Inner frame
Walking around the equator
It is estimated that during the day a person takes up to 30 thousand steps, that is, about 20 kilometers. Every 5.5 years it imperceptibly makes a journey equal to the circumference of the equator.
How much does a human skeleton weigh?
The mass of the human skeleton is about 11 kilograms.
When is a person taller: in the morning or in the evening?
Due to the flattening of the intervertebral cartilages, a person’s height decreases by about 1.5 cm in the evening. By the age of 80, a person’s height decreases by 5–7 cm compared to the age of forty.
How many bones are there in the skull?
The human skull consists of 23 bones. Only two bones of the skull - the mandibular and hyoid - are movable, the rest are firmly connected by sutures.
Stronger than brick and granite
Bone material is 30 times stronger than brick and 2.5 times stronger than granite. The large femur can withstand a vertical load of one and a half tons.
It can withstand a load of 350 kilograms
The strongest ligament in the human body, the ligament of Bertinius, which strengthens the hip joint, can withstand a load of 350 kilograms.
How many muscles does a person have?
The amount of muscle a person has is not the same for all people. Within normal limits, it ranges from 400 to 680 muscles. If all these muscles were tense, they would cause a pressure of approximately 25 tons. A grasshopper has about 900 muscles, and some types of caterpillars have even about 4,000. The total weight of all muscles is 40% of the total body weight in men, and 30% in women.
Which organ loses a lot of heat?
The efficiency of human muscles is 20%. The remaining 80% is spent on heat losses.
Where are the strongest muscles located?
The strongest are those located on both sides of the mouth and are responsible for clenching the jaws. They are capable of developing a force of about 70 kilograms.
Who loses more energy: a crying person or a laughing person?
According to research by French neurologists, a crying person uses 43 facial muscles, while a laughing person uses only 17. Thus, laughing is energetically more beneficial than crying.
What is the time of greatest muscle activity?
It is noted that muscles work most effectively at 13:00. 30 minutes.
Oxygen-consuming organ. Who is he?
Up to 60% of the oxygen entering the body is consumed by muscles.
Rhythm is your assistant
Rhythm is an important element of work, and everyone should learn from their heart in this regard: if you work rhythmically, then the work will be productive and you will have the strength to work for a long time.
When does the biological clock break?
Frequent disturbances in the physiological day-night cycle can lead to a painful disorder of a person’s internal “biological clock”.
Heart diseases
Heart disease has increasingly affected people in recent decades. This is caused by a low quality of life, poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle and a large number of bad addictions that every second person on earth has. Older people are more likely to suffer from heart disease. This is due to physical fatigue of the muscle, thickening of the blood, slowdown of all processes in the body and the presence of other concomitant diseases. According to statistics, heart disease is the most common cause of death. All diseases are conventionally divided into three groups, depending on which part of the organ is affected - blood vessels, valves and membrane tissue.
Let's look at the most popular heart diseases:
- Atherosclerosis is a disease in which blood vessels suffer. As the disease develops, they become blocked and atherosclerotic plaques form, which disrupt the blood flow process and, accordingly, interfere with the normal functioning of the heart muscle.
- Heart failure is a set of pathological changes in which the contractility of the organ is significantly reduced, resulting in the formation of stagnation in the pulmonary or systemic circulation.
- Heart defects are defects of the heart muscle, individual components of the organ, which disrupt its normal functioning. Congenital heart defects are more common; acquired ones are diagnosed much less frequently.
- Angina pectoris is a dangerous pathology that is characterized by oxygen starvation of the heart, and its cells die.
- Arrhythmia is a violation of the heart rhythm, which is characterized by its acceleration (tachycardia) or slowdown (bradycardia). This pathology is usually accompanied by a number of other heart ailments.
- Myocardial infarction is a disease in which there is insufficient blood supply to the myocardium.
- Pericarditis is inflammation of the outer lining of the heart - the pericardium.
Breath
How much air can you breathe?
Ventilation of the lungs (the number of breaths multiplied by the volume of inhaled air) in a healthy person reaches 5–9 liters per minute. At rest, a person makes an average of 16 respiratory movements per minute. This is about 23,000 per day. At the same time, about 7,000 liters of air pass through the lungs. The minute volume of human breathing (the amount of air passed through the lungs in one minute) is 5–8 liters per minute at rest, and during physical work it can reach more than 100 liters per minute.
Breathe calmly
A person at rest consumes 400–500 liters of oxygen per day, making 12–20 inhalations and exhalations per minute. The respiratory rate of a horse is 12 inhalations and exhalations per minute, a rat is 60, and a canary is 108.
Who cheers us up?
Negatively charged ions of air gases are friends of health; they make a person cheerful and efficient.
Biovacuum cleaner
The ciliated epithelium of the human respiratory tract carries out up to 20–30 g of dust per day.
Anatomical and physiological features
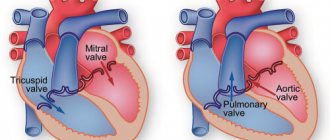
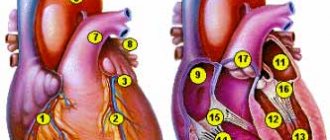
To understand the structure of the human heart, let's first look at it from the outside. We see a cone-shaped hollow muscular organ, to which branches of large vessels of the human circulatory system approach from all sides, like tubes or hoses to a pump. This is the living pump of our body, consisting of several functional sections (chambers), separated from each other by partitions and valves. Every eighth grade student knows how many chambers there are in the human heart. For those who missed biology classes, we repeat - there are four of them (2 on each side). What are these heart chambers and what is their role in the circulatory system:
- The cavity of the right atrium receives two vena cava (inferior and superior), carrying oxygen-free blood collected from all over the body, which then enters the lower section (right ventricle), bypassing the tricuspid (or tricuspid) heart valve. Its valves open only during compression of the right atrium, then close again, preventing blood from flowing in a retrograde direction.
- The right heart ventricle pumps blood into the common pulmonary trunk, which then divides into two arteries that carry oxygen-free blood to both lungs. In the human body, these are the only arteries through which venous rather than arterial blood flows. In the lungs, the process of oxygenation of blood takes place, after which it is delivered to the left atrium through two pulmonary veins (again, an interesting exception - the veins carry oxygen-rich blood).
- In the cavity of the left atrium there are pulmonary veins that deliver arterial blood here, which is then pumped into the left ventricle through the cusps of the mitral valve. In the heart of a healthy person, this valve opens only in the direction of direct blood flow. In some cases, its valves can bend in the opposite direction and allow part of the blood from the ventricle to pass back into the atrium (this is mitral valve prolapse).
- The left ventricle plays a leading role; it pumps blood from the pulmonary (lesser) circulation to the systemic circle through the aorta (the most powerful vessel in the human circulatory system) and its numerous branches. The ejection of blood through the aortic valve occurs during systolic compression of the left ventricle; during diastolic relaxation, another portion from the left atrium enters the cavity of this chamber.
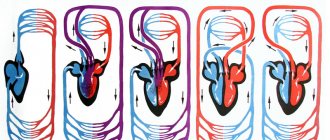
Circulation
Blood plasma... and ancient seas
The composition of blood plasma resembles the composition of the water of the ancient seas on Earth, in which life originated.
Twice the length of the equator
The total length of blood capillaries in the human body is approximately 100,000 kilometers. This is 2.5 times the length of the earth's equator, and the total internal area is 2,400 m2.
Pump that lasts a lifetime
Over 60 years of ordinary, not very stressful life, the human heart makes more than 2,000,000,000 contractions. A tractor would do the same work if it lifted a boulder weighing 65 tons from sea level to a height of 5,500 meters.
When is there more cholesterol?
100 ml of blood of a healthy person contains 20–250 mg of cholesterol in autumn and winter, and only 170–180 mg in summer and spring.
Heart "shirt"
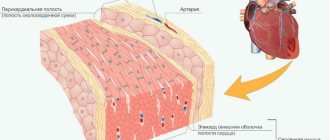
The heart has a chemise - a layer of connective tissue; There is a small amount of fluid between the heart and the “shirt”. The pericardial sac (“heart sac”) protects the working heart muscle.
Flattened red balls
Red blood cells, or red blood cells, whose total surface area is 3,400 m2. Every day, about 2,000,000,000 of them die in the body, which is 0.01% of their total number. The total surface area of all red blood cells is 3,400 m2. There are 5,000,000 red blood cells in each mm3 of blood, and in all five liters contained in the body of an adult there are 25,000,000,000,000. If you lay out all these red blood cells in a row, the resulting chain will stretch for 200,000 kilometers, encircling the globe five times along the equator.
"Sprints" within us
Almost all cells of the human body have nuclei that control all physiological processes in the cell itself and participate in the process of cell division. The only exception is red blood cells. They are born with a nucleus, but already in the early stages of development, they lose it, thereby losing the ability to reproduce. New red blood cells are formed in the red bone marrow from stem cells. About 2,500,000 red blood cells are produced every second and about the same number die. In one day, an erythrocyte travels about 15 kilometers in blood vessels, supplying tissues with oxygen and taking away carbon dioxide from them. During its existence, one red blood cell travels an average distance of 1,800 kilometers.
They live to die
Blood cells constantly die and are replaced by new ones. The life of erythrocytes (red blood cells) lasts 90–125 days, leukocytes (white blood cells) - from several hours to several months, depending on the type of leukocytes. In the blood of an adult, about a billion red blood cells and five billion leukocytes die every hour. They will be replaced by new blood cells. During the day, 25 grams of blood undergoes complete regeneration.
Thinner than a hair
Blood capillaries are 10 times thinner than hair.
That's the speed!
Within one minute, the heart pumps about 4 liters of blood into the aorta. The speed of movement in the aorta is 0.5 m/sec, and through the capillaries, blood flows at a speed of 0.5 mm/sec. A complete circulation of blood through both circles of blood circulation is completed in 21–22 seconds.
A special substance in blood
Each red blood cell contains 265,000,000 hemoglobin molecules. The assembly of its molecule takes only 90 seconds. Every second, 6.5∙1014 hemoglobin molecules are synthesized in the human body. 100 ml of human blood contains 13–16 g of hemoglobin. One gram of hemoglobin can bind up to 1.34 ml of oxygen. At rest, about 4 l/min flows through the human heart, which provides tissues with about 400 ml of oxygen.
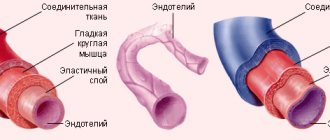
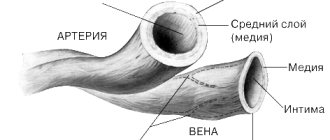
Ah, these “thin tubes”!
The thickness of the artery walls is 0.8–0.9 mm. The diameter of various human arteries is 0.4–2.5 cm. The average diameter of capillaries in humans is about 7 microns, which is slightly less than the diameter of a red blood cell. In the arteries, the blood volume is on average 950 ml.
"Sugar Queen"
This is what ancient Tibetan doctors called the liver. It stores nutritional reserves and, if a person is hungry, it turns them into sugar, thereby feeding him. At rest in a person, up to 50% of the blood can be in the “blood depot” - the liver and spleen, from where, if necessary, it is released into the bloodstream. The blood flow in the kidneys is 420 ml/min, in the heart - 84, in the liver - 5.7, in the brain - 53, in the striated muscles - only 2.7 ml/min. The liver consumes 10 times more oxygen than muscle of equal mass and produces more heat. It is a powerful protective barrier on the path of blood flow from the digestive organs to other organs. The liver breaks down alcohol most efficiently between 6 and 8 pm. 1.5 liters of blood flows through the liver within one minute, and up to 2,000 liters per day.
Women beat more often
The heart of an adult pumps about 10,000 liters of blood per day. A man's normal resting heart rate is 60–80 beats per minute. A woman’s heart beats 6–8 beats faster. Heavy physical activity increases the heart rate to 200 beats per minute. The pulse rate of an elephant is 20, that of a bull and a frog is 25, that of a rabbit is 200, and that of a mouse is 500.
Anatomy and physiology of the human heart
Our body is a complex structure consisting of individual components (organs and systems), the full functioning of which requires constant supply of nutrition and disposal of decay products. This work is performed by the circulatory system, consisting of a central organ (the heart pump) and blood vessels located throughout the body. Thanks to the constant work of the human heart, blood continuously circulates through the vascular bed, providing all cells with oxygen and nutrition. The living pump of our body makes at least a hundred thousand contractions every day. How the human heart works, what its operating principle is, what the numbers of the main indicators indicate - these questions are of interest to many people who care about their health.
Digestion
Even the saber gets dull
The tip of a saber becomes dull when it hits tooth enamel. In terms of hardness, enamel can be compared to quartz.
How many, two or four?
Baby teeth are replaced by permanent teeth. The last molar usually erupts by the age of 18–20, and sometimes later, when a person “acquires wisdom through learning,” as Hippocrates thought. He called this tooth the “wisdom” tooth. Half of humanity has only two, not four wisdom teeth.
The naked part of our skeleton
The specific gravity of tooth enamel is 2.9–3.05 g/cm2. Dentin of a tooth has a specific gravity of only 2.2 g/cm2. The dentin of an adult tooth contains about 65% mineral salts, 28% organic substances and 8% water. The composition of dental cement includes about 30% organic substances, more than 55% calcium phosphate, about 8% calcium carbonate, as well as calcium and magnesium fluorides.
Can't stand it!
The most painful place in the human body is the teeth. There are usually no more than 200 pain receptors per square centimeter of skin, and from 15,000 to 30,000 receptors per square centimeter of tooth dentin. There are even more of them at the border of enamel and dentin - up to 75,000 receptors.
"Acorn" or "stomach"?
The word “stomach” is derived from the word “acorn” (in the old days “small acorns were called stomachs”). There are one hundred gastric glands per 1 cm2 of gastric mucosa. They are located closely. Unlike other digestive juices, bile contains almost no enzymes.
"Toothed" enzymes
During the day, a person secretes about 1 liter of saliva, 3 liters of gastric juice, 2 liters of pancreatic juice, 3.5 intestinal juice, 2 one liter of bile. A person produces an average of one liter of saliva per day.
What does one o'clock in the afternoon mean for the stomach?
Most gastric juice is formed at 13:00, even if a person has not eaten anything.
And is it all in us?
The length of the human intestine exceeds the length of the body by 3–4 times. The total surface area of the villi of the jejunum is 37 m2, the duodenum is 1.3 m2, and the ileum is 5.3 m2.
Do we also have gases?
During the fermentation of food gruel, hydrogen and carbon dioxide are formed in the right (ascending) section of the large intestine, and during the process of decay, methane and hydrogen sulfide are formed in the left (descending) section. All this is mixed with air that enters the intestines during eating along with food. When digesting lunch, about 15 liters of gases are formed.
That's how lint is!
There are 3,000–4,000 villi on one cm2 of the inner surface of the intestine. Each is covered with 3,000 cells, which, in turn, have 100 suction tubes. The absorption surface in the small intestines is about 5 m2, i.e. three times the surface area of the body.
Short "life"
About 70,000,000,000 intestinal epithelial cells die every day, each of which lives only 1–2 days.
You need it to breathe, move, think.
At rest and on an empty stomach, the human body produces so much energy per day that it would be enough to heat 20 liters of water from 10ºC to boiling. The heat generated when a woodcutter works for eight hours is enough to heat 100 liters of water to a boil.
Who are gut bacteria afraid of?
Lingonberries and cranberries contain a lot of benzoic acid. It kills putrefactive bacteria in the intestines.
Treatment of heart diseases
A cardiologist treats heart diseases. Before starting therapy, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient, which includes: an electrocardiogram, ultrasound of the heart, general and biochemical blood tests, Holter ECG and other studies.
Only after complete diagnosis and diagnosis is therapy prescribed. Basic methods of treating heart disease:
- Conservative treatment: maintaining physical and emotional peace, taking prescribed medications, regulating proper nutrition.
- Drug therapy is used for any disease. Most often, drugs are prescribed to reduce bad cholesterol, blood thinners (especially in old age), inhibitors and many others, depending on the diagnosis.
- Surgical intervention is performed if it is impossible to achieve the desired effect using conservative methods, for example, when a pacemaker is required, a hole between the parts of the heart needs to be repaired, or the patient needs an organ transplant.
Diagnosis and treatment of heart disease should be carried out exclusively by a doctor (general practitioner, cardiologist or cardiac surgeon). Self-medication is strictly forbidden - at best it will not bring the expected result, at worst it will aggravate the situation and lead to a number of complications.
What are we “made of”?
Everything from cells
The human body consists of 100,000 billion cells. For comparison: the elephant's body consists of 6,500,000 billion cells.
Water, water...
Water makes up 80% of a child's body weight and 70% of an adult's body weight. Human brain cells contain 80%, muscles - 76%, bones - about 25% water. A sip of water is 20 milliliters of liquid for men, and 14 for women. The richest tissue in the human body is the vitreous body of the eye, which contains 99% of it, and the poorest tissue is tooth enamel. It contains only 0.2%.
Is water really that important?
Loss of moisture in the amount of 6–8% of body weight causes a semi-fainting state in a person, 10% causes hallucinations and impaired swallowing reflex. Loss of 12% fluid leads to cardiac arrest.
Are there gases too?
More than 96% of the human body's mass is made up of four chemical elements. Oxygen accounts for about 60% of the mass, carbon - about 20%. They are followed by hydrogen - 10% and nitrogen - 4%.
Not only there, but also from there!
A person per day can secrete 0.5–12 liters of sweat, which contains 9899% water, 0.1% urea, uric, lactic, pyruvic, citric acids, ammonia, creatinine, serine, fats, volatile fatty acids, cholesterol, aromatic hydroxy acids , acetone, mineral salts.
Anatomical structure of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ that is surrounded on the outside by the pericardium. The cavity between the two components is filled with liquid, which performs an important function - it reduces friction of the heart muscle and ensures its hydration. The pericardium includes three layers: epicardium, myocardium and endocardium.
The heart itself consists of 4 sections: two atria and two ventricles. The left ventricle and atrium circulate arterial blood enriched with oxygen, the right side of the heart helps pump venous blood. Entering the heart, blood accumulates in the atria and, upon reaching the required volume, is redirected to the ventricles.
All sections are separated by valves - the mitral on the left and the tricuspid on the right. Their main purpose is to ensure the movement of blood in one direction - from the atria to the ventricles.
During normal functioning of the heart, the right and left parts do not communicate with each other. With the development of pathology (usually congenital heart defects), holes may remain in the septum. In this case, during contraction of the heart muscle, blood from one half can enter the other.
Skin formations
Non-removable "clothes"
Skin is the heaviest organ of the human body. She weighs on average 2.7 kg. The skin does not allow water, germs, or dirt to pass through. Protects us from blows, injections, bites. About 2% of the oxygen consumed by a person enters the body through the skin. A person of average height loses about 800,000 skin microparticles every hour, and an average of 675 grams per year. By the age of seventy, total skin loss is just over 47 kg, that is, 70% of the average person's weight. The human body excretes about 0.5 liters of water per day through the skin. About 10 grams of solids are released.
Who can tell if we are cold or hot?
The entire skin surface of the human body contains about 250,000 “cold” receptors and only 30,000 “heat” receptors. Skin temperature varies in different parts of the body. So, in the armpit it is 36.6ºС, on the stomach - 34ºС, and on the face - 25ºС. Blood and internal organs have a temperature of 37.2–38.5ºС.
Is it better to be clean or dirty?
On one cm2 of dirty skin there are about 40,000 microbes.
Transmitting "SOS!"
Our skin contains 250,000 nerve endings that respond to cold, 30,000 that respond to heat, and about 1,000,000 that respond to pain.
Skin and time
The skin is least sensitive to injections at 9 am and most permeable to cosmetics between 6 and 8 pm.
Space "antennas"
Human hair is 500 times thicker than the walls of a soap bubble, 5 times thicker than a capillary, 12 times thicker than the walls of an alveoli and 20 times thicker than a spider's web. Hair grows in newborns at a rate of 0.2 mm per day, later - up to 0.3–0.5 mm per day. Eyebrow, eyelash and armpit hair lasts 3–4 months, scalp hair lasts 4–6 years. In a month, hair grows by one centimeter. About 100 hairs die on the head every day. Dead hair may not fall out immediately, so up to 20% of dead hair sometimes accumulates on the head.
The braid is not only a girl’s beauty
The longest braid of one Japanese woman is 3 meters, she grew it for 20 years. The longest hair was worn by Swami Pandarasannadi, the head of the Indian monastery of Thirudathurai. In 1949, his hair length was 7 meters 92 centimeters.
And beard and mustache
The longest beard belonged to Hans Langseth - 5 meters 33 centimeters, and the longest mustache belonged to the Swede Birger Pellas - 2 meters 90 centimeters.
Primate Heritage
The tips of all twenty fingers on our limbs bear dense flat horny formations - nails. Nails are the property of primates. The nail grows due to the epithelium of the nail bed. Nails protect especially sensitive fingertips. A fingernail grows at a rate of a hundredth of a millimeter per day, and a toenail grows at a rate of five hundredths. Over the course of a year, the fingernail lengthens by a total of three centimeters. The longest nail on the hand (on the thumb of the left hand) reaches a length of 101.6 centimeters. It belonged to Indian Sridhar Chillar. The total length of the fingernails on his left hand, when measured in March 1990, was 4 meters 40 centimeters. He hasn't cut his nails since 1952.
Selection
Why are we crying?
Children cry to get attention, to express their emotions: fear, anger or joy. And also so that with tears the harmful substances that are produced from pain and suffering are removed from the body. In addition, when we blink, tears wash the eyeball, clearing it of dust and germs. A healthy human body produces approximately 0.5 liters of tear fluid per year. Even the sternest man sheds 1–3 milliliters of tears every day.
Blood filters
The total length of the renal tubules is 120 kilometers. A person has about 2,000,000 nephrons in both kidneys. During the day, the kidneys pass 2,000 liters of blood through themselves, and this is a whole tank. An adult excretes 1,200–1,600 ml of urine per day and 15–45 mg of oxalic acid should be excreted in the urine.
What are uroliths?
The chemical composition of uroliths—kidney stones—may vary. 40% of uroliths are oxalates (oxalic acid salts), 27% are phosphates (orthophosphoric acid salts), 12–15% are urates (uric acid salts), 2% cystine, xanthine and protein stones and 20–30% are mixed stones type.
Disease Prevention
A healthy heart is the key to excellent health and normal functioning of the body. It is extremely important to take proper care of it to reduce the risk of developing heart disease. To do this, just follow the doctor’s simple recommendations:
- Monitor your diet, giving preference to healthy and healthy foods. It is necessary to exclude from your diet dishes that adversely affect the condition of blood vessels and the functioning of the heart muscle (fatty, fried, smoked).
- Avoid excessive physical activity, but this does not mean that you should completely exclude sports from your life. Moderate exercise and walking in the fresh air will only strengthen the heart muscle and help avoid illness.
- Minimize stress, strong emotions and experiences. An increase in adrenaline accelerates blood circulation and forces the heart to work harder - this provokes the development of a number of pathologies.
- Promptly treat diseases that can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, for example, sore throat.
The heart is an important organ that circulates blood in the body. It is extremely important to maintain its health and normal functioning. By taking care of your heart, you will ensure a long and healthy life.
Vision
Complex optical device
Up to 14 months in newborn girls and up to 16 months in boys, there is a period of complete non-perception of colors. Then the perception of red appears, then green, and even later blue. The formation of color perception ends at 7.5 years in girls and by 8 years in boys. The eye is able to distinguish 130–250 pure colors and 5–10,000,000,000 mixed shades.
After an hour in the dark
After one hour in the dark, the light sensitivity of the eye increases 200 times.
Rods and cones
The human retina contains 125,000,000 rods and 6,500,000 cones, and together they are so sensitive that a person could theoretically see the light of a candle at a distance of 200 kilometers.
How addiction is formed
Anyone can become addicted to alcohol: you don’t have to drink strong alcohol to do so. The body reacts to any ethanol-containing drink - alcohol poisoning occurs. Over time, physical cravings develop. The blood alcohol level is the same whether it is 100 grams of vodka or 2 liters of beer.
For each person, the maximum dose of ethanol is individual. The manifestation of the disease is loss of control over drinking. At the same time, there is no critical perception of one’s state when drinking alcohol.
Over time, natural biochemical processes change. Physical cravings are formed when a person constantly needs ethanol. However, this does not happen immediately, but after the onset of psychological dependence. Initially, drinking is needed to overcome complexes or in an attempt to cope with problems or relieve stress. Over time, such a solution becomes the only acceptable one.
Without the opportunity to drink, a person’s mood and well-being worsen. Therefore, the frequency of drinking alcoholic beverages and the dose of ethanol are increasing. The craving for alcohol becomes out of control and pathological. All new doses are needed to overcome withdrawal symptoms, while the pleasure from drinking becomes less and less. The emotional reaction to alcohol-containing drinks changes.
Hearing, smell, touch
“Hello, I can’t hear you!”
The human middle ear contains 2,500 cells that respond to sounds. The upper limit of the frequencies we perceive reaches 16–20 million hertz. Over the years, the ear's sensitivity, especially to high-pitched sounds, decreases.
Tasty when +24ºС
On the surface of the tongue there are about 9,000 nerve endings that respond to taste. They function best at 24ºC.
Small, but smart
The surface of the olfactory zone of the nose is only 5 cm2, but it contains about 1,000,000 nerve endings. The sensation of smell occurs when at least 40 nerve endings are excited.
That's why he's freezing!
The coldest part of the human body is the nose. The temperature of its tip usually does not exceed +22ºС.
Nervous system
A gigantic amount and... one percent
The human nervous system consists of 10,000,000,000 neurons and 70,000,000,000 supporting cells. Of this gigantic amount, only one percent performs independent work, that is, it receives signals and controls the work of muscles; the remaining 99% are intermediary cells.
The center of all centers or the main organ of the mind
At three years of age, the human brain is already 80% developed. It reaches its highest development at about 20 years of age. Subsequently, its mass decreases. The cerebral cortex makes up approximately 44% of the brain's volume. The surface area of the crust as a whole is 1,468–1,670 cm2.
We are in third place
Man ranks third in terms of brain mass (1,400 g) in nature after the elephant (5 kg) and whale (2.5 kg).
These are the squares!
The total area of the cerebral cortex in humans is on average 83,591 mm2, chimpanzees - 24,353 mm2, dogs - 6,523 mm2, rabbits - 843 mm2, rats - 254 mm2.
Nature is not fair
Starting from the age of thirty in humans, 30,000 to 50,000 nerve cells in the brain die every day.
Water and nerve cell
A nerve cell—a neuron—contains 65–68% water and 32–35% solids, of which proteins account for 68–70%. 20–25% are lipids, 2–5% are nucleic acids, 1–2% are carbohydrates.
With it the blood vessels are toned
Nitric oxide (II) can be formed in the human body. It ensures communication between neurons and maintains vascular tone.
The bigger, the better
The larger the diameter of the nerve fiber, the faster the excitation travels through it. In warm-blooded animals, the excitation speed is 0.5–120 m/sec.
"Nervous" assistants
Not a single human action can be carried out without the participation of the nervous system. To move the body from a horizontal to a vertical position, the human brain sends hundreds of nerve impulses—signals—through the nerves to the muscles.
Everything for vision
As part of the cranial nerves, 2,600,000 nerve fibers enter the brain and 140,000 exit. About half of the exiting fibers carry orders to the muscles of the eyeball, controlling rapid and complex eye movements. The remaining nerves control facial expressions, chewing, swallowing and the activity of internal organs. Of the incoming nerve fibers, 2,000,000 are visual.
Location and functions of the heart
The heart is an important human organ, which is located in the center of the chest between the lungs, with a slight shift to the left. In exceptional cases, it may be located on the right, when a person has a mirror structure of the body. At its core, it is a muscle that, by contracting, maintains normal blood circulation in the body. The heart has a cone shape, the average weight of the organ is 250-300 grams, and its dimensions are 10-15 cm in height and 9-10 cm at the base.
Heart function
Pumping blood is the main function of the heart. This process must occur continuously to ensure that the internal organs are supplied with oxygen and nutritional components.
The work of the heart muscle consists of two stages:
- Diastole is relaxation of the heart. At this stage, blood enters the left atrium and flows through the mitral orifice into the ventricle.
- Systole is a contraction of the heart, during which blood flows into the aorta and spreads throughout the body, transporting oxygen to the internal organs.
The cardiac cycle includes the following stages: contraction of the atria, which lasts 0.1 seconds, and ventricles (duration 0.3 seconds) and their relaxation.
Men and women
"The stronger sex"
- The male brain weighs 200 g more than the female brain.
- Boys aged 15–24 years old fall unsuccessfully 6 times more often than girls of the same age.
- Among outstanding mathematicians, there are 12 times more men than women.
- Deviations from the norm of color vision are much more common in men (8%) than in women (0.5%).
- Men have 20% more lung capacity than women.
- 48% of men and only 22% of women snore in their sleep.
- Boys are more likely than girls to be left-handed and generally use their left hand fluently, which is explained by the leading role of the right hemisphere of the male brain.
- 80% of all people who stutter are men.
- Blood volume averages 5.2 liters in men and 3.9 liters in women.
- The average weight of a man's heart is 330 g; a woman's is 250 g.
"Weaker sex"
- Girls start talking earlier than boys.
- A woman's sense of smell is 20% better than a man's.
- Mental depression occurs twice as often in women as in men.
- Women have a better ear for music than men: for every 6 women who are not out of tune, there is 1 man.
- Three quarters of all migraines occur in women.
- Women are twice as sensitive to alcohol as men.
- Women prefer sweet dishes, and men prefer salty ones.
- In women, the right eye sees sharper and the right ear hears better, while in men it is the other way around.
- Adipose tissue makes up 11% of a man's weight and 23% of a woman's weight.
- Women, more often than men, suffer from dental caries.
- 42% of men and 62% of women complain of insomnia.