Heart rhythm disturbances may be associated with changes in the driver of cardiac activity. In such cases, atrioventricular rhythm is often determined, which is also called atrioventricular nodal rhythm. This pathology poses a threat to human life, since the heart rate noticeably decreases.
Atrioventricular rhythm (AVR) is described as an abnormal heart rhythm resulting from impulses originating from the area of the atrioventricular node, the “connection” between the atria and ventricles.
Under normal conditions, the sinus node of the heart determines the speed at which the organ beats—in other words, it is the “pacemaker” or main driver of the heart. With its help, heart rate is maintained at the desired level - in an adult it is 60-90 beats/min.
Electrical activity of sinus rhythm originates in the sinoatrial node and depolarizes the atria. The signal then passes through the atria, the atrioventricular node, along the His bundle and then moves along the Purkinje fibers, finally reaching and depolarizing the ventricles. This sinus rhythm is extremely important because it ensures that the atria necessarily contract before the ventricles.
Video: How the human heart works
The mechanism of human existence
Man as a working multifunctional mechanism. He can perform many actions: eat, drink, walk, sit, look out the window - this list can be endless. The body's vital activity systems are responsible for all of the above. Each organ performs a specific function; it is impossible to replace it with another. Everything is very simple: our eyes are responsible for visual perception, our ears are responsible for auditory perception, our stomach is responsible for digestion, our lungs are responsible for breathing, our brain is responsible for mental and other operations, the spleen and liver are responsible for digestion processes and transport of food in the body, etc. d.
All organs are important and interconnected. Even without one, our body will not be able to function fully, and we, accordingly, will be susceptible to diseases. In the modern world, you can easily determine whether a person is healthy or not. A person’s illness is indicated by the color of his skin, the condition of his teeth, fatigue, exhaustion, etc. Therefore, each of us must take care of our health, namely the proper functioning of our internal organs.
The heart is a vital organ
The heart is a circulatory organ that transports blood through the vessels. It is capable of pumping 4-5 liters of blood per minute. But this is not the final figure; it can reach 30 liters. Based on research data, the weight of the heart is approximately 300 g, width - 7-10 cm, length - 12-13 cm. There is an opinion that if you clench a fist, its circumference will correspond to the size of the heart. But all this is relative and depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the rhythm of life.
The heart is an organ that is involved in transporting nutrients through the blood vessels to the brain and other organs. And as long as it works without deviations, our body does not experience difficulties in its functioning.
But do not forget that this organ does not last forever and can fail and require urgent restoration. Heart problems can appear due to heredity, the influence of the internal environment, alcohol and smoking abuse, frequent stress and lack of sleep, as well as other negative factors. The best prevention is exercise and a proper diet.
Heart structure
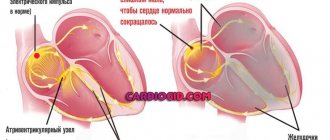
The heart consists of four chambers separated by special partitions. The two chambers are the left and right atrium. The sinoatrial node is located in the right atrium. The other two chambers are the left and right ventricles. The right side of the heart, where the right atrium and ventricle enter, is responsible for venous blood, and the left, where the left atrium and ventricle are located, is responsible for arterial blood.
Between the atria and ventricles there is a valve that prevents blood from flowing in the opposite direction. The heart also has vena cavae, which enter the right atrium, and pulmonary veins, which enter the left atrium.
Diseases associated with the atrioventricular node
Atrioventricular node block
The most common atrioventricular disorder is AV block . This is a cardiac arrhythmia that develops due to delayed or interrupted transmission of signals through the atrioventricular node. Often the block goes undetected and in such cases it is usually determined to be a first degree block. However, severe AV block causes the heart to beat very slowly. This phenomenon causes so-called bradycardia, which sometimes turns into temporary cardiac arrest with all the ensuing consequences. To treat such conditions, a pacemaker is usually used, which stabilizes the impaired transmission of impulses. With such a serious disruption of the AV node, they speak of third-degree AV block.
AV node block can be diagnosed using an ECG, where it is expressed as a prolonged PQ interval, depending on the severity. Congenital AV block is extremely rare, but may occur as part of another congenital heart disease. Most AV blocks are acquired. They usually result from degenerative changes in the heart. For example, inflammation or infection of the heart muscle may contribute to the formation of a blockage. Patients with this disease are first treated with medication to eliminate the arrhythmia. If the condition worsens, patients with 2nd and 3rd degree AV node block usually have a pacemaker implanted, since drug therapy is considered unreliable for severe symptoms.
Video: AV block and its degree on the ECG (atriventricular block)
Accelerated conduction between the atria and ventricles
The opposite of AV block is accelerated conduction between the atria and ventricles. This phenomenon is often determined against the background of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. With this cardiac arrhythmia, one or more additional conduction pathways are usually identified, connecting the ventricles and atria to bypass the AV node. Accelerated transmission is usually manifested by a significant increase in pulse, and tachycardia, that is, rapid heartbeat, can also be detected.
In most cases, tachycardia can be regulated by the patient himself. For example, the heartbeat and rhythm stop slightly when you hold in air while exhaling. In addition, the doctor usually prescribes appropriate drugs like ajmaline to patients with tachycardia. In contrast to the slow transmission of excitation of the sinus node, surgical implantation of a pacemaker with accelerated conduction and tachycardia is not performed in most cases.
Atrioventricular nodal re-entry tachycardia
It may occur suddenly and be accompanied by an increase in normal heart contractions between pathological ones. Symptoms can last from a few minutes to several days, and some patients report no symptoms at all.
Reentry tachycardia becomes a problem when it occurs frequently and continues for a long time, especially in the presence of other cardiac damage.
The main signs of the disease are:
- Fluttering in the chest
- Rapid heartbeat
- Irregular breathing
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Heaviness in the neck
- Fainting or pre-fainting
The most common types of re-entry tachycardia:
- Atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT). It occurs in men and women of any age, although it is more common in young women.
- Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT) . It is the second most common type of re-entry tachycardia. Most often diagnosed in young people.
In the treatment of clinically significant pathology, conservative treatment is initially used. It is very important to take any antiarrhythmic medications exactly as prescribed by your doctor to minimize complications. If medications do not help, catheter ablation is used. During this procedure, the doctor guides one or more catheters through the blood vessels to the heart. Electrodes at the tips of the catheter can apply heat, extremely cold temperatures, or radiofrequency energy to tissue. This allows you to damage a small area of the myocardium and create an electrical block along the path that was causing the arrhythmia.
Sometimes treatment for reentrant tachycardia involves the use of a small implanted device called a pacemaker, which generates electrical impulses that stimulate the heart to beat at a normal rhythm. The pacemaker is placed under the skin near the collarbone during minor surgery. An insulated wire is guided from the device to the heart, where it is permanently attached.
Cystic tumor of the atrioventricular node
Primary cardiac tumors are rare diseases, defined with an incidence of 0.0017% to 0.03% of the total.
Cystic tumor of the atrioventricular (AV) node, also known as AV node mesothelioma, is a benign congenital tumor that is located in the triangle of Koch in the AV nodal region of the interatrial septum of the heart.
The AV nodal region is formed during embryonic fusion, when disrupted, the tissue transforms into a similar tumor. Studies have shown that 10% of people with AV node cystic tumor also have defects in midline development along the central axis of the vertical body (1,9), suggesting a genetic defect associated with migration of embryological tissues and unfavorable heredity. It has been suggested that, unlike a true neoplasm, it is most likely the result of dilatation of cystic spaces rather than cellular replication. In addition, there are no mitoses in this tumor
Because pacemaker implantation does not prevent sudden death in patients with this tumor, surgery is most often performed. There are various options for excision of the lesion, however, due to the rarity of AV node cystic tumors coupled with the difficulty of diagnosing the lesion, surgical resection techniques and therapeutic concepts are not fully standardized. For example, it remains controversial whether the lesion should be completely or partially removed from the base of the interatrial septum.
The prognosis for a cystic tumor of the AV node is favorable with early diagnosis followed by prompt and complete surgical removal of the pathological formation. Cases of sudden cardiac death have shown that this tumor is associated with fatal cardiac dysrhythmia and partial/complete heart block. Thus, despite the fact that the tumor is benign, most patients receive a definitive diagnosis after autopsy. Additionally, it is worth pointing out that tumor size does not appear to be associated with symptoms of lethal arrhythmia or sudden death.
Where is
Today we will look in more detail at one of its components - the sinoatrial node. It's just a scary name.
It is also called the sinoatrial, sinus, and Keyes-Fleck nodes. The sinoatrial node is located in the right atrium, into which the superior vena cava drains. This explains why we previously looked at the structure of the organ.
The sinoatrial node of the heart is a node that is a collection of muscle tissue. The length of such a knot is usually from 1 to 20 mm, and the width is from 3 to 5 mm. The structure of the sinoatrial node includes two types of cells: those that excite electrical impulses for the heart to work, and those that are responsible for conducting the resulting stimuli from the node to the atria.
The outer shell of these cells (membrane) is characterized by high permeability to sodium ions. The presence of sodium ions leads to the occurrence of certain actions in cells that are nearby, this is the so-called excitation wave. Shocks of excitation pass through the heart muscles and provoke their contraction.
The main function of the sinus node is the excitation of electrical impulses. The impulses generated in the node lead to excitation and contraction of the heart. During normal operation this is 60-80 pulses/min.
In many respects, the sinoatrial node is often called the pacemaker of the heart, since a wave of excitation originates in it, which, in turn, provokes the next one.
The contraction propagates along the walls of the atrium at a speed of 1 m/s. This information makes it possible to understand how the node works and where its location is.
What symptoms may indicate impaired conductivity?
With sinoauricular block, an entire heartbeat is lost. After which there is a pause. Patients sometimes feel:
- “fading” or short-term cardiac arrest;
- a sharp, intensified “blow”.
Such isolated symptoms rarely lead to a doctor's attention. More often they are detected after an infection during targeted questioning. An ECG study can confirm the complicating factor of the disease and suspect myocarditis.
For a patient taking digitalis medications, the ECG pattern indicates the beginning of the negative effects of an overdose and the urgent need to discontinue the drug.
Sinoauricular block may occur at night, in which case one should think about the involvement of increased vagal tone. The same mechanism acts on the heart during eye injury (stroke), compression of the carotid arteries.
Intraatrial conduction disturbance is observed in mitral stenosis with hypertrophy of the right atrium.
Atrioventricular block rarely occurs as an accidental phenomenon. If characteristic signs are detected on the ECG, the patient should be carefully examined, since areas of incomplete conduction disturbance eventually develop into complete separation of atrial and ventricular contractions.
Without treatment, this can cause serious consequences, expressed in a decrease in blood supply to internal organs and the brain.
The atrioventricular type is characterized by the presence of a deep and widespread lesion
Often accompanied by:
- post-infectious or septic myocarditis;
- cicatricial changes in the myocardium in diffuse cardiosclerosis, myocardial infarction;
- severe atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary vessels.
There are 3 degrees of such violations. If, after treatment, changes in the ECG disappear, then we can retrospectively speak of incomplete or first-degree damage to the conduction pathways and their restoration.
The second and third degrees are distinguished by perseverance and constancy. Long-term pathology leads to interruption of connections between the atria and ventricles. Clinical manifestations depend on the frequency of spontaneous ventricular contractions.
If the heart rate is in the range of 40–50 per minute, patients experience dizziness and short-term fainting is possible.
The extreme degree of atrioventricular conduction disturbance is the development of Morgagni-Edams-Stokes syndrome. In this case, the frequency of ventricular systoles decreases to 25–20 per minute. The condition can be life-threatening because it causes hypoxia of brain cells.
Conduction system of the heart
The sinoatrial node (in Latin, nódus sinuatriális) is of great importance in the life of the body. Is it really as important as we say it is? The answer is simple, because the heart is a pump for our body, which pumps blood through the veins and arteries. This pump works only due to contractions in the organ. This is possible thanks to the conduction system of the heart.
Integral and very important components of this system are two components: the Kisa-Fleck node and the Aschoff-Tavara node.
Classification of blockades
Impaired conduction or blockades are most conveniently classified by the location of the heart lesion. Therefore they are divided into:
- sinoauricular - in the sinus pacemaker node;
- intraatrial;
- atrioventricular (atrioventricular);
- intraventricular at the level of disorders in the bundle branches.
Each type is divided into degrees and types depending on the ECG pattern. Clinical symptoms are of little importance here, since patients may not feel impaired conduction at all. It manifests itself as evidence of damage to an area of the heart muscle.
In clinical practice, the most common types of blockades are atrioventricular and intraventricular.
History of the origin of terms
The history of the origin of terms begins in the 19th century. The beginning of the 20th century is famous for its morphological studies of the heart, which have entered science and history. In 1806, S. Tavara discovered the atrioventricular node. He was named after the scientist. A. Kis and M. Fleck studied this issue; they accurately described the sinus node. They soon proved that this node is the main, one might say, irreplaceable generator of cardiac impulses.
It was also important that if the sinoatrial node loses its functions, the atrioventricular node automatically becomes the rhythm generator. Thus, these nodes complement each other in case of dysfunction of one of them.
Problems and pathologies
All organs of the body can be subject to the development of various pathologies. No one is immune from this. The heart is one of the organs that suffers most often. And of course, there are problems in the functioning of the nodes of the conduction system of the heart. You should be very careful about these disorders, as they can disrupt the functioning of the conduction system of the heart, which will lead to negative consequences. These problems lead to:
- Partial blockade. In this case, the impulse is carried out slowly.
- Complete blockade, when there is no impulse at all.
Such blockades can occur in different parts of the entire system. For example, it could be a sinus block - an area of disturbances and deviations in this particular node, an atrioventricular block - directly at the site of this node, etc. That is, the place where the blockage occurs is considered the name.
We already know that if the sinoatrial node does not work well, this entails dysfunction of the remaining components of the heart. Therefore, it is worth keeping all organs in order and protecting them as much as possible.
Even if a person leads a completely correct lifestyle, follows all recommendations, regulates work and rest time, and avoids stressful situations, he will not be able to avoid congenital blockages. They, as a rule, do not affect a person’s life and do not cause any discomfort.
Types of impaired conductivity
Depending on the physiological conditions that arise, types of impulse conduction disorders are distinguished:
- creating an obstacle in the area between normal myocardial tissue and the changed area;
- maintaining propagation at a slow speed in the pathology zone;
- involvement of the impulse in the affected area with subsequent blockade;
- the ability to pass in only one direction, interrupting the reverse flow.
One of the rhythm pathologies resulting from the latter option is paroxysmal tachycardia, in which impulses pass only from the ventricles to the atria along the additional bundle of Kent.
A disturbed and expanded form of the ventricular complex indicates extrasystole or altered conduction
Causes of diseases
The causes of heart disease can vary. Sometimes we may not even know that we are a carrier of any pathology. There are the following causes of pathology:
- acquired or congenital heart defects;
- surgical consequences, injuries;
- complications after illness;
- nervous system disorder;
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus, anemia;
- side effects from medications;
- alcohol and smoking;
- blockades that occur for no apparent reason.
People have the opportunity to solve such problems with medication and surgery.
Drug treatment involves taking vitamins and medications, following a diet (increasing the portion of fresh vegetables and fruits, avoiding too fatty and sweet foods). Surgery is used when drug treatment does not work. For example, a person often loses consciousness or the disease becomes malignant. In such cases, it is possible to install a pacemaker. After which such people should be under the constant supervision of specialists.
Features of intraventricular conduction disorders
Intraventricular conduction changes are divided into:
- monofascicular (single bundle branch) - depending on the specific location of the right leg, left anterior or posterior branches;
- bifascicular (two branches) - a common left trunk, a combination of the right leg with one of the left branches;
- trifascicular - 2 left branches and the right one are blocked;
- aborization - concerns the extensive terminal ropes of Purkinje fibers, is regarded as unfavorable in the prognosis of myocardial damage;
- focal or local - characterized by limited manifestation in single ECG leads, does not apply to everyone, the shape of the ventricular complex is not similar to other types of blockades.
In terms of frequency, damage to the left leg and its branches comes first. This correlates with the most common ischemia of the left coronary artery. Identified in elderly patients with severe atherosclerosis.
Disease Prevention
Nowadays, every person has some kind of health problem. These can be acquired diseases or congenital. Unfortunately, not every person will be able to afford regular treatment or wellness activities. But this does not mean that you need to resign yourself to health problems. Experts recommend following some rules that are effective and necessary in order to prevent disruption in the functioning of these organs. With their help, you can not only maintain your health level, reduce the risk of new ones, but also alleviate the form of existing diseases. These rules include:
- correct daily routine;
- balanced diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- avoidance of stressful situations;
- timely contact with specialists.
It will not be difficult to follow such rules, but the result will not be long in coming. The most important thing is to follow the systematic implementation and learn to enjoy them.
This is how we learned where the sinoatrial node is located, what it is responsible for, and how to maintain stable heart function for many years. Take care of yourself, don't get sick! And most importantly, monitor your health.
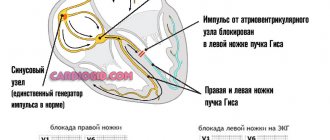
Right and left bundle branch block: causes, symptoms and treatment
If the conduction of impulses in the His system changes, an extremely serious pathology occurs that disrupts the normal functioning of the heart. Bundle branch block (BNBB) leads to changes in the nature or complete interruption of the contractility of the heart zones.
Most often, minor blockades do not bother the patient at all and are detected during preventive examinations. However, in order to prevent the condition from worsening, it is important to begin timely treatment. To understand what the His bundle is, it is important to understand the physiology of the conduction system as a whole.
Description of the conduction system of the heart
Conduction system of the heart
The heart is an amazing organ with a number of functions. One of them is the conduction function performed by the conduction system. It consists of several formations, namely:
Otherwise, this formation is called the Kisa-Flaca node, and it is from here that the impulse begins its journey. It is located between the vena cava, and more precisely, between their mouths. The length of this node is 10–15 mm, and the formation itself is represented by two types of cells. P cells are needed to create an impulse, and T cells are needed directly to carry it out.
Another name is the Aschoff-Tavara node, located in the right atrium. The length is half that of the previous knot. Also consists of T and P cells. Forms normal sinus rhythm.
One of the most important and largest formations of the conduction system of the heart. Consists of branching and initial segments. The latter is not associated with the myocardium.
The branching one is divided into 2 large branches - right and left. Both of these legs run along the two sides of the interventricular septum. The left one branches into 2 more branches, innervating the left ventricle.
The right one is responsible for transmitting excitation to the right ventricle.
Further branching leads to the formation of this formation, which is responsible for the contractility of the ventricular myocardium.
The process of conducting an impulse itself goes through several stages:
- Formation of an impulse in the Kisa-Flaca node. This process is not reflected on the ECG. The formed impulse reaches the atria.
- Next, the excitation, along three tracts (Thorel, Bachmann, Wenckebach), reaches the atrioventricular node.
- From the AVU, the impulse travels through the surrounding myocardium and also passes into the His bundle.
- Along the His bundle, the impulse travels to its right and left branches and further to the Purkinje fibers, excitation of the ventricles.
It is worth noting that normally the pacemaker is the Kisa-Flaca node. Excitation centers of the second and third order can play the role of a driver only in conditions of formed pathology.
Classification of blockades
Types of blockades
If we talk directly about conduction disorders in the His bundle, then depending on the number of affected bundles, the blockade should be divided into the following:
- Single-beam.
- Double-beam.
- Three-beam.
Also, some authors identify the following bundle branch blocks:
- Local. The problem is clearly localized and changes in impulse conduction are recorded exclusively at a given point.
- Transitional. There is a slight block, so normal excitation can alternate with pathological one.
- Alternating. There is no clear localization. During an inspection, a violation can be registered in any department and then change its location.
- Complete blockade of the right leg.
- Complete bundle branch block in the area of the left bundle branch.
- Incomplete block of the His bundle in the right or left leg.
The arborization blockade should also be highlighted. The disorder is located in the lower parts of the Purkinje fibers. Thus, there is a large number of various blockades, which can be distinguished using an electrocardiographic examination (ECG).
Important: incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch often does not cause any symptoms and does not imply danger. In diagnostic terms, such conditions are quite complex and are detected exclusively by performing an ECG.
Causes
Bundle branch block rarely occurs as an independent condition. Mostly it appears due to some pathology. So, the following causes of this disease are distinguished:
- Heartfelt. The most common pathological conditions in which conduction disturbances are noted in the right and left bundle branches are cardiovascular diseases. In particular, such blockades are observed during heart attacks, as well as coronary heart disease.
- Pulmonary. Against the background of prolonged hypoxia, which occurs due to problems with the respiratory system, disruptions in the conduction system of the heart are also observed.
- Neurological. Problems with the autonomic nervous system play a big role.
- Medicinal. Taking medications incorrectly can also lead to problems. Diuretics or glycosides can lead to this complication.
- Toxic. Against the background of poisoning, disturbances in the conduction system may occur. The most common toxic agents are alcohol and smoking products.
- Metabolic. Violation of electrolyte metabolism can also manifest itself as complete or incomplete blockade of the right bundle branch.
- Endocrine. Occurs against the background of any hormonal disorder. Most often, this may be a lesion of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands. Also, one of the diseases in which conduction disturbances can be detected is diabetes mellitus.
- Idiopathic. In this case, the cause of the bundle branch block cannot be identified on an ECG or other examination.
Thus, there are a number of reasons that lead to disturbances in the conduction system. To get rid of this problem, it is extremely important not only to identify the main etiological factor, but also to correct the underlying disease, which requires consultation with a doctor.
Symptoms
Symptoms of bundle branch blocks are:
- Dizziness.
- Feeling of heart failure.
- General weakness.
- Dyspnea.
- Bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
- Fainting.
It is worth noting that if there is an incomplete blockade of the right leg, the patient may not have any complaints at all. Its detection is possible only during an ECG examination, so it is determined during a preventive examination by the attending physician. This is why it is so important to visit specialists in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of “incomplete” or “complete” His bundle block, the doctor will need a number of data. The first thing that helps to suspect this problem is the patient’s complaints. So, the patient may complain of general weakness, shortness of breath, loss of consciousness. In some cases, chronic illnesses or the patient's lifestyle may play a role.
Auscultation plays an important role in the physical examination. In this case, heart rhythm disturbances can be detected. Percussion examination can reveal changes in the cardiac boundaries. In any case, most often this is a manifestation of the underlying disease, and therefore does not have much diagnostic significance.
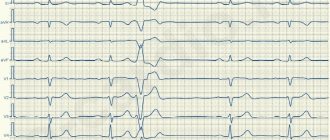
The most important examination for this pathology is an ECG. More details about the manifestations can be found in the table.
LOCATION ECG DATA
| Right leg (hereinafter PN) | On the ECG, with blockade of the right bundle branch, a deviation of the electronic axis of the heart (EOS) to the right is noted. There is an expansion of the QRS complex. |
| Anterior branch of the left leg | Q waves are detected in the first lead, as well as an R wave in the third lead. Deviation of the heart axis to the left. |
| Posterior branch of the left leg | An R wave is noted in the first, and a Q wave in the third. Deviation of the heart axis to the right. |
| Anterior and posterior branch | The axis of the heart is horizontal. In some cases, it may deviate to the left. A wide R wave is recorded in the first lead. |
| PN + anterior branch | A combination of the above symptoms is noted. Deviation of the heart axis to the right. |
| PN + posterior branch | A combination of the above symptoms is noted. Deviation of the heart axis to the right. |
| Three-bundle blockade | The ECG shows the atrioventricular type of block. |
If, during a regular ECG, the blockade of the legs cannot be detected, but the doctor suspects this particular pathology, Holter monitoring is prescribed. During this examination, throughout the day, the patient wears a compact ECG device that records all attacks of cardiac conduction disturbances. With this type of ECG, incomplete blocks of the right bundle branch are detected.
Therapy
In order to treat blockade of the right and left bundle branches, in addition to treating the underlying disease, the doctor prescribes the following therapy:
- Diet.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Physiotherapy.
You need to understand that to completely get rid of the problem, it is extremely important to treat the underlying disease. That is why it is so important to contact a specialist in a timely manner, as well as follow all his recommendations.
In particularly severe cases, surgical treatment may be prescribed. If drug therapy does not give the desired effect, and the patient complains of frequent fainting and the disease seriously threatens his life, an electrical stimulator is installed. The device generates the correct rhythm and allows the heart to work normally.
If an electrical stimulator has been installed, the patient must follow some recommendations:
- Do not undergo diagnostics based on the use of magnetic waves (MRI, nMRI).
- Avoid physical therapy.
- Avoid chest injuries.
Serious damage can be caused by exposure to electric current. Installing a pacemaker is an extremely serious method, which is used only in the most severe cases. To avoid this, it is recommended to undergo timely preventive examinations, as well as to properly treat the underlying disease.
Complete blockade of the right bundle branch is not always a direct indication for installing a stimulator. Typically, this method of therapy is resorted to if atrioventricular block occurs.
Life forecast
If the blockade of the leg is without clinical manifestations, the prognosis of the disease can be confidently called favorable. In this case, the disease does not require specific therapy. The main thing is to prevent the underlying disease from worsening and undergo timely preventive examinations with a doctor.
Even an incomplete block of the His bundle in the right bundle is easily detected during examination. This is why it is so important to visit a specialist and, if necessary, undergo therapy.