Description of the pathology
Changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle can provoke various diseases or metabolic disorders in the heart muscle.
Moderate cardiac dysfunction can be diffuse or focal. The first type is characterized by failure of the myocytes of the left ventricle, as a result of which they contract incorrectly. That is, the electrical impulse is carried out incorrectly through these cells. The second type is focal changes. In this case, scars form on the wall of the left ventricle. They consist of connective tissue that is not capable of conducting electrical impulses.
Moderate metabolic disorders can return to normal on their own, but if such disruptions occur frequently, the myocardium cannot recover.
Thus, changes can transform into irreversible ones. As the situation worsens, they can provoke cardiac pathologies.
When there is a discrepancy between energy consumption and its entry into the myocardium, the consequence will be degenerative changes. But even dystrophy does not always manifest itself, and if there are symptoms, it is often increased fatigue, which is not always paid attention to.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a condition that the body activates to compensate for the blood flow process. This happens especially often if there is mitral valve insufficiency. Hypertrophy affects the condition of the walls of the left ventricle; they lose elasticity. This also applies to the septum between the ventricles.
With hypertrophy, thickening of the walls also occurs. It is not always uniform; it can occur according to a focal principle, that is, only in a certain area of a given cavity. And myocardial dystrophy leads to the fact that the wall of the left ventricle becomes significantly thinner, and the chamber cavity stretches.
What is myocardial repolarization disorder?
Modern data on the mechanism of contraction of cardiac fibers and the conduction of nerve impulses along pathways are associated with the study of the electrophysiology of the heart. Understanding the role of these processes in the development of pathology helps to choose the right treatment for chronic heart failure, myocardial dystrophy, and cardiomyopathy.
Disruption of repolarization processes in the myocardium reveals the “secrets” of metabolic (metabolic) changes in the heart muscle, synthesis and conservation of energy reserves.
We will try to “translate” the scientific language of terms into an accessible interpretation of the biological properties of the cell.
Using electron microscopy, it became possible to study the structure of heart cells. Myofibrils—protein fibers of two types—were identified: thick fibrils turned out to be myosin, and thin ones turned out to be actin.
During the contraction process, thin fibers slide over thick ones, actin and myosin combine to form a new protein complex (actomyosin), muscle tissue shortens and tenses. When you relax, everything returns to normal. Between them there are bridges through which chemicals are transferred from one cell to another.
The heart is “started” by an electrical impulse. It is formed from multiple electrical currents from the junction of heart cells.
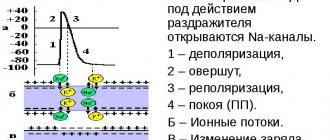
Every living cell has its own negative electrical discharge inside. The difference between the external and internal voltage on the two sides of the cell membrane is 80-90 mV. This is the transmembrane potential. It does not change throughout life and is characteristic of each type of cell.
But cardiac cells are characterized by a change in potential due to the movement of ions (charged particles of sodium, potassium, calcium) through open tubules. Thanks to them, an electric current arises. It is also called the action potential.
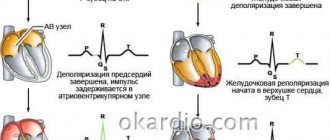
The occurrence of an impulse (electric current or action potential) in heart cells goes through two main periods:
- Depolarization - sodium and calcium ions enter the cell and the charge changes to positive. At a certain speed, the depolarization wave is transmitted to neighboring cells and covers the entire muscle. Actin combines with myosin and the heart contracts. The speed of wave propagation depends on the presence of healthy or altered cells (ischemic or scar tissue) in the path of the impulse.
- Myocardial repolarization is a longer period, it is necessary to restore the negative intracellular charge, the flow of potassium ions must leave the cells. This phase determines the accumulation of energy in the heart muscle and preparation for the next contraction. Visible rest actually includes all the biochemical mechanisms of energy production, enzymes and oxygen from the blood are consumed. Until complete recovery is completed, the heart is not able to contract.
The most important mechanism ensuring sufficient action potential is the sodium-potassium pump.
Diagram of depolarization (right) of a cell membrane
Violation of myocardial repolarization can be detected during an electrocardiographic examination by determining the repolarization time.
Diagnostics
Cardiac electrocardiography (ECG) is used to diagnose the correct processes of depolarization and repolarization.
The teeth and intervals mean nothing to the layman. Functional diagnostic doctors are familiar with subtle signs and changes in characteristic waves and can calculate the time of repolarization.
An increase in the depolarization time of the ventricles of the heart indicates a mechanical obstacle in the propagation of the impulse. This is possible with blockades of varying degrees.
Acute infarction most often affects the left ventricle. Here a connective tissue scar is formed, which serves as an obstacle to the impulse.
At the conclusion of the ECG, the doctor, in addition to signs of a heart attack, will definitely write about a moderate depolarization disorder.
When deciphering, the shape of the complexes, the height and width of the teeth, the level of the main line, and the duration of the intervals are taken into account
Impaired repolarization is indicated by a decrease in the T wave. This is typical for diffuse dystrophic changes and cardiosclerosis. In this case, the ECG conclusion does not make a diagnosis, but helps to understand the mechanism of formation of symptoms of the disease, stage and form.
Repolarization is disrupted by myocardial hypertrophy, taking certain medications, lack of microelements and vitamins in the diet, and dehydration. Such a patient should be examined in a hospital and a stress test with potassium chloride should be performed. After potassium administration, the ECG shows normalization of the shape of the ventricular complexes.
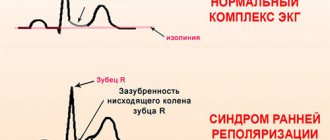
Early myocardial repolarization syndrome is characterized by a constant ECG pattern. In adults, differential diagnosis must be made with acute infarction.
A typical sign is that the symptoms resolve after an exercise test (20 squats).
When examining children and adolescents, the frequency of detecting changes in the myocardium of a metabolic nature increases. The child does not have any organic diseases of the heart or blood vessels. In such cases, importance is attached to energy disturbances.
Fetal suffering from cigarette smoke is not visible from the outside
The reasons for early repolarization in children, according to scientists, are associated with impaired development at the embryonic stage. The culprit is the mother, who did not follow the regime during pregnancy, ate poorly, and suffered from anemia. Children do not require special treatment, but observation by a cardiologist, reduction of physical and emotional stress, and proper nutrition are recommended.
Such changes are typical for athletes and people who have suffered from hypothermia. Some cardiologists prove the hereditary nature of changes in the conduction system of the heart.
Also read:Signs of cardiac arrhythmia
The detection rate of early repolarization syndrome ranges from 1 to 9%. It is found 3 times more often in men. Upon emergency admission with heart pain, the syndrome is found in 13 to 48% of patients.
It is believed that in this case a faster wave of excitation comes from the outer layer of the myocardium inward. A certain role is given to the predominance of the autonomic or sympathetic nervous system, and an increase in calcium levels in the blood.
Existing classifications subdivide early repolarization syndrome in relation to heart disease:
- with damage to the heart and blood vessels;
- without defeat.
According to the degree of expression on the ECG (manifestation in 12 leads) – 3 classes:
- minimal (available in 2-3 leads);
- moderate (at 4-5);
- maximum (6 or more).
No typical clinical symptoms were identified. There is a slight association with rhythm and conduction disturbances. Some cardiologists insist on the increased likelihood of sudden life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias in such patients.
The processes of electrical activity of the myocardium are important in the diagnosis of heart disease. They continue to be studied. Perhaps in the near future there will be new energy medicines or treatments that work through cellular potential.
Before we understand the violation, let's try to understand the norm. The heart is a universal organ. It acts in its own rhythm, without the control of our consciousness. The heart itself determines how much to work, how much to rest, and if the organ is healthy, it never upsets this balance.
All his work is based on the processes of excitation, contraction and relaxation. What we see on the electrocardiogram film shows how these processes occur.
Each cardiac muscle cell has an action potential, which is created by the flow of ions into and out of the cell. Its value directly depends on what state the cell is in: in the phase of excitation or rest.
Excitation is ensured by two processes ─ depolarization (the beginning of excitation) and repolarization ─ its end.
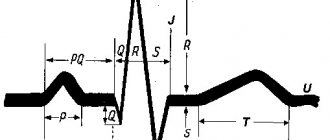
When repolarization occurs, the heart muscle is in a state of refractory or complete rest. On an ECG, this process is analyzed on the QT segment, which normally has a resting duration of 0.3-0.4 s.
An increase or decrease in the duration of this interval indicates a disruption of repolarization processes in the heart muscle. In addition to the duration, the functional diagnostics doctor evaluates the shape of the waves and the presence of additional waves in the QT intervals. In fact, disruption of this stage of excitation in the muscle tissue of an organ can develop in three syndromes. More on this later.
Repolarization is one of the cyclic phases of the functioning of the heart muscle (myocardium), accompanied by restoration of the electrical membrane charge. In the absence of disturbances in the functioning of the heart, sodium ions return to their original state during the process of repolarization, due to which the membrane electrical charge is restored, and normal indicators predominate on the cardiogram (there are no significant deviations).
If the repolarization process is disrupted, cardiac activity is destabilized. Tissues and organs lack the oxygen and nutrients transported by blood required for normal functioning. As a result, health deteriorates and the likelihood of developing many diseases of various systems increases.
The primary diagnostic method is an electrocardiogram.
The heart is the main organ that works in its own rhythm and is not controlled by the human consciousness - independently establishing the phases of work and rest. The absence of pathological processes in the body contributes to the stability of this balance. The basis of the work of the heart muscle is made up of three processes:
- Excitement.
- Abbreviations.
- Relaxation.
It is these phases that the electrocardiogram tracks. The most common change - a violation of repolarization processes on the ECG in adults - requires close attention from cardiologists. Every organ of the human body is made up of cells. Cardiac muscle has a special potential that can move ions out of the cell or vice versa. Its value depends on the state in which the cells are at the moment - excitation or rest.
The excitation phase consists of two processes:
- beginning – depolarization;
- the end is repolarization.
During the repolarization stage, the heart muscle is at rest, which lasts from 0.3 to 0.4 seconds. On the ECG film this phenomenon is displayed on the QT segment; a deviation from the norm characterizes a violation of this process.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor evaluates the shape of the teeth and determines the presence (or absence) of prolongation of the QT interval
Causes
Myocardial changes occur for many reasons, and it is very important to diagnose them correctly. Some of them are diseases that can even be life threatening.
The causes and results of myocardial disorders are:
- atrial fibrillation;
- steanosis of the heart valve (aorta);
- muscular dystrophy.
Pathological changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle can occur due to inflammatory diseases. This is myocarditis, which provokes both diffuse and focal disorders. And it, in turn, is caused by such pathologies as rheumatism, influenza, measles, rubella. Various autoimmune diseases also provoke changes in the myocardium.
It is very important for the body that metabolic processes function normally; otherwise, dystrophic changes occur, as a result of which the myocytes change. Metabolic disorders mean that the heart muscle does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen. This condition is also called cardiac dystrophy.
Cadydystrophy can occur due to:
- Kidney and liver failure.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland, namely its hyperfunction.
- Anemia.
- Infectious diseases of both acute and chronic nature, the most popular are influenza and tuberculosis.
- Intoxication of the body - alcohol, drugs, poisoning with drugs and other chemicals.
Additionally, the causes of cardiac dystrophy can be excessive physical exertion, emotional shock, and stressful situations. All these factors lead to chronic fatigue. Metabolic disorders are also caused by fasting or poor nutrition.
Children may also experience changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle, and the cause of this condition is cardiac dystrophy. Factors that provoke its manifestation in a child can be mental overload and decreased motor activity.
Metabolic disorders in the myocardium can occur due to a failure of the repolarization process. At the same time, the processes of potassium and sodium exchange at the intracellular level are disrupted. Metabolic disorders also arise due to the following factors:
- hypothermia;
- increased stress, both emotional and physical;
- obesity;
- chronic diseases.
In addition, changes in the LV myocardium occur as a result of the progression of atherosclerosis, ischemia, hypertension, and arrhythmia. These are serious diseases that provoke myocardial hypertrophy.
What is a violation of normal myocardial repolarization
The heart is a complex mechanism, any disturbance in which leads to disruptions in the entire circulatory system. One of the important aspects of functioning is the sequential contraction and relaxation of parts of the heart, which ensures proper blood flow. Contractions occur due to the transmission of nerve impulses - peculiar signals from the brain about the need for such a function.
Repolarization is a process during which the membrane potential of the cardiomyocyte is restored. The membrane is preparing to receive a new signal and, accordingly, to contract. At this moment, the ions return to their original place, which makes it possible to receive the next impulse. Speaking about repolarization, cardiologists describe the picture on the ECG at the time of ventricular diastole.
The correct course of myocardial repolarization processes is very important, since in the absence of treatment there is a risk of developing other diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- left ventricular hypertrophy;
- cardiac ischemia.
If we are talking about the entire muscle (diffuse changes), then the symptoms are often mild. Violation of myocardial repolarization may be accompanied by the following manifestations:
- disruption of blood flow;
- nervous system disorders;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- fast fatiguability.
Such symptoms are also common to many heart diseases, so after receiving alarming ECG results, additional studies are carried out.
Focal repolarization disturbances occur during blockades in different parts of the conduction pathways.
It is interesting to note that even people under 35 years of age who lead a healthy lifestyle and regularly engage in sports suffer from repolarization disorders.
Symptoms
Quite often, these changes are asymptomatic for several years, or appear slightly.
One of the most common signs of pathological changes in the heart muscle is angina pectoris. Because when the wall of the left ventricle thickens, compression of the vessels that feed the muscle occurs.
Atrial fibrillation and ventricular fibrillation can be the causes of the development of myocardial changes, as well as their consequence.
Another symptom of myocardial changes is “heart stopping.” In this case, the person feels that the heart does not beat for several seconds. As a result, he may lose consciousness.
Additionally, the following symptoms may occur:
- persistent increase in blood pressure, frequent changes;
- headache;
- pain in the heart area;
- weakness, fatigue;
- sleep disorders.
Diffuse changes
What are “diffuse-type changes in the left ventricular myocardium”? This type is the most common. In this case, not only the left ventricle is affected, but also the entire myocardium, since diffuse changes are characterized by uniform damage.
Diffuse disorders appear both in moderate pathological processes and in acute situations, such as myocardial infarction. In the latter case, there are changes in the structure of tissues and disruption of metabolic processes. Diffuse changes are an accumulation of myocytes in the left ventricle, which, under the influence of certain factors, have changed and do not conduct impulses.
With diffuse disorders of the left ventricular myocardium, swelling of the legs, tachycardia, and even fluid accumulation in the lungs are added to the general symptoms.
Diffuse changes in the myocardium of the left ventricle can provoke a deterioration in the circulatory process, myocardial hypoxia and the appearance of necrotic foci. The most dangerous consequence of these disorders is myocardial infarction.
Prevention of the development of myocardial fibrosis
Vladimir Trofimovich Ivashkin , academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences:
– Dear colleagues, I give the floor to Oksana Mikhailovna Drapkina with a message, which, in my opinion, is dedicated to the dreams of modern cardiologists about the prevention of the development of fibrosis
Oksana Mikhailovna Drapkina , professor, doctor of medical sciences:
- Thank you. On the first slide we see that the title of the lecture ends with the question: “Prevention of myocardial fibrosis. Where to begin?". Indeed, Sergei Rudzherovich correctly noted that this is probably more of a dream, but if there were no dreams, then, probably, there would be no planes, televisions, and so on, and we would not be sitting here, not communicating with you , Dear colleagues.
I’ll start, oddly enough, with the year 1867 and urge you to walk with me “back to the future.” Botkin Sergey Petrovich. It is no coincidence that I take our audience to the military medical academy, where Sergei Petrovich gave a lecture in 1867. He usually gave lectures in such a way that patients came, he demonstrated them and discussed with his listeners the main aspects of first the diagnosis and then the treatment. Here a young woman came with complaints of pain in the chest, in the left side, palpitations, shortness of breath and swelling of the neck, which prevented her from swallowing; often sweats both during the day and at night; urine is discharged in very copious quantities and frequently. I quote Sergei Petrovich: “Shaking in the legs and arms, especially when excited about something.” In general, we already, in principle, understand in which organ we should probably look for pathology.
Chest pain. It can be different. I will focus specifically on the pain that fascinated Sergei Petrovich more at that time. This young girl, as he says, “shows the place of pain under the left breast, where they usually begin, often spreading over the entire left side... The strength and duration vary... And they are most often caused by some kind of trouble or anxiety.”
You see a schematic history of the disease. It all starts in 1861. I calculated this because Botkin gave us detailed instructions on how everything happened. And we see that it all began, as often happened at that time, with fever, diarrhea and delirium - it was, apparently, typhus. Then the pain under the left breast began to increase. In 1866, her parents began to notice a swelling in the neck, and at the end an irregular rhythm appeared, this will also be clear in some aspects.
Inspection. “The patient is of good build, but pale. And at first glance you don’t notice any peculiarity in her face...except perhaps that the expression on her face is somewhat restless, as if she was frightened by something. And after that you begin to notice that her eyes are somewhat bulging. Then the increased volume of the neck due to the development of the thyroid gland sharply catches the eye...”
Percussion and palpation. Propaedeutics itself begins. It must be said that Sergei Petrovich, starting to percuss, percusses everything: the lungs, heart, liver, spleen, and so on. I will only dwell on the abnormalities that Sergei Petrovich identified. And these abnormalities lie mainly in the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum. Here the arrow shows that it occurs with a sharp dullness of tone along the parasternal left line in the region of the second rib and above.
Auscultation. In the same area, the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum “... listening to breathing, I find that it everywhere retains the vesicular character, but on the left side it is weaker, which is especially pronounced in the area of dull tone along the left parasternal line.” Dear colleagues, let’s briefly summarize. This means that in the second intercostal space to the left of the sternum there is a dullness of percussion sound, weakening of vesicular breathing and small, as he said, subcrepitating rales.
Please note that he also auscultates the thyroid gland. And I want to say right away that those symptoms of hyperthyroidism that we now know as Ringel’s symptom, as Moebius’ symptom, as Geoffroy’s symptom - all this is described by Botkin in this lecture, without calling it by its proper name. By the way, this later received the name Butman’s symptom, when we can hear a sharp arterial noise during auscultation of the thyroid gland.
Diagnosis. The diagnosis is beyond doubt. He says that you see a subject with a highly developed goiter, a certain degree of protrusion of the eyes, which, moreover, changes in size before your eyes, a frequent and uneven pulse, undulation of the neck veins, frequent and intermittent breathing. And just from this alone you can assume that you are dealing with Graves' or Graves' disease.
But the question arises: in which part of the heart should we look for the cause of pulmonary circulation disorder? We remember that the patient is choking, and this is basically what brought her to the doctor. What did Botkin find with his not very thin finger? So there was an airless state of the lung tissue, that is, atelectasis. That is, with the help of his hands and ears, Botkin in 1867 found compression of the lung tissue by the left atrium. And he says that this is where we need to look for the cause of shortness of breath. Moreover, he says that “enlargement of the right ventricle, which occurs more often than the left in patients, as he says with hyperthyroidism, is still a variable phenomenon, and the volume of the left atrium increases, I repeat, without fail. And you see on it, in addition, fluctuations in size (that is, one day one way, another day another) coinciding with the deterioration and improvement of the subjective state of the patients, which thus goes along with this increase or decrease in the size of the dull sound.” .
What was it? A forgotten disease? I'm not talking about hyperthyroidism now. I now want to turn my attention to the atrium. In these same clinical lectures, he says that “the weakness of the atrium alone is enough for blood to stagnate in it, as well as in the veins flowing into it, which thus expand, their valves become insufficient, and conditions are provided for the appearance of this undulation , which we observe in various forms of weakened cardiac activity and insufficiently rapid emptying of the atria.”
This year, as I already mentioned, we are celebrating the 180th anniversary of the birth of Sergei Petrovich Botkin. And when you read Botkin, you understand how modern he is, how far, on the one hand, we have come, and on the other hand, we have not gone very far in the diagnosis of some diseases.
So, atrial disease, has it been forgotten? No, and many scientists are working on this problem. There are different definitions, one of them is presented on the slide and belongs to Academician Ivashkin: Atrial disease is a primary or secondary pathology of the atria, which manifests itself with atriomegaly, various rhythm and conduction disorders, and symptoms of circulatory failure.
And the same risk factors for the presence of atriomegaly. We can also divide them into correctable and non-correctable. Of course, we are interested in correctable diseases, and today I will mostly talk about arterial hypertension. In general, we have just seen that arterial hypertension and chronic heart failure are practically the main cause of atrial fibrillation, heart rhythm disturbances. And I was always tormented by the question: after all, arterial hypertension is a condition when the left ventricle hypertrophies. Why do supraventricular arrhythmias occur more often than ventricular arrhythmias? I still can't figure out why, but this pattern probably has some answers. Because the atria are the weak link. And when there is an increase in pressure in the atria along the pressure gradient, since the left ventricle is thick or hypertrophied, it also increases the pressure within itself, then the atrium cannot hypertrophy for a long time, it dilates - and, please, atrial fibrillation. Therefore, fibrosis in the atria, atriomegaly - and hence the disruption of the electrical impulse, when fibrillation already generates fibrillation. This, in fact, seems to me to be what characterizes this patient.
And so we talk about fibrosis again. We, on the other hand, seem to approach fibrosis from a clinical perspective. And again, there are many definitions, but I, for example, like simple definitions that you don’t have to think about for a long time and can be remembered well and easily: this is the predominance of collagen synthesis over its breakdown. We are, of course, talking about structural collagen, the collagen that then forms a three-helical structure, which is very strong. And it is clear that once it has already formed, it is very difficult to reverse it or increase degradation.
Various types of fibrosis. Here are two portraits of the patient. Red – cardiomyocyte, gray – fibrosis. It is clear that the subject of our interest, of course, is the top picture, where there is reactive fibrosis - this is exactly the same hypertensive patient who seemed to be treated correctly. He didn't die from a heart attack or stroke, it didn't happen. But what happened to him? He developed left ventricular hypertrophy, which we consider to be an almost integral feature of arterial hypertension. But, in principle, it is probably necessary to intervene a little earlier - when even this reactive fibrosis has not yet appeared.
So I want to postulate that I think fibrosis is one of the earliest manifestations of atrial disease. And so the question arises: how to evaluate, how to prevent, is this even possible, and when to start treatment and what kind?
Please note, dear colleagues, in this picture we also see a cardiomyocyte, such a ubiquitous cytokine - transforming growth factor b-type - it is responsible for the initiation of fibrosis processes, the formation of collagen and other proteins of the intercellular matrix.
Let's look at what activates this cytokine - angiotensin-II, which is well known to us, and on the other hand, mechanical stretching. That is, any large chamber, ventricle or atrium, will itself cause its TGF-beta activity to increase. It will lead to the fact that cardiomyocytes are replaced, as if genotypically transformed into fibroblasts, and collagen is formed, and then fibrosis is formed.
We are extremely interested in this point, and I would like to briefly show the chronicle, facts and comments about atriomegaly. The first work aimed to substantiate the clinical consequences of atrial dilatation in diseases of the cardiovascular and bronchopulmonary systems. First, we realized that when the size of the left atrium is more than 4.7 cm, and the size of the right atrium is more than 4.8 cm, 100% of the clinical symptoms of chronic heart failure appear and persist: shortness of breath, cyanosis, fine rales in the lungs. That is, the presence of fine bubbling rales in the lungs clearly correlates with the size of the left atrium.
These, in my opinion, are very interesting, strange at first glance curves. But what do they characterize? The green curve depicts the percentage of patients with atriomegaly in whom the first tone is preserved. And we see that the larger the size of the left atrium, the fewer patients with preserved first sound. We always know that the first sound is a characteristic of the left ventricle, it is a systolic sound. And at the same time, the larger the size of the left atrium, the more patients with a weakened first sound. So, isn't this a manifestation of heart failure?
First step. Thus, the first step was a search, and we found that the “critical” dimensions of isolated dilatation of the left atrium, after which dilatation of the right atrium will necessarily join, are 4.2X4.4X4.7 cm.
Second step. Is it necessary to evaluate the contractile function of the atria, and why is it needed in general? It seemed to be as low as 25% or sometimes as low as 15% in left ventricular filling. And in principle, this is also a certain characteristic of diastolic heart failure. Please note, dear colleagues, this curve very much resembles the curve of the Frank-Starling law: the greater the maximum volume of the left atrium, the greater the volume of active emptying increases up to a certain point. But, as I already said, the “weak link” of the 4-chamber organ: it is quickly depleted, and with a large increase in the left atrium, the volume of activity decreases.
We are well aware of the assessment of the fibrosis fraction in the interventricular septum. The right picture shows how we circle it and calculate it using special methods. It is also possible to determine the size of fibrosis fractions, a little more, probably, this process will be labor-intensive, in the interatrial septum.
Wave R. If you look at P, then, of course, we are given a unique opportunity to assess the speed of electrical impulse transmission through the atria. These are traditional p-mitrale, p-pulmonale, but not only PQ as an interval, but also the PQ segment, of course, and the ratio give us a lot of information about what is happening with the atrium. In addition, to help the practitioner, it is very easy to calculate the volume of the left atrium using this formula: Left atrium end-systolic volume index (ml) = 8.0 + 0.2* (P wave duration in ms).
And absolutely amazing information in terms of the readiness of the atria to supraventricular rhythm disturbances is provided by the left atrial function index, which is calculated as the ratio of the emptying fraction to the integral of the linear velocity of the outflow tract of the left ventricle to the left atrium volume index.
In the same work, the speed of electrical impulse transmission through the atria was assessed. And also this interval, more than 165 ms, which is measured using an echocardiographic study, plus ECG sensors, says that this patient poses a risk in terms of atrial fibrillation.
Here's our data. The speckled gray is the volume of the left atrium, and the plain gray is the ejection fraction of the left atrium. Control – patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (first two columns). It turned out that the greater the volume of the left atrium, the inevitably the left atrium ejection fraction will decrease. Why do this? Is this just a theory? In my opinion, no. And today, assessing the contractile function of the left atrium gives us the key to diagnosing atrial heart disease, identifying patients not just with atriomegaly, but with reduced contractile function. And, in my opinion, this is, of course, the search for new antiarrhythmics (and we practically only have two antiarrhythmics, and all with different side effects), and the search for something that is probably not the only thing we can and should use our usual antiarrhythmics.
Step three. Clinical and morphofunctional characteristics of atriomegaly in patients with chronic heart failure and impaired thyroid status. Please note, patients with CHF along with hyperthyroidism with hypothyroidism and the control group: in all patients the size of the left atrium is changed. Let's remember Botkin again, he said: “I always see a change in the size of the left atrium, which coincides with the deterioration and improvement of subjective states.” The hypothesis has been verified - it is so. But with the right atrium we did not find such differences in this work.
Step four. Biological markers of heart failure. And finally, once again about fibrosis. In patients with diastolic heart failure who met all the criteria, we looked at galectin-3, a soluble beta-galactoside binding protein. It is a family of lectins. It turned out that in patients with preserved ejection fraction, the level of galectin-3 release is 100% higher than in patients with reduced ejection fraction, which also, with a certain dose of assumption, suggests that fibrosis in such patients will be more pronounced.
Thus, we can postulate that fibrosis is the morphological basis of tachyarrhythmias. There are a lot of literary results here, here is an illustration taken from a magazine, a section of the pulmonary vein near its mouth. As a matter of fact, it is there that various manipulations are usually carried out in order to convert the praxial form of atrial fibrillation into sinus rhythm.
And again, angiotensin-II is to blame. This means that, in addition to conventional antiarrhythmics, agents that will reduce the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system should be added to this therapy.
If we look at all the hormones and how they affect collagen synthesis, collagen degradation, and collagen accumulation, the worst character here is angiotensin II. It increases synthesis, it reduces degradation, and collagen accumulation is much greater. The second worst thing is aldosterone.
This is an example of a patient who suffered a myocardial infarction. Notice his heart, four weeks after myocardial infarction: yellow and red are the angiotensin-converting enzyme binding sites. Here we not only see in the area of myocardial infarction, as if from the side, but also EF - this means endocardial fibrosis. PF is pericardial fibrosis. There is a lot of fibrosis - there is a lot to act on, and the same with the AT receptor density, for example, after four weeks.
I exclaim again: we need a new approach! And we need to think about creating agents that selectively affect the atria. Are there such means? Here is their list so far. I will dwell on each of these medications every Internet session.
Today is the turn of ACE inhibitors. And indeed, Olga Nikolaevna showed this, ACE inhibitors both in the experiment, and not only in the experiment, demonstrated an effect on fibrosis. We see, for example, in six months the total Lisinopril is 9%. Over the year, Perindopril is 22%. And Losartan also showed its potential - 36% in a year.
It is with great pleasure that I want to present not only numerous foreign data, but also our work, the esteemed Professor Tatarsky from St. Petersburg. He looked at the paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation, the addition of Lisinopril to standard therapy led to a decrease in the frequency of paroxysms, the duration of arrhythmia episodes, easier tolerability and transformation into an asymptomatic form.
In our practice, we most often use Lisinopril and Diroton. Diroton is not an original drug, it is also a generic, but nevertheless its potential, in general as an ACE inhibitor, in terms of fibrosis has not yet been revealed.
"Atrial cross". Molecular and cellular mechanisms.
We will deal with this “atrial cross”. We have only just gotten closer to it, but there is so much more that is written in small letters. I think this will all be extremely exciting and probably difficult. I encourage you to work with us.
Thank you very much for your attention.
Nonspecific abnormalities
These violations are recorded on the ECG. The diagnosis sounds like “moderate nonspecific changes in the myocardium.” They have a direct connection with repolarization processes. This pathological condition affects the process of recovery of myocytes after an impulse has passed through them.
As a rule, such disorders are not dangerous, and, if necessary measures are taken, are completely reversible, since they are provoked by various past diseases, hormonal imbalances, and impaired metabolic processes.
Complications can include angina, heart failure, and even myocardial infarction.
Changes in the left ventricular myocardium may not be dangerous to human health. Quite often they are diagnosed during routine examinations, that is, by accident. This means that there are almost no characteristic symptoms. But you should not underestimate this condition - if you do not take the necessary measures, the condition may worsen. Usually, with moderate changes, doctors recommend changing your diet, giving up bad habits, and improving your psycho-emotional state.