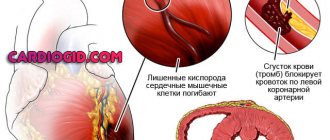
Myocardial infarction is always a great risk to a person’s life. The cause of almost every third death in our country is cardiac arrest due to insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the heart muscle (myocardium), as a result of which the organ tissue begins to die. Up to 40% of people with this diagnosis die in the first 15-20 minutes after the onset of the disease. That is why it is so important for patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system to undergo examinations, to know the first signs of the development of myocardial infarction in women and men, and to always be ready to call an ambulance. Your health and life, as well as the lives of your loved ones, next to whom you find yourself at the right moment, may depend on the ability to correctly identify the symptoms of the disease, competent and prompt actions.
What it is
Myocardial infarction, or heart attack, most often occurs in older patients. The risk group includes women over 55 years of age and men over 45 years of age.
Doctors classify pathology according to the time of its occurrence:
- primary infarction – occurring for the first time;
- recurrent infarction – diagnosed within 1.5 months after the first attack;
- repeated heart attack – occurring after 6 weeks from the date of the first incident.
Several departments can be affected at once. In this case, we are talking about an extensive heart attack. Pathology can only affect the left ventricle - its septum or walls. The tissue of the right ventricle dies less often.
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
Usually, complaints and symptoms characteristic of coronary heart disease help to suspect the disease.
To confirm myocardial ischemia, instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used. Tests for coronary heart disease may include:
- Leukocytosis and decreased hemoglobin in a general blood test.
- Increased cholesterol and glucose, changes in the lipid profile according to biochemical blood tests.
- An increase in specific enzymes formed during the destruction of cardiomyocytes - creatine phosphokinase (its special fraction - MB) during the first 3-4 hours of a heart attack (lasts 48-72 hours), troponin-I, troponin-T (their level increases 6 hours after a heart attack and remains elevated for 7-14 days), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (exceeds the normal level 8-12 hours after the onset of pain, normalizes within 3-4 days), lactate dehydrogenase (begins to exceed the normal level 14-48 hours after the onset of symptoms, returns to normal on days 7-14), myoglobin (increases 2 hours after the onset of symptoms and normalizes within 24 hours) in the blood.
- Elevated C-reactive protein and homocysteine levels are a risk for sudden cardiovascular events.
- Increased blood clotting according to the results of a coagulogram may also increase the risk of developing certain forms of coronary artery disease.
Instrumental research methods can be invasive or non-invasive. In the latter case, the following is used to diagnose coronary heart disease:
- electrocardiography;
- ultrasound examination of the heart - Echo-CG;
- Holter ECG monitoring;
- stress ECG tests: treadmill and bicycle ergometry;
- PET/CT of the heart.
Functional load tests are widely used.
They are used, among other things, to detect the early stages of coronary artery disease or a painless form of the pathology, when the disorders cannot be determined at rest. Walking, climbing stairs, exercises on exercise machines (an exercise bike, a treadmill), accompanied by ECG recording of current indicators, are used as stress tests for suspected coronary heart disease. The standard and most accurate method for this is diagnostics using a treadmill (treadmill) and an exercise bike (bicycle ergometry). Positron emission tomography (PET) is used to diagnose viable cardiac muscle cells. Radiopharmaceuticals are used, the accumulation of which in heart cells reveals viable and necrotic areas.
Among the invasive techniques, coronary angiography is used - x-ray examination of blood vessels using a contrast agent.
What could cause it to appear?
The main cause of the pathology is damage to the inner lining of the coronary artery. This is a vessel that nourishes the tissues of the heart. As long as its diameter does not narrow and the walls remain elastic, no negative changes occur. Reducing the lumen limits blood flow. A similar picture emerges when:
- atherosclerosis;
- spasm of the coronary arteries;
- increased blood viscosity;
- formation of blood clots - thrombi.
The disease can be triggered by the influence of negative factors, which include:
- hormonal disorders;
- long-term treatment with corticosteroids;
- hypertonic disease;
- obesity;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- emotional overload.
In rare cases, myocardial infarction can be triggered by other internal pathologies: rheumatism, cancer, severe allergic reactions.
Risk factors for the development of myocardial ischemia
Factors predisposing to this disease are conventionally divided into two groups – modifiable and non-modifiable.
By eliminating or correcting the former, the risk of coronary heart disease is significantly reduced. This group includes situations in which the myocardium needs more oxygen than usual (or oxygen delivery is reduced without increasing its consumption):
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excess weight;
- unhealthy diet – a large amount of fatty and high-calorie foods in the diet;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- high levels of “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood;
- high blood pressure – arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- endocarditis and heart defects;
- decrease in the concentration of high-density lipoproteins in the blood.
Factors that cannot be changed:
- male gender;
- age over 65 years;
- IHD, especially myocardial infarction in the past in close relatives of the patient;
- the onset of menopause.
The likelihood of coronary heart disease in women increases significantly with the onset of menopause.
Signs and symptoms
Timely diagnosis can save a person’s life, so it is extremely important to know all the main signs of myocardial infarction at an early stage of its development.
Clinical picture of a heart attack:
- sudden pain in the chest;
- feeling as if the chest is being squeezed from the outside;
- irradiation of pain to the shoulder, forearm, elbow;
- unpleasant shooting sensations in the neck, back, jaw;
- feeling of lack of air;
- sticky cold sweat;
- nausea or vomiting;
- dizziness;
- feeling tired.
For a more accurate diagnosis, we focus not only on subjective sensations, but also on the results of instrumental studies. The patient is referred for a cardiogram. The technique allows you to distinguish pathology from an attack of angina. The main ECG signs of myocardial infarction are ST segment elevation.
The main signs of a heart attack vary depending on the stage of the attack. It goes through five successive stages. The success of treatment and the favorable prognosis depend on the speed of care.
- Pre-infarction period. It can last 1-2 hours or several weeks. Initially characterized by mild pain. The duration of the attacks gradually increases.
- The most acute period. Lasts no more than two hours. Characterized by rapid death of cardiac tissue. The pain subsides, the pressure drops.
- Acute period. Lasts from 2 to 14 days. Necrosis is replaced by melting of the myocardium.
- Subacute period. Lasts up to 45 days. The main clinical signs of myocardial infarction subside. Connective tissue forms at the site of necrosis. The heart adapts to the new state.
- Post-infarction period. It can take up to six months. A full-fledged scar and granulation tissue appear on the muscle tissue.
Heart attack and other age groups
In recent years, the number of young people suffering from heart attacks has tripled in Russia. In children 10-16 years old, doctors diagnose fibrous cholesterol plaques - indirect signs of a heart attack. The disease is becoming a threat not only to older people.
The modern rhythm of life in big cities is invariably associated with unhealthy eating on the go, a sedentary lifestyle, stress at work, and prolonged depression. People do not pay enough attention to their health, rarely spend time in the fresh air, and do not get enough sleep. All this negatively affects the condition of blood vessels and the functioning of the heart.
It is necessary to check your health regularly. Diseases may remain dormant for a long time and not cause trouble, but this does not mean that they do not exist. The employer obliges its employees to undergo a medical examination annually and this should not be taken lightly. Often with such examinations it is possible to identify and eliminate pathology in time.
To avoid problems, you should use the universal recipe for health - engage in accessible sports, review your diet, give up tobacco and alcohol, and learn to control your emotions!
What complications can there be?
The patient's condition may worsen at any stage of the development of myocardial infarction. Main complications:
- heart failure;
- cardiogenic shock;
- pericarditis;
- thromboembolism;
- rupture of the heart wall;
- ventricular fibrillation.
Mortality in the early stages of myocardial infarction is 35%. The cause of death is most often cardiogenic shock or acute failure. In the late period, the death of the patient is possible due to thromboembolic disorders or aortic aneurysm.
The first symptoms in men
Male gender is one of the risk factors for the development of cardiovascular pathologies. Men are more likely to drink alcohol, smoke and experience stress. With age, the likelihood of the disease gradually increases.
Statistics show that in men, acute heart attack can be the initial manifestation of coronary artery disease. Many of them, even with pronounced signs of illness, do not always go to the doctor and undergo examination. Therefore, the disease is constantly progressing. Symptoms of a heart attack in men appear suddenly. They may be preceded by physical exertion, emotional distress, sudden hypothermia or overwork. Initial signs may be the following:
- Sharp dagger pain behind the sternum;
- Dyspnea;
- Smokers have an increased cough;
- Sticky sweat.
A person experiences a feeling of fear, which is clearly visible on his face. Painful sensations do not allow you to fully inhale or exhale.
They manifest signs of ischemia against the background of alcoholism and prolonged heavy drinking, atrial fibrillation, and atherosclerosis of the lower extremities. The pathology is combined with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which occurs due to smoking. Coronary syndrome can masquerade as acute pancreatitis, which occurs in patients with alcoholism. The following symptoms are of concern:
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Abdominal pain and bloating;
- Hiccups.
In older people, a heart attack can occur against the background of an existing arrhythmia. These can be various types of extrasystole or atrial fibrillation. The first and only sign is sudden cardiac arrest, which is manifested by loss of consciousness.
How to give first aid
The main sign of a heart attack is pressing or sharp pain behind the sternum. The patient needs emergency care, so the first action if a heart attack is suspected should be to call the cardiac team.
Pre-hospital assistance:
- Make sure that the victim is not exposed to physical stress.
- Place the patient in bed with the pillows slightly raised under the head.
- Relieve external pressure - take off your shoes, remove your belt or tie, unbutton your shirt collar.
- Provide a flow of fresh air into the room.
- Monitor heart rate and blood pressure. Provide the numbers to the emergency physician.
- Calm the victim, make sure that panic does not increase.
- Give a glass of water to drink.
It is possible to take medications before the team arrives. If a person has previously suffered from angina, he is given the usual drug to improve cardiac circulation. The tablet should be placed under the tongue so that the victim slowly dissolves it. To protect against thromboembolic disorders, the use of blood thinners is recommended. They prevent platelet aggregation and slow down the death of cardiomyocytes.
If there is no consciousness, a weak pulse and unstable breathing, cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed. This is a complex consisting of indirect cardiac massage and artificial respiration. Its goal is to support life until doctors arrive. To pump blood, rhythmic pressure is applied to the sternum area, and to ventilate the lungs, air is forcibly inhaled into the victim’s mouth while the nose is pinched.
Prevention and rehabilitation
The duration of the rehabilitation period after suffering an attack depends on the person’s age, concomitant pathologies, and the severity of the heart attack. The recovery course can be carried out at home, but it is better to use the services of rehabilitation centers that specialize in helping retirees with cardiovascular diseases.
The rehabilitation program for patients after a stroke consists of:
- from drug therapy that supports the functioning of the heart muscle;
- physical therapy, which increases the endurance of an elderly person;
- physiotherapy with hydrotherapy to train the heart and reduce pain;
- massage of individual areas of the body to improve nutrition of the heart and stimulate blood circulation.
In boarding houses, the condition of patients is monitored by medical workers. The therapeutic load is increased gradually, regularly measuring vital signs, studying ECG data and ultrasound of the heart.
Reliable means of preventing a recurrent heart attack will be:
- rejection of bad habits;
- excess weight loss;
- moderate physical activity;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
It is important for relatives to create a calm, friendly atmosphere at home so that the pensioner does not experience anxiety and stress.
How to treat
Myocardial infarction at any stage of development is life-threatening, so treatment is carried out in a hospital setting. Main goals of therapy:
- normalize blood flow and thereby prevent cell death;
- limit the area of necrosis - the larger the lesion, the higher the risk of death;
- relieve pain, additionally relieving the patient of panic;
- protect against complications.
Drug treatment is carried out simultaneously in seven directions. The patient receives medications with different spectrum of action:
- Analgesics. Their task is to block the pain center. In the hospital, powerful drugs are administered that act within 3-5 minutes. They relieve nervous excitement, anxiety, and fear of death.
- Tranquilizers. Needed to relieve psychomotor agitation in the most acute phase. Rarely used.
- Thromboembolic therapy. Needed to reduce the area of necrosis. It does not bring dead cells back to life, but restores nutrition to the myocardium by dissolving blood clots in the coronary arteries.
- Anticoagulants. Strengthen the effect of thromboembolic therapy.
- Antiplatelet agents. Prevents the formation of blood clots and facilitates the passage of red blood cells through narrow capillaries. Increases blood flow speed.
- Beta blockers. They reduce the load on the heart muscle and adapt to oxygen deficiency.
- ACE inhibitors. They expand the diameter of blood vessels and reduce blood pressure.
Surgical intervention is also possible - stenting of coronary vessels, aimed at widening the bed, or bypass surgery - open heart surgery, in which the doctor creates a bypass path for the blood that does not affect the area of blockage.
Cardiologist Mikhail Tashnik: “In acute myocardial infarction, the first 2 hours are decisive!”
Interventional cardiology Apr 07, 2016
Myocardial infarction is a condition that occurs suddenly, and the urgency of treatment is critical. The patient can fully recover after a myocardial infarction, provided that he receives the correct professional assistance as soon as possible. The Myocardial Infarction Center is the only center in the country that provides a full range of medical services, both therapeutic and surgical, for acute myocardial infarction, specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular pathologies according to international standards, therefore NKMS has entered into a contract with the Myocardial Infarction Center in order to receive emergency cardiovascular conditions. Here, every patient receives the best care and emergency intervention, ensuring the best chance of recovery. It is extremely important that each of us is able to recognize the manifestations of a heart attack, and, if symptoms are detected, call an ambulance immediately in order to save our own life or the lives of loved ones.
What is acute myocardial infarction?
When one or more branches of the heart's arteries become blocked or narrowed for various reasons (eg, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots), blood cannot reach the area of the heart muscle, which will therefore not receive the oxygen it needs to function. In such cases, it is said that ischemia of the heart muscle occurs. Myocardial ischemia (the heart suffers from a lack of oxygen) can manifest itself as angina pectoris (typical cardiac chest pain) within a short time. However, after 20 minutes of ischemia, the heart muscle cells begin to die, causing a myocardial infarction, known as a heart attack and acute coronary syndrome. Myocardial infarction impairs the contractile function of some areas of the heart (depending on the affected vessels).
Causes of acute myocardial infarction
The reasons for the decrease in coronary blood flow, as a rule, are atherosclerosis - the progressive thickening of artery walls due to cholesterol deposits. Sometimes, myocardial ischemia is caused by an increased need for oxygen at the cardiac level, for example, during physical activity, when some coronary vessels are severely narrowed.
What are the risk factors for acute myocardial infarction?
Risk factors increase the chances of developing atherosclerosis, and therefore the risk of death or disability as a result of a myocardial infarction. These factors fall into 2 categories:
- Constant - that is, not subject to influence, such as gender, age or heredity. Some families have a greater risk of exposure to acute myocardial infarction. The likelihood also increases with age (especially after 65 years), and men are more at risk of experiencing a myocardial infarction than women at a younger age.
- Changeable - it is very important to know them, because they can be eliminated with the help of medications or giving up bad habits. Unfortunately, cases of myocardial infarction are becoming increasingly common among young patients (30-40 years old), for whom the only risk factor is smoking. Stress, the disease of this century, should be kept under control before it has an adverse effect on health. Other risk factors such as obesity, sedentary lifestyle, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus and kidney failure can be corrected with healthy lifestyle and treatment
Sometimes just one of the above factors is enough to increase the risk of coronary disease. Thus, we once again draw your attention to the importance of timely contacting the Medpark Cardiology Center.
How can you prevent the disease?
Preventing a heart attack is the best thing a person can do for their heart health. It's never too late to give up habits that are bad for your heart. This means that it is necessary to undergo regular medical examinations and reduce coronary risk factors.
A patient suffering from heart pain is always at high risk of developing myocardial infarction, therefore periodic examinations, exercise tests, ultrasound of the heart, diagnostic coronary angiography, identify coronary pathology in the early stages and help prevent the development of myocardial infarction.
How does acute myocardial infarction manifest?
Acute myocardial infarction remains barely recognizable to most people. Considering that providing medical care in the first 2 hours can mean a complete recovery, it is necessary to pay attention to alarming symptoms.
Typically, patients complain of severe or pressing chest pain with the following characteristics:
- localization - most often retrosternal (in the middle of the chest), radiating to both arms, often to the left shoulder and arm (sometimes with tingling in the fingertips), neck and lower jaw, in other cases to the epigastrium (in the stomach area), less often to the back ;
- character – when pressed, deep, burning, pressing, squeezing or itching over a large surface, varying in intensity, from mild to severe pain;
- duration - from 20 minutes to several hours, not stopping for a short time after taking nitroglycerin tablets under the tongue (3 tablets taken at intervals of 5 minutes);
- combined symptoms - anxiety, shortness of breath, sweating, pallor, fainting and sometimes nausea and vomiting;
- provoking factors - in more than 50% of patients at least 1 provoking factor can be identified, most often it is physical activity, emotional stress, surgery; Precursors (sometimes) – a few days or weeks before a heart attack, less intense and prolonged chest pain may appear more often during exercise or at rest
Atypical symptoms of a heart attack
There are cases where the symptoms are atypical, such as epigastric pain, indigestion, stabbing chest pain, general unexplained weakness, increased sweating, dyspnea, irregular heartbeat, nausea or other non-specific symptoms. Most often, atypical symptoms appear in young patients (25-40 years old), elderly (over 75 years old), women, patients with diabetes mellitus, renal failure or dementia.
When should you see a doctor?
Don't waste a minute! Seek help immediately! Remember the clinical signs because it could save someone's life. There is a tendency to deny the presence of myocardial infarction! This leads to untimely initiation of treatment, which is unfavorable. Even if you are not sure that you are experiencing symptoms of a myocardial infarction, still call a doctor immediately! Not all chest pain means the development of a myocardial infarction, but most often, severe, long-term chest pain requires a visit to the doctor for a consultation and an electrocardiogram, as well as some additional tests. There are many risks due to ignoring the warning signs of myocardial infarction: sudden death, severe forms of arrhythmia, angina pectoris, which further increases the patient's risks during heart failure. However, timely and adequate treatment significantly reduces the risk of any of the complications.
Treatment of acute myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is a complex emergency condition, the only treatment for which is the rapid restoration of blood circulation in the affected area, that is, the release of a blocked vessel as early as possible (in the first hours), in order to reduce the area of necrosis of the cardiac muscle tissue to prevent complications. If pain occurs, if there are nitroglycerin tablets on hand, the patient should place one under the tongue. If the pain does not go away, you can take 2 more tablets with an interval of 5 minutes. The disappearance of pain against the background of nitroglycerin in a short time after taking it indicates that the pain is of cardiac origin. Requesting an ambulance as soon as possible, which will take the patient to the Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center is a chance to save a patient with a heart attack.
At Medpark-e, at the Emergency Center, a diagnosis is made using a clinical examination and ECG, venous catheters are installed, blood is taken for analysis, special medications are prescribed: sublingual nitroglycerin and intravenous drip, analgesics, aspirin and, ultimately, clopidogrel, heparin . In the case where myocardial infarction is confirmed by the ECG, the patient's clinical picture and positive tests for degrading cardiac cells (troponin and CK-MB), the patient is urgently transported to the cardiac catheterization room.
Modern treatment of myocardial infarction is based on a minimally invasive interventional approach using diagnostic coronary angiography. If a coronary block is detected, angioplasty will be performed, the vessel will be restored either with a balloon or a stent, which normalizes blood flow. Prompt implementation of the procedure to restore blood circulation reduces the negative effects of acute coronary syndrome on the heart. Coronary angiography is performed by inserting a thin tube into the artery, and through it a catheter to the arteries of the heart, then a contrast agent is injected, which allows you to see the location of the coronary arteries. Coronary angiography is performed under local anesthesia in order to minimize discomfort during the procedure. The patient remains conscious and talks with the doctor throughout the procedure, watching the details of the procedure on the screen. If necessary, a stent (a small metal frame) is inserted into the diseased coronary artery through the same pathways and catheters, which restores blood flow to the heart, or the artery is uncorked using a balloon that is inflated inside the vessel. The consequences of a heart attack depend on the speed at which a patient contacts the Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center. If a patient with a myocardial infarction undergoes angioplasty within the first 90 minutes of the onset of pain, complications are minimized, and the patient can return to their usual lifestyle and previous activities. In case of late presentation (as usually happens), the effectiveness of angioplasty is minimal, the patient will experience restrictions in activity and a decrease in the level of endurance and stress.
Another approach to acute myocardial infarction, in centers with coronary angiography labs, is to dissolve clots by fibrinolysis: substances that dissolve clots throughout the body, including the arteries of the heart, are injected into the blood. This procedure is much more unsafe, with many associated risks, but is often the only solution in areas without access to modern cardiac services.
Recovery after acute myocardial infarction
After restoration of coronary circulation, the patient with myocardial infarction will undergo gradual recovery under the strict supervision of doctors. The myth that a patient must remain in bed for several weeks after a heart attack is not true and can lead to adverse consequences. A patient who has survived a myocardial infarction, depending on the damage to the heart, requires regular and constant use of special drug treatment prescribed by the attending cardiologist, in accordance with international standards. The presence of a stent requires antiplatelet therapy prescribed by a cardiologist. Since the stent is a foreign body, the body will try to cover the stent with blood clots for at least 6-12 months, so it is necessary to take two types of antiplatelet drugs simultaneously, such as aspirin and clopidogrel (at least 6 months in the case of metal stents or 12 months in the case of medical ones), which will prevent them from being blocked.
Attention! If the patient does not comply with the prescribed instructions and interrupts the medication for at least one day, there is a risk of recurrent myocardial infarction due to blockage of the stent. It is necessary to understand that angioplasty and stenting are effective only when the patient simultaneously treats coronary risk factors (weight loss, smoking cessation, reduction of lipids and glycemia, blood pressure control). Otherwise, there is a risk of narrowing of the dilated artery.
Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center
Medpark is the only private medical institution in the Republic of Moldova that has developed, based on international standards, a center of excellence dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular pathologies - the Myocardial Infarction Center. In 2013, the Ministry of Health included the Medpark Myocardial Infarction Center in the National Program for the Control of Cardiovascular Pathologies. Thus, 3 days a week (Sunday, Monday and Wednesday) our Center receives patients from all over the country with acute myocardial infarction admitted from Emergency Medical Services. In these cases, our specialists perform a coronary angiography procedure and, if necessary, stenting. Assistance is provided on the basis of a compulsory health insurance policy issued by the National Health Insurance Company (CNAM).
The Myocardial Infarction Center deals with the diagnosis and modern methods of treatment of ischemic cardiopathy, as well as invasive cardiology, unique for the Republic of Moldova, available daily and around the clock, within the framework of which urgent myocardial revascularization is carried out in the case of acute coronary syndrome with or without ST segment elevation.
Why choose the services of Medpark Cardiology Center:
- We are the only center in Moldova that has everything necessary for all stages of diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases, including cardiac surgery;
- We have the best cardiac surgeons and interventionalists, both in the country and abroad;
- We have a specialized consultation department where you can get the necessary advice about your heart health at any time;
- We have the most modern medical equipment, which allows for quick and accurate diagnosis, and as a result, correct treatment;
- International accreditation by Joint Commission International guarantees the safety of medical practice and the best results;
- We are at your service 24 hours a day, 7 days a week and can come to your aid at any time for any cardiac emergency.
A gift from the heart from Medpark
All cardiac treatments begin with a visit to a cardiologist, therefore, Medpark gives you a unique offer for your heart: until April 15, 2021, you have a 50% discount on a consultation with a cardiologist and a 20% discount on all subsequent tests recommended by the best specialists at the Medpark cardiology center. We are waiting for you for a consultation. Sign up by number 0 22 40 00 40
* * *
Author: Mikhail Tashnik, cardiologist, head of the Medpark Emergency Center with more than 5 years of experience in the field of cardiology.
Medpark has been taking care of your heart for 5 years.
Diagnosis and treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition in Medical
When should you see a doctor?
A person needs to consult a cardiologist if symptoms of a cardiovascular system pathology appear (chest pain, dizziness, cough, shortness of breath, bluish skin, etc.). You should not self-medicate. Numerous methods of traditional medicine are permissible for use only after the doctor’s permission and after treatment of the acute period of the disease.
Drug treatment of myocardial infarction and pre-infarction condition
Patients in a pre-infarction state are prescribed drugs that improve blood supply to the heart muscle, anti-atherosclerotic agents, and vitamin-mineral complexes.
In the acute period of a heart attack, analgesics, anticoagulants (prevent blood clotting) and thrombolytics (dissolve an already formed blood clot) are indicated.
Surgery
It is possible to more effectively restore blood supply to the myocardium through surgical intervention, which must be carried out in the first hours of a heart attack, then the chances of successful healing are greatest.
Coronary artery bypass grafting
The method of operation is to create a bypass route for blood supply to the affected area of the myocardium. The aorta and coronary vessel beyond the blockage are connected using a section of vein taken from the patient's lower leg.
Coronary artery angioplasty
Narrowing of the artery can be relieved by inserting an instrument that widens the artery through the femoral vein. Next, a stent is installed, which fixes the shape of the vessel, preventing its narrowing and restoring blood flow.