Features of the pathology
Bull heart syndrome can be congenital or acquired.
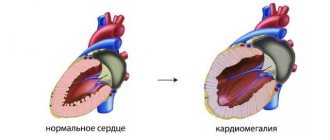
In the first case, the presence of pathology is detected if the baby’s heart muscle volume is more than 3x4x1.8 cm (length, width, thickness). In adults, the diagnosis of “cardiomegaly” is made when readings are higher than 11x11x8.5 cm. The permissible weight of the heart during life varies (from 25 to 230 g). Babies can only have a congenital form of a “bull” heart. It is rarely detected and has a predominantly negative prognosis. According to statistics, every 2 children survive. Of these, 25% will suffer from left ventricular failure. Approximately every 3 babies die before reaching 3 months. Due to severe hypertrophy of the walls and chambers, the weight of the heart exceeds the permissible limits by 2 or more times. Pathology can even be diagnosed in the fetus during an ultrasound examination. A child born with cardiomegaly often suffers from shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat and frequent infectious diseases.
If a “bull” heart is detected in a person in adulthood, then we are talking about an acquired form. It occurs due to the effects of various pathologies of the cardiovascular system. However, in professional athletes, enlarged heart muscle indicates general muscle growth due to intense training, and not a pathology. The essence of its growth lies in the increased nutritional needs of tissues due to heavy physical activity. The heart works harder, and like any other muscle, it increases in size.
People with a hypersthenic body type can have an enlarged heart without pathologies. Their body weight is greater than that of normosthenics and asthenics; accordingly, the size of their organs is slightly higher than normal.
This reason for the growth of the heart muscle does not apply to people suffering from obesity. They are often confused with hypersthenics.
Bull's heart in humans has similar features to other heart diseases, for example, myocardial hypertrophy. But with cardiomegaly, volume and weight increase due to the simultaneous thickening of the walls and expansion of the chambers. Myocardial hypertrophy is characterized only by an increase in one of the atria or ventricles (mainly the left one).
Characteristics of the condition
Cardiomegaly is often called "bull's heart." This term implies an increase in heart size of more than 500 g (with a normal adult size of 300 g) due to:
- enlargement of the heart chambers without thickening of muscle tissue (dilatation);
- thickening of muscle tissue.
Cardiomegaly develops more often in men.
Causes of the congenital form
The development of a “bull” heart in babies is influenced by the following factors:
- birth defects;
- genetic predisposition;
- Ebstein's anomaly.
Much depends on the condition of the mother and her behavior during pregnancy:
- past infectious diseases;
- abuse of bad habits (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs);
- environmental exposure;
- taking medications;
- poorly designed diet;
- injuries received.
Risks and possible complications
An enlarged heart can entail significant risks for the patient, which depend on the underlying disease that caused the enlarged heart. When the heart becomes too large, some parts of the myocardium are subject to greater pressure and therefore an increased risk of ischemia and dangerous complications such as stroke and heart attack.
However, statisticians note that one can live with the pathology without serious consequences, keeping it under control with the help of appropriate treatment. In Russia, in fact, about 9.4 million people have an enlarged heart, especially in the left ventricle.
Reasons for the acquired form
A “bull” heart in humans in adulthood is formed under the influence of heart disease and other pathologies. The first category includes:
- Valve defects, which impair the flow of blood due to congenital abnormalities, placing additional stress on the heart.
- Hypertonic disease. It creates disruptions in blood flow due to vascular resistance.
- Viral myocarditis, which is characterized by inflammation of the heart muscle. It is caused by systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages in large quantities.
- Cardiomyopathy. It is manifested by thickening of the heart muscle, mainly due to endocrine (hormonal imbalances).
- Neoplasms, such as rhabdomyomas and myxomas, which change the structure of the heart and increase its mass.
- Cardiac arrhythmias. They lead to its hypertrophy. Failures occur due to a violation of the conductivity of the pulse.
- Cardiac ischemia, which manifests itself as cardiomegaly due to compensation for lack of nutrition.
- Atherosclerosis. It clogs the coronary arteries, causing the heart to activate a compensatory mechanism.
- “Pulmonary” heart, which is a consequence of increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation.
Among other pathologies affecting the development of cardiomegaly, the most common are:
- Diabetes. It appears due to poor production of insulin (the hormone that transports sugar) or its poor absorption by the body's cells. The pathology is characterized by high glucose levels, which have an adverse effect on the cardiovascular system. A person develops atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels, which contribute to the development of cardiac ischemia and hypertrophy of its tissues.
- Cardiomyodystrophy. Develops due to poor nutrition, anemia, excess body weight and other factors. It is characterized by an increase in several or all cameras at the same time, as compensation.
- Anemia. It manifests itself as increased work of the heart muscle, which causes its insufficiency and hypertrophy to develop.
- Thyroid diseases. Cause hormonal imbalances that disrupt the functioning of the heart.
Sometimes “bull” heart in humans occurs due to long-term use of certain medications (cardiotoxic and antitumor):
- "Methyldopa";
- "Daunorubicin";
- "Idarubicin";
- "Novocainamide";
- "Adriamycin".
Cardiomegaly develops under the influence of pathologies or medications over a long period of time. Patients can detect it in the early stages, for example, during an annual examination, and stop the pathological process without much harm to the body.
What types of disease?
According to the modern classification, cardiomyopathies can be divided into two main types and several characteristic groups. As previously mentioned, the disease can appear either on its own or as a result of other diseases. In the first case, the causes are often not identifiable and cannot be established using traditional diagnostic methods.
Considering the causes of cardiomyopathies, we can distinguish different types of this disease :
- Primary origin, when the etiology of occurrence is not determined;
- Secondary form with determination of the cause of the development of pathological changes in the myocardium.
Classification is also carried out according to the mechanism of development, pathogenesis:
- Hypertrophic;
- Alcoholic;
- Dilation;
- Dishormonal;
- Restrictive.
Clinical picture
A “bull” heart does not appear in a person who plays sports or has a hypersthenic physique. Such an increase is not considered a pathology at all. If the development of the disease is provoked by other factors, then the clinical picture may be as follows:
general weakness;- fast fatiguability;
- shortness of breath after any physical activity and at night;
- attacks of tachycardia;
- abdominal growth due to the development of ascites;
- heaviness in the right side of the chest;
- protrusion of the neck veins;
- swelling of the lower extremities.
Symptoms mainly indicate heart failure. A complete examination will help to accurately diagnose and identify the cause of heart enlargement.
The congenital form of cardiomegaly is more difficult to detect in a timely manner due to the lack of opportunity to find out from the child what is bothering him. Parents need to pay attention to the following nuances:
- presence of shallow rapid breathing;
- pale skin color and blue discoloration around the lips;
- decreased appetite;
- the occurrence of edema;
- excessive sweating;
- tachycardia.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of illness, you should follow several rules.
- It is necessary to play sports. To prevent such a problem as an enlarged heart from affecting you, you don’t have to be a professional athlete - it’s enough to lead an active lifestyle, regularly work out in the gym;
- You should refuse or minimize the consumption of alcoholic beverages, and this is especially true for beer;
- You need to adhere to the principles of proper nutrition - it should be balanced, rich in healthy elements and low in fats, preserves, fried and flour foods.
Knowing what bovine heart is, how this diagnosis is made, how this disease is treated, if it develops, you can immediately suspect it, and knowing about preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of its occurrence. Do not delay visiting your doctor at the first signs of illness.
Source: “1poserdcu.ru; asosudy.ru; knowhowmed.org; o-krohe.ru; sosudinfo.com; esthetology.com.ua; healthy2life.com; nmed.org; prososud.ru; vashflebolog.ru; sekretizdorovya.ru"
Therapy methods
A bull's heart in humans cannot be completely cured. The course of therapy is aimed at reducing the load on the heart muscle, treating the underlying pathological process and maintaining the general condition normal. With timely detection, it is possible to stop the development of pathology using conservative treatment methods. In advanced situations, surgical intervention will be required.
Conservative treatment
A patient suffering from bull's heart will have to change his lifestyle:
- reduce physical activity;
- give up cigarettes and alcoholic drinks;
- lose weight;
- get enough sleep (at least 6-8 hours a day);
- reduce salt content in food;
- do not drink more than 2 liters. fluids per day;
- enrich the diet with vegetables and fruits;
- reduce the amount of animal fats consumed.
Treatment of cardiomegaly should include medications aimed at stopping the development of heart failure:
- Beta blockers. They reduce the effect of adrenaline on the heart, stabilize blood pressure and pulse.
- Diuretics. Remove moisture from the body, preventing the development of edema.
- ACE inhibitors. Stimulate the pumping function of the heart muscle and dilate blood vessels.
- Anticoagulants. They prevent the development of blood clots.
Surgery
If there is no result from conservative treatment, the doctor will recommend surgery. Its purpose is to eliminate structural defects of the heart and improve its nutrition. It will not be possible to completely cure the pathology, but it will be possible to prolong the patient’s life and eliminate the main provoking factor.
The most commonly used types of operations are:
- Installation of artificial heart valves.
- Restoring blood flow in the coronary vessels using shunts.
- Installation of a pump in the left ventricle (for severe heart failure).
- Installation of a pacemaker or defibrillator to control the heart rhythm.
Diagnostics
ABOUT
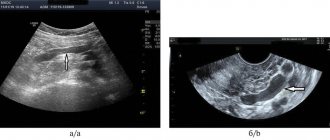
The generally accepted standard for determining cardiomegaly in medical circles is ultrasound diagnostics. This is the main diagnostic method, especially for identifying pathology in newborns and children 1 year of age.
Radiation and MRI are less commonly used. It is very rare that a biopsy sample is required for examination. Invasive methods are considered possible if the growth of malignant tumors in the heart area is suspected.
If the method of detecting changes was radiography, it should be remembered that false diagnosis or detection of pseudocardiomegaly is possible for the following reasons:
- Accumulation of fluid in the heart sac (pericardium).
- Formation of exudate in the pleural cavity due to injury or pleurisy.
- With ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity).
- With mild physiological curves of the spinal column (with “straight back syndrome”).
In addition to radiography, to confirm that the myocardial volume is indeed increased, the following hardware methods can be used: ECG, EchoCG.
Forecast
Congenital cardiomegaly does not have a good prognosis. Many children do not even live to see 3 months. Every second child recovers, but there is a chance that he will develop heart pathologies in the future.
Treatment for acquired bull's heart depends on the cause that triggered its development. In heart failure caused by dilated cardiomyopathy, cardiomegaly can progress to an advanced stage within 3 years, leading to disability or death. In other cases, the disease can develop without symptoms for decades if you change your lifestyle and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Cardiomegaly in adults develops due to the influence of various pathologies. The basis of treatment is lifestyle correction, elimination of the underlying pathological process and reducing the load on the heart. It is equally important to try to protect yourself as much as possible from irritating factors that can cause increased blood pressure, ischemia and lung disease. Drawing up a treatment regimen should be entrusted to a cardiologist, since self-medication can harm health and worsen heart failure.
Adjusting your diet
All patients must follow a diet. Basic principles of therapeutic nutrition:
- For breakfast you should eat porridge from all kinds of cereals. The ideal dessert is fruit.
- For lunch, you need to eat foods high in protein and foods of plant origin.
- Dinner should consist exclusively of low-calorie dishes.
- In between meals, you can snack on vegetables, fruits and low-fat yogurt.
If you have cardiomegaly, it is forbidden to consume canned food, sugar, fatty foods, and animal products.
Why is it developing?
There are several factors that may cause the disease:
- hypertension;
- kidney disease;
- coronary heart disease (angina pectoris);
- viruses or infections that affect the heart;
- drug or alcohol abuse;
- genetic factors, since the symptom sometimes occurs in newborns or fetal children;
- development of a heart valve with abnormalities;
- consequences of pregnancy and childbirth.
Article on the topic
How to lower blood pressure without medications? The simplest methods from a cardiologist
Therefore, those who are at risk for such triggers should undergo regular examinations with a cardiologist to identify the problem in a timely manner. After all, any disease detected as early as possible is easier and simpler to correct.