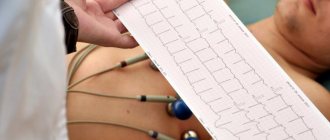
Indications for ECG
The referral for the procedure is given by a cardiologist
.
Many groups of people should undergo regular ECGs in order to detect diseases early. Risk factors for heart disease include:
- smoking;
- age over 40 years;
- obesity;
- increased cholesterol levels in the blood;
- poor nutrition;
- passive lifestyle;
- the presence of abnormalities in the structure of the heart;
- increased level of stress;
- diseases of the nervous or endocrine system;
- diagnosed vascular atherosclerosis.
- increased physical activity
An unscheduled ECG is recommended for the following symptoms:
- chest pain;
- palpitations and interruptions;
- shortness of breath;
- high blood pressure;
- chest injury;
- suspicion of acute and chronic heart disease (for example, with symptoms of coronary heart disease).
If you notice the above symptoms, do not worry right away. Many of them - for example, shortness of breath or high blood pressure - occur during stress and physical activity. It is necessary to monitor your own condition and the dynamics of symptoms. If signs of heart disease bother you even in the absence of exercise, or do not improve over a long period of time, you should consult a cardiologist.
for examination.
How to install electrodes on limbs?
For better memorization, you can use the traffic light rule. Place red on the right hand, yellow on the left hand, green on the left leg and black on the right leg. It is the last electrode that is grounding.
All placement is performed on the proximal part of the limbs. But, be sure to lubricate the place where the terminals are applied with gel. If there is no gel, you can take an isotonic solution or a gauze pad. If one of the limbs is missing, you need to install clamps on the stump. For better contact, you need to secure the terminals with rubber bands.
correct application of electrodes
Preparing for an ECG
The procedure does not require hospitalization. Performing an ECG
takes 10-15 minutes and, as a rule, is combined with an appointment with a cardiologist. Proper preparation for an ECG will help avoid false results and the need for repeated examination.
- On the eve of the procedure, the patient is advised to get enough sleep and rest, and try to avoid stress.
- You should not exercise before the procedure.
- It is not recommended to use greasy lotions and creams in the chest area before an ECG.
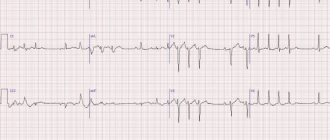
ECG of a sick heart
Electrocardiography
(abbr.
ECG
) - a technique for recording the electrical fields of heart activity, carried out in real time. The main diagnostic technique in modern cardiology. The procedure is carried out using a special device, an electrocardiograph, which reads data from electrodes attached to the body.
The first electrocardiogram was taken more than 100 years ago
. Despite the technical simplicity of the method, it remains informative, allowing for differential diagnosis of many cardiac pathologies. The result of the procedure is a recording of an electrocardiogram, where the nature of all recorded electrical impulses is indicated in chronological order.
Information content of the ECG
The function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body. This is a cavity muscular organ, which in a calm state contracts with an average frequency of 60–80 beats
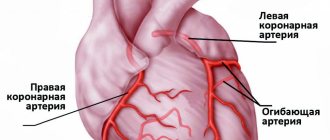
in a minute. Muscle contraction always occurs due to electrical impulses. Currents are generated directly inside the heart, in a special center, the sinoatrial node.
The nature of the impulse determines how complete the contraction will be. This is a rather complex mechanism, since anatomically the heart consists of 4 chambers and 4 valves. In the systolic phase, the muscles of the atria contract first, followed by the ventricles. The delay is a fraction of a second, but it plays a key role. Any deviations from the norm lead to various forms of circulatory failure.
What pathologies can an ECG detect:
- heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia, bradycardia, extrasystole, fibrillation);
- cardiac conduction disorders (bundle block, sinoatrial block, etc.);
- cardiac hypertrophy, increase in cardiac muscle mass;
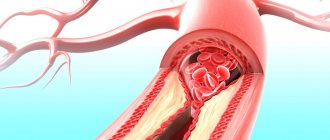
- focal coronary circulation disorders (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction);
- changes in the structure of heart tissue, scars, consequences of inflammation or thrombosis.
In what cases is it advisable to take an ECG:
- chest pain and other symptoms of heart pathologies;
- routine screening of healthy people, medical examinations, medical examinations;
- routine examination of patients with cardiovascular pathologies;
- when planning pregnancy, during preparation for operations.
Heart diseases can remain asymptomatic for a long time until the development of serious organic lesions that cannot be corrected. Therefore, it is recommended that every adult take an ECG at least once every 2 years.
, even in the absence of any complaints. And after 35–40 years - every year.
Preventive examinations are especially important if there is an unfavorable family history (relatives with severe cardiovascular pathologies), smoking and other bad habits, as well as a high level of stress. This applies mainly to men, since in women before menopause, serious cardiac pathologies develop relatively rarely.
Electrocardiography techniques
Classical
. It takes about 5–10 minutes, including preparation for the procedure and decoding of the received data. It is carried out in the doctor's office. The patient takes a horizontal position, several chest electrodes are attached to his body, as well as one each on the upper and lower extremities. The basic procedure that is performed most often.
Intraesophageal
. The reading electrode is placed inside the esophagus, as close to the heart as possible. This study is usually performed for the purpose of differential diagnosis of certain forms of cardiac conduction disorders. It can be carried out within a few minutes or throughout the day.
Load test
. A classic ECG, which is taken in two stages - at rest and after exercise (for example, squats, or exercise on an exercise bike or treadmill). An electrocardiogram can be taken both during physical activity and immediately after it.
According to Holter
. Daily ECG monitoring is a highly informative technique that allows you to assess the electrical activity of the heart in the normal state of the patient, when he is engaged in everyday activities. For this purpose, a small-sized portable electrocardiograph is attached to the body.
Preparing and taking an ECG
No special training required
. However, the day before, it is recommended to avoid the consumption of alcohol, tonic drinks (energy drinks, strong coffee or tea), and not to smoke 1–2 hours before the procedure. If you are constantly taking medications that affect cardiac conduction or rhythm, you should consult your doctor before taking an electrocardiogram. It is also advisable to refrain from intense physical activity and emotional stress. In general, the impact of negative factors that can temporarily distort ECG results should be minimized.
The classic version of the ECG is taken within a few minutes
. There are no contraindications to the procedure, since it is not associated with any effect on the body. The electrocardiograph only records received impulses from the heart, but does not itself produce any signals or radiation.
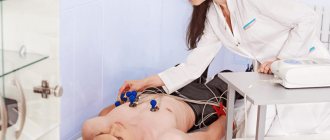
Carrying out the procedure
Before the procedure, the patient undresses to the waist and lies down on the couch. The doctor attaches electrodes or special suction cups to the patient's chest, after which the device turns on and the heart impulses are recorded on paper.
The resulting electrocardiogram includes teeth of different lengths and heights, which display cardiac impulses. The ECG is interpreted by a cardiologist. When deciphering, heart rate, contraction intervals and other indicators of heart function are assessed.
In the branches of the “My Clinic”
On
Gorokhovaya St., 14/26
(metro station Admiralteyskaya, Admiralteysky district) and on
Varshavskaya st., 59
(metro station Moskovskaya, Moskovsky district) there are cardiologists who will conduct a heart examination and draw up a treatment or prevention plan.
You can sign up for an examination by calling 493-03-03 or on our website. Make an appointment
Basic rules for electrode placement
To record an ECG, you need to install electrodes on special points on the body. This is the only way to correctly record the electrical impulses produced by the heart. It is the correct location of the terminal that ensures a clear recording of the cardiogram. Be sure to lubricate the ECG electrode with alcohol.
If the patient has a lot of body hair, then you need to treat the skin with a soap solution or shave the hair. For better electrical conductivity, you need to lubricate each electrode with gel. If you don’t have the gel at hand, you can take an isotonic solution or gauze pads. But if the study is long, then gauze pads cannot be used.
If stationary ECG devices are used, they must be grounded.
Electrodes are either single-use or reusable. The choice of electrodes depends on the preferences of the healthcare professional performing the ECG.
ecg how to do it correctly
How to do an ECG for women
ECGs are done for women in the same way as for men. The only peculiarity is that the girls take off their bra, since the impulse does not pass through the fabric of the bra. For the same reason, it is not advisable to wear tights or stockings.
Are there any special features during pregnancy?
There are no contraindications for ECG during pregnancy. This is the same stage of monitoring the health of the expectant mother as an ultrasound. That is why women should not refuse to perform such a study.
During pregnancy, the heart experiences increased stress. During pregnancy, an ECG is prescribed 2 times. In addition, an electrocardiogram is performed not only on the woman, but also on the fetus - this study is called CTG (cardiotocography).
During pregnancy, the following changes appear on the cardiogram:
- displacement of the electrical axis of the heart to the left;
- increased heart rate, single extrasystoles;
- negative T wave in the third and fourth leads;
- shortened PR interval;
- pathological Q wave in the third lead and aVF (right arm lead).
Decoding indicators
ECG is assessed according to several criteria:
- The rhythm is correct and regular. No extraordinary contractions (extrasystoles).
- Heart rate. Normally - 60–80 beats/min.
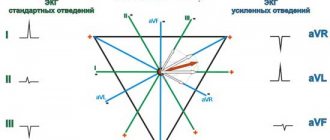
- Electrical axis - normally R exceeds S in all leads except aVR, V1 - V2, sometimes V3.
- Width of the ventricular QRS complex. Normally no more than 120 ms.
- QRST - complex.
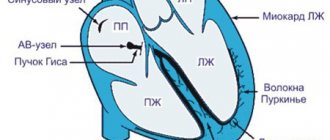
QRST - normal complex
Brief designation of the main elements of the film:
- P wave - shows atrial contraction;
- PQ interval is the time the impulse reaches the atrioventricular node;
- QRS complex - shows ventricular excitation;
- T wave - indicates depolarization (restoration of electrical potential).
Video about ECG norms from the Mass Medika channel.