Brief description of the procedure
Total procedure time: 30 min Use of contrast agent: yes, intravenously Preparation and preliminary examinations: no
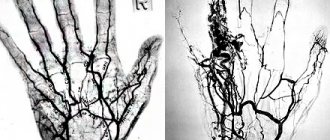
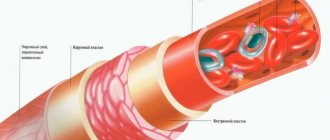
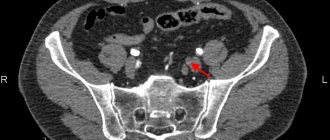
CT angiography of the iliac arteries and lower extremities CT angiography of the iliac arteries and lower extremities with bolus contrast and 3D reconstruction - a procedure for multispiral tomographic scanning of the area under study to obtain high-precision imaging of blood vessels. The study is carried out with contrast enhancement, which allows you to see the most minor deviations from the norm precisely at the time of the examination as contrast passes through the vessels. Subsequent image processing and 3D reconstruction allows you to visually assess the structure of the vessels, the presence of pathological changes in them, and also provides accurate preoperative planning.
How is the procedure performed?
- During the examination, the patient lies on the scanner table, and the X-ray tube rotates around the patient.
- The patient is given contrast before the procedure.
- The computer converts the images obtained using X-rays into three-dimensional ones, which allows for high-quality visualization of the tissue structure of the area being studied. Visualization of vessels requires the use of a contrast agent, since the determination of morphological changes in vessels without contrast has low information content.
- The patient must remain motionless during scanning to avoid blurring of the images. Sometimes you may need to hold your breath for a short period of time.
- CT angiography takes an average of 5-10 minutes
Indications and contraindications
Due to the fact that the method is invasive, it is used only for strict indications, which include:
- suspicion of vascular occlusion (acute or transient, permanent or transient), for example, intermittent claudication, acute ischemia of the lower limb;
- to determine vascular anomalies (diverticula, aneurysms, the presence of anastomoses);
- for the diagnosis of systemic vascular pathologies;
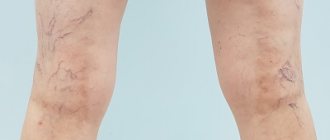
- confirmation of varicose veins and determination of the degree of its progression; diagnosis of angiopathy in diabetes.
CT angiography of the vessels of the lower extremities is performed using iodine-containing contrast agent. Therefore, this diagnostic method is contraindicated for persons with an allergy to iodine. It is also not recommended for persons with thyrotoxicosis and renal failure. The following diseases are relative contraindications:
- chronic heart failure during decompensation;
- CT scanning is not advisable for children under two years of age;
- pregnancy (especially the first and second trimester), lactation period;
- liver failure;
- the presence of plates in the lower extremities, the Ilizarov apparatus;
- unstable angina, early recovery period after myocardial infarction;
- diseases in which any of the stages of blood clotting is disrupted.
Since the examination is carried out through puncture of a vessel in the groin area (femoral artery), there should be no rashes or inflamed skin in this area before the examination.
How to prepare for the procedure?
CT angiography uses a contrast agent to better visualize the vessels.
- If a CT scan with contrast is planned, the patient is advised not to drink or eat 6-8 hours before the test. A contrast agent is usually administered intravenously immediately before the scan.
- The presence of a reaction to contrast must be reported to the doctor before the study. If necessary, antihistamines can be prescribed.
- If the patient suffers from diabetes and takes metformin, then it is necessary to inform the doctor in advance to adjust the use of this drug.
- The contrast agent is excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, if renal function is impaired, the administration of contrast must be agreed with the attending physician.
- CT scanners have weight restrictions and if the weight is large, it is necessary to find out the technical capabilities of the scanner.
- Before the examination, you must remove your jewelry and change into a hospital gown.
Diagnosis and treatment of thrombosis in Medical
Specialists from the Paracelsus Medical Center will help in diagnosing and eliminating this pathology, provide support during the rehabilitation period, and give recommendations for further prevention.
Our center uses expert-class equipment from leading global manufacturers for diagnosis and treatment. The consultation is conducted by practicing phlebologist surgeons.
On the basis of "Operating Room No. 1" phlebological operations are performed for venous disease. The key advantage of the Paracelsus Medical Center network is highly qualified professional surgeons with extensive practical experience.
Drug treatment
The basis of drug therapy is anticoagulants (thin the blood, prevent the growth of a blood clot), fibrinolytics and thrombolytics (dissolve existing clots), antiatherosclerotic drugs (lower cholesterol levels). If necessary, analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, cardiotonic drugs, vitamins, minerals, etc. may be needed as symptomatic therapy.
Surgery
There are such methods of surgical treatment of the disease:
- thrombectomy ー removal of a blood clot;
- stenting (expansion using a frame) and shunting (creating a bypass path for blood flow) for atherosclerotic artery disease;
- arteriovenous shunting.
If the thrombus cannot be removed, a vena cava filter can be installed - the device is placed in the vein above the level of blockage to prevent it from moving and closing the lumen of the vessels of vital organs.
Indications for CT angiography
A patient may need a CT angiogram if they have symptoms of a stenosis or blockage of a blood vessel in the legs.
CT angiography is indicated for diagnosis:
- pathological enlargement (expansion) of part of an artery (aneurysm)
- vessel damage or bleeding
- the presence of an inflammatory process or swelling in the walls of blood vessels (vasculitis)
- Determining the cause of intermittent claudication
- blood clots
- other arterial diseases
- Buerger's disease (thromboangiitis obliterans)
When is the study ordered?
CT angiography of the iliac arteries and lower extremities with bolus contrast and 3D reconstruction is prescribed for:
- suspected stenosis of the arteries of the lower extremities;
- progressive atherosclerosis;
- traumatic injuries to the area being examined;
- observation of acquired and congenital defects;
- postoperative monitoring of the condition of the iliac arteries and arteries of the lower extremities after bypass or stenting.
The obtained CT angiography data is processed by special programs with the ability to obtain three-dimensional images and multiplanar reconstructions. The method allows you to build a visual 3D model of blood vessels and assess the extent of the changes.
Risks
Risks of CT angiography include:
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
- Allergy to contrast agent
- Damaging effects of contrast on the kidneys
CT scans result in much more radiation exposure than X-rays, and frequent procedures can increase the risk of developing cancer. But with the development of technology, the radiation dose from CT is decreasing.
- Most often, agents containing iodine are used to contrast CT scans. If a patient has a reaction to iodine, then the risk of developing a reaction to contrast is quite high
- If a patient with a reaction to iodine requires CT angiography, then it is possible to use antihistamines or steroids before the procedure.
- Given that iodine is excreted by the kidneys, it is recommended to take more fluids after contrast angiography to minimize the effect on the kidneys.
- Very rarely, contrast can cause a very dangerous reaction - anaphylactic shock. If a patient develops symptoms such as shortness of breath or weakness, he should immediately notify the x-ray technician.
Symptoms of thrombosis
The clinical manifestations of this pathology vary depending on the location.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis
When a vein is blocked, the outflow of blood is hampered, so the tissues beyond the blockage swell and turn blue. The waste products of cells accumulate, therefore tissue intoxication develops, this is accompanied by pain, impaired sensitivity (the sensation of “crawling goosebumps”). If you do not intervene in time, the tissues begin to die.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis of the lower extremities:
- swelling of the leg, a sharp increase in size, cyanosis;
- cramps of the calf muscles;
- constant pain in the leg, which intensifies when walking;
- increased venous pattern on the thigh.
Cavernous sinus thrombosis:
The dura mater contains channels into which venous blood from the brain drains. Blockage of one of these sinuses, the cavernous sinus, is dangerous because several cranial nerves and the internal carotid artery pass through it. The most common causes of cavernous sinus thrombus formation are inflammatory diseases of the nose, sinuses, facial skin and scalp. Signs:
- headache;
- decreased visual acuity, double vision;
- confusion;
- heat, fever;
- swelling of the eyelids and periocular area;
- pain in the neck when turning or tilting the head;
- impaired facial skin sensitivity.
Among the consequences of such thrombosis: stroke, loss of vision, coma.
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis
Develops against the background of hemorrhoids. Chronic constipation, physical stress, pregnancy and childbirth, and alcohol abuse contribute to it. Signs:
- pain, burning and itching in the anal sphincter area;
- discharge of blood with feces and regardless of the act of defecation;
- prolapse of hemorrhoids.
Retinal vascular thrombosis
The pathology is a typical complication of diabetes mellitus and hypertension, but can also develop for other reasons. Symptoms:
- deterioration of vision, up to complete loss (usually one-sided);
- the appearance of spots, mesh, veils before the eyes.
Symptoms of arterial thrombosis
Blockage of the artery leads to oxygen and energy starvation of tissues, which quickly leads to their death. Arterial forms of the disease are often acute.
Thrombosis of the cerebral arteries
This process leads to necrosis of the area of the brain that the affected artery supplies blood to - ischemic stroke. Signs:
- hemiparesis ー lack of movement in the right or left half of the body (opposite affected area);
- asymmetry of the smile - one corner of the mouth is lowered, does not take part in conversation and smile;
- unclear speech;
- when the patient sticks out his tongue, it deviates to the side.
Thrombosis of the coronary arteries of the heart
Partial blockage of these vessels leads to attacks of angina pain, complete blockage leads to myocardial infarction. Symptoms:
- pressing, burning pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left shoulder blade, arm, shoulder, half of the face and neck;
- dyspnea;
- with angina pectoris, rest and nitroglycerin help, with a heart attack there is no improvement, urgent medical attention is needed.
Pulmonary artery thrombosis
It is a complication of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, endocarditis, myocardial infarction. It develops rapidly and has a high mortality rate. Signs:
- sharp stabbing pain in the chest;
- swelling of the veins of the neck;
- shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- hemoptysis;
- increased heart rate.
Hepatic artery thrombosis
Death (infarction) of liver tissue is a complication of endocarditis, myocardial infarction or liver transplantation and manifests itself as follows:
- severe pain under the right rib;
- nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes.
Femoral artery thrombosis
This form of pathology is manifested by pain when walking, coldness, and paleness of the limb. The pulse in the popliteal fossa and on the foot is palpable weakly or not detected at all.
Advantages
- Low radiation exposure (due to the use of latest generation equipment).
- The duration of the study is 20 minutes.
- Very high information content.
- Opportunity to conduct research any day of the week, from morning to evening.
- A modern device designed for patients of different sizes.
- Qualified doctors of the first and highest categories; candidates of sciences also work in medicine.
- The conclusion for each examination must be checked by the chief physician.
Sign up for a test today
The cost of the examination includes angiography of the abdominal aorta and leg vessels. The price for MSCT contrast examination of the vessels of the lower extremities and abdominal aorta at the Novaya Hospital is 6,400 rubles. (including the cost of contrast). You can get a consultation or sign up for an examination in several ways:
- call a multi-channel number;
- through an online form on the official website (indicate your full name and phone number, and hospital managers will call you back);
- via an online form to radiologists working at the New Hospital.
The head of the X-ray department is Olga Viktorovna Kolmakova, a doctor of the highest qualification category.