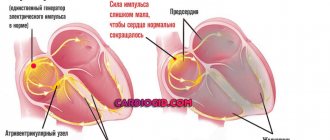
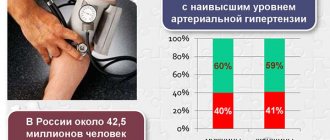
Hypertension, a disease that affects a large number of people, is called a nationwide disease; it is diagnosed in half of people aged 18–50 years. A sharp jump in pressure up to 230 characterizes a hypertensive crisis. You need to be able to distinguish the symptoms that precede such a jump and know the rules of first aid during a crisis. It is necessary to undergo specialized treatment to prevent possible pressure surges to the critical level of 230.
Causes of extreme high blood pressure
The blood pressure of a healthy person should normally be approximately 120 to 80. Depending on the body, fluctuations in the upper and lower levels are allowed in the region from 110 to 130 and from 75 to 85, respectively.
If the indicator is already 140 to 90, we can talk about high blood pressure. If this condition is not an isolated case, this is a signal of the development of hypertension. Many people suffer from it and many do not even know about their illness. Often, news of the presence of a disease comes during a routine examination.
The absence of characteristic symptoms in this case should not be a reason to refuse treatment. The development of hypertension can over time lead to a sharp jump in pressure, the magnitude of which will lead to a hypertensive crisis.
Indicators during such an event are purely individual and can be 200 to 100 or 220 to 110. But the value of 230/120 is critical, which is why it is used to characterize this dangerous condition.
There is a high likelihood of a hypertensive crisis if medication is suddenly stopped
The main reason for the occurrence of such an event is the uncontrolled development of hypertension. There is a high probability of a hypertensive crisis if the use of antihypertensive drugs is abruptly stopped. In medicine, there is a special term for this: “withdrawal syndrome.”
Other reasons for a sharp increase in blood pressure are as follows:
- excessive activity associated with physical exertion;
- brain pathologies, in particular ischemia;
- serious stressful conditions;
- salt abuse;
- lack of potassium in the body;
- alcohol abuse;
- increased sensitivity to sudden changes in weather;
- changes in hormonal levels during menopause in women;
- ischemic myocardial disease, during exacerbation.
Reasons for rapid increase in blood pressure
It is important to diagnose a hypertensive crisis in time. This manifests itself in an increase in pressure, sometimes up to 230. Everyone's critical threshold is personal. There may be cases when 160 will be a critical indicator for a person. Not only high blood pressure itself is dangerous, this condition threatens to impair the functioning of the kidneys and brain.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
120
on
80
There are many reasons for the development of a hypertensive crisis. The root cause is chronically high blood pressure. A serious provocateur is the completion of a course of antihypertensive medications, which leads to “withdrawal syndrome.” Other causes of high blood pressure include:
- excessive physical activity;
- stress;
- oxygen starvation of the brain;
- excess salty foods;
- lack of potassium in the body;
- weather dependence;
- alcohol abuse.
Arterial bleeding due to high blood pressure is deadly.
For women, jumps are typical during menopause. With the development of a hypertensive crisis, 2 types of course are possible:
- 1st - with complications, with damage to internal organs, arterial bleeding, brain damage. Requires immediate hospitalization of the patient.
- 2nd – without complications. Requires the necessary medical care, hospitalization is not required.
Symptoms
Blood pressure equal to or close to 230/120 mmHg may be accompanied by the following conditions:
- a feeling of anxiety and acute anxiety, developing into nervous overexcitation;
- facial redness;
- cold sweat all over the body;
- cardiopalmus;
- so-called “goose bumps”;
- difficulty breathing, expressed in the “lack of air” syndrome.
In the initial stages of a sharp increase in blood pressure, a person experiences severe migraine attacks and accompanying attacks of nausea, sometimes with vomiting. There may be tinnitus, pain in the eyeballs, and hypersensitivity to light.
An intense headache may indicate complications such as brain swelling. An additional symptom of this condition is a sharp deterioration in vision.
There are two types of hypertensive crisis. In the first case, blood pressure rises sharply to 230/120 or even higher. The duration of the attack in most cases does not exceed 3 hours, but high intensity of symptoms is observed. During a crisis, diastolic pressure can take on a normal value, while systolic pressure always remains at a high level.
During a crisis, diastolic pressure may return to normal
In the second, the increase in pressure occurs gradually, and the duration of the attack can be several days. Symptoms are not as pronounced and conditions such as:
- persistent migraines of moderate intensity;
- confusion;
- stuffy ears;
- lethargy and drowsiness.
Measures for hypertensive crisis
What should you do if your blood pressure is 230/120 or close to it? This condition and hypertension in particular require comprehensive and long-term treatment. But at the moment of crisis, it is necessary to provide first aid to the person, simultaneously calling emergency medical care.
These primary measures involve the following:
- Correct position. At the moment of crisis, you need to position the human body in the optimal position for this moment. This will be a half-sitting position. This position helps stop suffocation and restore normal breathing, which often accompanies a sharp increase in blood pressure.
- Taking medications. If a person is being treated for hypertension, it is necessary to force him to take medications prescribed by a doctor to lower blood pressure.
- Dynamics tracking. Periodic blood pressure measurements are needed to know how this indicator behaves. A sharp decrease in blood pressure can be extremely dangerous; it can lead to problems with blood supply to the brain. The optimal rate of decline is 40 mmHg/hour.
Blood pressure 200/110: hypertensive crisis
Blood pressure 200/110 corresponds to stage 3 hypertension. It is accompanied by sharp painful sensations:
- The head hurts severely and “pulsates”;
- Digestion is disrupted, the person feels sick;
- Blood rushes to the head: the skin of the face turns red, small blood vessels in the eyes burst;
- Vision is impaired: spots flash before the eyes;
- A strong heartbeat appears.
In addition to grade 3 hypertension, pressure 200/110 can occur in earlier stages of the disease, during hypertensive crises. A crisis is a sharp increase in blood pressure, a jump of 30-40 or more mmHg. Art.
Both chronic high blood pressure and hypertensive crisis are dangerous due to their complications. A sick person experiences very painful sensations and also risks a heart attack, stroke or internal hemorrhage. Therefore, it is necessary to provide the person with first aid in a timely manner, try to reduce blood pressure, and be sure to take him to the hospital.
Prevention
Traditional medicine methods can be used as preventive measures against sudden increases in blood pressure. The most effective will be:
- Infusion of motherwort, cudweed, valerian, horsetail. To prepare it, you need to take a teaspoon of each herb, mix them and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave until completely cooled, then strain. The infusion is taken 3 times a day before meals, 100 ml. It is recommended to prepare a fresh product every day.
- Infusion of marsh cudweed, motherwort, horsetail, hawthorn and adonis. It is prepared and taken in the same way as the previous recipe.
- Beetroot juice. This remedy has a beneficial effect on the entire hematopoietic and blood supply system. Freshly squeezed juice is taken 3 times a day, 100 ml after meals. The course of treatment is 21 days. To enhance the therapeutic effect, it is recommended to add honey and lemon juice to beet juice in a 1:2 ratio. In this case, the dosage regimen is as follows: 2 times a day, 100 ml, 50-60 minutes after meals.
- For high blood pressure, hawthorn juice (not tincture!) will be useful. It is taken 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- Cranberry juice. It has a vasodilating property, which allows it to effectively reduce blood pressure. Due to the difficulty of extracting juice and its special taste, it is recommended to use berries that have been previously ground with sugar. Cranberries prepared in this way are consumed 3 times a day after meals, in the amount of one tablespoon.
Measures to prevent the occurrence of a hypertensive crisis include regular walking, adequate sleep, and protection from serious stressful situations.
Don't forget about nutrition. People suffering from hypertension should limit their intake of salt and fatty foods. The amount of fresh fruits and, of course, vegetables, on the contrary, should be increased as much as possible.
People suffering from hypertension should watch their diet
Seafood, dairy products and fresh beef will be beneficial. If you have problems with fluid removal, regular consumption of watermelon will help - along with the outflow of excess water, your blood pressure will also decrease.
After a hypertensive crisis, it is strictly not recommended to eat foods that increase blood pressure. It is recommended to completely limit alcohol and smoking.
Periodic measurements of blood pressure will allow you to monitor the dynamics of its changes and prevent a crisis when it approaches.
A pressure of 230 to 120 or close to it is a serious stress for the body. Its consequences can be very negative, and in some cases irreversible.
Therefore, a person suffering from hypertension needs to be able to notice the signs of impending collapse in time and prevent it. His relatives must have the necessary knowledge of first aid in a negative situation. These measures will help you wait for emergency medical help, which sometimes is tantamount to saving your life.
The first action, after getting rid of a hypertensive crisis and its consequences, should be to contact a specialized specialist to undergo a full examination and prescribe the necessary treatment. Only this will prevent a relapse of the dangerous condition in the future.
A persistent increase in blood pressure (BP) is a sign of hypertension or arterial hypertension. The critical threshold and optimal blood pressure value are individual for each person. Someone feels unwell at 160, but for another person even a large jump in pressure may not be noticeable. It depends on age, weight, lifestyle, nutrition, bad habits, etc. It is important to know what to do if the tonometer shows 230 to 120 mmHg. Art.
Causes of high blood pressure
Arterial hypertension is a leading factor in increasing blood pressure to a critical level. A hypertensive crisis can occur after diabetes mellitus, kidney disease or atherosclerosis of the arteries. In women it occurs during menopause, in pregnant women during hormonal fluctuations. Elderly people with impaired vascular tone especially often suffer from high blood pressure.
Blood pressure increases for the following reasons:
- excessive physical activity;
- stressful situations;
- cerebral ischemia was diagnosed;
- excessive consumption of salty foods;
- with hypokalemia, hypernatremia;
- weather sensitivity;
- stopping medications for hypertension;
- alcohol abuse.
Return to contents
Why does blood pressure rise sharply?
The reasons for the development of a hypertensive crisis may be different. The main one is the presence of arterial hypertension.
Also, a surge in pressure can be triggered by a sudden stop in taking antihypertensive medications. Doctors call this condition “withdrawal syndrome.”
Blood pressure may also increase for the following reasons:
- Excessive physical activity;
- Stressful situation;
- Presence of cerebral ischemia;
- Excessive consumption of salty foods;
- Presence of hypokalemia;
- Sensitivity to weather changes;
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
In addition, blood pressure can rise sharply in women during menopause. Similar symptoms may occur during exacerbation of coronary heart disease in the form of cardiac asthma, acute heart failure and cerebrovascular accident.
Hypertensive crisis can have two types:
- A complicated hypertensive crisis develops with acute damage to internal organs, which are considered the main target during a stroke, arterial bleeding, head injury, acute left ventricular failure, acute coronary syndrome, dissection of aortic aneurysm. In this case, it is important to know what to do to provide emergency medical care. A patient in this condition is hospitalized.
- In case of an uncomplicated hypertensive crisis, everything must be done to provide emergency assistance, but the person is not hospitalized.
How to recognize a hypertensive crisis?
A pressure of 230 over 120 causes dizziness, nausea, and short-term loss of vision and hearing. Heart rate increases, heavy sweating. Some people experience changes in the nervous system, they become irritable, and a feeling of fear appears. Signs of impaired blood flow in the brain develop, a sharp deterioration in the general condition in the form of vomiting, frequent urination and diarrhea, and headaches. Cerebral edema that occurs at the peak of a hypertensive crisis lasts 2-3 days. Convulsions, loss of consciousness, disorientation, and amnesia begin.
These symptoms are present when both the upper (systolic) and lower (diastolic) pressure increases. At the same time, the heart rhythm and pulse are disturbed and often increase. The duration of this attack varies from several hours to 2 days. It is classified as uncomplicated when there is no threat to life. And complicated, during which you need to be careful and take responsibility for diagnosis and therapy.
Symptoms of hypertensive crisis
Enter your pressure
130
on
90
Search in progress Not found
During a hypertensive crisis, all sorts of symptoms can be observed, but the main symptom is a sharp increase in blood pressure up to 230/120 mm Hg. Art. Other symptoms include:
- The appearance of anxiety and restlessness;
- Presence of cold sweat;
- Goose pimples;
- Tremor of the upper extremities;
- The face turns red;
- The heart beats faster;
- Nervous overexcitation is observed;
- The man lacks air.
At an early stage of the disease, a person develops a severe headache, which is often accompanied by nausea, dizziness, vomiting, photophobia, eye pain and tinnitus. The pain in the head may intensify if you make a sudden movement of the head or sneeze.
Also, a severe headache occurs during a complicated hypertensive crisis, when the brain swells and blood pressure increases greatly. Additionally, the patient may experience nausea and vision impairment.
A hypertensive crisis can develop in different ways. In the first case, blood pressure rises sharply and suddenly up to 230/120 mmHg. Art., this state lasts a short period of time, no more than three hours.
- The patient experiences symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, and decreased vision.
- The person feels tearful, excited, pulsation and palpitations are clearly felt, the heart hurts, sweating increases, a feeling of fear appears, and reddish spots can be found on the chest.
- At the end of the crisis, loose stools and a frequent urge to urinate are often observed.
- In such a condition, first of all, systolic pressure increases sharply, which can reach 230. This leads to increased heart rate, increased venous and pulse pressure.
In the second case, the hypertensive crisis is not acute, but it can last up to several days. At this moment, a person has a headache, consciousness is confused, and he feels dazed and drowsy.
Sometimes an attack of hypertension is accompanied by nausea and vomiting. At this moment, diastolic pressure increases greatly, while systolic pressure most often remains unchanged.
Complications of high blood pressure
The tonometer readings are 240 by 130 mmHg. Art. have extremely negative consequences and dangerous complications. A sharp jump is accompanied by a deterioration in blood circulation. Vascular rupture is a serious complication of a crisis that can lead to a stroke or heart attack. The risk of developing severe diseases of the brain, lungs, kidneys and cardiovascular system increases. Blood transports the oxygen necessary for breathing to all human organs. If blood flow is disrupted, cells are no longer saturated with oxygen and accumulate toxins. After 15-20 minutes, tissue death (necrosis) occurs. Cerebral and coronary circulation are most important for human life. They provide oxygen to the brain and heart. These disturbances in blood flow are often fatal.
Blood pressure complications 200/110
High blood pressure is dangerous with a number of serious complications. What can a hypertensive crisis lead to, and why is it urgent to reduce high blood pressure?
- Vascular rupture is possible - it occurs in the most depleted areas of the vessels, or where high pressure is localized (with cardiac hypertension, the pressure is localized in the heart area, it can also be localized in the brain, kidneys). Possible: stroke (rupture of a vessel in the brain tissue), heart attack (rupture of a vessel in the heart area), internal bleeding. Stroke and heart attack are life-threatening conditions. They can be fatal.
- Pulmonary edema.
- Kidney failure (develops with high renal pressure).
What to do during a hypertensive crisis?
During an attack, it is very important to provide first aid:
- Move the patient to a semi-sitting position, this will make it easier for him to breathe.
- Provide fresh air in the room and a favorable psychological environment.
- Call an ambulance and follow all recommendations of specialists.
It is not recommended to lower blood pressure by more than 25% of the initial values.
To reduce blood pressure before the ambulance arrives, you need to offer the patient to take valerian, Validol or motherwort. If the patient has previously consulted a doctor, follow all prescribed requirements. It is better to take those that can be placed under the tongue until completely absorbed. Do breathing exercises with it or put your feet in hot water for 10-15 minutes. Complete rest, diet, physical therapy or bed rest are required. To prevent recurrent attacks, strictly monitor blood pressure dynamics. Monitor your weight, eliminate bad habits and avoid stressful situations.
Blood pressure problems can occur at any age. This deviation most often appears against the background of serious disturbances in the functioning of any organs. There are, of course, cases with a single increase in blood pressure, but most often this is still a consequence of various diseases. Each adult has his own “working” blood pressure; as a rule, it is in the range of 120-130 at 80-90 mmHg. Art. What to do with a pressure of 230 to 130 mm. Hg Art., and is this the norm?
What to do if the pressure is 230?
During an attack, it is important to provide first aid:
- Place the patient in a semi-lying position. During an attack, a person remains in bed; it is necessary to place pillows under his back. This will help stop suffocation and make breathing easier.
- If this is not the first case, the person has already been prescribed treatment, it is necessary to take the prescribed medications. It is recommended to keep the tablets under the tongue for the fastest effect.
- Constant monitoring of the level of pressure reduction. A sharp decrease is strictly prohibited due to impaired intracerebral circulation.
It is important to relieve a person from feelings of fear and anxiety. In this case, sedatives are taken. Other medications should be taken after emergency assistance arrives. Having stopped the attack, you need to contact your family doctor and undergo medical examinations to prescribe the correct treatment.
Normal or deviation
Pressure 230 to 130 mmHg. st is not the norm and is considered high for any category of people. In medicine, such indicators are defined as hypertensive crisis. In addition to the fact that both indicators are elevated, there is also a large difference between the lower and upper blood pressure.
Blood pressure 230/130 requires immediate medical attention
With such pressure, blood circulation is disrupted and malfunctions of almost all organs occur. This is very dangerous for a person’s life and in this case it is impossible to do without medication, since an immediate decrease in blood pressure is required.
What if it's not hypertension?
Hypertension is understood as a persistent increase in blood pressure relative to normal values (normal is 120/80, elevated is 130/95 mm Hg, anything higher is hypertension). It is against the background of constant elevated blood pressure that hypertensive crises occur. During a crisis, blood pressure increases sharply, and health worsens.
In addition to hypertensive crises, blood pressure levels may increase with certain diseases and changes in atmospheric conditions. Let's list under what conditions:
- Kidney diseases;
- Brain diseases;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Poisoning with alcohol, drugs, tobacco, as well as some medications, diet pills;
- Spinal cord injuries.
A significant increase in blood pressure with concomitant diseases is also dangerous for human life and health. Therefore, it must be reduced with available medications and go to the hospital.
Doctors call hypertension the “silent killer.” This disease can occur unnoticed, with a minimum number of symptoms. And to manifest itself - during the first hypertensive crisis.
If the process has gone too far, the crisis may be the last. Therefore, if the listed symptoms of high blood pressure appear, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Causes and symptoms of high blood pressure
There are many factors that can influence the occurrence of a hypertensive crisis. Experts consider the most common reason to be self-cessation of antihypertensive drugs for hypertension.
If you have hypertension, you need to constantly take a large number of pills, but abruptly stopping them can provoke a strong jump in blood pressure.
In addition, an attack may occur due to:
- Abuse of bad habits;
- Large amounts of salt in the diet;
- Frequent overwork and stress;
- Excess body weight;
- Diseases of the heart, kidneys, thyroid gland;
- Meteorological dependence;
- Excessive physical activity;
- Oxygen starvation of brain cells;
- Genetic predisposition.
Also, jumps in blood pressure can occur due to a deficiency of any macro and microelements in the human body, for example, potassium. In addition, increased blood pressure often occurs in women during menopause, as well as in people with diabetes and vascular atherosclerosis.
Blood pressure 230 over 120 - what to do?
A pressure of 230 to 100.120 and above is life-threatening, so it is necessary to take all possible measures to reduce the readings to normal. For these purposes, the doctor prescribes medications with a lowering effect, as well as medications to relieve symptoms. Patients often resort to traditional medicine, but only after eliminating a hypertensive attack. Tinctures and decoctions prepared at home are not suitable as primary therapy.
First aid
If a person experiences a hypertensive crisis, he needs to immediately provide first aid and call a doctor. To alleviate the patient's condition, it is necessary:
- Open the windows to bring in fresh air to help the person breathe.
- Place the patient in bed in a “half-sitting” position. It is best to place a high pillow under your back and a bolster under your feet to normalize blood circulation.
- If a doctor has previously prescribed medications for hypertension, then it is necessary to give the victim the dose indicated in the prescription.
- If anxiety and panic arise in the patient, you need to calm him down and, if necessary, give 20-25 drops of valerian tincture, previously diluted in 50 ml of water.
- Often, various compresses, for example, vinegar, are used to reduce blood pressure by several units. To do this, you need to moisten a cloth in apple cider vinegar diluted 50 to 50 with water and apply compresses to the patient’s heels for 15-20 minutes.
While waiting for the ambulance to arrive, you need to measure the victim’s blood pressure every 15 minutes and record the data in a notebook. This will help the doctor track the dynamics of pressure changes over a certain period of time and make the correct prescription of medications.
When monitoring blood pressure, it is necessary to pay attention to the patient’s pulse.
Medicines
In case of a hypertensive crisis, complex therapy is used, based on reducing pressure and eliminating symptoms. To bring blood pressure back to normal, doctors prescribe:
- Drugs with a hypotensive effect to lower blood pressure and strengthen the cardiovascular system - Enalapril, Captopril (ACE inhibitors);
- Vasodilator medications (calcium antagonists) - Nifedipine, Verapamil;
- Diuretics for removing excess fluid from the body - Furosemide, Indapamide;
- For patients with heart rhythm disturbances, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol and other beta blockers can be prescribed.
The name and dosage of drugs is prescribed by the doctor based on the individual condition of the patient.
Also, to relieve symptoms and improve the patient’s condition, antispasmodics, sedatives, vitamin complexes, and medications containing magnesium can be prescribed.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies very often help out hypertensive patients and help improve their well-being. If you use them daily along with medications, the therapeutic effect will be achieved fairly quickly.
Folk remedies are effective in eliminating the consequences of a hypertensive crisis, and not at its very peak
The most effective means are considered:
- Natural juices. For hypertension, freshly squeezed juices help well, for example, beetroot mixed with carrots, and grapefruit with the addition of a few drops of lemon. You can also make juice from hawthorn fruits and add natural honey to it. Drinks are consumed 3 times a day, 100 ml. It's best an hour after eating.
- Tincture for normalizing blood pressure. Mix 1 tbsp. l - motherwort, horsetail, valerian, marsh dried grass. Place the composition in a thermos and pour 500 ml of boiling water. The medicine is infused for 2-3 hours, 50 ml is taken 3 times a day.
- A decoction to strengthen the cardiovascular system. Mix 1 tbsp in a saucepan. l onion peel, 1 tbsp. l pine needles, 1 tbsp. l chopped lemon zest, 1 tbsp. l rose hips. Pour 300 ml of water, boil for 10-15 minutes over low heat. Next, the medicine needs to be cooled, filtered through gauze, and then put in the refrigerator. The composition is taken 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. L.
After the hypertensive attack is stopped, under no circumstances should you drink alcohol or smoke. You should also pay attention to nutrition. It is better to eat low-fat foods, steamed or boiled. Fried, salted, smoked foods must be excluded. Evening walks in the fresh air and taking soothing baths with valerian will be useful.