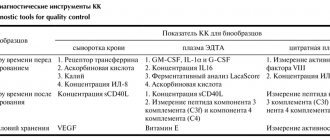
November 14, 2018
All tests in 1 day
One type of laboratory diagnosis is a general blood test. It allows you to identify a large number of pathologies, such as malignant tumors, infectious, inflammatory diseases, etc. It can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of patient treatment. After all, a general blood test can tell a lot about the state of the body.
Only specialized doctors can correctly decipher a general blood test. Therefore, without the appropriate medical knowledge, you should not even try to do it yourself. But it will not be superfluous to know by what indicators the blood is analyzed, as well as the norms of the test result. You will find this information in our article.
Types of leukocytes
The leukocyte formula reflects the ratio of five main types: lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils. Different types of white blood cells are different in structure and purpose. Depending on whether they contain granules that are capable of perceiving color, leukocytes are of two types: granulocytes, agranulocytes.
Granulocytes include:
- basophils - can perceive alkaline color;
- eosinophils – acidic;
- neutrophils - both types of dyes.
Agranulocytes include:
- two types of lymphocytes (B- and T-lymphocytes);
- monocytes.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils come from red bone marrow, they are formed from a single stem cell, which is the ancestor of all blood cells. However, stem cells do not immediately turn into neutrophils. Between these two forms there are several stages, several intermediate forms.
There are 6 types of neutrophils:
- myeloblasts;
- promyelocytes;
- myelocytes;
- metamyelocytes;
- band neutrophils;
- segmented neutrophils.
Most of all is in the blood of the latter. They are present in an amount of 40–75% of the total number of leukocytes. The number of rod-shaped neutrophils is significantly smaller, they can be 1–6%. The number of young cells does not reach 1%.
Functions of white cells
Lymphocytes. T lymphocytes destroy foreign microorganisms and cancer cells. B lymphocytes are responsible for producing antibodies.
Monocytes. They participate in phagocytosis, directly neutralizing foreign bodies, as well as the immune response and tissue regeneration.
Eosinophils. Capable of active movement and phagocytosis. They actively participate in the formation of inflammatory and allergic reactions, capturing and releasing histamine.
Basophils. They ensure the migration of other types of leukocytes into tissues to the site of inflammation and take part in allergic reactions.
Neutrophils. The main purpose is phagocytic protection, that is, the absorption of foreign bodies. In addition, they release bactericidal substances.
Definition and Purposes of Purpose
CBC (complete blood count) is a laboratory diagnostic method for assessing the condition of the body and searching for the source of pathology. This test can be prescribed by a doctor of any specialty. In what cases is OAC prescribed:
- For prevention during medical examinations. The composition of the blood is relatively constant and rarely goes beyond the normal range in a healthy person. And some diseases may not affect your well-being for a long time, and then a preventive test will become a reason for subsequent examination.
- When the first symptoms of illness appear. Analysis in this case can make it possible to determine the nature of the disease, the degree of intensity of inflammation or an allergic reaction.
- OAC may be re-prescribed to monitor the course of the disease over time. Also to assess the effectiveness of the therapy.
Normal leukogram values
The leukocyte formula of the blood of healthy adults is as follows:
| Kinds | Content % | Absolute value (number of cells X 10?/l) |
| Lymphocytes | 19-37 | 1,2-3 |
| Monocytes | 3-11 | 0,09-0,6 |
| Band neutrophils (immature) | 1-6 | 0,04-0,3 |
| Segmented neutrophils | 47-72 | 2-5,5 |
| Basophils | 0-1 | 0-0,065 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5-5 | 0,02-0,3 |
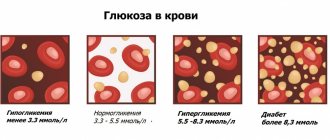
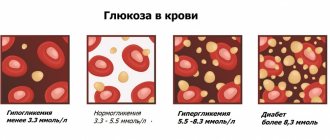
Changes in the leukogram are usually denoted by terms with specific endings. As the level increases, endings such as “oz” (“ez”) or “ia” are added to the name of a particular type of leukocyte. For example: lymphocytosis, eosinophilia, monocytosis, etc. When the level of leukocytes decreases, it is customary to add the ending “singing” to the name: lymphopenia, neutropenia, eosinopenia, etc.
In this case, a distinction is made between relative and absolute change. In the first case, we are talking about a deviation from the norm in the percentage of leukocytes. In the second, they talk about a deviation from the norm both in percentage terms and in absolute terms, which is understood as a change in the total number of cells per unit volume of blood.
Leukocytes differ in their structure and purpose
It should be said that the leukocyte formula depends on age. This must be taken into account when assessing it during examination and diagnosis of diseases in children.
When is the test prescribed?
A clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula is indicated for patients with various pathologies. It allows you to assess a person’s health status with a comprehensive and timely diagnosis of diseases, including those occurring in a latent form.
Indications for a clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula are:
- medical examination or routine medical examination;
- preparation for surgical treatment;
- infection or suspected infection;
- suspicion of inflammation or parasitic infestation in the patient’s body;
- allergic reactions;
- prescribing certain medications;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Before donating capillary blood, it is recommended not to drink alcohol during the day, not to eat for 2-3 hours, not to smoke for 30 minutes and to avoid stress and excessive physical activity.
How to determine
The leukocyte formula is calculated by a laboratory assistant by viewing the blood under a microscope (leukogram count per hundred cells).
In addition, a hematology automatic analyzer is used. In case of deviations from the norm, a microscopic examination of the smear is additionally carried out, while the morphology of the cells is described and the leukogram is clarified.
The use of automatic equipment allows you to obtain the most accurate result: more than 2000 cells can be analyzed, while under a microscope - a maximum of 200. When examined using an analyzer, the result is more objective.
Automatic counting also has a drawback: the inability to divide neutrophils into segmented and band neutrophils. But in the case of a large number of young forms, the equipment records a shift to the left.
Monocytes
Monocytes are cells of the immune system that are among the first to respond to the penetration of aggressors into the body. If the forces of local immunity could not contain the attack of bacteria, fungi or viruses, then it is monocytes that are the first to rush to protect health.
Monocytes are formed in the red bone marrow and released into the blood. There they begin to actively function, but this does not last long, only 2-3 days. Then, using their ability to move, they move beyond the vessels through special small pores between the cells and penetrate into the tissue. There, monocytes slightly change their structure and turn into macrophages - more effective phagocytes.
Reasons for changes in leukogram
An increase in the level of lymphocytes (lymphocytosis) is observed in the following pathologies:
- acute viral infections: chickenpox, measles, mononucleosis, rubella;
- chronic bacterial infections: syphilis, brucellosis, tuberculosis;
- lymphomas, lymphosarcoma, lymphocytic leukemia;
- hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis);
- adrenal insufficiency;
- folate deficiency anemia;
- aplastic and hypoplastic anemia.
Lymphocytopenia can develop for the following reasons:
- acute infections;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- renal failure;
- immunodeficiency;
- radiation sickness (acute form);
- taking corticosteroids.
An increase in the level of neutrophils in the blood (neutrophilia) is observed in the following conditions:
- bleeding is acute;
- intoxication;
- bacterial diseases in acute forms;
- taking corticosteroids;
- tissue necrosis.
The content of neutrophils decreases for the following reasons:
- bacterial infections: typhoid fever, brucellosis, tularemia;
- viral infections: measles, hepatitis, rubella;
- toxic effects to which the bone marrow is exposed: drugs, ionizing radiation;
- autoimmune diseases;
- hypersensitivity to medications;
- Benign chronic neutropenia is hereditary.
Monocytosis, in which the level of monocytes in the blood is increased, may indicate the following disorders:
- subacute, chronic infections caused by bacteria;
- hemoblastoses;
- systemic autoimmune diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis;
- parasitic infections.
A low level of monocytes is assessed in combination with lymphocyte indicators, which is important when diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis.
Basophilia (increased levels of basophils in the blood) is observed in chronic myeloid leukemia and erythremia.
An increased level of eosinophils is observed in the following conditions:
- allergies;
- Loeffler's endocarditis;
- scarlet fever;
- parasitic infections;
- chronic skin diseases: eczema, psoriasis;
- eosinophilic leukemias;
- recovery phase of infectious diseases.
Causes of low eosinophil levels (eosinopenia) may include:
- typhoid fever;
- increased adrenocorticosteroid activity.
References
- Atlas of medical microbiology, virology and immunology / ed. A.A. Vorobyova, A.S. Bykova. - M.: Medical Information Agency, 2003. - P. 37.
- Prevention of streptococcal (group A) infections. Federal clinical guidelines, 2013 - 43 p.
- Clinical recommendations (treatment protocol) for providing medical care to children with tonsillitis (acute streptococcal tonsillitis), 2015. - 29 p.
- Levanovich, V.V., Bannova, S.L., Timchenko, V.N. Evolution of streptococcal infection. Guide for doctors. - SpetsLit., 2015. - 495 p.
- Kanwal, S., Vaitla, P. Streptococcus Pyogenes. — In: StatPearls, 2021.
- Lab Tests Online: website. Antistreptolysin O (ASO), 2021. - URL: https://labtestsonline.org/tests/antistreptolysin-o-aso.
Leukogram shift
Modern automatic blood analyzers quickly and accurately calculate the complete leukocyte formula, which greatly facilitates diagnosis
When the leukogram is deciphered, nuclear shifts are taken into account. These are changes in the ratio of mature and immature neutrophils. In the blood formula, the different forms of neutrophils are listed in order from young to mature (from left to right).
There are three types of shifts: left, left with rejuvenation, and right.
With a left shift, myelocytes and metamyelocytes are present in the blood. This change occurs through the following processes:
- acute inflammation: pyelonephritis, prostatitis, orchitis;
- purulent infections;
- acidosis;
- bleeding is acute;
- poisoning with toxins;
- high physical activity.
With a left shift with rejuvenation, forms such as myelocytes, metamyelocytes, promyelocytes, myeloblasts, and erythroblasts can be found in the blood. This is observed in conditions such as:
- leukemia (chronic, acute);
- erythroleukemia;
- metastases;
- myelofibrosis;
- coma.
Video about the types and functions of leukocytes:
With a decrease in the number of band (immature) neutrophils and an increase in the level of segmented (mature forms containing 5-6 segments), they speak of a right shift. With such a change in the leukogram, we can talk about the following pathologies and conditions:
- liver and kidney diseases;
- megaloblastic anemia;
- consequences of blood transfusion;
- radiation sickness;
- vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency anemia.
The degree of shift is assessed using a special index, which is determined by the ratio of the total number of all young neutrophils (myelocytes, metamyelocytes, promyelocytes, band neutrophils) to mature segmented ones. The norms for healthy adults are in the range of 0.05-0.1.
Why is a leukocyte blood formula needed?
The leukocyte formula is the percentage of leukocytes in the blood serum (eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, basophils, monocytes).
This analysis allows you to determine the current state of the immune system, identify inflammatory processes in the patient’s body and determine the etiology of allergies. It is known that leukocytes protect the human body from dangerous microorganisms. One of the main tasks of leukocytes is the destruction of foreign particles. If an inflammatory process occurs in the patient’s body, it is immediately reflected in the leukocyte count.
Complete blood count (CBC/Diff - 5 fractions of leukocytes) - capillary blood in Moscow from day 1
from 290 ₽
Sign up
Clinical blood test (CBC/Diff - 5 leukocyte fractions) + ESR in Moscow from day 1
from 294 ₽
Sign up
Complete blood count (CBC/Diff - 5 fractions of leukocytes) in Moscow from 1 weekday
from 290 ₽
Sign up
When leukocyte counts change in the blood, it is necessary to determine in which direction the deviation occurs. This study will help you quickly find the problem and make a diagnosis. However, it should be taken into account that changes in blood parameters without in-depth diagnostics are not a characteristic and final sign for making a diagnosis.
Platelets
Platelets are also red blood cells. They look like small plates. Their main purpose is normal blood clotting.
Platelets in test results indicate:
- tr.;
- PLT;
- platelets.
Table No. 6: platelet norms in children
There are:
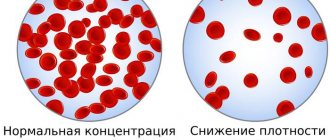
- Thrombocytopenia - when platelets in the blood are less than normal;
- Thrombocytosis - if more than normal.
Let's decipher the results:
- Clinical blood analysis: from light microscope to hematological analyzers
In modern laboratories, platelet indices are also determined.
Structure
Leukocytes are divided according to their structure into granulocytes, which have pinpoint granules in the plasma, and agranulocytes, without additional inclusions. Unlike red blood cells and platelets, these cells are endowed with a nucleus and are able to exit blood vessels and move towards inflamed tissues.
There are two neutrophils in the center, their nuclei are divided into parts (segments)
Granulocytes differ in relation to staining using the Romanowsky method for basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils.
The group of neutrophils is also not homogeneous: according to the shape of the nucleus, they are divided into segmented (the nucleus is divided into parts by constrictions) and rod-nuclear (the nucleus has the shape of an elongated ball).
In the normal blood composition of an adult, the level of segmented neutrophils is 47–75%, and band neutrophils are only 1–6%. “Rods” are considered the precursors of nuclear division; their small number is normally explained by the rapid process of transformation into a segmental, more mature form.
If you are interested in the norms of this indicator in children and the reasons for their deviation, we recommend reading this article.