Author: Strokina O.A., therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. February, 2021.
One of the most informative methods for studying the heart is scintigraphy (nuclear scanning). To carry out the procedure, a medication containing radioactive isotopes (radionuclides) is used. The drug is injected into the patient's body intravenously and, circulating in the bloodstream, is gradually absorbed by the heart muscle.
Based on the degree of saturation of myocardial tissue with radionuclides, experts evaluate its functionality: active absorption indicates normal heart function, and vice versa, “empty” areas may indicate ischemia (death) of cardiac tissue.
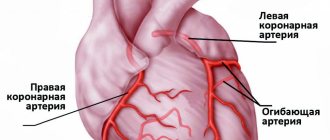
Perfusion scintigraphy is a specific method for diagnosing coronary heart disease (CHD) using radioactive thallium. The procedure is performed with functional tests, and unlike conventional electrocardiography (ECG) and even echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) with physical activity, it allows you to most accurately determine the location of the ischemic zone.
Indications
Myocardial scintigraphy is prescribed by cardiologists both to patients with already confirmed ischemic heart disease, and to clarify this diagnosis. Based on the results of the study, the doctor plans further treatment tactics or determines the need for surgical intervention on the coronary vessels.
Scintigraphy is prescribed for the following indications:
- preventive examination of persons at risk for coronary artery disease: patients with diabetes and/or hypertension,
- heavy smokers with extensive experience,
- patients with heredity unfavorable for cardiovascular diseases,
- people with high cholesterol,
- women over 55 years of age and men over 45 years of age;
Myocardial scintigraphy (myocardial perfusion scintigraphy) is a study of the blood supply (perfusion) of the left ventricular myocardium using radiopharmaceuticals (RPs), which are distributed in healthy heart tissue. The radiopharmaceutical is administered intravenously and accumulates in the heart muscle, then the radiation from the accumulated drug is captured by the detectors of the recording device.
Myocardial scintigraphy is a unique diagnostic method that makes it possible to objectively assess the blood supply to the heart muscle.
Indications for myocardial perfusion scintigraphy:
- Detection and differential diagnosis of coronary heart disease (CHD): Angina pectoris and stable angina pectoris, episodes of unstable angina pectoris.
- Assessment of the significance of coronary artery lesions in patients diagnosed with coronary artery disease.
- Assessment of the risk of cardiovascular complications (myocardial scintigraphy is performed if the diagnosis of coronary artery disease has already been made).
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of coronary angioplasty, bypass surgery and thrombolysis; assessment of the effectiveness of revascularization.
- Repeated scintigraphy for resumption of angina after interventions on the coronary vessels.
- Confirmation of the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the presence of a questionable ECG.
- Study of the blood supply to the myocardium of the left ventricle in its non-coronary lesions (cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, early complications of diabetes mellitus).
- Determination of treatment strategy and quality control of treatment provided.
There are 2 options for performing myocardial perfusion scintigraphy:
- Myocardial scintigraphy at rest - performed within 1 day.
- Myocardial scintigraphy at rest and with load (bicycle ergometry) - carried out over 2 days.
According to experts, scintigraphy of the myocardium at rest, i.e. without stress test, not very informative.
However, in some cases this diagnostic method is indicated for:
- Chest pain of unknown etiology.
- If it is impossible to perform physical activity, permanent cardiac pacing (PAC), left bundle branch block (LBBB).
- Asymptomatic disorders during other stress tests and when they are not informative.
Due to the current impossibility of performing a functional load, myocardial perfusion scintigraphy is performed only at rest.
When studying cardiac perfusion at rest, it is actually possible to confirm the presence of scar changes (infarct zones) of the myocardium, as well as assess blood supply, while studying the myocardium at rest and with stress expands the diagnostic capabilities of the technique.
Contraindications for scintigraphy:
- pregnancy, restriction during breastfeeding (cancellation for 48 hours).
to perform a load test:
- myocardial infarction in the last two days (48 hours);
- unstable angina with a high risk of cardiovascular complications;
- untreatable arrhythmias accompanied by hemodynamic disturbances;
- severe clinical aortic stenosis;
- severe heart failure;
- pulmonary embolism;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- acute myocarditis, pericarditis or infective endocarditis;
- severe non-cardiac diseases that may affect the performance of the test, or may worsen during the test (including infections, renal failure, thyrotoxicosis);
- severe emotional disorders, psychoses.
Preparing for the study
If you plan to do only the study at rest, medications are not canceled.
During exercise tests, after consultation with your doctor, it is recommended to discontinue β-blockers (atenolol, bisoprolol, nebivolol, etc.) 3 days before the exercise test.
Features of the study: it is advisable to conduct a stress test of the heart as part of hospitalization in a hospital for several days to monitor the patient’s condition before and after the stress test and conduct additional diagnostic tests.
The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, and have full-fat yogurt (sour cream or cheese) with you.
The procedure is carried out 30–60 minutes after the administration of the radiopharmaceutical and takes up to 30 minutes.
The conclusion is issued on the day of the study.
Patients must have with them an extract from the outpatient card/medical history with an examination by a cardiologist or therapist, an archive of electrocardiograms, the results of heart studies, if available (ECHOCG, Holter monitor, ABPM, VEM, Treadmill test, etc.), which he must provide to the radiologist.
To examine the patient under load, you must bring comfortable shoes and sweatpants for bicycle ergometry.
Cost of radioisotope research:
| Service code | Name of service | Cost, rub. |
| A07.03.001.001 | Whole body bone scintigraphy | 8 700 |
| A07.03.001.002 | Whole body bone scintigraphy combined with single photon emission computed tomography of bones and computed tomography of the thoracic spine | 20 500 |
| А07.03.001.003 | Whole body bone scintigraphy combined with single photon emission computed tomography of bones and computed tomography of the lumbosacral spine | 27 500 |
| A07.03.001.004 | Whole body bone scintigraphy combined with single photon emission computed tomography of bones and computed tomography of the pelvic bones | 27 500 |
| A07.03.003 | Single photon emission computed tomography of bones | 7 400 |
| A07.09.004 | Single photon emission computed tomography of the lungs (perfusion) | 14 000 |
| A07.09.004.001 | Single-photon emission computed tomography of the lungs (perfusion), combined with computed tomographic angiography of the pulmonary artery and its branches | 29 300 |
| A07.10.003 | Single-photon emission computed tomography of the myocardium at rest | 8 800 |
| A07.10.003.002 | Single-photon emission computed tomography of the myocardium, perfusion with functional tests | 15 700 |
| A07.10.005 | Single photon emission computed tomography combined with myocardial computed tomography | 18 800 |
| A07.14.002 | Scintigraphy of the liver and spleen | 9 800 |
| A07.14.002.002 | Liver scintigraphy with labeled red blood cells | 22 200 |
| A07.14.004.001 | Single-photon emission computed tomography of the liver and spleen combined with computed tomography of the hepatobiliary zone | 19 800 |
| A07.22.002 | Thyroid scintigraphy | 6 500 |
| A07.22.010 | Single photon emission computed tomography of the parathyroid glands | 9 600 |
| A07.22.010.001 | Single photon emission computed tomography of the parathyroid glands combined with computed tomography of the parathyroid glands | 29 700 |
| А07.28.002 | Scintigraphy of the kidneys and urinary system | 8 700 |
| A07.28.004 | Angionephroscintigraphy | 8 000 |
| A07.30.031 | Three-phase scintigraphy of soft tissues and bones | 11 400 |
Contraindications
You should not undergo cardiac scintigraphy during pregnancy and breastfeeding (except in emergency situations). There are no more contraindications for conventional scintigraphy.
A much larger list of absolute contraindications is available when performing scintigraphy with stress tests (exercise test or pharmacological test):
- severe general infections with high fever;
- acute stage of myocardial infarction
- unstable angina;
- severe heart failure;
- severe pathologies of the heart valves (aortic stenosis);
- myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle);
- the presence of a chronic aneurysm with a thrombus;
- acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke);
- acute thrombophlebitis;
- severe respiratory failure.
Relative contraindications for testing with stress tests include:
- arterial hypertension with blood pressure? 180/100 mm Hg;
- high heart rate, more than 110 per minute;
- serious rhythm and conduction disturbances;
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- hypothyroidism;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- psychoneurological disorders.
Osteoscintigraphy
What it is?
Bone scintigraphy is a diagnostic method based on the introduction into the patient’s body of a drug that quickly and easily accumulates in bone tissue and contains an isotope (common name - radiopharmaceutical). Flashes of radiation emitted by the isotope are then recorded using a special gamma camera. This method allows you to study the entire skeleton at once, in contrast to x-rays, which contain images of individual bones. Bone scintigraphy is the main method for early diagnosis of primary tumors and metastatic lesions of the skeleton, assessment of the effectiveness of treatment after chemotherapy and radiation therapy of a malignant tumor, as well as differential diagnosis of tumor and inflammatory bone lesions.
How it works?
The essence of the method is that damaged bone tissue accumulates radioactive isotopes much faster than healthy bone tissue. As a result, on the images, pathological lesions in the bones will appear as zones of increased or decreased accumulation (black and white). It is noted that metastases can be detected using osteoscintigraphy much earlier than with other studies.
Indications for scintigraphy
- Primary damage to bones and joints.
- Metastatic lesion of the musculoskeletal system.
- Arthritis, arthropathy and poliomyelitis.
- Hidden injuries of the skeletal system.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of chemotherapy for subsequent treatment prediction.
- Inability to make a diagnosis for pain symptoms of unknown etiology.
- Control of inflammatory processes in the area of prosthetics.
How is the research conducted?
No preparation is required, the study is carried out in two projections, anterior and posterior in the whole body mode, 2 - 2.5 hours after intravenous administration of the drug. Before the study, the patient is intravenously given a small dose of a radiopharmaceutical containing the technetium isotope Tc99 and capable of accumulating in bone tissue, its distribution is then assessed using a gamma camera and a series of scintigrams.
Is scintigraphy dangerous?
Although radioactive isotopes are used to conduct this study, the degree of patient exposure during scintigraphy is so low that this research method using technetium 99 can be performed even on children of the first year of life. For all the years of clinical use of radiopharmacological drugs in world practice, not a single allergic reaction has been described reactions. This is due to the minimal amount of radiopharmaceutical administered, as well as its biological inertness. All isotopes used for research are short-lived - they quickly decay, stopping irradiation, and radiopharmaceuticals are quickly eliminated from the body after the study
The radiation exposure does not exceed the level of radioactive radiation that accompanies a chest x-ray or CT scan.
Contraindications to skeletal scintigraphy are pregnancy and the presence of already established individual intolerance to the contrast agent .
Nursing mothers can continue feeding the baby a day after completion of the procedure.
After the study, the patient does not pose a danger to others and should not experience any discomfort. However, within 24 hours after administration of the drug, it is necessary to avoid close contact with children and pregnant women, and it is also necessary to increase the volume of fluid consumed to 2-2.5 liters.
Preparing the patient for scintigraphy
Scintigraphy does not require special preparation, but the patient must follow some recommendations.
- The day before the test, you need to exclude products containing caffeine (coffee, tea, chocolate, cola) from your diet;
- Before the procedure (for 12 hours) you should not eat (diabetes patients are allowed to eat light, low-fat food);
- You will have to temporarily interrupt or limit the intake of certain medications, for example, cardiac glycosides, nitrates, beta locators (your doctor will advise you on this matter);
Women who are breastfeeding should express breast milk beforehand to use after the procedure. Radioisotopes are excreted in the secretions of the mammary glands within 2 days, so it is not recommended to feed a child with this milk.
The patient must notify the doctor if:
- he suffers from bronchial asthma;
- he takes drugs to increase erection (during the procedure, a man may develop an attack of angina, which can only be controlled with nitrates, which are incompatible with Viagra, Levitra, etc.).
Before the procedure, women need to make sure that they are not pregnant.
Methodology
Half an hour before the start of the study, a radiopharmaceutical (RP) is administered intravenously to the patient. During the examination, the patient lies on the tomography table with his arms thrown back behind his head to reduce the likelihood of artifacts appearing in the images. The gamma camera then scans the myocardium, capturing radio waves and converting them into a series of images.
Scintigraphy lasts from 2 to 4 hours. During this time, the heart is examined at rest and during physical or pharmacological stress. By comparing the obtained images, the doctor can determine the presence or absence of areas of ischemia in the heart muscle - during exercise, the blood supply to the myocardium increases, so all existing disorders are clearly visualized in the images.
Load scintigraphy
For exercise scintigraphy, an exercise bike or treadmill is used. A functional test is carried out starting with low intensity and gradually increasing its level. At the same time, the dynamics of blood pressure and heart rate are monitored, and an electrocardiogram is taken.
If it is impossible to conduct scintigraphy with natural physical activity for the patient, it is simulated with the help of medications that cause increased heart rate and increased blood pressure.
At the peak of the intensity of physical activity, the patient is again given a radiopharmaceutical (radiopharmaceutical), and 30 minutes later the heart is re-scanned in different projections.
Advantages of scintigraphy at the Sofia Oncology Center
Advantages of treatment in oncology:
- Use of modern equipment. In oncology, the scintigraphy procedure is carried out using the latest equipment that meets international standards of medical practice.
- High level of specialist training. Examination and diagnosis of patients in oncology are carried out by experienced specialists who regularly undergo training in leading American and Israeli clinics.
- Convenient location. The oncology department is located in Moscow (TsAO). There are several metro stations in our immediate vicinity: Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya, Belorusskaya and Mayakovskaya.
Myocardial scintigraphy results
When reading the scintigraphy results, the doctor can determine:
- intensity of coronary circulation;
- degree of blood supply insufficiency;
- localization of necrotic areas;
- foci of ischemia during exercise;
- scars after a heart attack.
Also, based on the results of the study, the likelihood of developing possible complications is calculated, a program of conservative treatment is planned, or the method of surgical intervention is determined.
Scintigraphy is not informative in assessing the size of the heart and the condition of the coronary vessels. That is, this method will not allow one to determine the location and degree of narrowing of blood vessels.
Indications for scintigraphy
Using scintigraphy, you can evaluate the blood supply to the heart muscle, determine the degree of failure (if detected), see scarred areas and necrotic areas. Myocardial scintigraphy also allows you to assess the likelihood of complications. The treatment strategy depends on the study. Cardiologists may prescribe scintigraphy in cases such as:
- diagnostics before operations, sports activities;
- study of cardiac contractility, diagnosis of coronary artery disease;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment;
- assessment of heart function after myocardial infarction;
- identifying the causes of pain in the chest area;
- repeat scintigraphy for resumption of angina after surgery;
- confirmation of certain types of diseases, in particular myocardial infarction with a questionable ECG;
- assessment of the effectiveness of coronary angioplasty and thrombolysis.
Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy is also performed in other cases. We suggest contacting a cardiologist at our clinic, who will conduct a detailed consultation and tell you about the details of scintigraphy.