What Can Cause Tension Headaches?
The true reasons for the development of tension-type headache have not yet been clarified, but doctors have identified two provoking factors.
Mental stress
We are talking about a chronic stressful condition, which is accompanied by severe muscle tension. During such tension, compression of the blood vessels located in the thickness of the muscles occurs, which leads to disruption of metabolic processes. It is precisely this “mechanism” of development of the problem that provokes a severe headache - this is a signal that something needs to be done to prevent the development of serious pathologies of a neurological nature. In this case, you need to remove the stress factor.
Incorrect ratio of pain and anti-pain impulses
This problem occurs with frequent anxiety, anxiety, and depression, which cause disturbances in the functioning of mediators. This situation ends with a decrease in the threshold of pain perception, and the person experiences severe headaches from any even minor touch.
Doctors do not separate these two provoking factors, since they are always interrelated. The described condition in almost every case is associated with hypochondria, neuroses and asthenia.
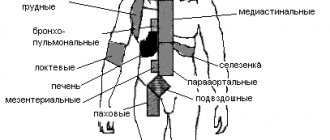
Hemolytic disease of the fetus
In pregnant women, no specific pattern of pathology is observed; sometimes an increase in intrauterine reactions can cause a woman to experience a symptom complex similar to preeclampsia. Hemolytic disease of the fetus can manifest itself in the following ways: intrauterine fetal death in the period from 20 to 30 weeks of pregnancy; edematous, icteric or anemic forms. Common manifestations characteristic of all forms of hemolytic disease of the fetus are the presence of normochromic anemia with an increase in erythroblasts in the blood, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly.
With the edematous version of hemolytic disease in the fetus, the size of the spleen, liver, heart, and glands increases, and hypoalbuminemia increases. These changes are accompanied by pronounced swelling of the subcutaneous fat, ascites, pericarditis, pleurisy, and an increase in the child’s weight by 2 times compared to the norm. With the edematous variant of hemolytic disease of the fetus, pronounced anemia (Er -1-1.5 x 1012/l, Hb 35-50 g/l), erythroblastemia, enlargement and swelling of the placenta are observed. Severe metabolic disorders can cause intrauterine fetal death or the death of a child shortly after birth. The edematous form of hemolytic disease of the fetus is characterized by an extremely severe course, which in most cases leads to death.
With the icteric variant of hemolytic disease of the fetus, the child is more often born from urgent labor, full-term, often with normal skin color. In this case, hemolytic disease of the fetus manifests itself several hours after birth - the child’s skin becomes jaundiced; Less commonly, jaundice is congenital. In newborns with the icteric form of hemolytic disease, the spleen, liver, lymph nodes, and sometimes the heart are enlarged, and there is an intense increase in indirect bilirubin in the blood.
Hyperbilirubinemia is dangerous due to the possibility of damage to hepatocytes, cardiomyocytes, nephrons, and neurons with the development of bilirubin encephalopathy. With kernicterus (bilirubin intoxication), the child is lethargic, sucks poorly, often regurgitates, and develops hyporeflexia, vomiting, and convulsions. The critical level of indirect bilirubin, dangerous in terms of damage to the central nervous system, is more than 306-340 µmol/l in full-term infants and 170-204 µmol/l in premature infants. The consequence of bilirubin encephalopathy may be the death of the child or subsequent mental retardation.
In the anemic form of hemolytic disease, the damaging effect on the fetus is usually small. Anemia, pale skin, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly come to the fore. The severity of the manifestations of hemolytic disease of the fetus is determined by the antibody titer in the pregnant woman and the degree of maturity of the newborn: the disease is more severe in premature infants.
How does HDN manifest?
The symptoms of the disease in question are quite characteristic and can form the basis for making a preliminary diagnosis. The patient will complain of constantly present dull sensations of pressure in the muscles of the neck, temporal muscles, and scalp muscles. They are often described as looking like they are wearing a hoop, hard hat or helmet on their head. Characteristics of pain with TTH:
- Most often, bilateral localization of unpleasant sensations is recorded, sometimes it is unilateral;
- may have a clearly circumscribed location, but is often described as “spill over”;
- the pain becomes more intense with any touch, shock, going down stairs, moving the head, and even blowing wind.
Please note: tension headaches may be accompanied by sensitivity to light and sound. Nausea and vomiting are not typical for HDN.
Based on how often symptoms appear, TTH is divided into two types.
- Episodic pain. Appears up to 15 times a month, each attack lasts no more than 30 minutes, and can occur during physical activity.
- Chronic pain. The frequency of attacks is more than 15 times a month, and the total duration is 3 months.
The episodic form of the disease always becomes chronic if the person has not received any treatment.
At CELT you can get advice from a neurologist.
- Initial consultation – 4,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,500
Make an appointment
Diagnostic methods
As a rule, a patient with a headache consults a neurologist. At the first appointment with a doctor, the patient must answer a number of questions - how often does a headache occur, what can it be associated with, what time of day does it occur, where is it localized. Then a life history will be collected - the doctor will find out what diseases were previously diagnosed, whether head injuries have occurred recently, and so on.
Often such a full-fledged survey is enough to make a diagnosis, but in order to prevent mistakes, specialists prescribe an instrumental examination, often a computed tomography of the brain. If there are no morphological pathological changes in the structure of the brain, blood pressure levels are within normal limits, and no other reasons for the occurrence of the condition in question have been identified, then the diagnosis is considered complete.
Prevention of tension-type headache
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is a pathological condition of the newborn, accompanied by massive breakdown of red blood cells, and is one of the main causes of the development of jaundice in newborns. Hemolytic disease of newborns (morbus haemoliticus neonatorum) is hemolytic anemia of newborns, caused by incompatibility of the blood of mother and fetus according to the Rh factor, blood group and other blood factors. The disease is observed in children from the moment of birth or is detected in the first hours and days of life.
Hemolytic disease of newborns, or fetal erythroblastosis, is one of the serious diseases of children in the newborn period. Occurring during the antenatal period, this disease can be one of the causes of spontaneous abortions and stillbirths. According to WHO (1970), hemolytic disease of the newborn is diagnosed in 0.5% of newborns, the mortality rate from it is 0.3 per 1000 children born alive.
Clinical symptoms depend on the form of the disease.
The edematous form (or hydrops fetalis) is rare. It is considered the most severe form among others. As a rule, it begins to develop in utero. Miscarriages often occur in early pregnancy. The skin of such a newborn is pale, waxy in color. The face is round in shape. Muscle tone is sharply reduced, reflexes are suppressed. The liver and spleen are significantly enlarged (hepatosplenomegaly). The belly is large and barrel-shaped.
The anemic form is the most favorable form according to the course. Clinical symptoms appear in the first days of a child’s life. Anemia, pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, and an increase in the size of the liver and spleen gradually progress. The general condition suffers slightly.
The icteric form is the most common form. Its main symptoms are:
- jaundice (yellow coloration of body tissues due to excessive accumulation of bilirubin (bile pigment) and its metabolic products in the blood);
- anemia (decrease in hemoglobin (the coloring substance in the blood that carries oxygen) and red blood cells per unit volume of blood);
- hepatosplenomegaly (enlargement of the liver and spleen in size).
Forms.
Depending on the type of immunological conflict, the following forms are distinguished:
- hemolytic disease of newborns (HDN) due to a conflict on the Rh factor;
- hemolytic disease of newborns (HDN) due to blood group conflict (ABO incompatibility);
- rare factors (conflict with other antigenic systems).
Clinical forms:
- edematous;
- icteric;
- anemic.
The following forms of the disease are distinguished according to severity.
- Mild form: diagnosed in the presence of moderate clinical and laboratory data or only laboratory data.
- Moderate form: there is an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood, but there are no bilirubin intoxication or complications yet. This form of the disease is characterized by jaundice that appears in the first 5-11 hours of the child’s life (depending on the Rh-conflict or ABO-conflict), the hemoglobin level in the first hour of life is less than 140 g/l, the level of bilirubin in the blood from the umbilical cord is more than 60 µmol /l, increased size of the liver and spleen.
- Severe form: this includes an edematous form of the disease, the presence of symptoms of damage to the nuclei of the brain by bilirubin, respiratory disorders and cardiac function.
Prevention of hemolytic disease in newborns.
The basic principles of prevention of hemolytic disease of newborns are as follows.
Firstly, given the great importance of previous sensitization in the pathogenesis of hemolytic disease of the newborn, each girl should be treated as a future mother, and therefore girls should undergo blood transfusions only for health reasons.
Secondly, an important place in the prevention of hemolytic disease of newborns is given to working to explain to women the harm of abortion. To prevent the birth of a child with hemolytic disease of the newborn, all women with Rh-negative blood factor are recommended to administer anti-O-globulin in an amount of 250-300 mcg on the first day after an abortion (or after childbirth), which promotes the rapid elimination of the child’s red blood cells from the blood mother, preventing the synthesis of Rh antibodies by the mother.
Thirdly, pregnant women with a high titer of anti-Rhesus antibodies are hospitalized for 12-14 days in antenatal departments at 8, 16, 24, 32 weeks, where they are given nonspecific treatment: intravenous infusions of glucose with ascorbic acid, cocarboxylase, prescribed rutin, vitamin E, calcium gluconate, oxygen therapy; if a threat of miscarriage develops, progesterone and endonasal electrophoresis of vitamins B1 and C are prescribed. 7-10 days before birth, phenobarbital 100 mg three times a day is indicated.
Fourthly, when a pregnant woman’s anti-Rhesus antibody titres increase, delivery is carried out ahead of schedule at 37-39 weeks by cesarean section.
Treatment for tension headaches
This type of headache requires the use of certain medications. If the type of tension headache in question occurs infrequently, then a single dose of non-steroidal/anti-inflammatory drugs will help. With frequent repetitions of episodic TTH, doctors suggest that the patient take a course of the same medications in order to “break” the cycle of repetitions.
Please note: if after the first course of the described therapy there is no relief, then repeating the treatment is not advisable.
Acupuncture
- Cost: 3,000 rub.
- Duration: up to 20 minutes
More details
Often, TTH is accompanied by spasm of the pericranial muscles (muscles of the back of the neck, masticatory, temporal, scalp muscles), which worsens the patient’s well-being and intensifies the main symptom. To get rid of this unpleasant feeling, it is recommended to take muscle relaxants. Also for this purpose, injections of local anesthetics (lidocaine, naropin) are performed into spasmodic muscles.
People with pronounced symptoms most often do not seek qualified medical help, but try to solve the problem on their own by taking painkillers. This will not solve the problem - treatment of tension-type headache requires an integrated approach. As an additional therapy, a specialist may prescribe vitamins, nootropic or sedatives.
Additional treatment methods play an important role in successful therapy:
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- auto-training and psychotherapist assistance;
- physiotherapy (electrosleep, electrophoresis on the cervical spine with various drugs).
Treatment of chronic tension headache
If a tension headache occurs in a chronic form, then it is forbidden to take classical drugs with an analgesic effect! Not only will they not relieve pain, but they will also complicate the process of full treatment. Doctors prescribe antidepressants, which must be taken for six months according to a specially developed individual regimen. It is also possible to prescribe other medications from the group of antidepressants; the course of therapy is at least 60 days.
This treatment tactic involves not only getting rid of pain, but also eliminating the cause of tension headaches - for example, antidepressants solve the problem of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Physiotherapeutic procedures (the same as in the case of therapy for episodic pathology) will also have an additional therapeutic effect.
Tension headaches require a professional approach to treatment. If symptoms of this disease appear, it is advisable to contact specialists at CELT - all necessary diagnostic measures will be carried out and treatment will be prescribed.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Almost every second newborn baby has physiological jaundice - this is not a dangerous phenomenon. However, the skin of babies can turn yellow for another reason - due to the so-called hemolytic disease of newborns, the consequences of which are often much more serious. If your baby has been diagnosed with this, do not despair! With timely medical care, all processes in his small body will quickly return to normal and the risk of damage to the nervous system will be eliminated. To understand what the consequences of hemolytic disease will be, you first need to understand what this disease is and why it urgently needs to be treated. Let’s look at the example of hemolytic disease of newborns with group incompatibility, because it occurs more often and is somewhat easier than with Rh conflict. In this case, the mother has the first blood group 0 (I), and the fetus has another, usually the second A (II) or the third B (III). The basis of this disease is the massive breakdown of the fetus’s red blood cells due to the incompatibility of its blood and the mother’s blood. “Hemolysis” translated from Latin means destruction. The expectant mother, having the first blood group, has no antigens. Let’s denote the mother’s body in the picture with a “minus” sign. And the future child, i.e. the fetus has a second blood group, i.e. there is an antigen in his blood. In the picture, we will denote the fetus with a “plus” sign. If the fetus has an antigen, the mother’s immune system will begin to consider this antigen as a foreign enemy agent and will begin to produce protective antibodies (JgG) against this antigen. These antibodies can begin to be produced early - even during pregnancy, or they can appear almost during childbirth. The shorter the pregnancy period at which antibodies began to be produced, the more they accumulate and the more likely the baby will become more severely ill. These antibodies rush into the bloodstream to the fetus through the placenta, settle on the baby’s red blood cells and begin to destroy them. A lot of them are destroyed, and a large amount of bilirubin pigment is released from the destroyed red blood cells. This bilirubin is the "bad" bilirubin, it is called indirect bilirubin and is very toxic. It must be neutralized in the liver. But since at birth the child’s liver enzyme system is immature (it matures postnatally), it will not be able to completely utilize all bilirubin, there will be a lot of it, and its peculiarity is to accumulate in those body tissues that contain fat, then the ideal place for accumulation of bilirubin will be subcutaneous fatty tissue and clinically we will see jaundice of the skin. In addition, you should know that red blood cells also perform the function of delivering oxygen to all organs. And once they are destroyed, the oxygen supply function is disrupted, and first of all, one of the most vulnerable and not yet very developed organs of newborns will suffer - the brain, because it primarily needs oxygen supply. Why is indirect bilirubin toxic? Because it damages the cells of the heart, liver and, to a greater extent, brain cells, bilirubin intoxication occurs, characterized by lethargy, regurgitation, vomiting, pathological yawning, and decreased muscle tone. And at high critical values above 340 μmol/L in full-term infants and at 160 μmol/L in premature infants, “kernicterus” occurs - this is bilirubin intoxication of the brain, when the nuclei of brain cells are stained with bilirubin: muscle hypertonicity, stiff neck, and sharp “brain” appear. scream, the child reacts to all stimuli, a large fontanel bulges, muscles twitch, convulsions, strabismus, and breathing problems appear. The brightness of the icteric shade depends on the amount of this pigment in the newborn’s body. Jaundice can occur early (perhaps even in the first day of a child’s life) and persists for a long time. The liver and spleen are characterized by enlargement. The child's skin color is bright yellow, the sclera - the whites of the eyes - may be stained. If there is anemia, and there certainly is, because... red blood cells die, the baby will be pale and the jaundice may not seem so bright. Treatment for mild and moderate forms of this conflict is often carried out conservatively. Children undergo phototherapy, i.e. treatment with light, because When exposed to light, indirect bilirubin is destroyed. Adsorbents are also prescribed to help the intestines fight toxins. In severe conditions, a replacement blood transfusion is performed. If treatment is started late, the consequences of hemolytic disease can be dangerous - from the death of the baby to severe neurological disorders with signs of cerebral palsy, delayed psychophysical development, deafness, and speech impairment. Mild and moderate forms of pathology rarely (up to 10%) can leave a slight delay in motor development with a satisfactory state of mental abilities; conduct disorder; impaired movement functions, strabismus, hearing and speech impairment. Children with previous HDN do not tolerate vaccinations well, are prone to developing severe allergies and can often suffer from infectious diseases for a long time; teeth are often susceptible to enamel destruction and caries. During the treatment period, the baby is removed from breastfeeding, because Through breast milk, antibodies (JgG) will flow to the baby and jaundice will increase. After 15-20 days, after the antibodies disappear from the milk, the woman can breastfeed. Diet is very important for the mother of a newborn. Proper nutrition for a woman will ensure the supply of vitamins and eliminate exposure to harmful chemical additives. The mandatory diet must contain vegetables and fruits, fish, and liver. The main thing is that the products are fresh and natural. Children who have suffered from tension-type headache should be observed by a neurologist in a clinic and receive rehabilitation treatment. And in conclusion, I want to say that even having understood very little of what I described above, any reasonable person, including one who is far from medicine by occupation, is able to understand the consequences of hemolytic disease. The article was prepared by Natalya Fedorovna Kononova, head of the department of organizing medical care for children in educational organizations of the State Budgetary Institution of Healthcare of the Yamal-Nenets Autonomous Okrug “Gubkinsky City Hospital”.