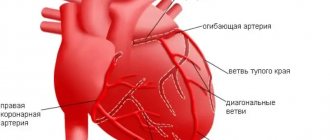
An unusual and strange feeling, as if the heart is pounding in the throat, can disturb absolutely anyone. Only a qualified specialist will tell you exactly what this symptom is and whether you should be afraid of it.
In most cases, such ailment indicates problems associated with the functioning of the cardiovascular system. However, this symptom is not always a consequence of a disruption in the functioning of these organs. There are other factors that lead to similar discomfort.
What are extrasystoles?
Extrasystoles are heartbeats that occur outside the physiological rhythm of the heart and can cause unpleasant symptoms.
Extrasystole is also referred to as skipped heartbeats or "cardiac hiccups", and is medically considered a form of cardiac arrhythmia. In most cases, the additional heartbeats are hardly felt or felt very faintly. Regular and severe symptoms are a reason to consult a doctor and diagnose or rule out possible heart disease.
What to do if your ears are blocked
Surely everyone has had their ears blocked at least once in their life.
The situations that lead to this are quite diverse; they can be either completely physiological or signal problems in the functioning of our hearing organ.
In what cases should you be wary and listen more closely to your body, and when should you not worry? How to get rid of unpleasant feelings?
“Safe” causes of ear congestion
Pressure drop.
This usually happens when taking off and landing an airplane, riding an elevator, and traveling at high speeds. In this case, congestion in the ears is not a pathology.
Read also: Tinnitus
The appearance of the symptom is due to the fact that due to a sharp drop in pressure between the middle ear cavity and the environment does not have time to equalize, which leads to a decrease in the mobility of the eardrum and unpleasant sensations.
What to do?
In order to quickly get rid of the feeling of congestion, you can use a few simple techniques. During a pressure drop (or before):
- drink water in small sips;
- sucking a candy cane or chewing gum;
- to yawn.
All these techniques are aimed at opening the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear and nasopharynx (the pressure in the nasopharynx is the same as in the environment). When the pipe opens, the pressure between the cavities is equalized, and the unpleasant feeling disappears.
Water getting into the ear.
In this case, water is a kind of obstacle to the sound, which causes congestion.
What to do?
In order to quickly remove water from the ear, you need to pull the auricle up and back and tilt your head towards the affected ear. If this does not help, you can drop a few drops of an alcohol solution into your ear to help the water dry out faster.
Both of these causes, as a rule, do not pose a threat to the body, are not accompanied by other symptoms and can be easily dealt with on your own.
“Dangerous” ear congestion
But there are more serious reasons for the appearance of the symptom. As a rule, these are diseases of the hearing organs, which, in addition to congestion, are accompanied by a number of other symptoms and require consultation with a doctor. These include the following conditions.
Sulfur plug.
Congestion, as with simple exposure to water, appears after bathing and is associated with a mechanical obstruction in the path of sound, but differs from the “water obstruction” by a longer feeling of congestion that does not go away on its own, a sharp decrease in hearing, a feeling of itching and pressure in the ear.
What will the doctor do?
The doctor will remove the wax plug by rinsing the outer ear canal.
Otitis and eustachitis.
Inflammatory diseases of the ear and eustachian tube can also cause ear congestion.
Due to inflammatory swelling of the mucous membrane of the middle ear and the Eustachian tube, the function of the latter is disrupted, which leads to a disruption in the pressure equalization between the middle ear and the nasopharynx and the appearance of congestion. In addition to this symptom, pain in the ear area, decreased hearing, sometimes discharge of pus from the external auditory canal, as well as general reactions of the body to inflammation - increased body temperature, general weakness, fatigue. What will the doctor do?
The doctor will prescribe a course of antibacterial drugs according to the clinical picture of the disease.
Inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx.
The mechanism of ear congestion here is approximately the same as in the previous group of diseases.
The inflammatory process in the nasopharynx is usually accompanied by involvement of the Eustachian tube with all the ensuing consequences. As a rule, this group of diseases is accompanied by pain in the throat, nasal congestion, runny nose, and increased body temperature. What will the doctor do?
The doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics or antiviral drugs depending on the specifics of the disease.
Diseases of the inner ear.
These include Meniere's disease, damage to the auditory nerve, acoustic trauma, etc. The appearance of congestion is associated in this case with a disruption in the functioning of the auditory nerve and distortion of sound perception.
The diseases are accompanied by dizziness, hearing loss, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. What will the doctor do?
The doctor will conduct a series of special tests to determine the level of damage to the auditory nerve and, based on the data obtained, prescribe the necessary treatment.
The article lists the most common causes of ear congestion, but this symptom can accompany a variety of unexpected diseases. Therefore, if ear congestion appears regularly, you should consult a doctor for examination and to identify the causes of this condition.
Be healthy!
Olga Starodubtseva
Photo depositphotos.com
Related products: (salicylic alcohol), (boric acid)
How do extrasystoles occur?
The main cause is an abnormal heart rhythm that occurs outside the sinus node. Extrasystoles can occur in both cardiac patients and healthy people, and often go unnoticed.
Most extrasystoles are harmless. However, they may be symptoms of heart disease. Therefore, if you experience any of the symptoms described below, you should always consult your doctor to rule out or diagnose heart disease.
Depending on the exact location of origin in the heart, they are classified as supraventricular extrasystoles (SVES), which are generated above the level of the ventricle, or ventricular extrasystoles (VES), which are generated in the ventricle.
Extrasystoles can occur in isolation, in pairs or in so-called “short bursts”.
Acute thyroiditis - symptoms and treatment
Acute thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid tissue, which is characterized by an acute onset and is accompanied by a rise in body temperature to 38-40 ° C, chills, acute pain in the anterior surface of the neck, swelling, a feeling of pressure in the neck and hoarseness.
Translated from Latin, “thyroid” is the thyroid gland, the ending “itis” indicates inflammation. The disease is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person or to animals. It is dangerous because it can spread to surrounding organs and be complicated by the formation of an abscess.
Acute thyroiditis is quite rare, with equal frequency in men and women. In the structure of all thyroid pathologies, this disease accounts for a small share - 0.1-0.7% [8]. It is most often found in autumn and late spring [9]. According to the literature, the disease occurs extremely rarely in children [2].
Acute thyroiditis is caused by damage to the thyroid tissue. Damage, in turn, can be caused by both infectious causes (pathogenic microorganisms) and non-infectious ones.
Infectious causes:
- Viruses - adenovirus, influenza virus, mumps, chickenpox [1][3][9]. Pneumocystis infection has been detected in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome [5].
- Bacteria - staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella, etc.
Non-infectious causes:
- Injuries to the anterior surface of the neck.
- Radiation or beam effects on the thyroid gland [1].
- Hemorrhages into the thyroid tissue.
Acute thyroiditis can develop due to various diseases:
- Any acute or chronic infectious disease of the ENT organs (otitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, acute tonsillitis).
- Respiratory diseases (acute and chronic bronchitis and pneumonia).
- Chronic inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, stomatitis and periodontitis) and untreated teeth (caries and pulpitis).
Infection from the above foci travels through the blood or lymph into the thyroid gland, causing inflammation.
When the inflammatory process spreads, it is necessary to take into account the anatomical features of the blood supply and lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. The organ has a very abundant blood supply (two superior and two inferior thyroid arteries, small arterial branches of the anterior and lateral surfaces of the trachea) and quite active lymphatic drainage. This explains the rapid involvement of thyroid tissue in the inflammatory process and a more vivid, violent clinical picture of inflammation.
Infectious agents (microorganisms) can enter the thyroid gland not only through blood and lymphatic vessels, but also directly - through damage to the thyroid capsule. This is a very rare route of infection, which is possible during a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (when the medical worker does not follow antiseptic measures) or with injuries to the thyroid gland (for example, as a result of an accident). When pathogenic microorganisms enter the thyroid gland, they cause acute inflammation of its tissues.
Acute thyroiditis can also be observed with developmental defects - the presence of a thyroid-lingual cyst or thyroglossal fistula [3].
The degree of involvement of thyroid tissue in the inflammatory process can vary widely. Inflammation can affect part of a lobe, the entire lobe (usually the left) or the entire thyroid gland (very rarely) [1].
What are the symptoms of extrasystoles?
Typical symptoms of extrasystoles causing abnormal heart rhythms include:
- The heartbeat feels irregular and stronger than usual, or too strong, with a feeling of the heart beating in the throat;
- Feelings of anxiety or panic;
- Sweating;
- Chest pain;
- Feeling of respiratory distress;
- upset stomach or frequent urge to urinate;
- Headache or nausea.
Always consult a cardiologist if these symptoms occur in connection with a pre-existing underlying heart condition.
What does it mean to feel like your heart is pounding in your throat?
A person who has no health problems is unlikely to feel a heartbeat somewhere in the throat area. In addition, he certainly will not have thoughts about the fact that his organ has moved to another place, which is why such a strange sign arises.
Experts identify several conditions that may be accompanied by a heartbeat in an unusual location. If they are the cause of the illness, then everything is fine with the human body. Do not worry about your own health if you feel your heart pounding in your throat in the following situations:
- After intense physical activity that lasted for a long time.
- When feeling intense fear or while expressing another similar emotion.
- When experiencing severe stress.
As a rule, if these conditions lead to discomfort, it will soon go away. It is enough for a person to simply calm down and relax as much as possible.
Sometimes a strange symptom is accompanied by a sharp jump in body temperature. In this situation, we can talk about possible disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. A knock in the throat will mean a special reaction of the body to a change in the usual temperature.
In all other cases, doctors will associate discomfort with the development of a pathological process that reveals itself as this symptom. To identify it, you will need to conduct a series of diagnostic studies.
What causes extrasystole?
Among the causes of extrasystoles in healthy people:
- Overwork;
- Lack of sleep;
- Stress;
- Excessive physical and mental stress;
- Potassium or magnesium deficiency;
- Consumption of alcohol, nicotine or coffee.
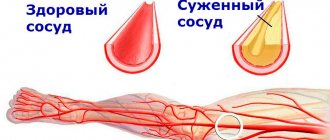
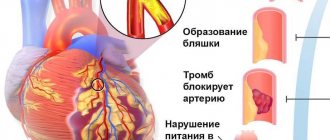
Extrasystoles can, however, also be a symptom of heart disease, such as:
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Inflammation of the heart muscle;
- Heart valve defect;
- Heart failure;
- Hyperthyroidism.
Difficulty swallowing and lump in throat
Causes and their symptoms
In infants, swallowing disorders most often have a congenital nature. Provoking factors include cerebral palsy, esophageal stenosis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and congenital facial defects. In the latter cases, treatment is carried out surgically; in others, the use of special mixtures or tube feeding is required.
It is also necessary to differentiate between true dysphagia and pseudodysphagia. The first is accompanied by a violation of the act of swallowing, when the second only causes a sensation of a lump in the throat, making it difficult for food to move through the esophagus.
True dysphagia
True dysphagia is associated with the following reasons:
- Catarrhal processes in the esophagus, oropharynx. Inflammation causes dysphagia, hyperthermia, deterioration of general condition, a feeling of suffocation and a lump in the throat.
- Thyromegaly is associated with the growth of the thyroid gland, which compresses the esophagus, impairing swallowing function.
- A stroke is accompanied by difficulty swallowing, drooling, coughing, weakening of the muscles of the face and body, impaired coordination of movements, and speech function.
- Parkinson's disease. Swallowing disorders are associated with degerant processes in the central nervous system, which leads to damage and weakening of the muscles of the oropharynx, tremors of the limbs, and impaired vestibular function.
- Multiple sclerosis. The problem can be recognized by tremors of the limbs, muscle weakness, disturbances in chewing, swallowing and speech activity.
- Achalasia is associated with insufficient reflex weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter. The pathology is characterized by food dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food, chest discomfort, flatulence, heaviness in the stomach, nausea and vomiting.
- Benign and malignant tumors of the neck, mediastinum, head. As the tumors grow, they can put pressure on the blood vessels, trachea and esophagus, disrupting the swallowing process and causing weight loss, chest pain, and suffocation.
Pseudodysphagia
Most often, swallowing dysfunction is functional. A person feels a lump in the throat, but there are no structural changes in the body. The cause may be stress or emotional overstrain (psychosomatics). However, most often organic causes of discomfort are caused by infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, peritonsillar abscess), which are accompanied by a lump and sore throat, increased body temperature, and general malaise. Diagnostics
Frequent disruption of the act of swallowing, the feeling of a lump in the throat should not be ignored, as it can lead to (choking while eating and food entering the respiratory tract - aspiration) inhalation of food. Aspiration provokes acute and chronic pathologies of the lungs, including suffocation with a fatal outcome.
To determine the cause of discomfort, you need to contact several specialists - a therapist, ENT specialist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, psychotherapist. Only a comprehensive examination will determine the true cause.
To obtain a clinical picture, the doctor collects anamnesis and prescribes:
- general clinical and biochemical blood test, blood test for thyroid hormones;
- radiography (MRI or CT as indicated) of the head, chest, throat, videofluroscopy;
- esophageal manometry, gastroscopy;
- Dopplerography of head and neck vessels;
- electromyographic study.
Treatment
Treatment of lump in the throat syndrome and dysphagia is complex and depends on the cause. Patients are prescribed:
- antiphlogistic, antibacterial, antiviral therapy in the presence of catarrhal processes in the ENT organs and gastrointestinal tract;
- antidepressants, antipsychotics, tranquilizers for the relief of neurotic disorders;
- hypnosis, cognitive behavioral therapy, individual and group rehabilitation for mental health disorders;
- reflexology, physiotherapy;
- breathing exercises, physical therapy.
In the presence of obstructive processes or tumors, surgery is prescribed to remove them, and in case of inoperable esophageal cancer, stenting is prescribed.
How to feed a patient
If the act of swallowing is impaired, but the reflex is preserved, it is important to maintain the ability to feed independently. The patient is recommended soft, semi-liquid and liquid meals, which are taken under the supervision of medical personnel or people caring for him. It is important to eat at regular intervals and reduce your portion size. Foods that irritate the mucous membrane should be excluded from the diet.
If swallowing function is not restored within three days, the patient is fed through a nasogastric tube.
The ENT Center offers a wide range of services, which allows not only to determine the cause of dysphagia and lump in the throat, but also to provide the necessary treatment within the walls of our clinic. To do this, we employ specialists of various profiles - otolaryngologists, endocrinologists, psychologists. You can get acquainted with our doctors and make an appointment with them on the clinic’s website.
The main reasons for the sensation of a pulse in the throat
Few people notice exactly how their heart works. You can feel its beating only if you put your hand on your chest or try to feel the pulse. However, sometimes a palpitation in the throat area can be felt without these manipulations.
An alarming symptom may occur for the following reasons:
Panic attacks
Every person knows this unpleasant feeling. This condition occurs in people when experiencing a stressful situation. In extreme cases, a panic attack develops when a person is completely calm. If the cause of the pulse in the throat lies in this condition, then symptoms such as sweating, trembling of the limbs and dry mouth will appear in parallel.