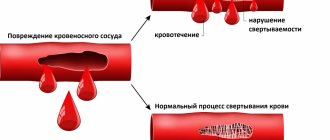
Complexes with this research
For those at risk of COVID-19 Diagnosis of diseases complicating the course of coronavirus infection 4,620 ₽ Composition
Preventive check-up Universal annual preventive screening 6,300 ₽ Composition
Male check-up No. 1 39 studies for annual preventive examination 18,920 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUB 29,710
- Vegetarians and vegans 5,890 RUR
- Biochemistry of blood. 19 indicators 6,430 ₽
- Biochemistry of blood. 13 indicators 4,110 ₽
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 12,280
Analysis procedure
What to pay attention to before taking the test?
No special patient preparation is required.
The research material is blood. Blood sampling is performed strictly on an empty stomach.
Some medications may affect test results. Tell your doctor about the medications you take. You should not cancel treatment on your own.
What happens during an albumin blood test?
The healthcare professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a small needle. Once the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected in a tube or vial. You may feel a slight tingling sensation as the needle is inserted or withdrawn. The procedure takes less than five minutes.
Are there any risks to the test?
The risk of having a blood test is very low. There may be some mild pain or bruising where the needle was inserted, but most symptoms go away quickly.
Detailed description of the study
Albumin is a blood plasma protein that, by mass, occupies more than half of all plasma proteins. It performs a number of important physiological functions:
- Maintaining physical and chemical blood parameters: viscosity, pH, oncotic pressure;
- Regulation of circulating blood volume and its balance with intercellular fluid;
- Transport of certain hormones, drugs, fats and their complexes;
- Calcium binding and participation in its metabolism;
- Protein reserve: if there is not enough protein in food, albumin can become its source.
Albumin is synthesized in the liver under the influence of thyroid hormones and growth factors, and is excreted by the kidneys. If too little of it is produced in the liver or if it is excessively excreted in the urine, its plasma concentration decreases. This condition is called hypoalbuminemia.
The causes of low albumin levels can be acute and chronic liver diseases, which affects its synthetic function, kidney pathologies, and insufficient protein intake from food. Hypoalbuminemia can be a manifestation of hormonal diseases, intestinal pathologies and cancer. Regardless of the cause, a decrease in plasma albumin levels manifests itself externally as edema.
Physiologically, this is reflected in the properties of blood and transport functions. For example, the content of free molecules of drugs taken in the blood will increase. This may increase their side effects.
Increases in plasma albumin levels are rare: with dehydration or recent intravenous protein administration.
In what cases does a doctor prescribe a test?
Your doctor will order albumin tests for:
- assessing liver disease progression;
- diagnosis of liver cirrhosis and evaluation of therapy;
- differential diagnosis of edema.
This test may be needed if the patient has symptoms of liver or kidney disease.
Symptoms of liver disease include:
- jaundice – this condition causes the skin and eyes to become yellow;
- fatigue;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite;
- dark colored urine;
- pale stool.
Symptoms of kidney disease include:
- swelling in the abdomen, thighs or face;
- more frequent urination, especially at night;
- foamy, bloody, or coffee-colored urine;
- nausea;
- itchy skin.
When should you take an Albumin test?
- Diagnosis of liver diseases with impaired synthetic function;
- Assessment of the severity of liver cirrhosis (Child-Pugh scale);
- Detection of kidney pathologies;
- Irrational diet, insufficient consumption of protein foods, fasting (assessment of nutritional status);
- Malabsorption of proteins in the intestine: short bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease;
- Identifying the cause of local or widespread edema;
- Condition after burns, to assess albumin loss;
- Infectious, rheumatological, oncological and endocrine diseases that may be associated with hypoalbuminemia.
Albumin price, where to buy
You can buy Albumin in Moscow in many pharmacies. The price of Albumin 10% 100 ml ranges from 1317-1590 rubles, and the drug 20% 100 ml from 3099-4042 rubles. Egg albumin, used in the food industry, is produced in bags of 5-20 kg, and is also sold by weight in specialized stores.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Albumin human solution for inf.
20% fl. 50mlBaxter AG RUB 2,129 order - Albumin human solution for inf. 20% fl. 100mlBaxter AG
RUR 3,935 order
- Uman albumin solution for inf. 25% fl. 50 ml No. 1Vetter Pharma-Fertigung GmbH and Co. KG
RUB 2,946 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Albumin (vial 10% 100ml) Microgen Tomsk (Virion)
RUR 1,984 order
- Albumin (flask 20% 50ml)Baxter Oncology
2170 rub. order
- Albumin (flask 20% 100ml) Microgen (ImBio N.-Novgorod)
RUR 3,791 order
- Albumin (vial 20% 100ml)Baxter Oncology
RUR 4,208 order
- Albumin (flask 20% 50ml)Baxter AG
RUB 2,141 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Hematovit with albumin and dried apricots 40 g TOV Vitapak, Dnipropetrovsk
9 UAH order - Albumin-Biopharma 20% 50 ml solution TOV "Biopharma Plasma" , Ukraine
981 UAH order
- Hematovit with albumin and coconut flakes 40g TOV Vitapak, Dnipropetrovsk
9 UAH order
- Albumin-Biopharma 10% 100ml solution for infusion TOV "Biopharma Plasma" , Ukraine
1044 UAH order
- Hematogenium classic with albumin 50g TOV "RIF", Ukraine
7 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Albumin infusion Albumin solution 20% 100ml Ukraine, Biopharma Plasma LLC
1810 UAH order
- Albumin infusion Albumin solution 20% 50ml Ukraine, Biopharma Plasma LLC
1245 UAH. order
- Albumin infusion Albumin solution 10% 100ml Ukraine, Biopharma Plasma LLC
1013 UAH. order
show more
Total protein
To assess the total amount of albumin and globulins, total protein is determined. For newborns, its norm is 46–68 g/l, for babies under one year of age – from 48 to 76, for older ones – no higher than 80. The norm for adults ranges from 65 to 85 g/l. This test is usually performed by examining serum. An absolute increase in concentration is rare and is a sign of myeloma, polyarthritis, cirrhosis or hepatitis.
A biochemical blood test shows that a relative increase in protein is observed with burns, vomiting, diarrhea, nephritis, and peritonitis. A decrease indicates starvation, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, deterioration in the formation of proteins (including congenital disorders) or an increase in their breakdown. A physiological decrease in protein is recorded in women in the final trimester of pregnancy, with insufficient nutrition during breastfeeding.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Albumin is a plasma replacement drug that is obtained by fractionating blood, plasma and serum of donors. Its administration replenishes the lack of plasma albumin (a source of protein), maintains oncotic pressure, increases plasma volume (in some patients this effect lasts for several hours) and blood pressure, and has detoxification properties. Available in the form of 5%, 10% and 20% solutions. After filling, the vials are pasteurized at 600 C for 10 hours to avoid transmission of serum hepatitis. A 5% solution is iso-oncotic plasma, and a 20% solution is hyper-oncotic.
Pharmacokinetics
T1/2 is 19 days. Elimination by intracellular pathway involving lysosomal proteases . In healthy individuals, 10% of the administered solution is removed from the bloodstream in the first 2 hours. Severely ill patients lose significant amounts of protein, so the rate of release is difficult to predict.
Reference values for albumin in blood
Important! Standards may vary depending on the reagents and equipment used in each particular laboratory. That is why, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to use the standards adopted in the laboratory where the analysis was carried out. You also need to pay attention to the units of measurement.
Normal values of albumin in blood serum according to the independent laboratory Invitro:
| Age | Albumin (in blood), g/l |
| up to 6 months | Reference values for children under 6 months. not validated. |
| 6 months -14 years | 38-54 |
| 14-90 years | 35-52 |
| over 90 years old | 29-45 |
Helix laboratory standards:
| Age | Reference values |
| < 4 days | 28 - 44 g/l |
| 4 days - 14 years | 38 - 54 g/l |
| 14 – 18 years old | 32 - 45 g/l |
| > 18 years old | 35 - 52 g/l |
Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Important Notes
Material for research Capillary blood
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood. Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications)! According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible: in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
Contraindications
- increased sensitivity;
- severe heart failure ;
- hypervolemia;
- pulmonary edema;
- arterial hypertension;
- severe anemia ;
- thrombosis;
- ongoing bleeding.
It is prescribed with caution during pregnancy (only if the potential benefit to the pregnant woman outweighs the risk to the fetus), renal and heart failure, and hemorrhagic diathesis .
results
Patients were followed for 18 months or until refractory ascites, the need for a portosystemic shunt, liver transplantation, or death.
- The primary endpoint of overall survival at 18 months was achieved by 78% of the albumin group and 66% of the control group (P = 0.028).
- There was a significant improvement in the number of secondary events in the albumin group. This is a 45% reduction in days spent in hospital (19.4 days in the standard therapy group; P < 0.0001).
- Albumin use was significantly associated with a decrease in paracentesis (P < 0.0001), refractory ascites (P < 0.0001), spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (P < 0.0001), renal dysfunction (P < 0.0001), hepatorenal syndrome type 1 (P = 0.0039) and hepatic function. encephalopathy grades III and IV (P <0.0001).
- However, the incidence of bleeding from varicose veins did not differ between groups.
The researchers note that the mechanisms explaining the beneficial effects of albumin are not entirely clear. Albumin may have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- In the group of patients who were prescribed albumin, 2 patients had moderate allergic reactions, which resolved. One patient was diagnosed with pneumonia, another with disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Source:
International Liver Congress (ILC) 2021: Abstract LBO-08. Presented April 22, 2021.
conclusions
The amount of ALB is required to diagnose a number of diseases and select the optimal treatment tactics. It characterizes metabolism and overall health. In case of severe symptoms of kidney problems, this test is prescribed first. It can also be carried out as part of a comprehensive examination or after it, if deviations are identified and it is necessary to clarify their nature and cause. Interpretation of the results can only be carried out by a doctor; the test is not intended for self-diagnosis
. In some cases, deviations from the norm are possible in the absence of diseases.
Albumin food grade black
Soviet pharmaceutical factories began producing Hematogen in 1930. The taste of the drug is reminiscent of the famous “Iris” candy. According to the instructions, its composition contains black albumin mixed with condensed milk and sugar syrup. In nature, large amounts of this element are stored in egg whites, beef, and potatoes. The drug has a low price, so it is prescribed for the prevention of anemia. To increase the therapeutic effect of hematogen, its composition is enriched with iron sulfate.
Dietary albumin is obtained from the blood of cattle that have undergone defatting procedures. Polyphosphates are used to stabilize elements. The substance includes amino acids, carbohydrates and fats. The disadvantage of bovine protein is the high content of allergens in animal red blood cells. With prolonged use of the product, adults experience itching, swelling, and skin rashes. You can add medicine to your daily diet only on the recommendation of a doctor.
Albumin medicine
The drug is obtained from the blood plasma of humans and animals. The drug Albumin has gained popularity in serum form. A protein solution demonstrates great effectiveness in treating low blood pressure and eliminating various critical conditions - it is administered using a dropper. The rate of delivery of the medicine is determined by the condition and age of the patient. The drug in powder form is easily soluble in water. The medicine cannot be combined with other protein-based medications.
Albumin solution
The substance is a light brown or yellowish liquid. Albumin solution is obtained from human blood plasma, dividing it into fractions. The drug quickly increases blood pressure, restores blood circulation and plasma pressure. After administration of the solution, the amount of tissue fluid in the bloodstream increases, which leads to better absorption of drugs. The drug is administered intravenously every 10-12 hours.
Albumin tablets
This form of the drug has reduced effectiveness. Albumin tablets are used to treat anemia, anemia and as a means of stabilizing blood pressure in elderly patients. The reduced effectiveness of the tablets is due to the membrane resistance of red blood cells. Solid dosage medications are broken down by the duodenum by 50 percent. One tablet contains excipients to accelerate the absorption of the element.
- How to make a dog out of a balloon
- Badger fat - medicinal properties and contraindications for children and adults
- How to clean vessels - quickly at home. How to clean vessels using folk remedies at home, video
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Perftoran
Gelofusin
Poliglyukin
Stabizol
Ceruloplasmin
Refortan
Gemodez-N
Reopoliglyukin
Plasbumin 20 , Albumin 20% , Alburex , Zenalb-20 , Postab solution .
Indications for use
- burns;
- shock;
- hypoalbuminemia against the background of nutritional dystrophy, glomerulonephritis , liver cirrhosis , purulent processes, ulcerative colitis and gastrointestinal tumors ;
- therapeutic plasmapheresis ;
- replenishment of bcc ;
- cerebral edema;
- during operations under artificial circulation;
- preoperative hemodilution .