Why does a heart attack develop?
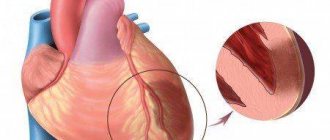
This is a special case of coronary heart disease (CHD). With coronary artery disease, the blood supply to any part of the heart is disrupted. The area deprived of blood flow is first damaged, and then may die completely (necrosis). Naturally, the heart muscle, whose job is to contract rhythmically, cannot work normally in this state.
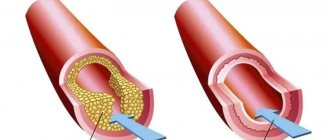
Blood supply may be impaired due to vascular atherosclerosis (approximately 95% of cases), as a result of complications after angioplasty, due to vascular embolization or spasm.
Some people are at higher risk of developing CAD.
Factors that increase risk include:
- High blood pressure;
- Age over 45 years;
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes;
- Cases of IHD in the family;
- Detected atherosclerosis or its precursors (high levels of triglycerides of “bad” cholesterol in the blood, low levels of “good” cholesterol);
- Poor nutrition.
Symptoms and signs of a heart attack
Typical cases of heart attack are associated with severe pain in the chest, which radiates to the left shoulder, collarbone, neck, left half of the face, lower jaw, and interscapular area. The larger the area of damage to the heart muscle, the more severe the pain. The pain lasts more than 30 minutes and is not relieved by taking medications.
In the atypical course of the acute stage of a heart attack with unexpressed pain, acute weakness, sticky sweat, pale skin, tachycardia, arrhythmia, cough and suffocation, swelling and distorted consciousness may occur.
In the acute stage of a heart attack, the pain usually goes away. Due to necrosis, the temperature may rise and arterial hypotension may develop.
In the subacute period, the condition normalizes, tachycardia and systolic murmur disappear, pressure and temperature normalize.
How to avoid myocardial infarction
You cannot be 100% insured against cardiovascular diseases. But it is possible (and necessary!) to minimize risks. To do this, you need to normalize your diet, try to move more and give up bad habits. This is especially important if tests show that you are at risk of developing atherosclerosis.
You can prevent a heart attack if you reduce your consumption of fatty, fried, smoked foods, pickles, try to eat more vegetables and fish (for example, follow a Mediterranean diet), and include nuts and foods rich in potassium in your diet. Some researchers recommend switching to vegetarianism after 50 years - this helps improve the condition of blood vessels and reduce the level of “bad” cholesterol.
Physical activity is an excellent workout for the heart and blood vessels. Even if you haven't exercised before, it's worth starting to maintain vascular health. Morning exercises and an evening walk will help you meet your body's need for movement, prepare your cardiovascular system for stress and protect your heart.
First aid for heart attack
If acute pain occurs, you must urgently call an ambulance
. In the absence of contraindications, you can take acetylsalicylic acid in a dose of 150-300 mg, after crushing the tablet.
Before the ambulance arrives, the patient must be kept in a reclining position and at rest.
In the room, you need to open the window and unfasten tight clothes and belt.
Doctors call the first hour of the most acute stage of a heart attack “golden”; the outcome of the disease most often depends on this time.
How to prevent a stroke
A stroke is also a circulatory disorder, but not in the heart, but in the brain. It can manifest itself either in the form of a violation of blood flow to the brain (cerebral infarction or ischemic stroke), or in the form of hemorrhages (in the brain or in the space between the brain and the meninges).
The causes of a stroke are in many ways similar to the causes of a heart attack, but there are also specific features: for example, a stroke often occurs after emotional stress. Therefore, stress is an additional risk factor.
It is important to know: within two years after suffering an attack, the likelihood of another stroke increases significantly!
To stay healthy, eat right, be sure to exercise (especially aerobic exercise - running or swimming), avoid nervous shock and emotional overload.
If you are at high risk for developing cardiovascular diseases or if something worries you, make an appointment with a general practitioner for a detailed consultation or call a specialist at home.
Treatment
In the most acute stage of a heart attack, first of all, doctors relieve pain. For this purpose, various analgesics and narcotics (morphine) can be used intravenously. For a faster effect, painkillers are administered intravenously.
After the electrocardiogram is taken, thrombolytics are administered to restore coronary blood flow. To eliminate a pain attack, neuroleptanalgesia is performed.
Next, the patient is prescribed a set of drugs to reduce the myocardial oxygen demand, beta blockers to reduce the load on the heart, medications to thin the blood and reduce the level of blood clotting. If necessary, inhibitors, sedatives and hypnotics are prescribed. The combination of drugs depends on the presence of concomitant diseases in the patient and the severity of the heart attack.
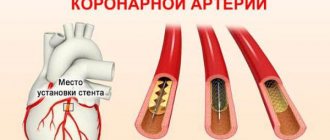
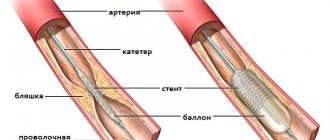
To treat a heart attack, surgical methods of restoring blood flow are used (coronary artery bypass grafting, balloon angioplasty).
During the first days of treatment, the patient is prescribed bed rest, and starting from days 3-4, the patient can sit on a chair for about an hour twice a day. With an uncomplicated heart attack, the patient is allowed to walk 5-7 days after the heart attack. In case of an uncomplicated form of myocardial infarction, the patient is discharged from the hospital on days 10-12; in case of complications, hospitalization can last up to 4 weeks.
Clinical guidelines
Clinical recommendations “Acute myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation of the electrocardiogram” were developed by the Russian Society of Cardiology with the participation of the Association of Cardiovascular Surgeons of Russia, approved by the Scientific and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and approved by the Ministry of Health in 2021. The document contains information about the disease, forms of its diagnosis, symptoms, treatment methods, possible complications, care and rehabilitation.
Appendix B of the document contains recommendations for patients who have had a heart attack related to secondary prevention of the disease. The recommendations say that patients should stop smoking, ensure regular physical activity, follow a diet designed for such cases, lose excess weight, follow the doctor's recommendations, maintain low blood cholesterol levels with the help of medications, ensure stable normalization of blood pressure (if present). arterial hypertension), maintain normal blood sugar levels (in the presence of diabetes mellitus). In addition, with extensive damage to the heart muscle and/or complications of myocardial infarction, additional treatment is required, which is prescribed by a doctor. Stopping essential medications early is known to significantly increase the risk of another heart attack, death, and heart failure, which can significantly limit your daily activities. You should not stop taking medications without consulting your doctor. To reduce the risk of recurrent events (myocardial infarction, its complications), it is highly advisable for you to participate in a special rehabilitation program, including regular dosed physical activity, psychological support, and monitoring of risk factors.
“You are cured, you can live as before”
This is a very common misconception among patients who were quickly put on their feet by doctors and did not realize how serious their illness was. “Now we can cure a person who has suffered such a deadly disease, so that he returns to work, lives an active life and does not feel sick,” explains Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences Simon Matskeplishvili. “And here lies a great danger.” Because, having once suffered a heart attack, the patient often runs the risk of having another one if he behaves incorrectly.” The risk of a repeat disaster is from 10 to 20% in the first year.
How to reduce this risk? Continuity of treatment is extremely important. “A patient with a heart attack no longer spends a month in the hospital as before. He is discharged after a few days, feels fine and does not consider it necessary to follow our recommendations for continuing therapy,” says Professor Matskeplishvili. “It is especially difficult to convince that medications need to be taken long-term, often, for life.”
Types of recurrent heart attack
There are several types of recurrent heart attack.
- Painless form. In this case, the patient may not feel pain, but complain only of shortness of breath and general weakness. If the patient has recently suffered a heart attack, even these seemingly minor symptoms can be serious. Timely consultation with a cardiologist in this case is vital.
- Arrhythmic form. In this case, the patient feels shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, and rapid heartbeat.
- Asthmatic form. One of the most dangerous varieties. The main symptom is a cough producing pink, frothy sputum.
- Abdominal infarction causes nausea and vomiting and may be misdiagnosed as an intestinal disorder.
Heart attack marked "urgent"
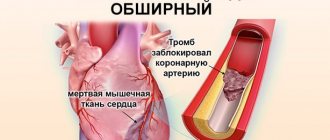
The disease acts quickly. Changes in the vascular wall lead to changes in its elasticity and narrowing of the lumen of the vessel. First, ischemia develops (blood supply decreases), and then at some point the plaque ruptures, a thrombus forms in the path of blood flow, it completely blocks the lumen of the vessel and causes necrosis of the myocardium. A heart attack is dangerous because if the blood supply to the myocardium is not restored in the first 6–12 hours after the cessation of blood flow, the heart may stop altogether.
Article on the topic
After a heart attack. What exercises will strengthen your heart?
But even if a heart attack occurs, it should not be fatal. Doctors have several treatment options to prevent a person from dying. It is possible to restore blood supply to the vessel that is closed by a thrombus by using thrombolysis (that is, dissolving the clot). Another way is to restore the patency of the vessel surgically by placing a stent. To do this, a special device is inserted through the artery, which opens in the right place like an “umbrella”, and thus expands and strengthens the vascular wall, restoring blood supply through it. The third method is coronary artery bypass grafting. Its essence is that in those arteries where blood flow is impaired, new bypass paths are created. This is done using healthy vessels that are attached to the coronary arteries.
Moreover, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment started, the better the survival prognosis. It is possible to save a person if doctors act immediately - open the lumen of the vessel. But how can you fit into the allotted “window” of 6–12 hours if it is not always possible to make a diagnosis of “heart attack”. 30% of heart attacks pass without pain, nausea, vomiting, or dizziness. In a fourth of cases there are not even changes on the electrocardiogram!
What is bypass surgery?
More details
Rehabilitation and recovery after a heart attack
The main tasks of rehabilitation after a heart attack are the restoration of the circulatory system, ability to work and a normal lifestyle. Rehabilitation includes a set of measures, consistently and continuously carried out under the supervision of doctors.
Rehabilitation measures are individual and depend on the patient’s condition, the severity of the heart attack, and chronic diseases. At the same time, the stages of rehabilitation are associated with being in a hospital, in a sanatorium and at home.
In the hospital, the disease is diagnosed, treatment is carried out after restoration of the patency of the coronary vessels, risks are assessed and a prognosis for the recovery period and relapse is formed.
The inpatient rehabilitation period is the time of the acute period of a heart attack, which the patient spends in a specialized rehabilitation department of the hospital and then in a cardiological sanatorium.
An outpatient rehabilitation period is provided for home conditions under the supervision of a cardiologist and exercise therapy doctor.
Rehabilitation is medicinal and non-medicinal methods of recovery. These include:
- gymnastics to prevent the formation of repeated blood clots and increase blood supply and oxygen supply,
- physiotherapy,
- psychological help.
At the same time, an individual set of measures includes a gradual increase in physical activity. Typically, two weeks after a heart attack, patients are allowed to walk up to 2 km per day, assessing the ability of the heart to work using echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the heart), and performing exercise tests.
The exercise therapy complex gradually includes swimming, walking at a pace, and training on exercise machines. Depending on the functional class of ischemia, classes are held in a training or gentle mode.
During rehabilitation, measures of psychological recovery are important. Returning to normal life and overcoming fear, including before physical activity, is an important stage of recovery after a heart attack. The formation of depressive and anxiety states can delay the results of rehabilitation for a long time and worsen its quality.
Non-drug methods, in addition to physical rehabilitation, include lifestyle correction:
- quitting smoking and alcohol,
- diet,
- full sleep.
Medicines are used for:
- preventing angina attacks,
- blood pressure control,
- blood clotting,
- lipid metabolism,
- treatment of arrhythmia and chronic heart failure.
A comprehensive rehabilitation program helps patients recover in a shorter time and prevent recurrent heart attacks and other complications.
Who takes care of the heart?
But there is also another group of risks - the so-called behavioral ones. Who do you think has a higher risk of developing a heart attack: the poor or the rich? It turns out that the poor man has it. Observations conducted in the United States found that the higher the average annual income in a family, the lower the likelihood that its members will develop heart attacks and strokes in the next ten years. Because rich people have more opportunities to maintain a healthy lifestyle. They are more likely to buy a membership to a fitness club and be more active. If you have money, it is easier to adhere to a healthy eating style - give up fast food, go on a fasting diet, and include healthy foods in your diet that are necessary for the perfect functioning of your heart. And a wealthy patient always has the opportunity to visit a cardiologist on time and conduct the necessary tests.
True, there is a risk factor that is difficult for a person with any income to protect themselves from: stress. Modern man lives under conditions of chronic stress, and the hormones released in this state have the opposite effect of insulin, which lowers sugar levels. The state of constant, elevated levels of glucose in the blood leads to disruption of many metabolic processes and the development of metabolic diseases, the consequence of which is, again, a heart attack.
Catch it if you can. How to prevent a heart attack
More details