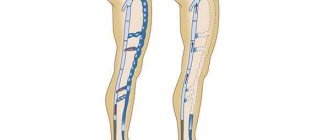
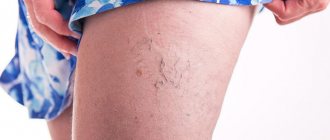
Varicose veins are a disease in which insufficiency of the valves of the veins occurs, which leads to their expansion and tortuosity. Most often, the vessels of the lower extremities are affected, resulting in a cosmetic defect and circulatory disorders. The most effective treatment method is surgery on the veins in the legs, which is highly effective and reduces the risk of relapse.
Surgeries on the veins of the lower extremities are performed at the Yusupov Hospital using minimally invasive and painless techniques.
Description of the disease
Varicose veins in the legs develop when the valves do not work effectively, obstructing the flow of blood. This leads to backflow of blood and congestion of blood vessels. Due to the heavy load of volume, the walls of the veins become thinner, lose their elasticity and, as a result, expand. Despite the fact that there is a lot of blood, its stagnation leads to the formation of clots, increased thrombus formation and lack of oxygen.
Among the causes of varicose veins, experts identify:
- Hereditary structural features of the connective tissue of the vein wall;
- Obesity;
- Hormonal imbalance (estrogens and progesterone can reduce the tone of the veins);
- Pregnancy (increased blood volume and compression of veins by the uterus);
- Lifestyle (poor nutrition, low physical activity, profession that involves standing for long periods of time).
Depending on the clinical manifestations, there are 4 stages of varicose veins of the lower extremities:
- Early stage. Manifested by heaviness in the legs, tingling sensation and swelling;
- Visible stage. Spider veins appear, the color of the skin in the affected area changes, there may be itching, eczema and trophic ulcers);
- Chronic;
- Chronic dysfunction (pronounced pain symptoms, leg cramps).
The main symptoms of varicose veins in the legs are as follows:
- Feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- Pain in the lower extremities;
- The appearance of a venous “pattern” of a bluish color;
- Swelling of the lower extremities in the evening;
- Redness of the lesion, the appearance of scratching and ulcers.
One of the most serious complications of the disease is the formation of blood clots. Therefore, when the first symptoms of varicose veins appear in the legs. symptoms, you should consult a doctor immediately. At the Yusupov Hospital, a phlebologist is a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins.
Preparing for treatment
Before surgery for varicose veins in the legs, patients should stop taking aspirin or aspirin-related medications for a week before the procedure. They should not eat or drink after midnight on the day of surgery. You should not apply any moisturizers or tanning lotions on the day of your procedure. The patient should arrive at the surgery center approximately one and a half hours before the procedure. He is asked to walk around the room or corridor for about 20 minutes so that the subcutaneous nodes appear. The surgeon marks the contours of varicose conglomerates with a marker. Ultrasound scanning is performed for preoperative marking.
Types of surgical operations
Treatment of varicose veins is carried out in several directions:
- Medication. The use of medications that improve vein walls;
- Surgical. It is performed if there are indications for surgery and allows you to completely eliminate the pathological focus.
The initial stages of the disease can be cured without invasive interventions, with the help of medications or compression bandages.
Indications for surgical treatment of varicose veins in the legs are:
- Severe pain, constant feeling of heaviness in the legs;
- Lack of effect from conservative therapy;
- Development of thrombophlebitis;
- Long-term non-healing ulcers in the affected area;
- High risk of thrombosis.
There are many types of operations on the veins of the lower extremities, but all of them are aimed at removing the affected area with minimal consequences. The most common types of surgical operations on the veins of the lower extremities include:
- Phlebectomy. The name of the operation comes from the Latin “phlebus”, which means vein, and “ectomy” is translated as removal, most often the method is used on veins in the legs. The essence of the manipulation is that the affected vessel is completely pulled out through an incision in the skin. A type of operation on veins in the legs is mini-phlebectomy, which is used for small areas of the lesion.
- Sclerotherapy is carried out using a special device that causes the vein to “stick together”, after which it grows together in the deep layers of the skin and does not function.
- Radiofrequency obliteration is a modern type of surgery for varicose veins of the lower extremities. This technique involves the use of high frequency radio waves.
- Laser endovascular coagulation involves the introduction of a probe with laser radiation, which causes a safe thermal burn of the vessel walls, their gluing and fusion.
Only a phlebologist can determine what kind of surgery is necessary for varicose veins, since any surgical interventions have contraindications. Surgical treatment of varicose veins is not performed if:
- Conditions that threaten the patient’s life (acute period of myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident);
- Acute infectious diseases;
- Pregnancy in the 2nd and 3rd trimester;
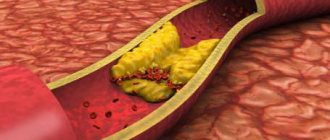
- Disorders of lymphatic drainage and atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities.
If there are contraindications, the doctor will choose another, more suitable method of treatment or type of surgery for varicose veins of the lower extremities.
How to spend the postoperative period
The postoperative period after phlebectomy on the legs lasts ten days: from the moment of the operation itself until the sutures are completely removed. At this time, the operated limb needs special attention and special care.
After the operation, the patient receives compression of the lower extremities using compression stockings. Compression is an important condition for the smooth course of the postoperative period, as it allows you to compress the saphenous veins, preventing stagnation of blood in them, and, accordingly, the formation of blood clots. Compression also accelerates the healing of small veins remaining after removal of the main venous trunk.
Places where stitches are placed should not be wet. For hygienic purposes in the postoperative period, wet wipes or gauze moistened with water are used. The sutures are regularly treated with iodine and a sterile bandage or sticker is applied to protect them from damage and contamination.
To reduce swelling of the lower extremities, it is recommended to keep them elevated - on a pillow, a fabric cushion up to 15 cm high. In case of intense pain after surgery, the doctor may prescribe painkillers, and antibiotics to prevent purulent complications.
Sclerotherapy
Sclerotherapy is a method of treating varicose veins of the lower extremities, in which a special substance is injected into the vessel, causing the walls to grow together. The effect of the drug is that the veins are replaced by connective tissue, that is, they become sclerotic. This manipulation is minimally invasive, does not require skin incisions and does not leave marks on the skin.
The essence of the procedure
Sclerotherapy of the veins of the lower extremities is carried out by a phlebologist, having previously established the exact localization of the pathological focus. In order to introduce the sclerosing agent, the specialist makes a puncture at the intended site of the lesion. To achieve the desired effect, 3 to 10 injections are required in one session. The number of injections depends on the stage and neglect of the process. On average, the operation lasts 15-20 minutes. If there is no effect after one session of the procedure, it can be repeated.
Sclerosis, or fusion, of the vein walls leads to its exclusion from the circulatory system. This does not harm the body; the blood flows through “spare” vessels.
Indications
Before choosing sclerosis of the veins of the lower extremities, the doctor prescribes a special examination to confirm the organic pathology of the veins.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing varicose veins:
- Occlusion plethysmography;
- Direct phlebotonometry;
- X-ray contrast venography;
- Ultrasound Dopplerography;
- USAS with color contrast of blood flow;
- Phleboscintigraphy.
After examination and test results, the doctor will determine whether there are indications for surgical treatment of varicose veins. Vein sclerotherapy is performed in the following cases:
- The appearance of trophic ulcers;
- Lesions of small vessels lying close to the surface of the skin;
- Prolonged pain in the legs;
- A pronounced cosmetic defect.
Sclerotherapy is also used as a treatment for other vascular pathologies such as hemorrhoids, lymphangiomas and hemangiomas.
Contraindications
Although sclerotherapy is a minimally invasive method, in some cases it can be dangerous to the patient’s health. The technique is never performed on patients with a proven allergy to sclerosant, with severe systemic and infectious diseases, as well as with thrombosis of superficial or deep veins.
Another method of treatment is indicated for lactating and pregnant women, since during pregnancy the blood volume increases and the load on the venous system also increases.
High obesity may interfere with the normal course of the procedure. Therefore, your doctor may recommend sclerotherapy after your weight has normalized.
Preparation for sclerosis of the veins of the lower extremities
Instrumental research methods are one of the main stages of sclerotherapy. After the doctor has established an accurate diagnosis and prescribed treatment, the patient must undergo standard tests:
- Coagulogram;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Hepatitis, HIV, syphilis.
Taking certain medications can affect the results, so if you are taking medication, you need to tell your doctor.
Drugs used for sclerotherapy
Substances used in sclerosis are divided into:
- Foam-like preparations are capable of remaining in the lumen of the vessel for a long time, provide good contact with the wall and are well visualized during ultrasound examination;
- Liquid - easily dissolves in the medium;
- Osmotic substances (sodium chloride) lead to dehydration and, subsequently, sclerosis;
- Detergents (Tamper) cause protein coagulation and blood clot formation;
- Corrosive substances (Ethoxysklerol) provoke specific reactions in the wall of the veins, which gives rise to the proliferation of connective tissue.
Types of procedure
In modern medicine, the following types of sclerotherapy are distinguished:
- Catheter scleroobliteration. The essence of the procedure is that the sclerosing agent is supplied via a catheter and allows the simultaneous insertion of a special bandage. This manipulation is only possible on veins with a diameter of up to 1 cm. This procedure is an alternative to a more invasive intervention - stripping. There are two options for catheter scleroobliteration: intraoperative and puncture. The first is one of the stages of phlebectomy. The puncture is performed without an incision and does not create a cosmetic defect. The disadvantage of the technique is that it is not reliable enough and there is a risk of relapse.
- Compression sclerotherapy of the veins of the lower extremities can be performed at the request of the patient for cosmetic defects in the form of spider veins and venous networks. Microsclerotherapy is effective in cases of damage to small-caliber vessels with a diameter of 1-3 mm. In this case, the drug is administered using special, small syringes with thin needles; no anesthesia is required. Immediately after the injection, skin redness and swelling develop, the full effect occurs on average after 1.5 months. After the sclerosing agent is introduced, a special bandage in the form of an elastic bandage is applied. This allows you to maintain the desired shape of the vessel.
- Echo sclerotherapy is used to harden deep veins. The difference between the technique is that the entire process from the injection to the application of the bandage takes place under the control of an ultrasound machine. To do this, the doctor places the sensor directly at the site of manipulation.
- Microfoam sclerotherapy involves the use of a sclerosing agent in the form of foam. Microfoam gives a good shadow on an ultrasound machine, which allows the specialist to fully control the process and the correctness of drug administration. The foam is able to establish tight contact with the wall of the vessel, which will provide a longer and more reliable effect.
All types of sclerotherapy can be combined. The use of the drug in the form of microfoam will increase the effectiveness of any method.
Advantages and disadvantages of sclerotherapy for veins of the lower extremities
The benefits of sclerotherapy of leg veins include:
- Affordable price;
- Short rehabilitation period;
- No skin trauma;
- Does not leave scars;
- Painless;
- Long lasting results.
The main disadvantage of the technique is its low versatility. Sclerosis as monotherapy is used only in the early stages of the disease. In addition, there is a high risk of relapse if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed.
Possible complications
Sclerosis can cause early and late adverse reactions. The early ones include:
- Pain, burning and itching at the injection site;
- Due to stress, predisposed people may develop dizziness, palpitations, and sweating;
- Bruises and bruises usually resolve within 3-4 days after manipulation;
- Allergic reactions to the drug (feeling of suffocation, Quincke's edema);
- Damage to nerve elements is rare and is associated with incorrect choice of injection site.
Late complications include:
- Thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of the vein wall. This is usually a reversible reaction of the vein in response to the injection of sclerositis;
- Formation of a cord at the site of a sclerotic vein. There is no threat, but sometimes it is a painful formation that can contour through the skin.
If you follow all the rules of the sclerotherapy technique, the risk of developing adverse reactions is minimal. Sclerosis of leg veins in Moscow can be done at the Yusupov Hospital. We have access to all modern methods for treating varicose veins. Modern technologies and high-end equipment make it possible to visualize even minimal changes in blood vessels. Prices and reviews for sclerotherapy of veins in the lower extremities in Moscow can be found on our website.
Observation after treatment
Regular classic phlebectomy is rarely needed by patients, as it usually requires an overnight stay in the hospital and 2 to 8 weeks at home. After vein removal in the lower extremities in our center, the patient is allowed to exercise, but should not drive a car for at least a day, since distal motor function may be impaired due to prolonged anesthesia, especially after anesthesia in the popliteal region. The patient is advised to walk for about 10-15 minutes before leaving the clinic.
In the future, you will need to take diosmin medications (detralex); it is not recommended to stand in one place for a long time for 2 weeks. This helps minimize the risk of blood clots forming in the deep veins of the leg. A compression bandage prevents post-operative bleeding and reduces the likelihood of pain, bruising and other complications. The bandages are removed 3-7 days after surgery, but the compression stocking should be worn for an additional 2-4 weeks to minimize bruising and swelling. The wearing time depends on the size of the veins removed and the degree of reflux treatment. Stockings can be removed when taking a shower.
Additional sclerotherapy should be postponed for several weeks and done after the postoperative swelling has disappeared. Many spider veins can spontaneously regress and also disappear spontaneously after the varicose veins are removed through outpatient phlebectomy. Patients should avoid early sun exposure because hyperpigmentation may appear at the puncture or incision site.
The patient is advised to monitor for redness, swelling, suppuration, fever and other signs of infection. If these signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation has replaced old surgical interventions for varicose veins of the lower extremities as another method. This type of intervention is a new technique that is characterized by low tissue trauma and high efficiency. The effectiveness of the method is confirmed by patient reviews after radiofrequency ablation of the veins of the lower extremities.
Stages of radiofrequency ablation of veins
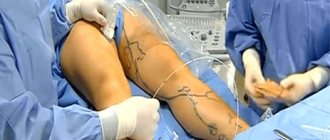
The preparation period before radiofrequency ablation of veins does not take much time. First, the patient undergoes an examination, which includes standard tests, an examination by a specialist and an ultrasound duplex scan with color mapping of blood flow. Using an ultrasound, the doctor evaluates the course and diameter of the vein, the characteristics of its anastomosis and the presence of varixes. On the eve of the procedure, the patient is advised to stop taking medications. Sometimes, in order to prevent blood clots, the doctor may prescribe aspirin for a month after RFA of the veins of the lower extremities.
When the site of varicose veins is identified, the patient takes the required position. You need to lie on your stomach or back, it depends on the location of the affected area. The intervention area is marked and treated with an antiseptic. Then pain sensitivity is eliminated by injecting an anesthetic.
The introduction of the waveguide, which is equipped with a special device for exposure to radio waves, is carried out through a skin puncture. In the middle of the waveguide there is a thermal capsule that supplies radio waves. The doctor regulates the impacts of radio waves on the device’s monitor, and the progress of the procedure is also displayed there. Gradually, the waveguide passes through the entire varicose vein, destroying it. Radiofrequency obliteration of the veins of the lower extremities leads to occlusion of the vessel, and healthy people do the work instead.
At the end of RFA, the puncture area is treated with an antiseptic, and a compression bandage is applied.
Side effects of RFO of the veins of the lower extremities
For two weeks after surgery, patients may experience:
- Low-grade fever;
- Soreness, a feeling of tension along the vein;
- Swelling and bruising at the puncture site;
- Peeling and redness of the skin.
These reactions are normal, but only if their duration is no more than 14 days. Severe, shooting pain and swelling of the leg can be a sign of thrombosis and requires immediate medical attention.
Difference between RFO and EVLO
When choosing a method for treating varicose veins of the lower extremities, many people wonder what is better and what is the difference between RFA of veins and EVLO. The similarity of the methodology is almost the same. In both, exposure to radio frequencies is used, with EVLO these are short-term discharges of a higher temperature. It should be remembered that both techniques do not leave marks or scars and are practically painless. Reviews of patients after RFO or RFA of the veins of the lower extremities are posted on the website of our clinic.
The final choice should be made by the doctor based on the general condition of the patient, since radiofrequency ablation can increase thrombus formation.
Recovery period after RFA
Radiofrequency catheter ablation allows the patient to return to their previous rhythm of life within 1.5-2 hours after surgery. The exception is people whose work involves heavy physical labor. After the intervention, you will need to wear compression stockings for the first 24 hours, then only during the daytime for about 3 days. On days 3-4, control ultrasound diagnostics are performed. The duration of compression depends on the degree and extent of the process.
After surgery, it is recommended to reduce your time on your feet to 4 hours. For the first month, you cannot visit saunas, steam baths, lift weights, jump or run long distances.
Cost of radiofrequency vein ablation
The price of radiofrequency ablation of the veins of the lower extremities depends on the qualifications of the doctor, the neglect of the process and the equipment of the phlebological center. At the Yusupov Hospital, RFO of the veins of the lower extremities is performed by doctors with many years of experience at an affordable price using modern equipment.
Rehabilitation period
After radiofrequency obliteration, it is necessary to use a special bandage for 5 days, sometimes the period is extended to several weeks. For the first couple of days, you should refrain from heavy physical activity, such as running, jumping, and lifting weights. You should avoid visiting saunas and baths for another two months. The maximum cosmetic effect occurs 3 months after surgery.
Under local anesthesia
The operation to remove veins for varicose veins is performed under local anesthesia, which allows you to fully numb the surgical field with a weak solution of local anesthetic - novocaine or lidocaine. The result of surgery should be the elimination of varicose veins with an excellent aesthetic result. The meaning of aesthetic phlebectomy is to remove varicose veins through punctures, but not skin incisions under local anesthesia. Only subtle scars remain, which are practically invisible after 3-6 months. Phlebologists at the Innovative Vascular Center have mastered this technique to perfection.
Laser endovasal coagulation
Endovenous laser coagulation (EVLC, EVLO) is a modern method of treating varicose veins of the lower extremities, which uses laser exposure. This method of eliminating varicose veins avoids invasive interventions, leaves no scars and is practically painless. However, the procedure is possible if the vein diameter is no more than 1 cm and there is no strong tortuosity.
The essence of the procedure
A doctor may prescribe laser treatment for varicose veins in the legs if characteristic symptoms of this disease appear. There is no need to be afraid of EVLT of the veins of the lower extremities, because thanks to the invention of the modern laser, incisions in the skin are not needed to access the vein, and patient reviews can confirm this. At the Yusupov Hospital, a phlebologist, after examining a patient, draws up a phlebological chart, which implies a detailed description of the affected vein, its diameter, course and the presence of tortuosity. Thanks to this, the laser is directed only to the affected area, while healthy tissue remains untouched.
After the doctor directs the device, laser beams penetrate the walls of the vein and cause a thermal burn. Next, the burn is provoked by the proliferation of connective tissue, a dense cord is formed in place of the varicose vein. Over time, this cord completely dissolves. Disabling a vein from the bloodstream does not harm health; the blood flows through collateral vessels.
Constant improvement in the use of laser as a treatment allows us to avoid many complications and makes it completely safe. At the Yusupov Hospital, laser endovasal coagulation is performed using the latest devices under the supervision of an experienced specialist, which eliminates the risk of adverse reactions.
Stages of endovenous laser obliteration
Laser vein surgery on the legs does not require special preparation. As a rule, to examine a vein, ultrasound with Dopplerography and standard studies are sufficient:
- Biochemical and general blood test;
- Coagulogram;
- Blood markers for hepatitis virus, HIV and syphilis;
- Electrocardiogram.
Then, directly during laser surgery on the veins in the legs, the doctor, under ultrasound control, marks with a marker the area to be laser obliterated. Then anesthesia is performed; for this, the phlebologist injects an anesthetic drug into the surgical site. The anesthetic injection is the most painful stage of the manipulation.
A catheter is inserted in the same place; it is a tube of very thin diameter. Its implementation is not noticeable, since the skin has already been anesthetized. First, another anesthetic is injected through the catheter to completely eliminate pain, and then the laser LED itself is injected. This anesthesia is called tumescent anesthesia - several types of drugs are used simultaneously. The combined solution contains lidocaine, adrenaline and saline. This infiltration not only provides anesthesia, but also protects surrounding tissues from burns.
The next stage is the actual exposure to laser and EVLO. Flashes of light cause the blood to boil at ultra-high temperatures, and a catheter is used to remove clots and sclerotic tissue. After laser surgery on the legs, a compression bandage is applied to the varicose veins. In general, the procedure lasts about an hour.
Advantages and disadvantages of EVLO
The advantages of endovenous laser coagulation for varicose veins of the lower extremities are:
- Painless;
- No need for general anesthesia;
- Short rehabilitation period, 2 hours after the procedure the patient can return to their previous lifestyle;
- Low trauma, healthy tissues are not affected;
- No cosmetic defect.
The main disadvantage of EVLO for varicose veins is the cost. Laser manipulation requires special, expensive equipment, which reduces the availability of the method.
Reviews from patients after laser surgery on the legs for varicose veins are overwhelmingly positive. Since this allows you to get rid of pain and cosmetic defects in a short time.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for laser coagulation of varicose veins include the main symptoms of the disease with a vein diameter of up to 10 mm.
Endovasal laser coagulation of the veins of the lower extremities is contraindicated in the following patient conditions:
- Acute infectious diseases;
- Exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the extremities impedes blood circulation, and shutting off the veins can aggravate trophic disorders. In this case, pre-treatment of cholesterol plaque deposits will be required;
- Acute period of heart attack, stroke and general serious condition;
- Pregnancy and lactation;
- Obesity III degree;
- Severe systemic connective tissue diseases;
- Musculoskeletal disorders;
- Frequent thrombosis and thrombophlebitis;
- The presence of inflammation or allergic reactions directly at the intended site of surgery.
Laser surgery for varicose veins can be performed before planning pregnancy if the symptoms of varicose veins are severe.
Possible complications after laser vein surgery
After endovenous laser vein obliteration, general symptoms of malaise may occur, which are not dangerous and disappear within a few days. These include:
- Constant increase in temperature within 37.5-38.0°;
- Pain and feeling of tension at the intervention site;
- Bruises and bruises.
Thrombophlebitis is a serious complication. You can suspect it if the following signs appear:
- Severe pain in the limb;
- Temperature above 38.0°;
- Swelling of the leg.
The development of thrombophlebitis is possible a week after laser obliteration of the veins of the lower extremities. This condition develops very rarely and it is impossible to predict its development, since it depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. Reviews from our patients about endovasal laser coagulation of the veins of the lower extremities indicate the positive effect of the procedure and the absence of complications.
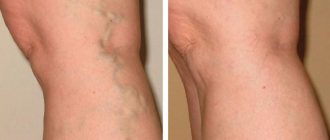
Removal of varicose veins in 3 hours, results for life!
Treatment results for our patients
Disease: varicose veins
Treatment method: EVLT + MINIFLEBECTOMY
Combined treatment of varicose veins. Endovasal laser obliteration of the vein on the left leg (EVL) + Miniphlebectomy
Disease: varicose veins
Treatment method: EVLT + MINIFLEBECTOMY
Laser treatment (EVLT) followed by miniphlebectomy of the tributaries of the great saphenous vein on the thigh and shin of the right leg. Miniphlebectomy of varicose veins.
Disease: Telangiectasia
Treatment method: Foam sclerotherapy
To remove the stars, the patient underwent a session of microfoam sclerotherapy (Foam-Form) of the reticular veins under the control of laser transillumination.
Disease: varicose veins
Treatment method: EVLT + MINIFLEBECTOMY
Upon examination of the patient, varicose veins were diagnosed on the right leg. Combined treatment with EVLT + miniphlebectomy was performed.
Phlebectomy
Phlebectomy is an operation to remove a vein to reduce the symptoms of varicose veins and eliminate a cosmetic defect. This intervention is considered one of the most radical methods of treating varicose veins and is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor.
Indications for phlebectomy
Since vein removal is a radical method of treating varicose veins, there are certain indications for its implementation. These include:
- Relapses of the disease after less invasive operations (RFA, EVLO);
- Late stage of varicose veins;
- Development or risk of trophic ulcers;
- The diameter of the veins is more than 1 cm, severe tortuosity and the presence of nodes;
- Thrombophlebitis.
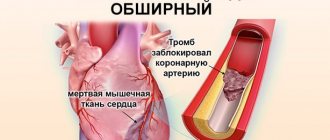
In most cases, surgery to remove leg veins is performed routinely after preliminary preparation. In emergency situations, if thrombosis develops, immediate venectomy may be necessary.
Preparation for the procedure
Before proceeding with the operation, the phlebologist will prescribe a series of studies to establish the location of the lesion, as well as the possible risk of complications. To do this you will need:
- Testing for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Blood clotting test;
- Fluorography;
- Cardiogram;
- General blood analysis;
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor;
- Duplex ultrasound examination of veins with color mapping.
Before surgery, consultation with an anesthesiologist is required to choose the appropriate method of pain relief. There are two options for the latter - general anesthesia and spinal anesthesia. The operation is performed on an empty stomach; you cannot eat 18 hours before the venectomy. Next, you need to prepare the immediate site of intervention, namely take a shower, shave the hair from the limb and in the groin area. You should purchase compression garments in advance; your doctor will help you choose them.
Types of phlebectomy
There are four main types of vein removal:
- Combined;
- Laser coagulation;
- Radiofrequency ablation;
- Sclerotherapy.
The last three techniques are modern and minimally invasive methods and are performed more often compared to traditional combined venectomy.
Classic phlebectomy of the veins of the lower extremities includes several stages:
- The Troyanov-Trendelenburg operation, or crossectomy, in some cases is an independent operation and is aimed at preventing the spread of a blood clot. In this case, the surgeon makes an incision in the groin area or under the knee, isolates the desired vein, ligates it, and then crosses it.
- The Babcock operation or stripping involves removing a vein using a special probe with a metal cone. A more gentle type of technique is PIN stripping, with the help of which the probe is attached to the wall of the vessel and the vein is removed. Cryostripping is rarely performed due to the need for expensive equipment and is performed using ultra-low temperatures.
- The Narat technique is aimed at preventing blood from entering the superficial vessels. To do this, the perforating vessels are ligated after isolating the saphenous veins.
- The Varadi operation or microphlebectomy can act as a separate manipulation. In this case, punctures are made in the skin through which small sections of veins are removed.
The use of traditional venectomy is advisable only when indicated; in other cases, less radical operations are preferred.
Postoperative period and possible complications
After the operation, the hospital stay takes about 7 days. The very next day you need to put on compression stockings and wear them around the clock for a month. The first couple of days there may be pain along the vein; for this, the doctor prescribes painkillers. To prevent thrombosis, drugs that reduce blood clotting are prescribed.
Sutures remain at the incision site, which are removed 6 or 7 days after the venectomy. After discharge, you cannot visit saunas, steam baths, or engage in heavy physical activity. Swimming, cycling, and eating more fresh fruits and vegetables are recommended.
As a rule, the operation proceeds without complications, but if the technique is violated, there is a possibility of development. Among them:
- Impaired skin sensitivity due to nerve damage;
- Wound infection;
- Hematomas;
- Thrombosis;
- Bleeding from subcutaneous vessels.
The development of complications can be prevented by a doctor by following the rules of leg vein removal surgery and taking into account the general condition of the patient.
Cons of phlebectomy
Traditional phlebectomy has a number of disadvantages:
- The need for hospitalization;
- Incisions in the skin leave scars and scars, their size may vary;
- Carrying out general or spinal anesthesia;
- Longer rehabilitation period compared to modern methods.
Despite its disadvantages, phlebectomy is widely used when other methods of treating varicose veins cannot be used. And visible results and disappearance of symptoms occur within a week after vein removal.
Phlebectomy: an operation that helps cope with varicose veins!
Phlebectomy is an operation prescribed when less radical methods of treating varicose veins have exhausted themselves. They can no longer prevent further development of the disease. In such situations, the risk of life-threatening complications such as thrombosis or trophic ulcers increases.
The stronger the changes, the more difficult it is to cope with them. In such a situation, the operation cannot be postponed. Phlebectomy involves surgical removal of a section of a vein damaged by disease. Thus, blood flow is normalized. Since only the saphenous veins, which carry only one tenth of the total blood volume, are removed, this procedure is generally safe for the circulatory system.
How is phlebectomy of the lower extremities performed?
Phlebectomy of the lower extremities is performed using specific probes. A blood vessel damaged by varicose veins is ligated and crossed at the point where it flows into a deep vein. A guide probe is then inserted into the vessel through the incisions, and this section is then pulled out.
All work is carried out through miniature incisions followed by cosmetic stitches. Traces after the operation thus remain almost invisible. Sometimes stitches are not applied at all, the edges of the incisions are glued together with special strips of adhesive.
Surgical treatment of varicose veins in Moscow
You can consult a phlebologist in Moscow at the Yusupov Hospital. We offer conservative and surgical methods for the treatment of varicose veins of the lower extremities. We offer modern and painless methods for treating varicose veins, including sclerotherapy, radiofrequency ablation and laser endovasal coagulation.
The Phlebology Department of the Yusupov Hospital uses advanced effective technologies to get rid of vascular diseases, including varicose veins. The best phlebologists in Moscow work in our clinic using modern, top-class foreign equipment. Our specialists regularly improve their skills abroad, master new techniques and implement them into the work of the clinic.
To obtain the maximum effect, we select treatment taking into account the individual characteristics of each patient. The use of a modern laser in the hands of experienced professionals makes it possible to get rid of varicose veins in a short time. You can make an appointment and consultation with a phlebologist in Moscow by leaving a request on our website.
Removal of leg veins: low prices, high quality!
If you suspect varicose veins, contact our doctor immediately. At an early stage, conservative treatment methods can still be used:
- compression jersey,
- specific drugs,
- exercise therapy complexes.
However, it is often necessary to remove veins in the legs. Prices in our clinic are quite reasonable. You can definitely afford it. In addition, the operation itself is relatively easy for the patient.
Physical therapy after phlebectomy – only with our specialists!
Our clinic does not leave patients immediately after surgery. We provide physical therapy after phlebectomy, which helps you quickly get in shape and return to normal life.
The best exercise therapy specialists will work with you. They will select a set of exercises specifically for you. They will also always be ready to help the patient, tell him how to behave in a given situation, and how best to restore health to his legs.
By listening to them, you can quickly return to your usual rhythm of life. You can continue to enjoy every minute - because now you will have absolutely healthy legs! Our specialists will do everything to achieve this goal! Contact us to make sure of this!
Complications
The success of surgical treatment of varicose veins depends on many factors: the age of the patient, the degree of advanced disease, concomitant diseases, etc. Depending on this, complications may arise after phlebectomy. The most common negative consequences of phlebectomy include:
- Bleeding. In the postoperative period, light bleeding from surgical wounds may occur during the first 24 hours. The reason for this is small cutaneous and subcutaneous vessels. The complication is nonspecific and is associated with errors in the surgeon’s operative technique. In some cases, bleeding may be associated with the use of anticoagulants (blood thinners). If the bleeding does not stop, revision of the wound (unraveling of sutures in the operating room) may be required.
- Hemorrhages and hematomas. The source of hemorrhage and the appearance of a hematoma after phlebectomy are small vessels that break during surgery. Hemorrhages are the soaking of blood into the skin and subcutaneous tissue (hemorrhages) or the accumulation of blood in cavities (hematoma) and are a natural complication of traumatic phlebectomy. Prevention of this complication is the use of modern low-traumatic methods of vein removal (intussusception stripping, cryostripping, miniphlebectomy), careful hemostasis both during surgery (manual compression) and after surgery (elastic bandaging and compression hosiery). Typically, hemorrhages and bruises after phlebectomy resolve on their own within 7-10 days, leaving behind slight pigmentation for up to 1-2 months.
- Infectious and inflammatory complications, such as inflammatory infiltrates (indurations) and wound suppuration. In case of development, removal of sutures and open wound management with local use of antimicrobial agents is indicated. Seals after phlebectomy are much more common (up to 15% of all phlebectomies) and represent an infectious inflammation without purulent fusion of tissue. Most often, the infiltrate forms in the area of maximum trauma and blood accumulation (hematoma infection). To treat infiltrates, antibacterial therapy and local use of anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents are used.
- Lymphorrhea (leakage of lymph through the surgical wound) and lymphocele (formation of a cavity filled with lymph in the surgical area) are the result of damage to lymphatic vessels and nodes due to rough handling of tissues. Lymphorrhea is treated conservatively. Lymphocele requires emptying by puncture or opening a wound. The main method of prevention is careful adherence to surgical technique and careful handling of tissues.
- Impaired skin sensitivity: decreased sensitivity on the inner surface of the leg and foot (hypoesthesia) or the appearance of unpleasant sensations such as crawling (paresthesia) is associated with damage to the nerves passing in close proximity to the trunks of the saphenous veins. This is observed when using traumatic methods of safenectomy. The method of prevention is careful handling of tissues.
- Thrombosis and embolism. Thrombosis of the deep veins of the leg, as well as the development of thrombophlebitis after phlebectomy, is extremely rare, which is associated with mandatory elastic compression after surgery and early activation of the patient.
Contraindications
Despite the large number of advantages and indications for use, phlebectomy has some limitations. These include:
- Acute viral or infectious diseases. Such conditions increase the possibility of developing postoperative complications in the form of sepsis.
- Severe hypertension, uncontrolled by medications.
- Chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
- Pregnancy period. An absolute contraindication is the second half of gestation. This is due to the fact that any intervention can provoke the development of spontaneous abortion.
- The presence of inflammatory diseases in the lower extremities. These conditions can trigger the spread of inflammation to other organs and tissues.
- Age over 65 years. With age, surgical interventions are more difficult to tolerate. This is due to the presence of a sufficient number of concomitant pathologies. Phlebectomy of veins can lead to exacerbation of chronic diseases, which will negatively affect the course of the recovery period.
Some of the listed contraindications are temporary. This means that after removing the restrictions, the surgical intervention can be carried out in full. Depending on the severity of the condition and the type of affected vessel, the doctor selects a phlebectomy technique that will be most effective in each specific case.