01 Aug 2021 at 10:37 MRI of the heart in Tushino 7915
“Aneurysm of the aorta of the heart - what is it?” Many patients in whom a specialist has just discovered this disease ask a similar question. An aortic aneurysm is a widespread or limited dilation of the largest vessel in the human body. With this disease, the diameter of the aortic lumen exceeds the norm by two or more times. Aortic aneurysm is one of the most dangerous heart diseases.
Cardiomegaly or enlarged heart?
Every year, hundreds of thousands of citizens die from cardiovascular pathologies around the world. In most cases, the reason for this is untimely consultation with a doctor and deterioration of cardiac function.
Enlargement of the organ is associated with the development of ventricular hypertrophy, accumulation of metabolic products and neoplastic processes. Cardiomegaly often occurs in healthy people, this includes athletes and pregnant women.
The volume of the heart varies within different limits for each person. If we talk about gender differences, then in men this organ is larger than in women. So for the age category from 20 to 30 years, the approximate heart volume will be the following values:
- women – 580 cm3;
- men - 760 cm3.
This figure also depends on body weight. A diagnosis of cardiomegaly should be made only after a thorough examination, because in some cases a slightly enlarged heart is the norm, which is strictly individual for each person.
Diagnostics
To diagnose the disease, the following measures are taken:
- radiography;
- echocardiogram;
- CT scan;
- blood chemistry;
- caterization.
Palpation and auscultation are also performed to detect cardimegaly. As practice shows, it is very difficult to diagnose a large heart, since the disease has symptoms characteristic of other cardiovascular diseases.
The size of the heart can be determined using the following methods:
- Percussion (tapping the surface of the chest with fingers). Allows you to determine the boundaries of the organ during the initial examination.
EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart). It helps not only to find out the size of the heart, but also to determine the reason for its enlargement.
Dilatation of the right or left ventricle: causes
Enlargement of the walls of the right or left ventricle is called hypertrophy. In this case, the functioning of the myocardium is disrupted and, as a result, their functional activity worsens. Depending on the location of the depletion of the heart muscle, different etiologies are distinguished.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Enlargement of the walls of the right ventricle is most often observed in children with congenital defects of intrauterine development. Also, one of the main reasons is associated with an increase in pressure in the pulmonary circulation and the discharge of blood into the right ventricle. In this case, the load on the right ventricle increases.
In adults, the cause of right ventricular hypertrophy is often diseases that interfere with normal breathing. These include the following pathologies:
- rachiocampsis;
- pulmonary vascular diseases (compression, embolism, thrombosis, etc.);
- bronchial asthma;
- tuberculosis;
- bronchiectasis;
- Chronical bronchitis;
- polio, etc.
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy is dangerous due to sudden cardiac arrest, causing myocardial infarction and death. Thickening of the walls of the left ventricle can result from the following cardiac pathologies:
- developing atherosclerosis of the aorta;
- hypertonic disease;
- congenital or acquired heart defects;
- obesity.
To prevent the development of such serious diseases, you need to follow preventive measures, which means sticking to a healthy lifestyle and seeing a doctor in order to diagnose all disorders in a timely manner.
What to do
If a child is diagnosed with an increase in heart size, you should go with the baby to a cardiologist and undergo the necessary laboratory and instrumental examinations. Only after identifying the cause of cardiomegaly will it be possible to make a correct diagnosis, after which the treatment for children with an enlarged heart should be selected by a cardiologist.
Depending on the cause of cardiomegaly, the child may be prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs, antiviral or antimicrobial agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretics, glycosides and other drugs. In some cases, such as birth defects, surgical treatment is recommended. In severe cases, it is necessary to resort to an organ transplant.
For information on what to do if you have pain in the heart, see Dr. Komarovsky’s program.
Causes of cardiomegaly
Most often, an enlarged heart in diameter is diagnosed in adults. Predisposing factors that contribute to the expansion of the boundaries of the shadow of the ventricles and atria are quite diverse, in most cases this is associated with cardiovascular pathologies. So, the etiology of the appearance of cardiomegaly includes the following reasons:
- excessive exercise;
- pregnancy;
- idiopathic cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects;
- anemia in severe forms;
- infectious diseases where the target organ is the heart muscle;
- complications after viral diseases;
- myocardial ischemia or infarction;
- inflammatory processes in the heart;
- severe stress loads;
- excessive alcohol consumption, drug addiction, smoking;
- kidney disease and renal failure;
- rheumatic carditis and endocarditis;
- hypertension, etc.
If an enlargement of the heart muscle is detected, the doctor prescribes the necessary diagnostics and treatment.
Diagnosis and treatment
How to treat aortic aneurysm (vasodilatation) and prognosis after myocardial infarction
Diagnosis of the syndrome requires studying the patient's medical history. Chronic diseases, reasons for recent hospitalizations, medical records, test data, etc. are studied. This includes the appointment of a hardware examination using special equipment.
Examination methods:
- Listening and heart rate monitoring.
- Blood test for biochemistry.
- Biopsy examination.
- Chest X-ray. It is on x-rays that the boundaries of the expansion of the contours of the organ are clearly visible.
- ECHO KG, because the examination shows when the heart muscle has signs of necrosis or ischemic pathology.
- ECG.
- Ultrasonography.
- A CT scan or MRI will show an increase in the volume of the organ.
- Coronary angiography.
- It is necessary to study hormonal levels, work schedule, attitude to sports and the general condition of the body, since often a harmful lifestyle affects the course of the disease.
Treatment
Patients are prescribed:
- Diuretic medications to remove fluid retention.
- Antithrombotic drugs that affect blood clotting, acting against the formation of plaques and blood clots in blood vessels.
- “Heart” tablets (captopril, for example).
- Valve replacement if there is pathology.
- Installation of a pacemaker.
- Antihypertensive drugs for hypertension.
- Hormonal drugs.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in emergency cases, when serious consequences are predicted, in particular, the diagnosis of “bull’s heart”. To correct the situation, a transplant is needed, the operation is expensive and requires a donor organ.
As part of the treatment complex, the cardiologist prescribes compliance with the correct diet, work and rest. Together with drug treatment, this tactic gives a good result.
Correct mode
The patient needs:
- Minimize salt and sugar in your diet.
- Avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Walk for 30 minutes a day.
- Measure blood pressure regularly.
- Perform special gymnastics.
Only timely diagnosis increases the chances of effective treatment. Every budget clinic offers methods for detecting the syndrome. This makes it possible to conduct the necessary examinations free of charge and at any time.
Clinical manifestations
When the heart expands across the diameter or in other parts, the patient may experience unpleasant symptoms. This includes the following clinical severity:
- increased fatigue;
- shortness of breath at rest or with minor physical exertion;
- increased blood pressure;
- the appearance of pain in the heart area;
- formation of edema in the lower extremities;
- headaches and dizziness;
- short-term loss of consciousness.
Other signs characteristic of a particular cardiac pathology, if present, may also be added.
During treatment, it is important to identify the focus, which means to determine the disease or disorder that triggered the occurrence of heart enlargement. As soon as this is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed aimed at eliminating this pathology.
As an auxiliary therapy, medications are prescribed, the purpose of which is to reduce the obstacle to normal blood outflow while simultaneously unloading the increased work of the ventricles. This will prevent the risk of complications such as myocardial infarction, angina, shortness of breath and arrhythmia.
If therapeutic actions are ineffective, the doctor may prescribe surgery to improve blood flow. However, they resort to it only in extreme cases.
Diagnostics
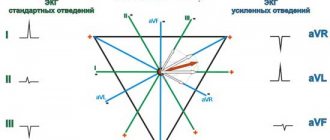
Sinus rhythm of the heart, what does it mean and ECG
Modern diagnostic methods do not allow detecting an increase in heart volume in the early stages, since the symptomatic manifestations of this dangerous condition can be a consequence of other diseases of the cardiovascular system, which often confuses even qualified cardiologists. To confirm the diagnosis, the following activities are carried out:
- radiography;
- palpation;
- listening;
- echocardiogram;
- catheterization;
- blood chemistry;
- CT;
- biopsy.
In rare cases, when an increase in heart volume is detected in the early stages, this process can be stopped with medication. When the disease has already entered into full force, the main treatment should be aimed at the root causes of this pathological condition.
As a rule, medications are prescribed that help stabilize the heart in case of one or another primary disease.
Among other things, the patient must observe a special regime of wakefulness and activity, as well as a special gentle diet
It is very important to eat small portions and avoid overeating
Surgical treatment involves ventricular myotomy. Such a surgical intervention cannot be performed on all patients, as it is associated with a high risk of death on the operating table.
In severe cases, when other treatments do not have the necessary effect, a heart transplant is required.
So when is the diagnosis of cardiomegaly valid and by what methods can it be confirmed? Of course, in first place in terms of diagnostic value is echocardioscopy (ultrasound of the heart).
Normal heart sizes according to ultrasound correspond to the following indicators:
- EDV – end diastolic volume – 110-145 ml,
- ESV – end systolic volume – 45-75 ml,
- EF - ejection fraction - 55-65%,
- SV – stroke volume – 60-80 ml.
EF, however, may be reduced, significantly, in patients with chronic heart failure or dilated cardiomyopathy. In addition to measuring the characteristics of the heart, the configuration of the organ and the activity of the valve apparatus are visually assessed.
As methods complementing echocardioscopy, chest radiography, electrocardiogram, cardiac MRI or puncture biopsy of cardiac tissue are used (if a cardiac tumor is suspected to verify the diagnosis, very rarely).
Heart ultrasound remains the “gold standard” for diagnosing cardiac pathology, especially in newborns and children in the first year of life. This study should definitely be carried out by athletes and people with a hypersthenic type of constitution, to exclude serious cardiac pathology.
Modern medicine has developed a large number of diagnostic methods for detecting heart diseases. Making a diagnosis begins with collecting an anamnesis, which is based on the patient’s complaints and examination. The doctor clarifies the presence of chronic diseases, bad habits of the patient, and previous surgical interventions. Next, the following research methods are prescribed:
- Chest X-ray - the image clearly shows the shadow of the expansion of the heart, and blood stagnation is detected.
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Echocardiography (EchoCG) determines the physical parameters of the heart muscle, including the size of the chambers, the presence of necrosis and ischemia of the heart.
- Ultrasound of the heart muscle.
- Computed tomography (CT).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Immunological and biochemical blood test, which determines the level of hemoglobin, bilirubin, urea, protein and hormones.
As medical statistics show, diagnosing bovine heart disease is often very difficult. The patient may complain of feeling unwell, and the symptoms may indicate the presence of other ailments. Experts use the following diagnostic methods:
- echocardiogram;
- palpation and auscultation;
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- blood chemistry;
- caterization;
- biopsy.
Timely consultation with a doctor, high-quality diagnosis, and a properly designed treatment regimen can quickly restore health and prevent the development of complications.
Further diagnostics may include an ECG, Holter monitoring, and various blood tests.
General recommendations
In addition to treatment recommendations, it is imperative to follow preventive measures. For heart problems, it is very useful to follow these tips:
- You should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages, which have a toxic effect on the myocardium (heart muscle).
- In order to prevent the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of blood vessels, foods high in cholesterol should be excluded from the daily diet. It is advisable to consume fish, olive, flaxseed, corn and soybean oil at least 2 times a week.
- To strengthen and maintain the heart muscle in normal working condition, it is useful to include viburnum, cranberries, cabbage, eggplants, peaches, dried apricots, apples, pomegranates, walnuts, melons, etc. in the daily diet.
- It is necessary to reduce salt intake to at least 2 grams. per day, especially for patients with increased swelling.
- If obesity is recorded, it is necessary to create a proper balanced diet aimed at eliminating extra pounds.
- Sleep at least 8 hours, do not become physically and emotionally overtired.
- Walk outdoors more often.
Enlargement of the heart is not a diagnosis, but only a temporary condition of the heart muscle. With correct and timely actions, you can get rid of this disorder and significantly alleviate your condition.
Expansion of the heart in diameter
Causes of heart enlargement
● The weight of a man's heart weighs approximately 330 grams, for women it is slightly less - 253 grams. The increase in size of the heart in both men and women occurs either due to the expansion of its cavities, or due to the growth of the heart muscle (myocardial hypertrophy). Today there is a whole list of diseases that contribute to the expansion (or dilatation) of the heart. One of the most classic diseases is hypertension. The mechanism of heart expansion in hypertension is as follows: narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels leads to increased pressure on the heart, an additional load is placed on it to pump blood, the heart muscles become more tense, and therefore increase in size.
● Diseases that lead to enlargement of the heart include inflammation of the heart muscle - cardiopathy. This happens as a complication after untreated scarlet fever or tonsillitis. These diseases deplete the muscles of the heart, they become flabby, and the cavities of the heart (its ventricles) expand. Enlargement of the heart (dilatation) is manifested by the following clinical symptoms: edema, mainly in the legs, shortness of breath during exercise, palpitations (tachycardia), cardiac arrhythmias (arrhythmia).
Symptoms of bullous emphysema
A number of studies published in the open international database PubMed emphasize that factors such as:
- Smoking (15-20 packs);
- Systematic inhalation of toxic substances (unfavorable environment, work in hazardous industries, substance abuse, drug addiction);
- Low level of quality of life (poor and unhealthy diet, hypothermia, illness, lack of qualified medical care).
And only next to these factors in terms of prevalence are past infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, and congenital characteristics of the body.
In the vast majority of cases, bullous emphysema is diagnosed in elderly or mature people, but bullae can also be found in young people.
Small bullae do not manifest themselves at all. In general, it is difficult for the patient to even suspect most diseases of the main respiratory organ - the lungs do not hurt, and when shortness of breath, coughing, and lack of air occur, the disease brings the patient to intensive care in a matter of hours.
Pathological symptoms may appear as the bullae enlarge and emphysema develops. Prevention of the disease is possible through regular screening - low-dose CT scan of the lungs. Examination in 3D mode and in high resolution will show even the slightest deviations from the norm.
To determine the (exact stage) of bullous emphysema, the method of spirometry is used - functional diagnosis of the lungs. As a rule, after spirometry, if the indicators are not normal, the pulmonologist sends the patient for a CT scan of the lungs.
Bullae in the lungs can be suspected if the following symptoms are present:
- Shortness of breath and breathing difficulties;
- Resistance to physical activity, fatigue;
- Hypotension, uncontrolled arrhythmias;
- Feeling of constant fatigue;
- Blue lips and fingertips;
- Painful pallor;
- Feeling of incomplete inspiration;
- Deformation of the chest (becomes barrel-shaped if there are large bullae).
Since the enlargement of bullae lasts quite a long time, the patient may not notice a deterioration in health, in particular, it becomes increasingly difficult to hold his breath due to a decrease in the vital capacity of the lungs, and hypoxia generally affects all internal organs - the person literally “fades.”
The heart is expanded in diameter
I ask you, if it is possible to provide an explanation of the medical term “the heart is expanded in diameter,” what does it mean? This is written on the results of my husband’s chest fluorography. He is 54 years old, second-degree hypertension, coronary heart disease, varicose veins in the legs, overweight - this is an incomplete list of diseases accompanying his life.
I ask you to give recommendations on how to improve his health. What is the reason for the enlargement in the heart, is it life-threatening, and if so, how to protect your husband from possible consequences?
Sincerely, Lyudmila Reutskaya
Unfortunately, everything you wrote about your husband’s health condition is very dangerous. The heart enlarges from constant stress caused by high blood pressure and excess weight. At the same time, it cannot adequately perform its function, working as a pump, and tries to cope with this by increasing muscle mass (myocardium). But at the same time, the cavities of the heart expand, the valves stretch, the hole between the ventricles and the atrium becomes larger, and so-called pseudo-defects develop, in which blood flows from the ventricle into the atrium. This leads to heart failure and various heart rhythm disturbances. It is not the diagnosis “enlarged heart” itself that is dangerous, but the fact that these changes can lead to myocardial infarction or cerebral stroke.
Diagnostics
The heart is enlarged to the left: what does this mean?
A pediatrician may suspect an enlarged child’s heart after examining the baby, because during the examination the doctor must evaluate what the chest looks like, whether it is symmetrical, whether there are any convex or flattened areas on it, whether it is enlarged or has changed shape. Next, the specialist palpates the chest, looking for pulse points and assessing whether they are in characteristic places. In addition, tapping and auscultation are used in diagnosis.
Having identified alarming changes, the baby is referred to:
- X-ray. In most cases, it is the X-ray that shows that the heart is enlarged, because its darkened area becomes larger with such a pathology.
- Echocardiography. This examination will confirm the presence of heart defects that could cause its enlargement.
- Electrocardiography. The examination will confirm the presence of hypertrophy in the heart.
- Biopsy of heart tissue. This analysis allows you to see changes inside the myocardium.
Dilatation of the right or left ventricle: causes
Synchronous cardiac hypertrophy to the right and left is an indicator of ventricular expansion.
The main reasons that cause changes in the boundaries of the organ are chronic diseases, heart diseases, drug and alcohol intoxication. The main provoking factor in the formation of enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart is excessive tension. It occurs in the process of increasing blood pressure in the pulmonary circulation, during the discharge of blood into the right ventricle in congenital heart disease.
In a child, the pathology is associated with a heart defect. There is a partial ejection of blood from the left ventricle through the hole in the septum into the right ventricle. As a result, it needs to pump out a much larger amount of blood, and the walls begin to thicken and thicken.
In adults, the organ can be enlarged due to the so-called “pulmonary heart”. A similar pathology appears in diseases that interfere with proper breathing. The pressure rises, the right ventricle becomes overloaded and begins to enlarge.
Changes in heart function are also affected by the activation of neurons located in the hypothalamus. There is a close connection between it and the pituitary gland. Changes in their functioning can lead to cardiomegaly.
The expansion of the left ventricle is formed by constant tension on the heart, which forces it to function with increased intensity. The reasons that can make it work at such a rhythm are the following:
- High blood pressure. Increases the risk of pathology formation.
- Heart defects:
- 1 ventricle instead of 2;
- aortic stenosis;
- defect of the septum between the 2 ventricles;
- pulmonary atresia.
- Idiopathic hypertrophy. Thickening of the heart muscle or some of its parts. For a long time it does not provoke disruptions in myocardial contraction.
- Excessive physical activity. Long periods of exercise force the heart to get used to greater physical stress.
- Diabetes. Coronary disorders provoke ischemia. This leads to the appearance of cardiomegaly, and if the patient has high blood pressure, the likelihood of dilation increases.
- Drinking alcohol. Regular use leads to alcoholic cardiomyopathy, and subsequently to ventricular dilatation.
What is this
An enlarged heart in a child is diagnosed based on changes in its size and shape. At the same time, a child’s heart may enlarge, either one chamber of the heart or the entire heart at once. Moreover, its increase can occur both due to the expansion of the chambers, in which the walls remain thin, and due to the thickening of the walls, which is called hypertrophy.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
The right ventricle allows blood to pass through and pushes it deep into the vessels connecting to the lungs. It is enriched with oxygen. Due to the fact that the right side of the heart and lungs are connected, various difficulties with the respiratory system lead to cardiomegaly.
The right ventricle is 3 times smaller in volume than the left, therefore the electrical activity of the latter is higher. The increase can be pronounced when the mass of the right one exceeds the left one. With moderate expansion, the sizes of the ventricles do not vary. Insignificant excitement is noted. At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms are mixed or absent at all. If there is a tendency towards stable expansion, symptoms are expressed in difficulty breathing, a feeling of heaviness in the chest, and the appearance of painful discomfort.
In addition to these signs, the patient experiences fluttering or freezing and delayed heartbeat. Possible dizziness and unconsciousness.
Left ventricular hypertrophy
This pathology is a typical heart lesion for those suffering from hypertension. Dilatation of the left ventricle is considered a rather unsafe phenomenon, which is characterized by high mortality. This process involves structural adaptation of the organ regarding metabolism and changes that occur in hemodynamic data.
Cardiomegaly causes significant thickening of the walls. Often it leads to a significant change in the septum, which is located between the 2 ventricles. Due to the expansion that occurs, the elasticity of the walls is lost. Thickening can be either uniform or in certain areas of localization. This specificity directly affects the course of the disease.
Bullae in the lungs on CT
Bullae in the lungs on CT are visualized as distinct, relatively darker, bubble-like areas of lung tissue, resembling holes or large pores of a sponge. The denser the tissue, the lighter it appears on CT scans—so, for example, bones are white, but airy lung tissue is a relatively uniform graphite gray color.
Using a CT scan of the lungs, a radiologist can accurately determine the diameter of the bullae, their number, and find out whether there are signs of emphysema, bronchiectasis or other diffuse pulmonary diseases.
Clinical manifestations
To understand what an enlarged heart means, it is necessary to identify its manifestations. The most common symptom indicating changes inside the left ventricle is angina. It develops against the background of compression of blood vessels that provide nutrition to the myocardium. As a result, its expansion in size and its consumption of a significant amount of oxygen in parallel with nutrients are noted. In addition to these symptoms, atrial fibrillation appears, signs of atrial flutter and starvation of the heart muscle are observed. Often a pathology occurs during which the organ freezes for 3-5 seconds and the beat is not visible, which leads to an unconscious state. In certain situations, shortness of breath may indicate the presence of cardiomegaly. The following symptoms are considered additional:
- high blood pressure;
- unstable blood pressure;
- headache;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
- disturbed sleep;
- poor condition and general malaise;
- painful discomfort in the heart area;
- painful discomfort in the chest.
Dilatation of the right ventricle is not accompanied by any complaints. Only its causes and adverse effects can be demonstrated in the laboratory:
- dilatation of the right ventricle;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
General recommendations
In addition to medical prescriptions, preventive measures must also be followed. During heart disorders, the following recommendations will be extremely useful:
- Avoid drinking alcohol, which has a toxic effect on the heart muscle.
- Exclusion from the daily menu of products with high cholesterol content. This helps prevent the deposition of cholesterol plaques on the vascular walls. It is optimal to add fish, olive, flaxseed, corn and soybean oil to your diet at least twice a week.
- Inclusion in the menu of such products as viburnum, cranberries, cabbage, eggplants, apples, pomegranates, etc. They will help strengthen and maintain the myocardium in proper condition.
- Salt intake should be limited to 2 g per day, in particular for patients with high swelling.
- When obesity is diagnosed, a proper balanced diet should be formulated that aims to eliminate those extra pounds.
- The duration of sleep should be at least 8 hours, avoiding physical and psycho-emotional fatigue.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
Cardiac enlargement is not a diagnosis, but only a temporary condition of the myocardium. With proper and timely treatment of this pathology, it is possible to eliminate the disease and significantly improve the patient’s condition.