In this article we will tell you:
- Why are proteins needed?
- Causes of protein deficiency
- Symptoms of protein deficiency in the body
- Diagnosis of protein deficiency
- How to make up for protein deficiency
- Protein-rich foods
Protein deficiency
is a ubiquitous problem that nutritionists face every day in their work. What are the main reasons for its occurrence and what threatens the body with a deficiency of protein molecules? What foods should you pay attention to and what dietary supplements should you add to your diet? Let's figure it out.
Why are proteins needed?
Proteins perform many functions in the human body. First of all, it is a building material - those bricks on which the foundation of all organs and tissues is laid. They create the framework of cells - their cytoskeleton, participate in the formation of organelles of movement - and by the way, thanks to the latter, leukocytes are able to leave the systemic bloodstream in the direction of the source of inflammation. It is the connective tissue collagen that largely gives structure not only to the skin, but, say, to blood vessels. In turn, keratin is part of nails and hair.
Protein molecules carry out signal transmission, mediating intercellular interactions, transport hormones, fatty acids, and form complexes with a variety of biologically active substances. Those of them that do not circulate in the serum, but are built into the plasma membrane - a selective barrier at the border of the intra- and extracellular environments - are an important factor in the regulation of water-salt balance: by forming ion channels, they facilitate the entry of potassium, sodium and some others into the cytoplasm charged particles.
One of the most important functions performed by this class of organic compounds is undoubtedly catalytic. All enzymes are protein in nature - and this mediates strict conditions (including a certain temperature and pH), deviations from which in the slightest direction lead to a kind of transport collapse at the molecular and cellular levels. So, say, many remember from school biology lessons: an excessive increase in temperature is fraught with denaturation of protein molecules - in essence, their destruction. Here, as a rule, the analogy with fried eggs is clear: just think what “metamorphoses” happen to a chicken egg as soon as it hits a hot frying pan.
In addition, a large number of hormones are also represented by polypeptides and proteins - this allows us to highlight the regulatory effect as a separate item: both local and at the level of the entire organism (take, for example, thyroid hormones, the influence of which begins with cellular metabolism and ends with entire organ systems ).
How to raise it?
In order for the body to function normally, the lack of protein in the blood must be replenished. First of all, you need to find out the causes of hypoproteinemia and eliminate them.
If low protein is caused by a disease, you need to see a doctor, get examined and find out the diagnosis. If treatment is effective, protein levels will return to normal.
Its content can be increased both with medications and proper nutrition. To increase it, a special diet and multivitamin complexes are prescribed.
You should know that not all proteins are broken down equally in the digestive system. Some of them are partially absorbed. Therefore, the diet should be developed by a nutritionist.
A nutritionist will help you create a nutrition plan for hypoproteinemia
Causes of protein deficiency
- Impaired liver synthetic function
- the central metabolic factory. It is here that blood plasma proteins are formed: albumins and most globulins, which largely mediate the maintenance of homeostasis in the body.
This is accomplished by forming oncotic pressure: protein molecules, due to their chemical nature, attract water, thus exercising control over water-salt metabolism. An important consequence can be drawn from this: when the concentration of proteins in the blood serum is low or when they increase in the intercellular fluid and tissues, which is especially characteristic of inflammatory processes accompanied by increased vascular permeability, edema develops - water goes beyond the arteries and veins.
In diseases manifested by damage to hepatocytes (toxic or infectious agents), edema also occurs - and mainly on the lower half of the body and limbs. We wrote about this in more detail in this article:
- Nutritional factors
- fasting, generally leading to protein-energy deficiency, or an unbalanced and uncompensated plant diet with nutraceuticals, accompanied by a lack of essential amino acids in the diet - that substrate for the construction of cells and tissues that the body cannot reproduce on its own, from available elements and with the help of those present enzymes.
Below we have provided a small table with essential amino acids and the foods in which they are concentrated. We hope that this will help you competently organize and choose the type of nutrition that suits you.
| Valin | Isoleucine | Leucine | Lysine |
| eggs | soybeans | peas | chum salmon |
| milk products | peanut | perch | lentils |
| beef | egg yolk | turkey | chicken and turkey |
| lentils | pink salmon | milk | mutton |
| Methionine | Threonine | Tryptophan | Phenylalanine |
| eggs | sunflower seeds | turkey | beans |
| meat | pollock | squid | almond |
| milk and dairy products | zander | milk | cashew |
| mackerel | sesame | pistachios | cod |
- One of the most common pathologies that leads to difficulty absorbing protein from food is reduced acidity of gastric juice.
Hydrochloric acid produced by the parietal cells of the mucosa activates proteolytic enzymes and, in addition, promotes the swelling of protein molecules, facilitating enzymatic processing of food. It is also a powerful nonspecific protection factor that has a strong bactericidal effect - in particular, against protozoa, parasitic worms, bacteria and viruses.
The widespread popularity of self-administration and frequent prescription of proton pump inhibitors (“Omez”) has become a cause of serious concern among scientists about the likely consequences of their long-term use not only on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, but on the body as such.
In addition to the effects of medications, disruptions in the folate cycle
(or rather, in the three main genes that regulate it: MTHFR, MTR, MTRR), since it is this that ensures the formation of the main mediator of the parasympathetic system - acetylcholine, which also stimulates the parietal cells of the stomach. When a mutation is detected, additional support for the body is necessary, aimed at reducing the concentration of homocysteine that accumulates in such conditions - an amino acid known for its damaging effect on the endothelium (the inner lining of the vessel) and plays an important role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic damage.
We recommend
“Vitamin D: top 30 foods with its high content” Read more
On the other hand, along with insufficient formation of acetylcholine, there is an increase in the inflammatory mediator - histamine. This occurs due to a disruption in the processes of its neutralization, normally carried out by methylation reactions. Considering that histamine is also an activator of gastric juice secretion, we can draw a logical conclusion: the effect of the folate cycle on the digestive system is somewhat ambiguous. It is logical to assume that under conditions of excessive intake of this biogenic amine, not only erosive lesions of the gastric mucosa develop, but also, due to increased permeability of the intestinal wall, structural elements of bacteria enter the systemic bloodstream - an inflammatory process is observed, and not limited to the gastrointestinal tract.
Another possible cause of hypochlorhydria is atrophic gastritis
- an autoimmune disease, accompanied by a decrease in the number of functioning cells due to their death during the “attacks” of antibodies from an immune system gone crazy, which ceases to clearly distinguish between what is “ours” and what is “foreign”.
- Damage to the gastric mucosa
: ulcers, gastritis, erosion. Despite the widespread belief in people’s minds that inflammation of the epithelial lining is purely caused by H. pylori, this cannot be compared with one hundred percent truth.
Firstly, infection occurs in early childhood, so the very concept of infection in adolescence or adulthood is more likely an ephemeral rarity than a truth as such.
Secondly, everything depends on the strain of the bacterium: not all of them are aggressive (or at least so strongly pathogenic that clinical manifestation and inflammation of the gastric mucosa itself appear) - and this entails mandatory diagnosis (at least before prescribing 2 weeks of antibiotic therapy). Considering the widespread distribution of the latter, which has already led to total resistance of the microflora (inhabiting both the distal parts of the small and large intestines of humans) to chemicals, as well as the bacterial past of mitochondria, our small power plants, selflessly producing energy, the decision to eradicate Helicobacter It should be well thought out by the doctor or nutritionist that resorting to more gentle therapy with nutraceuticals.
Helicobacter actually adapts (unlike most microorganisms) to the unfavorable conditions of the gastric environment: having a specific enzyme that breaks down urea, it alkalizes its habitat by releasing ammonia. However, pathology develops only when it disseminates - spreads from the pyloric region bordering the duodenum along the entire perimeter of the stomach.
Stress often leads to damage to the gastric mucosa
: it is accompanied by activation of the sympathetic nervous system with the subsequent release of adrenal medulla hormones into the blood, which, in turn, affecting the secretory apparatus of the kidneys, stimulate their release of a vasoconstrictor. It is the narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels, including those that supply blood to the stomach, that leads to subsequent ulceration of the mucous membrane.
- Impaired breakdown and absorption of proteins in the intestine.
The first is characteristic of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, in which its secretory cells cease to form and release a sufficient amount of enzymes into the blood (and not only proteolytic ones). The second accompanies malabsorption syndrome and celiac disease - another autoimmune disease that, unfortunately, has ceased to be such a rarity today.
- Violation of bile formation and bile outflow,
which leads to the impossibility of not only the emulsification of fats, but also the activation of pancreatic enzymes. Helminthic infestation, blockage of the biliary tract by stones, decreased fluidity of this secretion due to the predominance of cholesterol over other components (bile acids and phospholipids) - a large number of possible causes necessitate careful laboratory and instrumental diagnostics, which build the missing puzzles in the clinical picture of the disease.
- Kidney diseases:
Normally, protein molecules are not filtered into primary urine due to their bulky size. However, if the renal filter is damaged (the formation of “holes” in it), massive proteinuria is observed, as evidenced by the detection of proteins in a general urine test.
Symptomatic manifestations of hypoproteinemia
A drop in protein levels is not characterized by clear specific symptoms. Somatic and external manifestations of low protein in the blood depend on the disorders and diseases that provoked changes in blood composition. With a slight loss of proteins, weakness, decreased physical capabilities, and CFS (chronic fatigue syndrome) are observed.
With a more serious decrease in indicators, the following manifestations are added:
- dysania (sleep disorder), apathy, irritability;
- unstable functioning of the digestive and urinary system;
- frequent ARVI and colds;
- labored breathing;
- suppression of libido (sexual desire);
- hypertensive symptoms (increased blood pressure, headache).
An external sign is swelling (accumulation of excess fluid in the extracellular space). Edema occurs due to a violation of the stable level of colloid-osmotic and hydrostatic pressure on the walls of blood vessels, since an insufficient number of protein molecules cannot provide the necessary compression for the passage of water from the tissue fluid into the bloodstream.
A reduced level of protein inhibits the process of formation of new cells, therefore the processes of post-traumatic skin restoration are disrupted. Trying to make up for the lack of proteins, the body begins to pull them from muscle fibers, which leads to their destruction. The symptoms are:
- arthralgia – muscle pain not caused by physical stress or inflammatory processes;
- weight loss (due to muscle mass).
Lack of nutrients affects the health of hair and nails (brittleness, dryness, etc.). Hypoproteinemia can only be determined through a laboratory blood test. To do this, you need to donate blood for a biochemical analysis. Blood sampling is carried out free of charge upon referral from a doctor. You can undergo the procedure yourself for a fee at clinical diagnostic centers.
Symptoms of protein deficiency in the body
One of the most striking manifestations of insufficient intake and/or absorption of proteins is the appearance of edema. Their development is associated with a naturally occurring failure of water-salt metabolism: under conditions of reduced concentration of proteins in the blood plasma, which normally retain water, the latter passes into the tissues, which is accompanied by their subsequent swelling.
In addition, given the huge role of proteins in creating the skeleton, framework of all cells and organs, their deficiency leads to disruption of tissue structure: brittle hair and nails are noted, and the quality of the skin deteriorates.
Along with the plastic function, this class of organic compounds also performs a catalytic one. A decrease in peptide content leads to a decrease in enzyme activity. In essence, this is a real transport collapse on the highways of metabolism: it slows down and becomes sluggish.
A wide range of hormones also have a protein nature - the endocrine system begins to suffer no less than everyone else. Characteristic: absence of menstruation, decreased production of thyroid hormones (which adds fuel to the already weak fire of barely occurring metabolic processes), slowdown in growth and development due to inhibition of the pituitary gland's synthesis of tropic hormones - including somatotropin.
The lack of amino acids causes proteolysis of tissue proteins - there is a decrease in muscle mass, its tone and strength.
In other words, there is no organ that is not affected by protein deficiency - total dysfunction progresses at all levels of functioning: from molecular to organismal.
Risk factors
- Low standard of living;
- Vegetarian food;
- Following a mono-diet or fasting for the purpose of losing weight;
- Kidney diseases;
- Diseases of the digestive system;
- Hereditary factor;
- Occupation-related weight deficiency;
- Age 60+.
For children, the following risk factors should be considered:
- Prematurity;
- Intrauterine hyposkia;
- Use of alcoholic beverages and drugs by a pregnant woman.
Ascites in liver cirrhosis
Diagnosis of protein deficiency
The simplest method for initial diagnosis is to determine in a biochemical blood test such an indicator as “total protein”.
In addition, it is necessary to establish the level
of albumin in the blood plasma
- as a rule, in conditions of insufficient supply of proteins from the outside, the liver compensatory increases the production of this fraction.
Since all enzymes, as previously mentioned, have a polypeptide basis, you can additionally rely on ALT and AST - they are often prescribed by nutritionists and doctors. However, here it is important to remember the no less dominant role in the functioning of these vitamin B6 enzymes and to be able to correctly differentiate the causes and factors of a decrease in these liver panel indicators.
An increase in the amino acid homocysteine indicates a violation of methylation processes.
in blood serum - in this case, you can suspect polymorphism in one or more genes that regulate the folate cycle and do a genetic test. A little higher, we said that these “breakdowns” are accompanied by an increase in the concentration of histamine due to a decrease in its neutralization - patients experience allergies, skin rashes and even bronchial asthma.
Low acidity is determined by pH testing
, which necessarily accompanies fibrogastroduodenoscopy with the collection of biopsy material - this is fundamentally important for establishing the stage of the process and preventing the future development of stomach cancer. The following laboratory tests will be indicative:
- Amino acids in urine (tendency to decrease).
- Reducing the concentration in the blood of metals absorbed in an acidic environment: selenium, manganese, zinc and magnesium.
Diagnosis of Helicobacter
, which is necessarily carried out in order to establish indications for the use of antibiotic therapy, consists of:
- Determination of bacterial antigens in feces.
- Breath tests with labeled urea.
- Determination of antibodies in the patient's blood.
- Biopsy during fibrogastroduodenoscopy followed by histological analysis.
To the gastropanel,
which is quite often prescribed to diagnose the condition of the gastric mucosa, includes, along with the other 3 biomarkers, such an indicator as
gastrin-17
- another stimulator of hydrochloric acid secretion, produced by the pyloric region of the stomach. Its decrease indicates a high probability of atrophic gastritis, an autoimmune disease accompanied by a decrease in the number of functioning epithelial cells.
About the condition of the gallbladder
, as a possible culprit for impaired activation of pancreatic enzymes (including proteolytic ones) is judged by:
- Coprogram.
- Biochemical blood test:
- ALT, AST.
- Gamma glutamyl transferase.
- Direct and indirect bilirubin.
- Total cholesterol.
- HDL, LDL (additionally - apoprotein B).
- alkaline phosphatase.
- Organic acids in urine (for the diagnosis of bacterial overgrowth syndrome).
An increase in the number of colonies of residents of our intestines is accompanied by an increase in the activity of fermentation processes and, as a consequence, excess gas production. This, in turn, complicates the secretion of pancreatic juice and bile due to increased pressure in the intestinal lumen.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Diet
Proteins necessary for the body to function normally are found in both animal and plant foods. It is known that animals are digested better due to their composition. Doctors say that a person needs both. Proteins contain amino acids, and each of them is needed by the body, so it is important to eat both animal and plant proteins.
Foods high in animal protein include:
- low-fat cottage cheese;
- cheeses;
- egg powder;
- meat (veal, beef);
- poultry meat;
- fish;
- seafood (squid, shrimp).
The diet should include foods containing not only animal, but also plant proteins.
Plant-based foods that are high in protein include:
- peanut;
- dried apricots;
- beans;
- almond;
- walnuts;
- lentils;
- cereals;
- rye;
- chocolate (cocoa 70%);
- soy;
- seaweed;
- sprouted wheat grains;
- brown rice;
- bran bread;
- pasta made from wholemeal flour.
Foods containing an average amount of protein are:
- fat meat;
- fatty cottage cheese;
- full fat milk;
- chicken eggs.
Such foods will undoubtedly increase protein in the blood
The menu should include foods that do not contain a lot of protein, but are necessary to increase its level in the blood:
- vegetables,
- berries,
- mushrooms,
- fruits.
Some categories of people need to consume twice as much protein per day. These include:
- pregnant women;
- nursing mothers;
- persons engaged in heavy physical labor;
- athletes.
How to make up for protein deficiency
If protein deficiency was not caused by nutritional factors, then primary attention should be directed to the cause leading to their difficult breakdown and absorption. It is the elimination of this etiological factor that will provide the body with a sufficient amount of proteins - otherwise, everything eaten simply will not be absorbed.
As a rule, the leading role is occupied by hypochlorhydria - a decrease in the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the parietal cells of the stomach. If its cause is a violation of the folate cycle, it is worth starting to work with it, taking a course of active forms of vitamins involved in its mechanisms:
- methylfolate;
- methylcobalamin;
- riboflavin 5-phosphate;
- pyridoxal 5-phosphate.
Provided there is no damage to the gastric mucosa, you can also consider the use of dietary supplements that stimulate the secretion of hydrochloric acid:
- Betaine-pepsin.
- Iodine, chlorine and zinc.
In addition, exposure to stress factors that lead to vasospasm should be reduced or completely eliminated. Increase the tone of the parasympathetic system: as you know, it is the vagus nerve that controls the digestive processes. Take baths with magnesium salts, do relaxing practices like Pilates, yoga, breathing exercises.
Suitable as adaptogens for reducing cortisol levels:
:
- Rhodiola rosea;
- valerian;
- ginseng.
We recommend
“Enzyme deficiency: symptoms and treatment” Read more
Lifestyle changes play a key role in normalizing the condition of the entire body. Move more - let 10,000 steps become not something supernatural for you, but a familiar, everyday norm. Eliminate simple sugars from your diet as much as possible: especially if the cause of impaired secretion of digestive juices lies in the syndrome of excessive fungal or bacterial growth.
Go to bed early: at 11 p.m., the secretion of melatonin, an antioxidant hormone responsible for youth, beauty and actively counteracting the development of oxidative stress, begins. In addition, the release of other, no less important hormones: TSH and somatotropin is also tied to the sleep-wake cycle.
How to determine body mass index (BMI)?
Poor nutrition is a double-edged sword, both of which are unpleasant. On the one hand, it can lead to problems with excess weight. On the other hand, in the case of protein-energy deficiency, it leads to a lack of body weight, and it can hardly be said that this is not as dangerous as extra pounds.
You can determine your body mass index using our BMI Calculator.
- 16 or less – Severe underweight
- 16-18.5 – Insufficient body weight
- 18.5-25 – Normal
- 25-30 – Excess body weight (pre-obesity)
- 30-35 – First degree obesity
- 35-40 – Second degree obesity
- 40 or more – Third degree obesity (morbid)
Characteristics of the indicator
Total protein is an important component of protein metabolism in the body.
Protein is considered a building material that is simply necessary for all organs and systems of the human body. It, like a frame, forms the basis on which all cells and molecular structures of other types of metabolism are subsequently attached. In other words, protein is the main building material, without which it is simply impossible to restore the structure of cells and tissues.
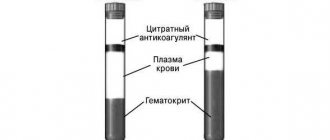
Total serum protein is the concentration of albumin and globulin in the fluid component of blood. The building blocks of protein and protein functions are complex amino acids. Proteins are actively involved in various biochemical processes occurring in the human body. In addition, they serve to transport nutrients such as hormones, pigments, lipids and minerals.
- Total protein in the blood is elevated - what does this mean and what to do?
Proteins are a kind of catalysts, and they are responsible for the immune function of the body.
Total protein helps maintain a constant pH environment in the blood circulating in the body and is actively involved in the coagulation system. Due to the presence of protein in the human body, all components of the blood are contained in the serum in a suspended state.
Based on the indicators of total protein, we can talk about the state of hemostasis, since thanks to this element the blood has such characteristics as fluidity and viscosity. Thanks to such qualitative characteristics of blood, the heart and the entire cardiovascular system as a whole work normally. Most often, in pathologies, the concentration of protein in the blood is reduced and this pathological condition is called hypoproteinemia.
Diagnostics and norms of the indicator
Blood sampling procedure to test total protein levels
Indications for determining blood protein are diagnostics:
- pathologies of the kidneys and liver
- repeated chronic infections
- burns and malignant neoplasms
- various specific pathologies
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- malnutrition and varying degrees of malnutrition
- anemia and metabolic disorders
In addition, identification of total protein and its concentration is carried out as the 1st stage of preparation for a comprehensive health examination. Such a study may be prescribed in order to assess the body's reserves before undergoing surgery, various medical procedures and before taking medications.
In addition, the indication for determining total protein is the need to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and the prognosis of the current pathology.
Total protein standards:
- In newborns, the normal level of protein in the blood is considered to be 45-70 g/l.
- Over the next 15 years, this figure increases to a level of 60-80 g/l.
- In adult patients under 60 years of age, the level of this compound in the blood reaches 65-85 g/l.
- After 60 years, the indicator of such organic matter decreases to 62-81 g/l.
In some cases, a person may experience slight deviations from the norm downward, and this may occur under the influence of the following factors:
- severe dehydration
- breastfeeding period
- pregnancy
- Insufficient protein intake from food
- taking certain types of medications
- strong physical stress on the body
The level of protein in the human body can be determined using a biochemical analysis, which is carried out in the morning and always on an empty stomach. The last meal before the study should be no later than 8-12 hours. On the day of the test, it is recommended not to eat too much protein food, not drink a lot of fluids and avoid heavy physical activity on the body. The fact is that all these factors can affect the final result of the study in one direction or another.
- Total protein in the blood: norms and causes of deviations
How to avoid trouble?
In order to never encounter this problem (and this, unfortunately, is possible), you need to think about its prevention. That is, learn as much useful information as possible about your body and its needs for important nutrients.
Understand why it is necessary to adjust your diet based on your current state of health and metabolism, taking into account all diseases.
And not only rejoice at new knowledge, but also convey it to loved ones, create useful “word of mouth”, which, perhaps, will protect someone from a frivolous attitude to nutrition.
Why is this happening?
We have found that without adequate protein in our diet, we face serious health problems. But you also need to know about the reasons why protein-energy deficiency occurs, and there are two of them.
The first reason is external, or exogenous, which is caused by systematic malnutrition (for example, if you chose a strict fasting method to lose weight). Also, an external cause may be difficulties in the functioning of the masticatory apparatus, interfering with normal food intake, or diseases in the field of neuralgia or the psyche.
The second reason is internal, or endogenous, and here problems with digestion and assimilation of food, the existing increased needs for nutrients and, accordingly, energy come to the fore (this happens with lung pathology, surgical interventions, radiation and chemotherapy). Congenital and acquired metabolic problems cannot be discounted.