Unfortunately, even the strongest and healthiest people who care about their health are faced with various diseases. Most often, suffering is caused by the heart and blood vessels, which cause not only considerable discomfort, but also fear for one’s life. Vibration in the heart area or trembling is accompanied by constant discomfort, expressed either only in the heart or in the entire body at once. To cope with such a pathology, you should urgently consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Types of arrhythmias
There are many different types and forms of arrhythmias, but those that affect the ventricles are usually more serious than atrial problems. Arrhythmias can be caused by either a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) or a fast heartbeat (tachycardia) . A low heart rate can occur due to sick sinus syndrome. This occurs when the heart's natural pacemaker fails, causing the electrical signals that contract the heart to be transmitted more slowly. The condition is more common in older people and may be worsened by certain medications (such as beta blockers) that also slow the heart rate.
Heart block occurs when the electrical signal sent from the upper chambers of the heart (atria) to the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) is interrupted. Without this signal transmission, the heart cannot contract effectively to pump blood to the body.
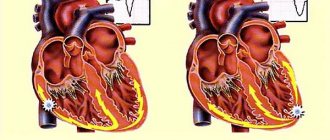
An increased heart rate may be the result of atrial fibrillation (AF). The arrhythmia clinic involves random signals that are fired in rapid succession. They cause fibrillation, which is an uncoordinated shaking of the muscular wall of the atria. It is often described as "heart cramps". The atria stop pumping blood effectively, but the ventricles receive enough blood for the heart to function. However, AFib is potentially dangerous because blood can pool in the atrium and lead to the formation of a clot. If one of these clots enters the brain, it causes a stroke. AF is the most common form of dangerous arrhythmia, affecting almost 1% of the population. It is more common in older people, affecting about 5% of the population over 69 years of age. One study showed that one in four people over 40 years of age develops FIP. Source: On the issue of classification of cardiac arrhythmias. Batyanov I.S., Batyanova E.I. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention, 2005.
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) is the most dangerous form of arrhythmia. The ventricles twitch but do not pump blood. If the twitching does not stop on its own or as a result of a defibrillator discharge, this complication of arrhythmia can be fatal.
Causes of cardiac arrhythmia in men or women
There are two common ways in which arrhythmias develop, which can be determined in a particular patient. There may be problems with the initiation of the electrical signal: either the sinus node is firing abnormally, or there is a competing impulse elsewhere in the heart. The second option is problems with the conduction of electrical impulses: connections from the atria to the ventricles are difficult (this is often called heart block).
People with heart disease are especially likely to develop arrhythmias, because heart disease, damage can prevent signals from the atria from reaching the ventricles, or certain areas of the heart may not fire normally.
High blood pressure and an overactive thyroid gland also increase the likelihood of arrhythmias. Alcohol can also cause atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Some medications, such as decongestants and many prescription drugs, can make the heart susceptible to arrhythmias and should be used with caution in people with heart disease.
There are also hereditary and congenital (present from birth) types of arrhythmia, often resulting in a weak or delayed signal reaching the ventricles. The ventricles can emit their own signal, but it is often less than 40 beats per minute instead of the usual 60-90 beats characteristic of the sinus node. Source: "New Arrhythmia Theory" Clarifies Causes of Arrhythmia. Ermoshkin V.I. Educational bulletin “Consciousness”, 2015. p. 22-30.
Symptoms
When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia . Symptoms and signs of arrhythmia include:
- chest discomfort
- cardiopalmus,
- dizziness,
- sometimes fainting.
When the heart beats slower than normal, it is called bradycardia . It can cause fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness and fainting as it usually causes low blood pressure.
Almost everyone's heart will flutter from time to time, and it usually doesn't mean anything. More often, symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia occur in men and treatment is not always necessary. But if a person has chest pain, feels weak, or notices that the pulse is irregular, either very fast or very slow for a long period, it is time to see a doctor. Source: Insider's View Focus on the Arrhythmia Patient. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199.
Symptoms of this disease may not appear. Arrhythmia can be detected by a specialist during a routine clinical examination: before any of its signs appear. But predominantly, heart rhythm disturbances are characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain in the chest;
- increased feeling of heartbeat;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- slow heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- loss of consciousness or fainting.
In most cases, in a person who has a certain type of arrhythmia, such arrhythmia occurs repeatedly.
Some types of arrhythmias are initially asymptomatic or with few symptoms. Other types of arrhythmias, on the contrary, manifest themselves in pronounced symptoms, but do not have serious consequences. Typically, the nature and severity of the underlying heart disease that causes the arrhythmia are more important than the arrhythmia itself.
Causes of vibration in the heart area
The occurrence of discomfort in the chest is one of the most frequently received complaints when identifying cardiovascular diseases. During the development of vibration in the chest area, the patient may feel a rapid pulse, the presence of goosebumps or weakness in the limbs.
There are factors that contribute to the formation of vibration sensations in the heart area:
- Formation of an attack of myocardial infarction;
- Myocardial conduction disorders;
- Development of arrhythmia;
- Manifestation of heart defects;
- Ischemic myocardial disease;
- The patient has hypertension;
- Mitral valve disease;
- Contractions of the heart muscle of a secondary nature.
Vibration or twitching of the muscle can be caused by a sharp decrease in glucose levels when an insulin injection is given for diabetes. Increased heartbeat is stimulated by the development of collapse, as well as the manifestation of hemorrhoidal shock, which is formed due to excessive blood loss. In most cases, trembling in the chest leads to a deterioration of the condition, which is dangerous for the patient’s life.
Diagnostics
The stethoscope is still a valuable tool for identifying arrhythmias, but there are modern tests that can pinpoint the problem and signs of cardiac arrhythmias in women or men. An electrocardiogram (ECG) displays a graph of the heart's electrical activity using small electrodes attached to the chest. The curve on these graphs shows the type of arrhythmia. Since the arrhythmia may not occur in the hospital, there are portable ECGs that the patient wears at home. Some are turned on continuously over a period of time (called a Holter monitor), while others turn on when a person senses an arrhythmia (called an event monitor or loop recorder).
Certain arrhythmias may be associated with exercise, so patients may be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike while connected to an ECG machine.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) is a more complex test. Thin tubes are inserted into a blood vessel in the leg and directed toward the heart. They hold electrodes that can find muscle tissue that may be causing abnormal electrical activity.
How to provide first aid?
Not everyone’s body tremors go away without significant symptoms. If you experience an attack of trembling and palpitations, you should get rid of the factors that provoked the attack. These could be, for example, being in a stuffy room or playing sports.
When a person becomes ill, you need to lay him on a horizontal surface, and it does not matter whether it is a bed or something more solid, for example, a bench. To reduce the load on the heart and blood vessels, you need to clear the airways, i.e. remove the scarf, unbutton your jacket, shirt, etc. In other words, a person must breathe freely and without any obstacles.
If your face turns pale, raise your legs higher than your body, as the person may faint or suffer an ischemic stroke. When it is not possible to immediately call an ambulance or see a doctor, use folk remedies - prepare a tincture of motherwort or valerian. It is worth noting that this is only a temporary measure and cannot be used as a treatment, as it will not be effective alone. In addition, the doctor may prescribe it as a comprehensive measure to combat pathology.
Modern methods of treatment
In some cases, arrhythmias occur due to bad habits, such as drinking too much alcohol. Giving up the habit will be a real help for arrhythmia. Reducing stress, avoiding caffeine, improving diet, and increasing the amount of exercise the patient does during the week can also reduce the incidence of arrhythmias. Before you begin making these changes, you should first talk to your doctor. For others, arrhythmias are a symptom of heart disease and will not go away unless the underlying problem is addressed. Fortunately, many people can benefit from invasive treatment of cardiac arrhythmias using modern medical interventions, especially surgery and special electrical devices.
Drug treatment for cardiac arrhythmia is also possible. There are several medications that can slow a fast heartbeat (known as "antiarrhythmic drugs"). Beta blockers are medications that are very useful in controlling heart rate in people with various heart conditions. Calcium channel blockers may also be used to control heart rate. Often these drugs can be used for more than one purpose (eg, to control heart rate, high blood pressure, protect the heart after a heart attack). The drug Digoxin is derived from a substance called Digitalis, which has been used for arrhythmias for over 200 years.
Other medications called antiarrhythmics can convert the abnormal rhythm to a normal one and prevent seizures from recurring (known as "rhythm control"). Patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) are usually prescribed the anticoagulant Warfarin, which thins the blood and prevents blood clots and strokes. Recent studies have shown that heart rate control and adequate anticoagulation are very important (perhaps even more important than rhythm control) for people with certain types of arrhythmias (eg, AF).
In some cases, AF returns to a normal rhythm with a treatment called cardioversion. The patient is given a small electrical shock that resets the heart's natural pacemakerSource: Innovations in the Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmia. Zh.A. Arzykulov, A.A. Omarov, B.B. Kituev, F.A. Tursunova, A.A. Yeshtay, N.G. Pavlova. Bulletin of Surgery of Kazakhstan, 2012. p. 4-5.
Many arrhythmias can be completely treated with radiofrequency ablation. Thin catheters are passed into the heart to send radio waves directly to electrical pathways carrying inappropriate signals. These waves destroy abnormal tissue, preventing it from causing abnormal heart rhythms. Artificial pacemakers can take over the job of generating electrical signals. They are not limited to treating low heart rates, newer pacemakers can also control high heart rates. They can operate for up to 15 years on a single battery to prevent heart arrhythmia. Some save energy by turning off when the heartbeat is normal. Most units are placed under the skin, requiring only minor surgery.
Symptoms of tremors in the chest
Patients who present with vibration in the heart area complain of fluttering, as well as increased tremors formed in the myocardium. The development of the pathological process is provoked by premature contraction of the heart muscle. In medicine, detected tremors are called extrasystoles.
Such tremors occur in 65-70% of the entire population. The process is usually of a functional type, but sometimes it can become a prerequisite for the formation of serious pathologies in the cardiovascular system. If myocardial diseases develop, then vibration takes on an organic character, occurring clinically. In such a situation, patients experience the following signs of a pathological condition:
- Increased tremors of the heart muscle from inside the chest;
- A feeling that the main organ of a person has frozen for several moments or has significantly slowed down its work;
- It feels like the heart has “turned over” or is “tumbling”;
- Lack of oxygen develops;
- Dizziness;
- Fainting.
Trembling in some patients begins immediately in the area of the heart muscle, and then spreads to the chest and radiates throughout the body. Other patients describe that tremors form in the sternum, gradually focusing in the area of the main human organ.
With the constant occurrence of trembling, you can notice that it manifests itself naturally:
- When waking up or going to bed;
- When playing sports;
- When traveling by public transport;
- In a stressful situation;
- In an uncomfortable position or during a change in position.
Usually the pathology is not accompanied by pain. But if any vibration occurs, you should consult a cardiologist. Trembling that occurs regularly can be a harbinger of a serious pathological process.
First aid for an arrhythmia attack
Defibrillators are devices that restart blocked heart muscles by delivering electricity to the chest. Defibrillators are effective in stopping the heart from ventricular fibrillation, but because ventricular fibrillation can be fatal in less than 4 minutes, they should be used as soon as possible. Most defibrillators are external devices, but there are now automated implantable cardioverter/defibrillators (AICDs). These devices can be as large as pacemakers. They can detect dangerous fibrillation and return the heart to normal before any damage is done.
Article sources:
- "New Theory of Arrhythmia" clarifies the causes of arrhythmia. Ermoshkin V.I. Educational bulletin “Consciousness”, 2015. p. 22-30
- Innovations in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. Zh.A. Arzykulov, A.A. Omarov, B.B. Kituev, F.A. Tursunova, A.A. Yeshtay, N.G. Pavlova. Bulletin of Surgery of Kazakhstan, 2012. p. 4-5
- On the issue of classification of cardiac arrhythmias. Batyanov I.S., Batyanova E.I. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention, 2005
- A look from the inside focuses on a patient with arrhythmia. Boqueria O.L. Annals of Arrhythmology, 2014. p. 196-199
- Cardiac arrhythmias from the point of view of their dimension. Ubiennykh A.G. Measurement. Monitoring. Control. Control, 2021. p. 70-76
- Epidemiology of arrhythmias (review of literature data). Zatonskaya E.V., Matyushin G.V., Gogolashvili N.G., Novgorodtseva N.N. Siberian Medical Review, 2021. p. 5-16