Cervical spinal stenosis is a process of reducing the lumen of the spinal canal due to the development of various pathological structures. As a rule, the tendency to form stenosis most often occurs in people over 55 years of age. In a quarter of cases of the disease, cervical vertebral stenosis is diagnosed. In the absence of timely measures taken, spinal stenosis causes disability and disability.
Types of cervical stenosis
This pathology is represented by the following groups.
- Congenital (primary) stenosis, when the disease develops as a result of congenital abnormalities in the structure of the spine.
- Degenerative , acquired or secondary stenosis of neck vessels is a consequence of destructive-degenerative acquired changes.
- Combined or mixed stenosis is determined in the presence of various causative development factors.
Based on the area of the lesion, a distinction is made between relative and absolute stenosis (area less than 75 mm² or more than 75 mm², respectively).
Lateral stenosis is defined as a narrowing of the intervertebral foramen to 0.4 cm or less.
The term sagittal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the canal in the same plane.
Anatomically, the following types of cervical spinal canal stenosis are distinguished:
- lateral or lateral , when the exit site of the roots (radicular canal) of the spinal cord decreases in volume;
- central , when on the arch of the cervical vertebra (at the point where the roots exit) the distance from the posterior surface to the lateral surface decreases.
Why does cervical stenosis occur?
Cervical spinal stenosis develops for several reasons:
- Spinal fracture with compression of the vertebrae (compression);
- Congenital pathological changes in the structure of the vertebrae;
- Inflammatory diseases of the spine;
- Ankylosing spondylitis;
- Tumor processes;
- Intervertebral disc herniation;
- Chronic diseases of the articular surfaces of the spine;
- Adhesions after surgery;
- Overweight;
- Intervertebral disc displacement;
- Bone growths and osteophytes;
- Violation of the structure of the posterior yellow ligament;
- Osteochondrosis.
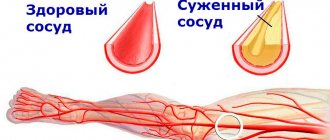
Stenosis of the neck vessels develops due to a decrease in the cavity where the spinal cord, nerves and vessels of the spine are located. First, complaints arise during certain turns and bends, then blood flow is disrupted and the situation worsens.
Over time, the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid increases, provoking congestion and inflammatory processes.
Causes
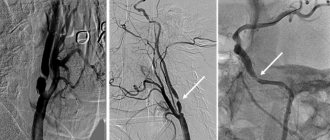
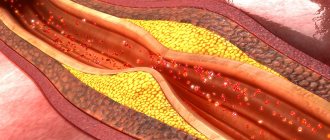
In most cases, vascular stenosis is caused by the presence of atherosclerotic plaques on their walls. A chronic vascular disease such as atherosclerosis gradually affects large arteries. Cholesterol is an element present in the blood of every person. Any of us is susceptible to a disease such as atherosclerosis, and vascular stenosis as its consequence. Provoking factors in this case are bad habits (smoking, alcohol), poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and old age. Diabetes mellitus can also aggravate arterial stenosis.
Cholesterol deposited on the vascular walls hardens and turns into dense plaques. If they block the lumen of the vessel, we are talking about stenosing atherosclerosis. Fragments of atheromatous plaques can separate and form blood clots, which leads to complete blockage of blood vessels. In addition, atherosclerosis weakens the walls, as a result of which they delaminate and aneurysms form on them - a vascular pathology, which you can learn about in detail here.
Symptoms
The symptoms of absolute sagittal stenosis are determined by which structures are being compressed. The disease progresses slowly.
- Pain in the neck occurs - first in a certain position, gradually turning into permanent pain, which can radiate to the arms, shoulders, back of the head or shoulder blades.
- Feeling dizzy with sudden bends and turns, fainting is possible.
- Headaches in the temples and back of the head.
- The sensitivity of the scalp, arms and neck is impaired.
- You feel discomfort and weakness in your hands.
- The tone of the upper limbs and muscle frame increases.
- Changes in the functioning of the pelvic organs are observed: diarrhea alternates with constipation, fecal and urinary incontinence.
- Weakness in the legs.
- Breathing is labored, shallow, or rapid.
- Paralysis of limbs or complete immobility.
Coronary heart diseases
| Cardiac ischemia symptoms | 122 |
| Cardiac ischemia treatment | 81 |
| Coronary heart disease | 52 |
| IBS coronary heart disease | 19 |
Coronary pathology involves damage to the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. A decrease in coronary blood flow leads to impaired blood supply and myocardial ischemia. Given this fact, the concepts of coronary heart disease and coronary heart disease (CHD) are identical.
Development mechanism
Schematically, coronary heart looks something like this:
- Atherosclerotic cardiosclerosis – occlusion of the coronary arteries by atherosclerotic plaques with subsequent sclerosis of the myocardium;
- Myocardial ischemia;
- Angina;
- Stable angina pectoris;
- Unstable angina - new, progressive;
- Myocardial infarction and its complications - arrhythmias, cardiogenic shock, pulmonary edema, sudden death.
All these manifestations of coronary disease are interconnected and are links in a pathological chain.
Ischemia most often forms in the left ventricle, which performs the maximum load when providing hemodynamics. The left ventricle receives blood from the branches of the left coronary artery - the circumflex and anterior descending. It is in these branches that atherosclerotic plaques form, leading to ischemia.
Symptoms to watch out for
The main symptoms of cardiac ischemia are:
- Acute pain behind the sternum, radiating to the interscapular space and to the left arm; usually does not last long and occurs during physical activity or stress
- Shortness of breath on exertion;
- General weakness, sometimes loss of consciousness;
- Unstable blood pressure numbers;
- In arterial hypertension – left ventricular hypertrophy.
This is a classic version of an ischemic attack. Atypical forms are also possible, mainly characteristic of myocardial infarction:
- Painless – complete absence of subjective sensations;
- Abdominal – severe abdominal pain;
- Arrhythmic – heart rhythm disturbances;
- Asthmatic – severe suffocation;
- Cerebral – dizziness, loss of consciousness, convulsions.
Diagnosis and treatment of coronary diseases at the clinic on Barclay
Treatment of cardiac ischemia involves the use of nitrates, antihypertensive drugs, antiplatelet agents and other drugs. This allows you to reduce the degree of ischemia and prevent the development of its complications.
If you observe alarming symptoms, be sure to consult a specialist. You can get more detailed information and make an appointment with a cardiologist at
t. + 7-495-979-99-82; +7-495-978-78-67
Diagnostic features
The doctor begins with a conversation with the patient, during which he finds out:
- complaints at the time of application;
- factors predisposing to the disease;
- previous diseases.
For the doctor, the body position that the patient is forced to take is important; he palpates the spine in order to determine the affected area.
The patient is prescribed additional examination:
- X-ray of the spine in two projections to determine bone growths, identify destroyed and fused vertebrae, disruption of the structure of joints, the presence of neoplasms, determine their size, location and structure;
- CT scan of the spine to find the cause of the disease, taking into account the smallest changes;
- MRI (if there are no contraindications) to detect changes in cartilage, nerves and blood vessels;
- myelogram to find changes in the structure of the spinal cord, the patency of the canal and the condition of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Prevention of atherosclerosis of heart vessels
Preventive measures must be taken after the disease and to prevent its occurrence. Basic recommendations from doctors:
- proper nutrition and dieting - exclude fatty foods from the diet, more often include seafood in the menu. It is better to steam, boil or bake. Eat often, but little by little;
- moderate physical activity - walking, morning exercises are useful;
- body weight control;
- positive psycho-emotional environment - avoid stress and moral turmoil;
- quitting smoking and alcohol abuse.
Remember to follow your doctor's recommendations and get diagnosed for heart disease promptly. The cardiology center of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency has several programs, you can find out about them here.
How is cervical artery stenosis treated?
Stenosis of the cervical arteries is treated using conservative methods (physiotherapeutic procedures and medications) and surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
The course of treatment is selected for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of his condition:
- painkillers (NSAIDs) with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- injections of hormonal agents into the spine to reduce swelling, tissue compression and pain;
- diuretics to reduce cerebrospinal fluid pressure and relieve swelling;
- electrophoresis with novocaine to relieve pain in the affected area;
- magnetic therapy to reduce swelling and relieve pain;
- when the muscle frame is tense, massage is used;
- physical therapy – special exercises for stenosis help strengthen the cardiovascular system, arm and neck muscles;
- manual therapy;
- acupuncture;
- spinal traction.
Surgical treatment
Surgical methods are used if a conservative approach does not provide a lasting effect or the development of the disease calls into question the patient’s life and ability to work. Today there are many methods of surgical treatment, but three operations provide maximum effectiveness:
- decompressive laminectomy - an operation to remove a structure that causes a narrowing of the canal (hernial protrusions, tumors, intervertebral discs and arches, osteophytes;
- installation of stabilizing systems;
- installation of an implant after removal of the affected fragment.
Drug therapy
— There is no specific drug treatment. Drug treatment is aimed at stabilizing hemodynamics - Prevention of infective endocarditis is indicated. Indications for surgery: - pressure gradient between the left ventricle and the aorta is more than 50 mm Hg. Art., or the area of the aortic opening is less than 0.7 cm2 (normally its area in adults is 2.5-3.5 cm2) - angina pectoris, fainting, signs of heart failure. Surgical treatment: — Radical treatment — aortic valve transplantation. — Balloon valvuloplasty of the aortic valve is indicated for elderly, debilitated patients who may not undergo valve replacement surgery
Prevention of cervical stenosis
To prevent the development of the disease, preventive measures should be used:
- kneading the neck - eliminating physical inactivity;
- exercise therapy;
- correct posture, including while working at the computer;
- proper nutrition;
- if necessary, timely contact a specialist.
Feedback from patients suggests that when contacting a medical facility in the early stages, within 6-12 weeks, the pain syndrome disappears in most of them. In advanced cases, as a rule, cervical vertebral artery stenosis requires hospital treatment for a long time.
Treatment
First of all, when treating vascular stenosis, it is necessary to follow a diet, increase physical activity and give up bad habits. In addition, the patient is prescribed medications to dilate blood vessels, accelerate blood flow, and lower cholesterol levels. In some cases, surgery is recommended.
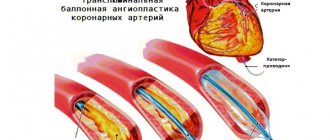
Stenting can quickly and effectively restore blood flow and eliminate stenosis. This is one of the most modern methods of treating vascular diseases accompanied by impaired arterial patency. It is characterized by minimal trauma to the patient. In this case, the effect on the vessel is carried out from the inside, using a special catheter inserted through a micropuncture into the artery. The essence of such operations as stenting of the carotid arteries, heart vessels or limbs is that an endoprosthesis (stent) is installed at the site of narrowing, which acts as a frame and holds the vascular walls. These operations are the safest and give the best results.