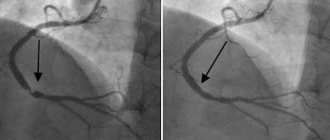
Ultrasound of the heart
Ultrasound examination of the heart or echocardiography is a method of studying the anatomy of the heart muscle. During the procedure, the diagnostician directs a special device to the heart. The device passes ultrasonic waves through the body. Our organs reflect and partially absorb waves. The ability of different human tissues to reflect/absorb ultrasound differs. The ultrasound machine receives the reflected waves and converts them into an image on the monitor.
What does an ultrasound of the heart show?
- Valve condition.
- Pathologies, for example, a tumor or a previous microinfarction.
- The speed of blood flow in the heart.
- Vessel diameter.
- Changes in the thickness of the walls of the ventricles and atria.
- Changes in large vessels.
- Blood clots.
- Is there fluid in the pericardial sac?
A professional cardiologist uses ultrasound results to detect many heart diseases. The doctor makes a conclusion based on the results of the study, taking into account age, gender, lifestyle and many other factors. Therefore, during the examination, answer the doctor’s questions in detail and honestly.
Indications for cardiac ultrasound
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the heart according to the following indications:
- weakness and dizziness;
- fainting and recurring headaches;
- nausea due to high blood pressure;
- dyspnea;
- swelling on the body in the late afternoon, especially on the legs;
- constant and recurrent pain in the chest or under the shoulder blade;
- rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations;
- pale or bluish skin;
- heart murmurs;
- suspicion of congenital or acquired heart disease;
- vascular pathology, for example, varicose veins or thrombophlebitis;
- suspicion of rheumatism, lupus erythematosus or scleroderma;
- upcoming surgery if there is a history of cardiac problems or if the patient is over 50 years of age.
If after a routine echocardiography the doctor still has doubts, he may prescribe an ultrasound of the heart through the esophagus. Such a study causes some discomfort to the patient, but gives a more accurate result.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound examination. It is safely prescribed to everyone, including children and pregnant women.
Features for various diseases
Painful sensations may have characteristics depending on the disease that causes them.
Myocardial infarction
Poor blood supply to the heart muscle can cause its necrosis, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- burning sharp pain;
- the attack lasts more than half an hour;
- additional symptoms are present (shortness of breath, nausea, panic and sweating);
- the pain radiates to the left side of the body.
IMPORTANT! With such signs, the patient urgently calls an ambulance, since the opportunity to stabilize the condition will only be 2 hours.
Angina pectoris
Severe pressing pain syndrome. This sensation occurs after a certain amount of tension and persists for half an hour. The main symptom is relief after taking nitroglycerin.
Myocarditis
The condition is characterized by inflammation of the heart muscle, aching pain occurs periodically. The more inflammation spreads, the longer and more intense the pain.
Valve damage
Pain sensations differ in localization (it all depends on the degree of damage to the valves). Usually the pain is aching and dull, occurring periodically, at the same time the heart rate becomes erratic and shortness of breath begins.
Cardiomyopothia
The pathological process is accompanied by contracting, pulling pains, the precise localization of which is difficult to determine. It is not always possible to relieve the syndrome with nitroglycerin.
Electrocardiogram
The heart is our “electric motor”. Electrical impulses are generated in a special group of cells in the atria. They cause parts of the heart to contract. An ECG is a recording of the electrical activity of the heart in the form of a waveform. Electrodes are placed on your body to take ECG readings. To increase the passage of electric current, the diagnostician lubricates the areas under the electrodes with a special gel. The procedure itself lasts several minutes. The study is usually carried out in a resting position, lying or sitting. There are types of ECG: stress testing, daily ECG monitoring according to Holper.
What does the ECG show?
- Heart rhythm disturbances: bradycardia and tachycardia, extrasystole, atrial fibrillation.
- Myocardial ischemia.
- Improper conduction of impulses or blockade.
The disadvantage of an ECG is that the study will show those disturbances in the functioning of the heart that affect its functioning at the time of recording. False-positive results are not uncommon for ECGs. If the doctor has doubts about the reliability of the ECG, he will additionally prescribe an ultrasound of the heart.
Indications for ECG
The cardiologist prescribes an electrocardiogram according to the following indications:
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- hypertension;
- infection, inflammation or other heart pathologies;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- pregnancy;
- increased blood cholesterol levels;
- previous sore throat;
- increased health requirements by profession for pilots, drivers, military personnel, athletes, etc.
Doctors prescribe an ECG for 80% of patients admitted for hospital treatment. There are no contraindications to the study. Now you can take an electrocardiogram even outside the hospital. For example, at the pharmacy or at the gym.
Remember! If you feel the slightest discomfort or pain in the heart area, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. Take care of your heart and be healthy!
Heart arythmy
Cardiac arrhythmia is a pathology in which there is a disturbance in the rhythm, frequency and sequence of contraction and excitation of the heart. Patients suffering from heart rhythm problems describe their condition in different ways, but they feel the same thing - first an increased heart rate, then a sinking heart and again a feeling that the heart is about to jump out.
Is arrhythmia dangerous? Types of arrhythmic disorders
There is a set heart rate of 60-80 beats per minute. When this indicator increases, a person develops tachycardia, and when it decreases, bradycardia develops. This is generally called an arrhythmic heartbeat disorder. Arrhythmia itself does not pose a threat to a person’s life, but it can lead to some complications that can negatively affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system and cause the development of a stroke or heart attack.
Some types of arrhythmic disorders ( atrial fibrillation, sinus
) can interfere with the normal blood supply to the heart, and cause its sudden stop.
For example, atrial fibrillation
is the cause of blood stagnation in the atria, and if a person’s body is prone to the formation of blood clots, then there is a high probability of the formation of an embolus, which breaks away from the walls, passes into the blood vessels and blocks blood circulation in the brain, which inevitably leads to either a stroke , or to death.
In addition, atrial fibrillation
negatively affects the heartbeat in general.
If a patient experiences erratic contraction of the fibers of the upper chambers of the heart, this leads to disruption of the ventricular rhythms. Atrial fibrillation
is a serious pathology and can cause diseases such as:
- Cardiac embolic stroke;
- Heart failure;
- Cardiomyopathy;
- Thromboembolism;
- Cardiac asthma;
- Arrhythmogenic shock;
Sinus arrhythmia
There are two types: respiratory - occurs at a young age and non-respiratory - occurs in old age and is determined by the difference between heart contractions, exceeding their average duration by 10%.
With sinus arrhythmia,
the heart rate increases to one hundred or more beats per minute.
It mainly appears after stressful situations, physical overload, taking medications, or is a consequence of some other reason. Tachycardia disorders lead to an accelerated heartbeat, indicating disturbances in vascular tone, and can occur after attacks of angina, anemia, heart attack, as well as with elevated body temperature and increased hormone production. Sinus arrhythmia
is dangerous due to unexpected fainting and dizziness, and when such symptoms become frequent, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo a therapeutic course of treatment. And if, with severe shortness of breath, chest pain and darkening of the eyes appear, then you need to immediately undergo a course of examination by a cardiologist, diagnose the disease and strictly follow medical recommendations. It is possible that hospital treatment will be required.
How to treat arrhythmia
To restore normal heart rhythm, doctors prescribe drugs with antiarrhythmic effects. Such drugs are divided into four groups: antiarthmics, beta-blockers, anticoagulants and metabolites.
Anti-arthmics.
To eliminate atrial fibrillation, Adenosine, Verapamil, Digoxin are prescribed from this group of drugs, and Propafenone and Amiodarone are used to treat other types of arrhythmic pathologies. The drug Cordarone has proven itself to be excellent, helping in the treatment of arrhythmia for people with heart failure and post-infarction conditions.
Important!
Cardarone is contraindicated in bradycardia (when the heart rate is reduced to 50 beats per minute), pregnancy, bronchial asthma, heart block and thyroid disease.
Beta blockers.
The drugs Sotalol, Carvedilol, Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Celiprolol and Betaxolol are prescribed when a patient develops coronary heart disease, heart attack, or hypertension. They quickly normalize pressure in blood vessels, lower heart rate and prevent the development of heart failure.
Important!
Drugs of the beta-blocker group are contraindicated for bronchial asthma and disorders of the respiratory function of the body.
Anticoagulants.
For a prolonged period of arrhythmic disorder (several weeks), drugs are prescribed that thin the blood and prevent the formation of blood clots in the atrium - Heparin, Enoxparin and for continuous use - Warfarin.
Metabolites.
This group of drugs increases the nutrition of the heart fibers, prevents pathology that provokes coronary artery disease and helps improve metabolism. Thiotriazolin, Riboxin, Cocarboxylase, Mildronate, Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and magnesium and potassium preparations are mainly prescribed. Metabolites normalize the conduction of impulses and restore heart function.
In cases where drug treatment does not bring positive results, radiofrequency ablation may be necessary.
During the operation, a small area of heart tissue is cauterized, stimulating impulses that cause heart block.
After this, to maintain a normal heartbeat, the patient is given a pacemaker. Doctors can also offer radiofrequency isolation of the pulmonary veins
. This operation eliminates the focus of increased excitation of the heart, and since this focus is located in the pulmonary veins, its isolation from the atrium reduces the development of arrhythmia by 60%.
To prevent the development of arrhythmic diseases, you should undergo regular examination by a cardiologist.
Treatment of heart defects
Drug treatment for heart defects is generally not considered effective. Therefore, therapy is aimed at antibacterial treatment for acute rheumatism, eliminating the manifestations of chronic rheumatic heart disease, heart failure and other severe complications. The only correct way to treat heart defects today is surgery.
Surgical methods for treating heart defects:
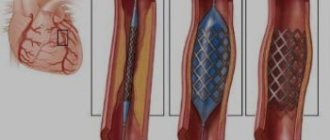
- valve replacement - in case of severe valve insufficiency and severe stenosis, the defective valve is replaced with an artificial one (there are mechanical and biological prosthetic heart valves);
- implantation of several prosthetic heart valves - for combined and combined defects;
- closing the atrial/ventricular septal defect - applying a suture or patch made of artificial material;
- ligation of the patent ductus arteriosus;
- X-ray surgery, transcatheter operations on the beating heart (closure of septal defects with Amplatzer, transcatheter implantation of the aortic valve - TAVI, application of a clip to the mitral valve leaflets in case of severe mitral valve insufficiency, closure of the patent ductus arteriosus, etc.).
In our clinic you can undergo diagnosis and treatment of heart defects. Our cardiologists are also knowledgeable in the outpatient management of patients with heart defects and in the outpatient management of patients with prosthetic heart valves.
Everything necessary for high-precision diagnosis of heart defects and other diseases of the heart and blood vessels is at the disposal of the cardiology department of the MedicCity clinic. You can undergo a full examination of the heart and blood vessels - ECG, ultrasound of the heart, bicycle ergometry, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring and ECG on a 12-channel holter at a convenient time by appointment.
Our clinic staff consists of only experienced specialists with serious scientific training and many years of medical practice!
Diagnosis of heart defects
After talking with the patient, collecting complaints and physical examination, the cardiologist prescribes laboratory and hardware tests.
Methods for diagnosing heart defects:
- biochemical and clinical blood tests;
- electrocardiography (ECG);
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring;
- Ultrasound of the heart (ECHO-CG);
- chest x-ray;
- MSCT or MRI of the heart and large vessels;
- Transesophageal ECHO-CG.
Most of the listed diagnostic methods are also used to determine indications for surgical treatment of heart defects.
Symptoms of heart defects
The manifestations of the disease depend entirely on the severity of the lesion.
Thus, mild congenital and acquired defects in the early stages of development can occur unnoticed and have no effect on well-being. However, it should be remembered that severe congenital heart defects often affect the appearance, physical development and resistance of the body. Therefore, blueness or pallor of the skin, low height and weight, as well as a tendency to frequent colds may themselves be symptoms of the disease.
With acquired and congenital defects of moderate severity, obvious symptoms of heart failure appear (shortness of breath during exercise, swelling of the legs), dizziness, tachycardia, weakness, and fatigue.
Severe congenital (for example, blue heart disease) and acquired (valve insufficiency in combination with aortic stenosis) heart defects may be accompanied by symptoms of acute heart failure (asphyxia, pulmonary edema).
Common symptoms of heart disease:
- dyspnea;
- arrhythmia (usually tachycardia);
- cyanosis of the skin (blueness) or pallor;
- dizziness, weakness;
- swelling of the veins of the neck and head;
- decreased blood pressure;
- fainting.
1 Diagnosis of heart defects
2 Diagnosis of heart defects
3 Stress test for heart defects
Causes of heart defects
Causes of congenital defects (CHD):
- chromosomal and genetic abnormalities;
- infections suffered during pregnancy (for example, rubella, etc.);
- maternal alcoholism and drug addiction;
- side effects of medications;
- irradiation.
Causes of acquired defects:
- infectious, rheumatic endocarditis (rheumatic heart defects, chronic rheumatic heart disease, infective endocarditis - usually insufficiency of the aortic, mitral and tricuspid valves);
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- heart injuries;
- sepsis;
- infectious diseases (especially syphilis);
- oncology.
Risk factors for developing heart defects
- hereditary predisposition (CHD);
- complications during pregnancy (CHP);
- taking medications (toxic to the fetus) during pregnancy (CHD).
1 Laboratory diagnostics for heart defects: tests
2 VEM for heart defects
3 ECHO-kg for heart defects
Types of heart defects
In most cases, heart defects affect the valve apparatus. Complications that arise as a result of this pathology can cause early disability and even death.
The main role of the valve apparatus is to freely pass blood through itself when the heart contracts and to delay the reverse movement of blood through the valve when relaxing, maintaining a rhythmic and continuous flow of blood. Defective valves cease to fully perform this work and function, which is why blood hardly flows through the narrowed valve into the cavity of the heart and does not fully leave the chambers or flows back through a closed valve.
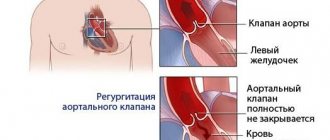
Acquired heart defects:
- valve insufficiency (incomplete closure of the valves or damage to the valves) - causes reverse blood flow;
- valve stenosis (narrowing of the lumen between the open valves) - complicates blood circulation;
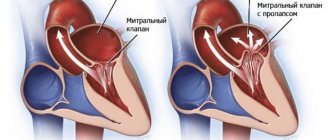
- prolapse (bulging) of the valve, as a result of which its leaflets bulge into the heart cavity, and often reverse blood flow occurs due to insufficient closure of the valve.
In cardiological practice, combined and associated defects are often encountered, in which several valves are affected at once.
Most often, the mitral (mitral heart disease) and aortic (aortic heart disease) heart valves suffer from abnormal changes.
Congenital heart defects:
- atrial septal defect;
- ventricular septal defect;
- patent ductus arteriosus;
- transposition (violation of position) of large great vessels;
- coarctation of the aorta;
- pulmonary stenosis, etc.
Congenital heart defects can occur either individually or in combination with each other. Thus, the combination of right ventricular hypertrophy, transposition of the aorta, ventricular septal defect and stenosis of the right ventricular outflow tract is called tetralogy of Fallot (or blue heart disease).
1 X-ray for heart defects
2 Diagnosis of heart defects using x-rays
3 Ultrasound for heart defects
What does a cardiogram show?
June 08, 2009
Myocardial infarction, angina pectoris. atherosclerosis, rheumatic carditis, hypertension - all these are heart diseases. They can occur as a result of any hereditary factors, excessive stress, anxiety, physical trauma, emotional distress, and so on. Another common cause of heart disease is poor diet. However, this is not about that now. The medical board of tiensmed.ru would like to draw your attention to the cardiogram . It is with its help that these pathologies are identified in people.
So what exactly can you see with a cardiogram?
Undoubtedly, this question torments many of you.
If we compare all the other analyzes and tests that people are exposed to every day, then the electrocardiogram is considered to be “a miracle of modern technology.” Why a miracle? Yes, because this is almost the only analysis that does not bring any inconvenience, no pain, and no radiation to a person. The person actually positions his body quite comfortably on the couch, after which electrodes with wires are attached to his wrists, ankles and chest. These wires are connected to a small device, from which a paper tape with the same cardiogram subsequently comes out. Quite a large number of people claim that this tape is the “secret place” of their hearts.
A cardiogram can indeed be called a “cache,” but it does not store all the information about a person’s heart, but only a separate part of it. This part includes: heart rate, condition of the heart muscle, general condition of the heart. This, of course, is not all that a cardiogram can “tell” about. However, these three points are the most important. Let's look at each of them in more detail.
The most accurate measurement of a cardiogram is heart rate. In another way, this frequency can also be called electrical activity or rhythm. A cardiogram accurately determines what rhythm the heart beats, whether a person has a rapid heartbeat or, in some cases, it is completely absent. This occurs due to the fact that electrodes attached to the human body pick up weak electrical signals, and the cardiogram, in turn, amplifies them.
Another less accurate measurement of the cardiogram is the condition of the heart muscle. It should be noted that any injured, dying or already dead tissue almost always has its own special effect on the passage of electrical signals through it. That is why, when deciphering a cardiogram, every cardiologist will be able to notice the possible likelihood of a heart attack in his patient. the location of the damaged heart muscle, a piece of dead tissue with a scar on it, and so on. With regard to this measurement of the cardiogram, any deviations regarding the general condition of the heart muscle must be confirmed by further studies.
And finally, the third less accurate measurement of the cardiogram is the general condition of the person’s heart. In this case, the cardiogram will be able to show any deviations only if the cardiogram is taken at the time of intense physical activity of the patient. In any other case, most likely, it will be normal. The fact is that as long as blood flows through the coronary artery, the cardiogram will not be able to reveal any general disturbances in the general condition of the heart.
So, to summarize, tiensmed.ru would like to draw your attention to the fact that medical specialists quite seriously recommend regularly performing an exercise cardiogram for people suffering from hypertension, smokers, and people with high cholesterol. as well as some other groups of people.
Don't forget, everything needs to be done on time. If you neglect your health, you can say goodbye to it forever. Get treatment and be healthy!
Before use, you should consult a specialist.
Author: Pashkov M.K.
Content Project Coordinator.