Bigeminy
The term " bigeminy"
"is used by doctors to describe a certain type of arrhythmia - ventricular or supraventricular (supraventricular) extrasystole.
An extrasystole is an extraordinary cardiac contraction recorded on an electrocardiogram.
In a healthy person, the number of extrasystoles can reach 30-60 per hour (720-1440 per day). In the case when extrasystoles occur very often, an alternation of normal heart contractions with extrasystolic ones is recorded on the ECG, and if they are so frequent that each normal complex is followed by an extrasystole, this is called bigeminy (the prefix “bi-” means “two”), that is every second contraction is extrasystolic.
Please note that bigeminy can appear and disappear within a day, therefore, without daily ECG recording (Holter or 24-hour monitoring), it is impossible to determine its prognostic significance. After all, as you already know, 720-1440 single extrasystoles per day (30-60 per hour) is a variant of the norm, that is, if bigeminy persisted, for example, for only 5-10 minutes for the whole day, this is one situation, if bigeminy lasts for hours, this will already be considered a pathology.
Symptoms of bigeminy
Often patients do not feel arrhythmia at all, but in some cases bigeminy can be determined by irregular pulse or interruptions in heart function. It may appear as a weak blow followed by a stronger blow. Sometimes a weak blow is not felt and then it feels like the pulse has become very low, even 30-40 beats per minute, while in fact the heart rate remains normal, 60-80 per minute. Such imaginary bradycardia is due to the fact that not every extrasystolic cardiac contraction creates a pulse wave perceptible in the periphery.
Treatment of bigeminy
Do bigeminy need to be treated? This question is ambiguous, as it requires a comprehensive assessment of the situation: arrhythmia tolerance, the number of extrasystoles per day, their characteristics (single, paired, ventricular, supraventricular), the presence of concomitant arrhythmias and cardiac pathology (after all, bigeminy itself is not a diagnosis). Only after weighing all the pros and cons does the doctor make a final decision.
The general principles of treatment of bigeminy coincide with the principles of treatment of extrasystole, which was discussed in the relevant articles - supraventricular extrasystole. ventricular extrasystole.
Finally, it should be noted that in some cases, bigeminia does not require special treatment; it is enough to eliminate psycho-emotional factors and chronic foci of infection (for example, chronic tonsillitis).
Features of disturbed heart rhythm
Bigeminy, together with trigeminy, is considered the most common type of allorhythmia, which is a manifestation of arrhythmia - impaired stability of the heart rhythm. The pathological condition is characterized by the formation of impulses in the area of the sinus node, which ensures their distribution through the muscles at regular intervals. Even a healthy person may experience extrasystoles (premature excitations of the heart muscle), but their number normally does not exceed 55-60 contractions per hour.
Bigeminy on ECG
Please note: Bigeminy is an abnormal heart rhythm when an extrasystole is recorded after each normal heartbeat (systole). As a result, correct and premature impulses appear in equal quantities for a long time throughout the day.
The category of allorhythmia - a certain type of alternation of a normal rhythm with extrasystole - includes several types of pathology characterized by similar disorders. In addition to bigeminy, when the ratio of standard and abnormal impulses is 1:1, the group of arrhythmias includes two more main types of abnormal scenarios:
- the picture of trigemy implies the appearance of two regular contractions with one extraordinary impulse - 2:1;
- We are talking about quadrigeminy when three normal beats correspond to an abnormal surge in heart activity - 3:1.
It is known from anatomy that the electrical signal necessary to excite the myocardium is generated in the sinus node, located in the upper part of the vital organ. At the same time, the activity of other pacemakers remains suppressed. Failure at any stage of the conduction system contributes to disruption of the rhythm of cardiac impulses. In the case of bigeminy (trigeminy), the pacemaker of the heart is not in the space of the sinus node, but in the cavities of the ventricles and atrium. This is clearly reflected in the ECG, the main method for diagnosing the early stage of the disease.
What is the danger of heart rhythm disturbances?
Deviations in the functioning of a vital organ are not considered normal. Although abnormal pulsation is not an independent disease, abnormal heart rhythm poses a certain threat to the patient’s life. Only an experienced specialist can judge how dangerous bigeminy of the heart is after identifying the causes of the impaired functioning of the organ and correctly assessing the manifestations of the disease.
The dangerous consequences of extrasystole include the development of the following pathological conditions:
- random contraction of myocardial fibers accompanying atrial fibrillation;
Atrial fibrillation on ECG - atrial flutter, manifested by an increased pulse rate (more than 200 beats per minute);
- frequent ventricular contractions leading to rapid heartbeat (tachycardia);
- ventricular fibrillation, developing due to the chaotic nature of uncoordinated impulses;
- cessation of active myocardial function (asystole), threatening cardiac arrest, which can cause death in a patient of any age.
With the advent of allorhythmic type impulses, the systemic blood flow is disrupted, which leads to the formation of stagnant zones, as well as turbulence. Areas of impaired blood flow become sites for the formation of blood clots, the rupture of which is fatal.
Extrasystole rarely leads to serious complications, but the ventricular type of bigeminy increases the likelihood of developing potentially fatal situations:
- cardiogenic shock due to a heart attack of particular severity, impaired hemodynamics;
- stroke accompanied by death of nerve structures;
- heart attack, which is accompanied by scarring of tissue covered by necrosis.
Please note: Arrhythmia developing as bigeminy is most dangerous for pediatric patients due to problems with controlling the pulsation rhythm of the organ. When signs of an anomaly are recorded for several hours in a row, the likelihood of the child’s death increases.
What is ventricular bigeminy?
Content
This is what the disease looks like on an ECG
Heart rhythm disturbances are called extrasystole. It is characterized by contractions of the heart that occur out of sequence. The same applies to individual parts of the heart. Extrasystole develops in different forms, one of which is bigeminy.
This is a form of arrhythmia in which premature cardiac excitations occur after the next contraction of the heart. This means that extrasystolic and sinus cycles alternate one to one. In this case, the same clutch interval is noted.
Often, by bigeminy, doctors mean supraventricular or ventricular extrasystole. when extraordinary contractions of the heart are recorded on the ECG.
A healthy person has about 55 contractions. If normal contractions alternate with extraordinary contractions, this is called bigeminy, especially if this is recorded on the ECG. If we are talking specifically about the ventricular form of this condition, this means that the only normal ongoing complex alternates with ventricular extrasystole, which is a type of allorhythmia.
In this case, premature excitation occurs, observed in the cardiac ventricle. If we are talking about the supraventricular form, this means that one extrasystole and one rhythmic contraction of the heart alternate correctly.
Causes
Rhythm disturbances may be psychogenic in nature
Speaking about the causes of the condition we are discussing, we must remember that it is directly related to extrasystole, so you should first consider the reasons leading to it.
Functional extrasystoles occur in patients who have the following diseases:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- VSD;
- Neuroses and so on.
In addition, rhythm disturbances can be psychogenic in nature and can be associated with chemical and nutritional factors, and also develop due to the use of alcohol, drugs, strong coffee and tea, smoking, stress, during menstruation, and so on.
Extrasystole, which is organic in nature, occurs with the following diseases:
- cardiosclerosis;
- IHD;
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiomyopathy;
- heart defects and so on.
Extrasystole of a toxic nature develops:
- with thyrotoxicosis;
- with fever;
- as a side effect of certain medications.
Extrasystoles develop against the background of a violation of the ratio of magnesium, potassium, sodium and calcium ions in the cells of the heart muscle, which negatively affects the conduction system. Physical activity can provoke diseases.
Ventricular bigeminy indicates that the body is undergoing a pronounced process of intoxication, which is a consequence of taking digitalis medications.
Ventricular extrasystole of the bigeminy type
Often this type of arrhythmia occurs in patients who were prescribed adrenaline, novocainamide, quinidine and novocaine for diseases of the cardiovascular system. In addition, this form can result from the use of certain types of anesthesia, for example, chloroform or cyclopropane.
Sometimes this pathology develops due to electrical stimulation of the heart. Other reasons for the development of this condition can be identified:
- severe poisoning with organophosphate substances during acute intoxication;
- electrolyte disturbances in the myocardium;
- coronary angiography;
- cardiac probing;
- heart surgery and so on.
All reasons are united by changes occurring in the heart muscle and having an organic origin. Even seemingly minor disturbances in the myocardium can lead to the appearance of an ectopic focus of excitation, especially if they are combined with certain functional factors.
Symptoms
Symptoms: irregular pulse and irregular heartbeat
Bigeminia is characterized by subjective symptoms, for example, a feeling of a beat in the heart, its short stop, or interruptions in the functioning of this important organ.
It is rare, but it still happens that cardialgia and angina pain appear and a strong filling is felt in the cervical region.
In addition, brain symptoms are observed:
- fainting;
- aphasia;
- dizziness;
- a transient form of hemiparesis.
Symptoms of a neurotic and vegetative nature are also observed:
- adynamia;
- pallor;
- nausea;
- feeling of fear;
- increased sweating;
- slight excitement;
- feeling of lack of air.
When a so-called attack occurs, the patient feels that his heart beats for a short time, and it seems to be compressed. He feels dull knocks or flutters. Sometimes there may be pain in the heart area, but this is very rare.
Diagnostics
A good method for studying extrasystoles is Holter monitoring. In this case, an electrocardiogram is recorded during the day, and the patient leads his usual lifestyle. However, simpler methods are also used, for example, taking an ECG, listening to the heart and feeling the pulse.
Treatment
Most often, bigeminy does not require special treatment. First of all, it is necessary to get rid of provoking factors that are emotional or psychological in nature. It is also important to eliminate chronic infectious foci.
For treatment, it is enough to eliminate psycho-emotional factors and chronic foci of infection
Before the doctor chooses the tactics of drug therapy, he determines the tolerability of the pathology, looks at the characteristics of extrasystoles and other factors.
This must be done due to the fact that the condition we are discussing is not an independent disease. After these factors and causes of the disease are determined, treatment for the underlying disease is prescribed.
If there is an arrhythmia of a neurogenic nature, sedatives are used, and it is also important to consult a neurologist.
If the reason lies in poisoning with certain drugs, they must be discontinued. For cardiac pathology, antiarrhythmic drugs can be used, however, before this it is necessary to be examined using Holter monitoring.
Bigeminy in itself is not dangerous, but the consequences depend on how actively the underlying disease that led to this condition develops. Therefore, it is necessary to treat any health problems in a timely manner and lead a healthy, active lifestyle!
We also recommend reading
Varieties of bigeminy heart
In the International Classification of Diseases system (ICD-10 code), the disease is classified in the section Extrasystoles, which is included in the group of Other heart rhythm disorders under number I49. At the same time, this group of conditions belongs to the subclass Other heart diseases I30-I52, which is part of the subgroup I00-I99, which describes diseases of the circulatory system.
Based on the location of the source of ectopic signals (atrium or ventricles), bigeminy and the similar trigeminy are divided into two types of arrhythmias.
| A type of abnormal rhythm | Characteristic features of rhythm disturbance |
| Ventricular | Allorhythmia of this type is called ventricular pathology, in which the source of excitatory impulses is located in the chambers of the ventricles. The anomaly, more often diagnosed in elderly patients, occurs in 55-60% of cases of registered disorders. Arrhythmia is accompanied by organic heart lesions, which are difficult to diagnose. |
| Atrial | The type of bigeminy, called supraventricular, is characterized by the location of the focus of ectopic signals in the space of the upper chambers of the organ. This is the atria or atrioventricular node in the structure of the interatrial septum. Supraventricular pathology with a minimum of pathogenic manifestations does not carry significant risks to life with an extremely low probability of complications. |
For prescribing therapeutic measures for any type of arrhythmia, the presented classification has minimal significance. The treatment tactics for both types of irregular rhythm are similar after identifying and neutralizing the causes of cardiac dysfunction. Treatment of ventricular pathology that poses a potential threat to the patient should be prescribed by an experienced specialist.
Causes of bigeminy and trigeminy
Ordinary single atrial and ventricular extrasystoles are normally found in a healthy person. They are practically not felt and do not cause discomfort. More frequent extrasystoles, such as allorhythmia, as well as frequent paired extrasystoles and runs of ventricular tachycardia, cannot be considered a variant of the norm and are a reason for a detailed examination of the cardiovascular system.
So, the main reasons for the occurrence of episodes of bigeminy and trigeminy are:
- Acute myocardial infarction,
- Overdose of cardiac glycosides, or so-called glycoside intoxication with digitalis and digitalis preparations - strophanthin, digoxin, korglykon, etc.
- Acquired defects of the mitral and aortic valves,
- Previous rheumatic fever (rheumatism) with damage to the inner lining of the heart - endocarditis,
- The consequences of myocarditis - an inflammatory process in the thickness of the heart muscle, and even minor scar changes are the basis for the pathological circulation of the impulse along the myocardial fibers,
- Post-infarction cardiosclerosis (PICS) is cicatricial changes in the normal structure of the myocardium.
If the patient, after a complete examination, does not find organic damage to the myocardium, it is most likely that the cause of bigeminy and trigeminy is a violation of the autonomic influences on the heart due to vegetative-vascular dystonia. This pathology requires consultation with a neurologist.
Causes of abnormal heart pulsation
Clinical practice shows that ventricular bigeminy is more common. The supraventricular type of allorhythmia is most typical for young patients exposed to stressful situations and high physical activity. After neutralizing the provoking factors, the symptoms of extrasystole fade away. In the idiopathic development scenario, the cause of the onset of cardiac type pathology cannot be determined.
Among the abundance of provoking agents, not all are associated with impaired functioning of the heart muscle. The causes of extrasystole can be both external (not accompanied by destruction of organ structures) and internal, due to the action of organic disorders.
The group of functional causes that caused episodes of interruptions in the rhythm of heart impulses includes the consequences of mental disorders, as well as intoxication of the body in the case of:
- long-term treatment with drugs based on cardiac glycosides, which stimulates myocardial contractile function;
Cardiac glycoside - constant use of corticosteroids, as well as aminophylline for the treatment of asthma;
- systemic use of hormonal products as oral contraceptives.
The development of signs of ventricular bigeminy can be triggered by bad habits (smoking, high doses of alcohol), abuse of energy drinks or caffeine-containing drinks (strong tea or coffee). Among the organic factors that cause abnormal pulsation of the heart muscle are manifestations of the following painful conditions:
- fever due to myocarditis, which accompanies inflammation of the heart tissue;
- load on the organ due to high blood pressure;
- consequences of myocardial infarction accompanied by necrosis of organ tissue;
- symptoms of any type of cardiomyopathy that change the size of the heart sac;
- signs of cardiosclerosis with replacement of cardiomyocytes by scar tissue.
Atherosclerosis of the heart vessels
The appearance of ventricular extrasystoles can be the result of a lack of control of physical activity during prolonged exercise, a consequence of genetic abnormalities, chronic heart failure, and endocrine disorders. The appearance of premature ventricular-type complexes is sometimes caused by surgery, coronary angiography, or probing procedures for cardiac structures.
Important: The ventricular type of bigeminy develops against the background of cardiac problems; in most cases, the pathology is caused by ischemic disease. Doctors call arterial hypertension the second provoking agent, the third place is occupied by the consequences of a heart attack.
Signals of ventricular extrasystole
Allorhythmia of the bigeminy type does not manifest itself as independent symptoms, since it is considered a sign of other pathological conditions. Patients tolerate both ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmia differently, reporting the presence or absence of subjective sensations. Some patients do not notice the appearance of extrasystoles at all and do not feel a strong cardiac impulse during pulsation of peripheral vessels with a pulse of up to 80 beats/min.
Another category of patients complains of a feeling of anxiety, a short duration of the organ’s beating due to its premature excitation. There may be a feeling of constriction of the heart muscle against the background of fluttering of the organ. Pain syndrome with the ventricular variety of bigeminy is considered rare, more often manifested by discomfort behind the sternum or compression in the cervical area.
The average symptoms accompanying premature contractions of the organ, leading to interruptions in the rhythm of its work, are usually divided into two groups.
| Cardiac type | Somatic type |
| Combination of strong shocks with pauses of absence of contractions | Feeling of weakness, lethargy in the body, increased drowsiness |
| The appearance of attacks of nausea with the possibility of vomiting | Symptoms of headache, dizziness, spots before the eyes |
| Feeling of lack of air, trembling throughout the body | Impaired visual perception, speech reproduction functions |
| Development of pallor of the skin surface with increased sweating | Reduced sensitivity of the upper as well as lower extremities |
| Signs of internal anxiety, the emergence of fear of death | High likelihood of fainting, difficulty taking deep breaths |
The advanced stage of pathological disorders may be accompanied by shortness of breath. At the initial stage of the disease, shortness of breath accompanies physical activity; with the progress of extrasystole, the inability to perform daily duties develops. The appearance of short bursts of pain is caused by overfilling of the ventricles during the pause between the premature heart impulse and the next vigorous contraction.
Manifestations of extrasystole are not a contraindication to planning pregnancy or childbirth. The ventricular type of arrhythmia in pregnant women does not require drug treatment, but correction of the woman’s mental status is necessary with the help of antidepressants and tranquilizers after consulting a doctor. This type of extrasystole does not threaten the fetus and is considered a transient disturbance in the rhythm of heart contractions.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
If the abnormal pattern of contractions of the heart muscle is not accompanied by additional symptoms of external manifestations, cardiac bigeminy is discovered by chance during the diagnosis of other diseases. When a person feels uneasy due to the freezing of an organ, the appearance of tremors in the chest area, accompanied by a feeling of fear, it is necessary to visit a cardiologist.
At the first stage of the examination, the doctor clarifies the features of the symptoms of the cardiac problem, finds out information about the presence of other diseases and hereditary pathologies. An important aspect of early diagnosis is the determination by palpation of the frequency of vibrations of the vessel walls. The basis for suspecting arrhythmia will be a decrease in heart rate to 40 or less beats per minute.
Please note: With extrasystole, the heart rate (HR) does not coincide with the pulse. The value is determined while listening to heart sounds, where the indicator can fluctuate within normal limits when the pulse in the neck or wrist is about 40 beats. The lag of the pulse from the heart rate is called pulse deficit.
Main diagnostic method
The most reliable way to detect any type of allorhythmia is considered to be electrocardiography. An abnormal heart rhythm is clearly visualized on the cardiogram by the appearance of early extrasystoles from the ventricle, which is manifested by the superposition of the R wave on the T wave belonging to the section of the previous cycle. A similar situation in the area of ectopic rhythmicity is a dangerous indicator. Signs of allorhythmia on ECG graphs differ in characteristics, which is due to the specific type of pathology.
| Belonging to a specific type of bigeminy | List of characteristics of impaired contractility rhythm |
| Supraventricular | Registration of the P-wave before the premature appearance of a narrow QRS complex with an incomplete pause of a compensatory type |
| Ventricular | The appearance of a premature QRS complex without a preceding P-wave with a complete pause of the compensatory type |
If the ECG records manifestations of rare extrasystoles, episodes of bigeminy are not classified as systemic disorders. However, if the patient complains of other symptoms of premature impulses, it is necessary to clarify the picture of the disease by prescribing other types of instrumental diagnostics.
Additional examination scheme
To identify the causes of extrasystoles of the ventricular or supraventricular variety of the disease, the doctor will need the results of an in-depth diagnosis of the patient’s body:
- using echocardiography, the activity of the conduction system is assessed, areas of impulse formation are detected;
- thanks to Holter monitoring, they receive information about the functioning of the organ at different times of the day;
- to obtain the most complete and reliable data on the condition of the myocardium and valvular apparatus, ultrasound of the heart is prescribed;
- By taking a cardiogram with stress tests, pulsation disorders are detected after physical exertion;
- Based on the results of chest X-ray, the degree of circulatory insufficiency is assessed.
In addition to instrumental testing, the patient donates blood and urine for laboratory analysis, which allows to identify traces of the inflammatory process. The blood test also evaluates the level of hormones (adrenal and thyroid), cholesterol, and electrolyte composition. A long program of complex examination allows you to prescribe the correct treatment for bigeminia, regardless of its type.
Please note: The detection of extrasystole of a functional nature in people of military age is not considered a reason for exemption from military service. If the persistent nature of the cardiac anomaly is proven, the conscript must undergo a course of treatment.
Treatment options for bigeminia
The main method of treatment at the early stage of pathology is drug therapy, which helps suppress the symptoms of rhythm disturbances by prescribing antiarrhythmic medications. When selecting drugs, you should take into account the degree of risk of consequences of supraventricular (atrial) bigeminy:
- development of supraventricular tachycardia with an increase in heart rate to 180 beats per minute, which requires urgent measures;
- the appearance of atrial fibrillation, which is accompanied by an alarming frequency of atrial contraction (over 300 beats).
Atrial fibrillation on ECG
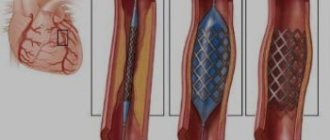
If blood flow through the body's systems is disrupted and there is an increased risk of death, surgical intervention cannot be ruled out. During the operation, the source of arrhythmia is destroyed by radiofrequency exposure of the organ.
Therapeutic measures
After identifying the factor provoking bigeminy, they begin to eliminate the cause that caused the interruptions in heart rhythm. According to the standard program, extrasystole is treated with the following medications:
- by prescribing beta-blockers, blood pressure levels are normalized along with the heart rate equalization (“Propranolol”);
- to protect against the appearance of blood clots, drugs that block platelet aggregation, antiplatelet agents (“Dipyridamole”);
- increased excitability of the nervous system and manifestations of nervousness are suppressed with sedatives (“Phenazepam”);
- To reduce heart rate, it is important to take calcium channel blockers that dilate blood vessels (Amlodipine);
- stabilization of vascular tone, equalizing blood pressure and heart rate, is achieved by prescribing potassium and magnesium in tablets (“Asparkam”);
- the addition of nitrates is justified in case of sudden pain syndrome, which is suppressed by “Nitroglycerin”;
- To urgently reduce blood pressure and heart rate, they use ACE inhibitors such as Captopril tablets.
It is forbidden to take medications on your own; a cardiologist selects medications based on the patient’s individual condition. In case of rare occurrence of extrasystoles of a functional rather than organic nature, instead of treatment, it is sufficient to follow the general recommendations of the doctor:
- exclude high physical activity, as well as stressful situations;
- give up all bad habits, do not abuse coffee;
- provide a proper diet with limited salt and animal fats;
- do not neglect moderate exercise and walking.
Important: If there is a sudden appearance of threatening symptoms or poor tolerance to arrhythmia attacks, the patient requires emergency assistance. Emergency treatment for bigeminia is carried out by intravenous infusion of Quinidine, Cordarone, Lidocaine, which help normalize the heart rate.
When is heart surgery needed?
The basis for prescribing surgical intervention using radiofrequency ablation is intolerance to antiarrhythmic drugs or the low effectiveness of drug therapy. During a minimally invasive operation performed in a hospital under local anesthesia, the focus of the extrasystole is cauterized by exposure to radio waves.
A surgical procedure performed under the control of fluoroscopic equipment is prescribed only after prehospital identification of the location of the source of pathological impulses. Access of electrodes to the source of arrhythmia is achieved by catheterization of the femoral vein, which ensures insertion of the instrument.
Help from traditional methods
The treatment program for mild forms of extrasystole can be enhanced by incorporating folk recipes. They help restore the nervous system by eliminating neurological symptoms, improve the condition of blood vessels and help restore normal heart function, saturating the body with useful elements.
At home, you can prepare healing infusions from well-known medicinal plants, which are taken 15-20 minutes before meals:
- Hawthorn. A tablespoon of fruit is crushed, poured with a glass of boiling water and simmered over low heat for 15 minutes. After infusion, filter the decoction and take a teaspoon 3 times a day.
- Valerian. A tablespoon of carefully crushed root is poured into a glass of boiling water. The drug is infused, covering the container with a lid, then filtered. Take 3 times a day, ½ cup.
- Calendula. Dried flowers of the plant (70 g) are steamed with boiling water (1 liter) and left to infuse for one hour. The strained infusion is taken 4 times a day, ½ cup.
The help of folk recipes for the symptoms of bigeminy will be most effective if used for a long time. To avoid allergic reactions and addiction of the body, after 2-3 months of taking the herbal medicine, you need to take a break. It should be remembered that infusions and decoctions do not eliminate the cause of the disturbed rhythm, but only have a beneficial effect on the body as a whole.
Treatment
If the patient has excluded organic heart disease as the cause of bigeminy and trigeminy, then he requires examination by a neurologist with treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
First of all, it is necessary to correct the lifestyle with adequate nutrition and a regime of work and rest. It is also necessary to normalize the patient’s psychological state and provide psycho-emotional comfort. Contrast showers, dousing and rubbing with a damp cloth are very good for training the cardiovascular system.
In the case when a patient is diagnosed with one or another heart disease as the cause, it requires mandatory treatment. In some cases, surgical correction of heart disease may even be indicated.
In addition to the main treatment, the patient is prescribed beta-blockers for constant use, for example, sotalol, nebilet, coronal, concor, etc., as well as calcium channel blockers - diltiazem, verapamil, etc. These drugs can reduce the heart rate and reduce the conduction of pathological impulses along the ventricular myocardium.
Cordarone, lidocaine and intravenous quinidine are used as emergency treatments for sudden frequent bigeminy or trigeminy.
In cases where antiarrhythmic therapy is contraindicated for a patient, or its poor tolerability and/or ineffectiveness is noted, the issue of the need for RFA (radiofrequency ablation) must be resolved - that is, cauterization of the tissue of the atrium or ventricle through which pathological impulses pass.
Forecast
Predicting the consequences of arrhythmia developing according to the bigeminy scenario depends on the age category of the patient, his general physical condition, as well as the presence of other diseases. In the absence of serious problems with the vessels and tissues of the heart, a person is not at risk of serious complications. If extrasystole is a consequence of the destruction of myocardial structures, then the lack of timely treatment increases the likelihood of death.
Despite the fact that short episodes of allorhythmia are not considered a disease, if there are minor disturbances in heart rhythm, you should consult a cardiologist. Even mild symptoms of extraordinary impulses can be a signal of the onset of serious heart pathology.
Did you like the article? Save it!
Still have questions? Ask them in the comments! Cardiologist Mariam Harutyunyan will answer them.
Ivan Grekhov
Graduated from the Ural State Medical University with a degree in General Medicine. General practitioner
Are there possible complications of bigeminy and trigeminy?
Complications can develop in patients with any extrasystole - ventricular and atrial.
Thus, atrial extrasystole can turn into atrial fibrillation and flutter, and ventricular bigeminy or trigeminy can turn into ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation and lead to asystole (cardiac arrest). Prevention of complications is the timely initiation of treatment for diseases that led to bigeminy and trigeminy.