Contraindications for CT angiography
For most CT angiography studies, the contraindications are the same as for other bolus contrast-enhanced CT studies:
- Having an allergy to the contrast agent;
- Kidney failure;
- Severe diabetes mellitus;
- Pregnancy (teratogenic effects of X-ray radiation);
- Severe general condition of the patient;
- High body weight (restrictions depend on the device);
- Thyroid diseases;
- Multiple myeloma;
- Acute heart failure.
There are additional contraindications for CT coronary angiography:
- High unstoppable tachycardia;
- Other severe intractable arrhythmias.
Before CT angiography, it is necessary to exclude the presence of contraindications (allergy to contrast agent, renal failure, thyroid dysfunction, etc.). To reduce the risk of developing an allergic reaction during the study, especially if there is a history of any allergic reactions, antiallergic drugs are prescribed. Before CT coronary angiography, premedication with beta-blockers is performed to reduce the heart rate.
It should be noted that modern radiopaque agents are much safer than their predecessors and the risk of complications from their use is extremely low. Despite this, before the study, the doctor must obtain written consent from the patient for the procedure.
PREPARATION FOR THE STUDY
Not required
Indications for the study
CT angiography of the abdominal arteries with bolus contrast and 3D reconstruction is prescribed if:
- the patient is suspected of having an abdominal aortic aneurysm or other changes in the vascular endothelium;
- Marfan syndrome is suspected, causing a dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- atherosclerosis progresses;
- there are traumatic injuries to the spinal cord and arteries;
- the patient has congenital or acquired vascular pathologies;
- there are manifestations of aortitis (infectious lesions of the vascular endothelium).
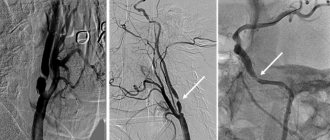
When performing CT angiography, the condition of the celiac trunk, its branches, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries, and renal arteries is assessed.
How is CT angiography performed?
CT angiography is performed on an outpatient basis. The patient is placed on the computed tomography table and an iodine-based contrast agent in a volume of ~100 ml is injected into a venous catheter (usually installed in the cubital vein) at a certain speed. During the administration of the contrast agent, a series of x-ray scans are made of the area under study. As the contrast agent spreads through the vascular system, the vessels become more contrasting. After this, a radiologist analyzes the resulting images using multiplanar and three-dimensional computer reconstruction.
The essence of the technique
Typically, computed tomography of the part of the body being examined, which doctors themselves abbreviate as CT, is only one of the components of the study of the head, brain and cervical region. The technique for obtaining a highly informative picture of deep and shallow vessels is based on the principle of layer-by-layer scanning of tissue using X-ray radiation.
Content:
- The essence of the technique
- Who is the examination contraindicated for?
- Preparation and technology
- Angiography results
All obtained data are summarized using a computer program. It provides the radiologist with detailed visualization, which is a three-dimensional model of internal organs, large vessels and capillaries. To make the picture even clearer and with good contrast, a contrast stage is additionally used. It involves the introduction of a contrast agent into the blood, which makes the vessels more prominent against the general background.
The basis for computer diagnostics is the same radioactive radiation that is used to obtain images through a standard X-ray machine. The only difference is that for angiography, scientists have designed detectors that generate a reduced background radiation rays.
This means that the modernized approach, aimed at studying vascular structure, is practically harmless for ordinary consumers. The only significant exception is pregnant women. And although for adults the radiation dosage received is within normal limits, the intrauterine fetus is too sensitive to the slightest fluctuations in the radioactive background.
Contraindication applies to women at any stage of pregnancy. If you ignore this medical recommendation, then the risk of developing physical abnormalities in the unborn baby increases several times. For others, obtaining a layer-by-layer image of the bloodstream is considered safe.
Due to the fact that blood flow to the head is closely connected with the cervical region, doctors suggest immediately examining the two parts of the body presented. Such an integrated approach gives refined results, which qualitatively influences the development of subsequent treatment. It often happens that the cause of cerebral circulation insufficiency is not the vessels of the head, which cope with the tasks assigned to them “excellently”. The problem lies in pinched arteries or veins located in the neck. This situation occurs quite often, especially among people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
The most important advantage of this non-invasive method for diagnosing the condition of blood vessels is the ability to conduct the study several times if it was not possible to obtain the required clarity the first time. Failures of this kind usually occur due to involuntary movement of the patient, who is located directly in the device.
The manipulation technique correctly reveals to the doctor the following aspects of the victim’s health:
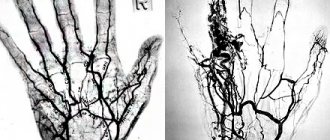
- anatomical location of blood vessels in the head and neck;
- structure of the vascular network;
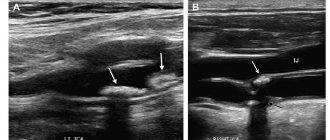
- the presence of atherosclerotic plaques;
- the dimensions of the veins, arteries themselves and their lumens;
- the presence of vascular constrictions and the original source of the problem;
- presence of collaterals.
Since the three-dimensional projection covers a fairly large area of the body under study, an experienced doctor will be able to examine not only the site of the disease, but also possible associated changes and complications.
Typically, a cardiologist or vascular surgeon refers the patient to the diagnostic room. But it happens that doctors of related specialties prescribe angiography to eliminate the risks of extensive damage. Among such doctors are phlebologist and vertebrologist.
The following diseases or suspicions of them are called the fundamental reasons for conducting such a comprehensive check:
- vasculitis;
- changes in the carotid artery;
- kinking syndrome;
- swelling of the neck;
- painful syndrome in the cervical vertebrae;
- embolism;
- thromosis;
- angiopathy, as an independent diagnosis, or as a consequence of the development of diabetes;
- tumors of benign or malignant type;
- control image after local surgery;
- compression of blood vessels by tumors of various etiologies or scar tissue.
All of the above can be determined by additional examinations and tests such as classic ultrasound and blood biochemistry. Also, before sending for a layer-by-layer scan, the attending physician must listen to the existing complaints of his patient and study the history from the medical record.
Having collected all the information together, the doctor will make a verdict about insufficient nutrition of the brain and problems with its blood supply, which is caused by inadequate vascular activity. CT angiography will help find the original source of the problem.
CT angiography on a multislice tomograph (MSCT angiography)
In multislice (multi-layer, multi-slice) computed tomographs (MSCT), unlike tomographs of previous generations, not one, but two or more rows of detectors are located around the circumference. This technology significantly increases the speed and information content of studies, and also reduces the radiation dose to the patient. MSCT has a number of advantages over conventional computed tomography:
- improved time resolution;
- improved spatial resolution along the longitudinal z-axis;
- increasing scanning speed;
- improved contrast resolution;
- increase in signal-to-noise ratio;
- effective use of the X-ray tube;
- large anatomical coverage area;
- reducing radiation exposure to the patient;
Is a CT scan indicated for children?
CT is the most informative and modern technique that allows you to identify various diseases at their early stages. The procedure can be performed at any age, but there are certain nuances when prescribing it for young children.
A child's body perceives radiation more subtly than an adult. For this reason, it is better not to do any CT scanning for children without unnecessary need. There is an adequate substitute for the procedure - magnetic resonance diagnostics without the use of x-rays. However, an unrecognized disease is the worst. And children should not refuse computed tomography. Our medical center offers computed tomography of the cervical spine for children aged five years and older. A referral from your attending physician is required to undergo the procedure.
Multislice CT angiography in Volyn hospital
The computed tomography room of the Volyn Hospital is equipped with a modern spiral tomograph “Bright Speed Elite”. Doctors at the CT office are at the forefront of the development of computed tomography in Russia and have unique, enormous experience and original research methods. Highly qualified personnel and the latest software allow us to conduct the widest range of research.
The department has extensive experience in computed tomography (CT) of the spine and extremities for degenerative diseases, trauma, tumors and inflammatory diseases. Three-dimensional and multiplanar image reconstructions are widely used.
Prices, discounts, benefits
High-quality computed tomography of blood vessels can be done at Medical. The procedure helps in identifying pathologies and prevents the development of serious diseases. The diagnostic cost includes:
- Examination with AQUILION Lightning tomograph (Canon, Japan)
- Detailed and comprehensive conclusions made based on the images by a highly qualified radiologist. The description of the study is checked by the chief physician.
- 24/7 access to your personal account to view all your research and conclusions
- Internal research quality control
- 100% guarantee of photo quality
Detailed information about prices can be found in the “Prices” section. You can find out about the benefits and ongoing promotions in the “Promotions” section.
CT head
Main diagnostic features
Features of Head CT
Thin-slice images allow high-quality three-dimensional reconstructions such as VR (volume imaging) or MPVR (multi-plane volumetric reconstructions), especially used in the evaluation of post-traumatic and vascular studies.
Diagnosis of the head in computed tomography consists of several separate procedures that require different patient preparation.
Computed tomography of the brain allows you to evaluate:
- nervous tissue (distinguishing between gray and white matter);
- spaces containing liquid;
- spinal (ventricular system and arachnoid reservoir system).
In emergency cases - in case of injuries, ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, as well as in the diagnosis of subarachnoid hemorrhages (SAH), the examination is carried out without preparing the patient.
This technology is proving to be extremely useful, especially in imaging structures located inside the human head. The quality of the result is influenced by the power and capabilities of the equipment on which the research is carried out. Computed tomography of the head in Moscow is available in our clinic using the latest generation tomograph, a high-precision 64-SLICE CT PHILIPS BRILLIANCE.
Preparing for diagnosis
Preparing for a CT scan of the head
Head tomography is performed on an empty stomach; before the procedure, approximately three hours before the examination, it is recommended to drink about 2 liters of still water. Before the test, tell the doctor performing the test about any chronic illnesses, medications you take, allergies or other conditions. Before performing a CT scan of the head, jewelry, glasses, and hearing aids (if the patient is wearing them) must be removed.
It is also important to bring your current blood creatinine and TSH results with you if the test will be done with contrast (contrast is removed from the blood naturally by the kidneys, so the doctor must assess their status before administering contrast).
Computed tomography technique
You do not need to dress in any special way for a CT scan of the head. However, items such as jewelry, glasses, or hearing aids should be removed as metallic objects may interfere with the examination image. The patient is wearing a protective gown (especially to protect the reproductive organs, which are sensitive to radiation).
The subject is placed on a special table, which then slowly slides into the round hole of the tomograph. Sometimes an additional pillow is placed on the table so that the head is fixed in one position and does not move. During tomography, X-ray tubes move around the patient 360° in a special frame and produce a series of layer-by-layer X-ray images. The entire procedure is painless and usually lasts only a short time.
It is important for the patient to remain still and, in addition, to hold his breath when the special light comes on or when the radiologist performing the CT scan asks to do so. During the diagnosis, the doctor is in a separate room, but throughout the entire examination he maintains contact with the subject through a special internal system of microphones and speakers. In this way, any alarming symptoms caused by, for example, the administration of a contrast agent (which is administered during a break in the study through an intravenous tube) can be immediately reported at any time during the study.
After the examination
If a contrast agent is administered, the patient is rarely asked to remain in the clinic after the examination is completed to ensure that there is no serious acute allergic reaction. Immediately after the examination, as well as in the days following it, you should drink plenty of fluids in order to remove the contrast from the body as quickly as possible.
If no contrast agent was used, the patient can return to their daily activities, eat normally, and maintain a normal rhythm immediately after the examination. Only if you use sedatives, which slightly impair concentration and reflexes, should you avoid driving and other activities that require concentration for several hours.
Indications for CT scanning
Head imaging is most often performed for head injuries such as brain contusions, skull fractures, and hematomas. Neoplastic diseases of the central nervous system are also indications for tomographic examination. For example, glioma, lymphoma, astrocytoma, malignant neoplasms of the middle ear, meningioma and tumor metastases to the face.
Head tomography is also performed for unclear bacterial and viral inflammations, for tuberculous meningitis, abscesses and brain abscesses, for toxoplasmosis and cysticercosis. Indications for head tomography also include any vascular changes in the brain, hematomas, intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral ischemia, hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral infarction, suspected pituitary disease, and monitoring of postoperative condition.
In children, head tomography is performed if developmental defects or, for example, hydrocephalus are suspected. This examination is also necessary for inflammation of the paranasal sinuses and meninges. Alzheimer's disease, cerebral dementia, craniofacial changes, cysts, and septal pellucid defects are other examples of complaints when performing a CT scan of the head.
Contraindications
Computed tomography of the head is performed in pregnant women in rare cases when the value of the diagnosis significantly outweighs the possible risks associated with the procedure. Also, CT is not recommended for young patients under the age of 14 years.
The decision to prescribe this study or replace it with another is always made by the attending physician based on the clinical characteristics of a particular case.
CT scanning of the head with contrast should not be performed in patients with allergies to iodine-containing drugs. It is also not recommended for patients with kidney failure and people whose thyroid hormone levels are too high.
Also, the weight of the subject over 200 kg will be a contraindication, since this is the maximum capabilities of the device.
Advantages and disadvantages of tomography
Advantages of head CT
Advantages of multi-row spiral computed tomography:
- non-invasive and painless examination method;
- short duration and reduced radiation dose;
- the ability to simultaneously obtain images of bones, soft tissues and blood vessels;
- the ability to examine a larger area of the body with one breath-hold;
- reducing the amount of contrast administered, which is equivalent to reducing the risk of complications;
- increasing patient comfort during the examination;
- CT provides very detailed images of various types of tissue, in contrast to classical x-ray studies, and makes it possible to obtain images with high spatial resolution;
- In most cases, a CT scan is faster than a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan; in both modalities, it is important that the patient does not move because any movement can cause errors in the resulting images (CT scans have a potentially lower risk if they have a shorter duration patient movements);
- it can also be performed on patients with implanted medical devices such as a pacemaker or neurostimulator (as opposed to MRI);
- it is performed quickly and easily, in emergency situations it allows you to immediately visualize internal injuries and bleeding, which can save the patient’s life;
- allows real-time imaging, making it a suitable tool for invasive procedures such as needle biopsies of various organs, particularly the lungs, abdomen, pelvis and bones.
CT scan of the head vessels may eliminate the need for surgery or surgical biopsy.
Disadvantages of diagnostics include the impossibility of examination during pregnancy, the dose of radiation received, and the need for additional preparation if the procedure is performed with contrast.
Research results
A CT scan provides valuable information about a patient's health and plays an important role in the diagnosis of diseases by assessing the condition of internal organs and possible abnormalities throughout the body.
The price for a head CT scan in our clinic is one of the best in Moscow. We provide diagnostic services at a guaranteed high level. You can quickly make an appointment and get tested.
Sign up for a head CT scan
Computed tomography is a non-invasive, accurate and fast diagnostic method. You can get a CT scan of your head at the Open Clinic. You can sign up for an examination by calling the specified phone number or using the feedback form.
You can also sign up for a head CT scan in Moscow upon arrival at the clinic at the registration desk in the Presnensky Center or on Mira Avenue, but we suggest calling in advance to choose a time that is suitable and convenient for you for the examination.