic amylase levels. In children of the first year of life, the level of the enzyme is much lower than in adults. This is due to the fact that the food they receive is devoid of sufficient amounts of complex carbohydrates.
Standard tables
We will talk about the most active form of the substance - the so-called pancreatic amylase.
Among women
| Age (years) | Blood amylase level (U/l) |
| 10-16 | Up to 31 |
| 16-25 | 37-39 |
| 25-50 and older | 35-50 |
If we talk about the alpha variety, the norm of amylase in women in the blood will be 20-160 U/liter, regardless of age.
In men
| Age (years) | Indicator in Units per liter of blood |
| 10-16 | Up to 35 |
| 16-25 | 36-37 |
| 25-50 and onwards | 35-50 |
The norms of amylase (alpha) in men will be approximately the same as in the fairer sex: 20-160 U/liter.
In children
| Life period | Norm in U/l |
| 6-12 months | Up to 23 |
| Up to 10 years | 31-32 |
The norm of amylase (alpha) in children under 2 years of age will be 5 - 65 U/l, then according to adult values.
During pregnancy
During gestation, the volume of the substance is determined by a number from 20 to 100 units.
As for pancreatic amylase, the amount is approximately equal to that found in women outside pregnancy, 20-160 U/liter of blood.
What is dangerous about changes in amylase levels?
In itself, the condition when amylase is elevated does not have clinical consequences for the body, however, it is an important marker of pancreatic damage. If an increase in the enzyme index is detected, the analysis is usually monitored within 24 hours, which makes it possible to assess the dynamics of the pathological process.
A decrease in the level of the enzyme against the background of deterioration in the patient’s well-being indicates severe destruction of pancreatic tissue.
You should pay close attention to the situation. full list of questions ‹ Previous page | Next page >
Decoding the results
Competent interpretation of the study results can only be performed by a doctor; self-medication is unacceptable. Normally, the enzyme concentration should not exceed 53 U/l. If the indicators deviate from the norm, the doctor prescribes an additional examination in order to make an accurate diagnosis and choose the most effective treatment method.
Important Notes:
- determination of the enzyme level is not included in the CBC;
- while taking a number of medications, it is possible to obtain false results;
- the test result is influenced by high cholesterol levels;
- In patients with chronic renal failure, false-positive results may be obtained.
Causes of increased and decreased alpha-amylase
An increase in indicators may be caused by the following reasons:
- pancreatic injury;
- inflammatory process;
- malignant degeneration of the pancreas;
- peritonitis;
- perforated ulcer;
- intestinal obstruction;
- pancreatitis;
- appendicitis;
- aneurysm rupture.
To determine the exact cause of the increase in the amount of enzyme and prescribe treatment (if necessary), additional examination is carried out. A decrease in indicators can be observed with cystic fibrosis.
When interpreting the results, not only the level of pancreatic amylase is taken into account, but also the total amount of enzyme. If general indicators are increased and pancreatic enzyme activity is decreased, this indicates that pancreatic pathologies are most likely absent. In such cases, an examination is carried out aimed at establishing an accurate diagnosis.
The most common cause of increased levels is pancreatitis.
Usually, enzyme activity increases significantly, but in some cases it may remain within normal limits. It must be taken into account that the results of this test cannot determine the degree of damage to the pancreas. When the disease becomes chronic, the indicators first increase and then can gradually decrease as the pathological process progresses.
Interference:
- Substances that cause reduction of the sphincter of Oddi (for example, betanehol, diphenoxylate, narcotic analgesics), secretin, ethanol, asparaginase, azathioprine, captopril, cimetidine, clofibrat, corticosteroids, ciproprogeptadin, didanosine, estrogen, eastrocrinic acid, fusemide, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen, and ibuprofen, and ibuprofen, and ibuprofen, and ibuprofen, and ibuprofen Enamic acid , methyldopa, nitrofurantoin, oral contraceptives, pentamine. Phenylbutazone, sulfonamides, sulindac, tetracycline, valproic acid.
- Anabolic steroid.
Diagnostics.
Preparation for the test is an important condition for the correct result.
Indications for examining the amount of amylase are:
- indigestion (vomiting, diarrhea, persistent nausea),
- decreased appetite due to general malaise (weakness, sleep disturbance),
- pancreatic diseases,
- abdominal pain (acute abdomen syndrome),
- damage to the exocrine glands,
- inflammation of the salivary glands.
In most cases, the level of enzyme content is diagnosed if there is a fear of the formation of inflammatory processes in the pancreas. Damaged gland tissue produces a release of amylase into the bloodstream. The amount of biologically active substance released can exceed the norm by tens of times. Enzymes fill the plasma already in the first hours of illness, reaching maximum activity within a day.
“No” to fatty and spicy foods on the eve of the test
Indicators of enzyme circulation in the blood are very important, so you need to prepare for the test in advance.
- Avoid eating spicy foods and fats.
- Don't drink alcohol.
- Avoid overeating.
- No smoking.
- Bring your emotional state into balance.
- Tell your doctor about the possible use of anabolic steroids, diuretics, painkillers, hormonal contraceptives and other medications.